Ansible(二十六)-- ansible 中的条件判断与错误处理 fail模块 failed_when changed_when关键字
一、fail模块
在编写shell脚本时,有可能会有这样的需求,当脚本执行到某个阶段时,需要对某个条件进行判断,如果条件成立,则立即终止脚本的运行,在shell脚本中实现这个需求很简单,只需要在条件成立时调用"exit"命令即可终止脚本的运行, 那么在编写playbook时,如果有类似的需求,我们该怎么办呢?
想要在playbook中按照我们的意愿中断剧本的执行,其实也很简单,我们只需要借助一个模块即可完成,这个模块就是"fail"模块。
我们知道,在执行playbook时,如果playbook中的任何一个任务执行失败,playbook都会停止运行,除非这个任务设置了"ignore_errors: true",在任务没有设置"ignore_errors: true"的情况下,任务执行失败后,playbook就会自动终止,而fail模块天生就是一个用来"执行失败"的模块,当fail模块执行后,playbook就会认为有任务失败了,从而终止运行,实现我们想要的中断效果,来看一个小示例:
[root@server4 ~]# vim block4.yml
[root@server4 ~]# cat block4.yml
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "1"
- debug:
msg: "2"
- fail:
- debug:
msg: "3"
- debug:
msg: "4"
如上例所示,上例playbook中一共有4个debug任务,在第2个debug任务之后,我们调用了fail模块,那么我们来运行一下上例playbook,执行后输出信息如下

从上图可以看出,当前两个debug模块输出了对应的信息后,playbook报错了,之后的debug模块并未被调用,实现了中断剧本运行的效果,当执行fail模块时,fail模块默认的输出信息为’Failed as requested from task’,我们可以通过fail模块的msg参数自定义报错的信息,示例如下
[root@server4 ~]# vim block5.yml
[root@server4 ~]# cat block5.yml
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "1"
- fail:
msg: "Interrupt running playbook"
- debug:
msg: "2"
当然,上述示例只是为了初步介绍fail模块的用法,我们通常并不会毫无理由的想要去中断playbook,通常需要对某些条件进行判断,如果条件满足,则中断剧本,所以,fail模块通常与when结合使用,比如,如果之前模块执行后的标准输出信息中包含字符串’error’,则认为中断剧本的条件成立,就立即调用fail模块,以终断playbook,示例如下:
[root@server4 ~]# vim fail1.yml
[root@server4 ~]# cat fail1.yml
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
tasks:
- shell: "echo 'This is a string for testing--error'"
register: return_value
- fail:
msg: "Conditions established,Interrupt running playbook"
when: "'error' in return_value.stdout"
- debug:
msg: "I never execute,Because the playbook has stopped"

上例中,我们使用shell模块故意输出了一个包含’error’字符串的文本,并且将shell模块执行后的返回值注册到了变量’ return_value’中,在之后调用了fail模块,并对fail模块添加了判断条件,对应的条件为 “‘error’ in return_value.stdout”,这个条件表示shell模块执行后的标注输出信息中如果包含’error’字符串,则条件成立,其中,'in’关键字的用法与 python 中’in’的用法相同,可以使用’in’关键字判断一个字符串是否存在于另一个字符串中,也可以用于判断一个特定的值是否存在于列表中,由于shell标准输出的信息中的确包含error字符串,所以fail模块对应的条件成立,最终调用fail模块,playbook终止运行。
不过需要注意的是,当使用"in"或者"not in"进行条件判断时,整个条件需要用引号引起,并且,需要判断的字符串也需要使用引号引起,所以,使用’in’或者’not in’进行条件判断时,如下两种语法是正确的:
when: ' "successful" not in return_value.stdout '
when: " 'successful' not in return_value.stdout "
二、failed_when关键字
其实,还有另一种方法可以实现类似的效果,我们可以借助’failed_when’关键字来完成类似功能,'failed_when’的作用就是,当对应的条件成立时,将对应任务的执行状态设置为失败,这样说可能不是特别容易理解,不如先来看一个小示例,如下:
[root@server4 ~]# vim fail2.yml
[root@server4 ~]# cat fail2.yml
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "I execute normally"
- shell: "echo 'This is a string for testing error'"
register: return_value
failed_when: ' "error" in return_value.stdout'
- debug:
msg: "I never execute,Because the playbook has stopped"
上例中,一共有三个任务,第一个任务通过debug模块输出 “I execute normally”,第二个任务调用shell模块,echo了’This is a string for testing error’这句话,并且将返回值注册到了’return_value’变量中,’ failed_when’关键字与shell关键字对齐,表示其对应的条件是针对shell模块的,’ failed_when’对应的条件是 ’ “error” in return_value.stdout’,表示"error"字符串如果存在于shell模块执行后的标准输出中,则条件成立,当条件成立后,shell模块的执行状态将会被设置为失败,由于shell模块的执行状态被设置为失败,所以playbook会终止运行,于是,最后的debug模块并不会被执行,那么,执行上例playbook,效果如下:
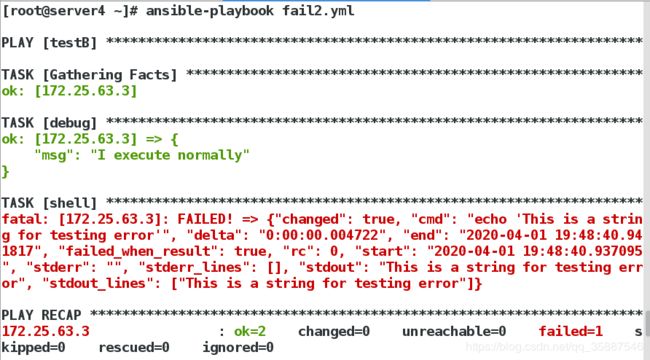 ’ failed_when’的作用就是,当’ failed_when’关键字对应的条件成立时,’ failed_when’会将对应的任务的执行状态设置为失败,以停止playbook的运行,但是需要注意的时,’ failed_when’虽然会将任务的执行状态设置为失败,但是并不代表任务真的失败了,就以上例来说,上例的shell模块的确是完全正常的执行了,只不过在执行之后,’ failed_when’对应的条件成立了,’ failed_when’将shell模块的执行状态设置为失败而已,所以,’ failed_when’并不会影响shell模块的执行过程,只会在条件成立时影响shell模块最终的执行状态,以便停止playbook的运行。
’ failed_when’的作用就是,当’ failed_when’关键字对应的条件成立时,’ failed_when’会将对应的任务的执行状态设置为失败,以停止playbook的运行,但是需要注意的时,’ failed_when’虽然会将任务的执行状态设置为失败,但是并不代表任务真的失败了,就以上例来说,上例的shell模块的确是完全正常的执行了,只不过在执行之后,’ failed_when’对应的条件成立了,’ failed_when’将shell模块的执行状态设置为失败而已,所以,’ failed_when’并不会影响shell模块的执行过程,只会在条件成立时影响shell模块最终的执行状态,以便停止playbook的运行。
三、changed_when关键字
’ failed_when’关键字的作用是在条件成立时,将对应任务的执行状态设置为失败
’changed_when’关键字的作用是在条件成立时,将对应任务的执行状态设置为changed
我们直接来看一个小示例:
[root@server4 ~]# vim changed1.yml
[root@server4 ~]# cat changed1.yml
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "test message"
changed_when: 2 > 1
我们知道,debug模块在正常执行的情况下只能是"ok"状态,上例中,我们使用’changed_when’关键字将debug模块的执行后的状态定义为了"changed",你可以尝试执行上例playbook,执行效果如下:

前文中总结过handlers的用法,我们知道,只有任务作出了实际的操作时(执行后状态为changed),才会真正的执行对应的handlers,而在某些时候,如果想要通过任务执行后的返回值将任务的最终执行状态判定为changed,则可以使用’changed_when’关键字,以便条件成立时,可以执行对应的handlers,其实,'changed_when’除了能够在条件成立时将任务的执行状态设置为"changed",还能让对应的任务永远不能是changed状态,示例如下:
[root@server4 ~]# vim changed2.yml
[root@server4 ~]# cat changed2.yml
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
tasks:
- shell: "ls /opt"
changed_when: false
当将’changed_when’直接设置为false时,对应任务的状态将不会被设置为’changed’,如果任务原本的执行状态为’changed’,最终则会被设置为’ok’,所以,上例playbook执行后,shell模块的执行状态最终为’ok’:
 而当不加
而当不加changed_when: false关键字时:

可以看出changed_when: false关键字可以让对应的任务永远不能是changed状态。
