2020年春季学期软件构造Lab 1
1 实验目标概述 1
2 实验环境配置 1
3 实验过程 2
3.1 Magic Squares 2
3.1.1 isLegalMagicSquare() 2
3.1.2 generateMagicSquare() 3
3.2 Turtle Graphics 6
3.2.1 Problem 1: Clone and import 6
3.2.2 Problem 3: Turtle graphics and drawSquare 7
3.2.3 Problem 5: Drawing polygons 8
3.2.4 Problem 6: Calculating Bearings 9
3.2.5 Problem 7: Convex Hulls 9
3.2.6 Problem 8: Personal art 10
3.2.7 Submitting 11
3.3 Social Network 11
3.3.1 设计/实现FriendshipGraph类 12
3.3.2 设计/实现Person类 13
3.3.3 设计/实现客户端代码main() 13
3.3.4 设计/实现测试用例 14
4 实验进度记录 15
5 实验过程中遇到的困难与解决途径 16
6 实验过程中收获的经验、教训、感想 16
6.1 实验过程中收获的经验和教训 16
6.2 针对以下方面的感受 16
1 实验目标概述
本次实验通过求解三个问题,训练基本 Java 编程技能,能够利用 Java OO 开发基本的功能模块,能够阅读理解已有代码框架并根据功能需求补全代码,能够 为所开发的代码编写基本的测试程序并完成测试,初步保证所开发代码的正确性。另一方面,利用 Git 作为代码配置管理的工具,学会 Git 的基本使用方法。
·基本的 Java OO 编程
·基于 Eclipse IDE 进行 Java 编程
·基于 JUnit 的测试
·基于 Git 的代码配置管理
2 实验环境配置
URL地址:https://github.com/ComputerScienceHIT/Lab1-1170300715
(1)Eclipse IDE

(2)JDK1.8
(3)搭建GitHub仓库、本地下载Git

3 实验过程
请仔细对照实验手册,针对四个问题中的每一项任务,在下面各节中记录你的实验过程、阐述你的设计思路和问题求解思路,可辅之以示意图或关键源代码加以说明(但无需把你的源代码全部粘贴过来!)。
为了条理清晰,可根据需要在各节增加三级标题。
请仔细对照实验手册,针对四个问题中的每一项任务,在下面各节中记录你的实验过程、阐述你的设计思路和问题求解思路,可辅之以示意图或关键源代码加以说明(但无需把你的源代码全部粘贴过来!)。
为了条理清晰,可根据需要在各节增加三级标题。
3.1 Magic Squares
这个实验要求写两个函数,一个是isLegalMagicSquare(),用来判断读入的矩阵是否为幻方,就是判断矩阵行、列及对角线的和是否相等,并且能够处理读入的文件里存在的各种特殊的情况,如矩阵中存在负数和非法字符,还有数值之间是否用\t隔开等,在main函数中调用五次该函数,判断提供的五个矩阵是否为幻方。
第二个函数是generateMagicSquare(),为提供的代码绘制流程图,并以此为代码加上注释。并分析函数在输入偶数和负数时为何会产生异常。然后对实验提供的代码做扩展,将产生的矩阵写入到文件6.txt中,调用第一个函数判断其是否为幻方;当输入的数据不合法时,提示错误,返回false结束函数的运行。
3.1.1 isLegalMagicSquare()
这个函数要求要实现的功能是判断一个矩阵是否为幻方
首先将矩阵从文件中以字符串的形式按行读取进来
(1) 然后对读进来的存在字符串里的矩阵进行判断,如果数据间不是用\t隔开的,则不是幻方,即矩阵中两个数字间出现空格,则不是幻方,这里可以用String.indexOf(“ “)!=-1来判断矩阵中出现了空格,一旦出现了空格则返回false,判断该矩阵不是幻方
(2) 然后对存在字符串中的数据按\t来分割,并将分割后的结果存在字符串数组里面然后再用的正则表达式来判断矩阵中是否存在非数字的字符,若存在,则返回false,然后再用Integer.parseInt()将分割的字符串转换为整数类型,并将其存在int类型的二维数组中,如果数组中存在小于0的数,则也返回false,若矩阵的行列数不相同,也可返回false,判定该矩阵不是幻方;
(3) 对存在矩阵中的每一行,每一列及对角线进行求和,并将其求和的结果存在一个数组中,如果有某一行,某一列或者某一对角线的和的结果和第一行的和的结果不相等,则也可判断该矩阵不是幻方
public static boolean isLegalMagicSquare(String fileName) {
int[][] a = null; //用来存储文件中矩阵的数据
int[] b = null; //用来存储矩阵行、列以及对角线的和
int order = 0;
int inorder = 0;
File file = new File(fileName);
try {
FileReader fw =new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(fw);
String tempString; //用来存储BufferedReader读取的文件的内容
int rowNum = 0; //统计行数
String[] tempRow;
String regex = "^[-\\+]?[\\d]*$"; //正则表达式,用来判断是否为int类型的数据
boolean isCreateSquare=false;
while ((tempString = reader.readLine()) != null) { //安行读取文件
if(tempString.indexOf(" ")!=-1){ //矩阵不是用制表符隔开,而是用空格隔开时,提示错误,返回false
System.out.println("数字之间没用制表符");
return false;
}
tempRow = tempString.split("\t"); //对读进来的文件内容按制表符进行分割
if(!isCreateSquare){
order=tempRow.length;
a=new int[order][order];
isCreateSquare=true;
inorder = order;
}
inorder = tempRow.length; //将按字符串读进来的文件的内容转换为int类型
if(inorder == order){
for(int i=0;i<order;i++){
for (int j = 0; j < tempRow[i].length(); j++) {
if (!tempRow[i].matches(regex)) { //判断矩阵中存在非int类型数据,返回false
System.out.println("矩阵中有非整数类型");
return false;
}
}
a[rowNum][i]=Integer.parseInt(tempRow[i]); //将转换好的数据存储到矩阵a中
if(a[rowNum][i] < 0){ //矩阵中存在负数时,返回false
System.out.println("矩阵中有非正整数");
return false;
}
}
}else{
System.out.println("行列数不同"); //行列数不同,返回false
return false;
}
rowNum++;
}
b=new int[order*2+2];
for(int i=0; i<order; i++){
for(int j=0; j<order; j++){
b[i] +=a[i][j]; //计算矩阵每一行的和
}
}
for(int i=0; i<order; i++){
for(int j=0; j<order; j++){
b[i+order] +=a[j][i]; //计算矩阵每一列的和
}
}
for(int i=0;i<order;i++) { //计算矩阵对角线的和
b[b.length-2] += a[i][i];
b[b.length-1] += a[i][order-1-i];
}
for(int i=1;i<b.length;i++){
if(b[i] != b[0]){ //将矩阵的每一行每一列以及对角线的和与矩阵第一行的和作比较
System.out.println("和不同"); //和不相同就报错,返回false
return false;
}
}
reader.close();
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); //打印错误信息
}
return true;
}
3.1.2 generateMagicSquare()
(1) 这里要求对给出的代码绘制流程图,并为其添加注释,并解释它是如何根据输入的参数n生成一个n*n的矩阵的;
这是给出的代码
public static boolean generateMagicSquare(int n) {
int magic[][] = new int[n][n];
int row = 0, col = n / 2, i, j, square = n * n;
for (i = 1; i <= square; i++) {
magic[row][col] = i;
if (i % n == 0)
row++;
else {
if (row == 0)
row = n - 1;
else
row--;
if (col == (n - 1))
col = 0;
else
col++;
}
}
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
System.out.print(magic[i][j] + "\t");
System.out.println();
}
return true;
}
流程图如下:

这是幻方生成算法中的劳伯法,生成幻方的步骤是:
把1(或最小的数)放在第一行正中;按以下规律排列剩下的(n×n-1)个数:
· 每一个数放在前一个数的右上一格;
· 如果这个数所要放的格已经超出了顶行那么就把它放在底行,仍然要放在右一列;
· 如果这个数所要放的格已经超出了最右列那么就把它放在最左列,仍然要放在上一行;
· 如果这个数所要放的格已经超出了顶行且超出了最右列,那么就把它放在底行且最左列;
· 如果这个数所要放的格已经有数填入,那么就把它放在前一个数的下一行同一列的格内。
但这个函数只能生成正奇数阶的幻方,如果输入的参数是偶数,则会产生数组越界的错误,

当输入的参数是负数时,会产生抛出数组个数是负数的异常

(2) 这里还要求对函数做扩展,将产生的magic square写入文件/src/P1/txt/6.txt中,当输入的参数n不合法时,不会抛出异常退出,而是提示错误,发挥false退出,并用第一个函数检测产生的6.txt是否为幻方;这里我用if语句对输入的参数n做了一个检测,如果输入的参数不合法时,就直接返回false,并提示参数输入不合要求,不会执行后面的语句了
下面是修改后的代码:
public static boolean generateMagicSquare(int n) {
if(n % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println("输入的n值为偶数,不符合要求,请输入奇数");
return false;
}else if(n < 0) {
System.out.println("输入的n值为偶数,不符合要求,请输入奇数");
return false;
}else {
File file = new File(".//src//P1//txt//6.txt");
try {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);
BufferedWriter bufw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
int magic[][] = new int[n][n];
int row = 0, col = n / 2, i, j, square = n * n;
for (i = 1; i <= square; i++) {
magic[row][col] = i;
if (i % n == 0)
row++;
else {
if (row == 0) //顶上越界,将数字放在最下面一行
row = n - 1;
else
row--;
if (col == (n - 1)) //到达最右一列,下一数字放在矩阵的最左边的一列
col = 0;
else
col++;
}
}
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) {
System.out.print(magic[i][j] + "\t");
bufw.write(String.valueOf(magic[i][j]) + "\t"); //将产生的矩阵存到6.txt文件中
}
System.out.println();
bufw.newLine(); //为文件换行
}
bufw.close();
fw.close();
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
}
main函数:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String fileName = null;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a;
for(int i=1; i<=5; i++) { //将1到5的txt文件一次调用函数isLegalMagicSquare来判断是否为MagicSquare
fileName = ".//src//P1//txt//" + i + ".txt"; //设置文件的相对路径
boolean result = isLegalMagicSquare(fileName);
if(result == true) {
System.out.println(i + ".txt是MagicSquare");
}else {
System.out.println(i + ".txt不是MagicSquare" + ",原因如上。");
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("请输入你想要创建的幻方的阶数:");
a = sc.nextInt();
boolean genResult = generateMagicSquare(a);
boolean imResult1 = isLegalMagicSquare(".//src//P1//txt//6.txt"); //将generateMagicSquare函数产生的矩阵用该函数进行判断
if(genResult == false) {
System.out.println("创建" + a + "阶MagicSquare失败,原因如上");
}else {
System.out.println("创建" + a + "阶MagicSquare成功,已经存到文件6.txt中");
if(imResult1 == false) {
System.out.println("函数generateMagicSquare创建的"+ a +"阶矩阵不是MagicSquare" + "原因如上");
}else {
System.out.println("函数generateMagicSquare创建的"+ a +"阶矩阵是MagicSquare");
}
}
}
3.2 Turtle Graphics
此任务是利用添加到徽标语言中的turtle图形,向屏幕上的“乌龟”发送一系列指令,这只“乌龟”会移动,并随着它画一条线。首先需要获取该任务的源代码,然后创建和管理本地仓库,开发环境配置完成之后。需要首先完成画正方形、根据内角求边数、根据边数求内角三个简单任务,在此基础上绘制正多边形,计算方位,计算凸包,最后完成个性化创作
3.2.1 Problem 1: Clone and import
点击实验报告里提供的链接下载了实验所需要的代码,把下载好的文件移动到相应的文件夹,然后在eclipse中导入文件夹。
打开项目的文件夹,然后右键单击git gui here
然后点击create new repository,选择好文文件夹点击创建,git本地仓库就创建好了

3.2.2 Problem 3: Turtle graphics and drawSquare
通过turtle的forward和turn函数就可以完成相应操作,每次画线长度为sideLength,转角4次且每次转90度,即可完成正方形,完成代码如下:
public static void drawSquare(Turtle turtle, int sideLength) {
try {
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
turtle.forward(sideLength); //向当前方向画线sideLength长度
turtle.turn(90); //顺时针转90度角
}
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("implement me!");
}
}

3.2.3 Problem 5: Drawing polygons
3.2.3.1由公式180-360/sides即可求得多边形的内角,代码如下:
public static double calculateRegularPolygonAngle(int sides) {
try {
double angle = 180.0 - (360.0/sides); //side为正多边形的边数,angle为多边形内角
return angle;
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("implement me!");
}
}
3.2.3.2由内角求边数的代码如下:
public static int calculatePolygonSidesFromAngle(double angle) {
try {
double angleOut = 180.0 - angle; //求多边形外角
int sides = (int)Math.ceil(360.0/angleOut); //由外角度数求多边形边数
return sides;
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("implement me!");
}
}
3.2.3.4根据上述函数即可由边数求出内角,180-angleout即为要绘制的多边形的外角的度数,乌龟旋转sides次,即可绘制出多边形:
public static void drawRegularPolygon(Turtle turtle, int sides, int sideLength) {
try {
double angleout = 180.0 - calculateRegularPolygonAngle(sides);
for(int i=0; i<sides; i++) {
turtle.forward(sideLength);
turtle.turn(angleout); //多边形外角的度数即为绘制多边形时画笔旋转的度数
}
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("implement me!");
}
}
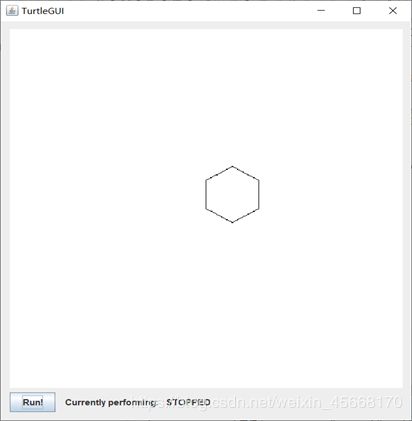
绘制的长度为40的六边形:
3.2.4 Problem 6: Calculating Bearings
3.2.4.1首先实现函数calculateBearingToPoint
首先用上述公式求出两点连线的向量与x轴正向的夹角(取值范围为0到360度),然后再求出currentBearing与x轴正向的夹角,两者之差即为要旋转的角度,代码如下:
public static double calculateBearingToPoint(double currentBearing, int currentX, int currentY,
int targetX, int targetY) {
try {
if (currentX == targetX && currentY == targetY) //起点与终点相同
return 0.0;
double degreess = Math.atan2(targetY - currentY, targetX - currentX) / Math.PI * 180.00; //求两点间连线与x轴正向的夹角
if (degreess < 0) //两点连线向量在二四象限,加360度
degreess += 360.00;
currentBearing = 90.00 - currentBearing; //偏角与x轴正向的夹角
if (currentBearing < 0)
currentBearing += 360.00;
double ans = currentBearing - degreess; //偏转角及两点连线与x轴正向夹角之差即为要旋转的角度
if (ans < 0)
ans += 360.00;
return ans;
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("implement me!");
}
}
3.2.4.2实现List calculateBearings函数,基于上一个问题,此时有若干个点,想知道从第一个点开始到第二个点,再从第二个点到第三个点……以此类推每次转向的角度。
(1)将“起点”选为第一个点(坐标为(xCoords.get(0),yCoords.get(0)));
(2)循环n-1次(n为点的个数)
(3)每次将第i+1号点设置为“终点”,通过上一个函数计算旋转角度并存储到List中;
(4)将下一次的“起点”用当前“终点”更新,继续循环;
(5)退出循环后返回List。
代码如下:
public static List<Double> calculateBearings(List<Integer> xCoords, List<Integer> yCoords) {
try {
double currentBearing = 0.0;
/*将起点选为第一个点*/
int currentX = xCoords.get(0);
int currentY = yCoords.get(0);
int targetX, targetY;
int length = xCoords.size();
List<Double> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=1; i<length; i++) {
targetX = xCoords.get(i);
targetY = yCoords.get(i);
ans.add(calculateBearingToPoint(currentBearing, currentX, currentY, targetX, targetY));
currentBearing = ans.get(i-1);
currentX = targetX;
currentY = targetY;
}
return ans;
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("implement me!");
}
}
3.2.5 Problem 7: Convex Hulls
凸包(Convex Hull)是一个计算几何(图形学)中的概念。
在一个实数向量空间V中,对于给定集合X,所有包含X的凸集的交集S被称为X的凸包。
X的凸包可以用X内所有点(X1,…Xn)的线性组合来构造.
在二维欧几里得空间中,凸包可想象为一条刚好包著所有点的橡皮圈。
用不严谨的话来讲,给定二维平面上的点集,凸包就是将最外层的点连接起来构成的凸多边型,它能包含点集中所有的点。
上图中由红色线段表示的多边形就是点集Q={p0,p1,…p12}的凸包。
这里用的是边界漫游法,其基本步骤如下:
(1) 首先遍历所有的点,找出位于最左下角的点
(2) 以找到的点为基点,y轴正向为目前偏移角,开始依次找顺势针转角最小的点,记录这个点并将他加入到凸包集合中,以这次的偏向角累加上之前的角度度作为下一次的目前偏向角。
(3) 循环直到再次遇到最左下角的点为止退出。
public static Set<Point> convexHull(Set<Point> points) {
try {
Set<Point> shellPoint = new HashSet<Point>();
Point minPoint = null;
double nowBearing;
double nextBearing;
double preBearing;
double nextLength;
Point nowPoint;
Point nextPoint = null;
if(!points.isEmpty())
{
//元素小于3个时,必是凸包直接返回
if(points.size() <=3)
return points;
//求最左下元素
for(Point point : points)
{
if(minPoint == null){
minPoint = point;
continue;
}
if(minPoint.x() > point.x())
minPoint = point;
else if(minPoint.x() == point.x())
{
if(point.y() < minPoint.y())
minPoint = point;
}
}
shellPoint.add(minPoint); //最左下元素定时凸包元素,加入集合
nowPoint = minPoint;
preBearing = 0; //之前凸包元素指向最近凸包元素的角度(相对与y轴顺时针)
while(true)
{
nextBearing = 360;
nextLength = Double.MAX_VALUE;
for(Point point : points)
{
if(point.equals(nowPoint))
continue;
nowBearing = calculateBearingToPoint(preBearing,(int)nowPoint.x(),(int)nowPoint.y(),(int)point.x(),(int)point.y());
if(nextBearing == nowBearing){
if(nextLength < (Math.pow(point.x()-nowPoint.x(), 2)+Math.pow(point.y()-nowPoint.y(), 2)))
{
nextLength = Math.pow(point.x()-nowPoint.x(), 2)+Math.pow(point.y()-nowPoint.y(), 2);
nextPoint = point;
}
}
else if(nextBearing > nowBearing) {
nextLength = Math.pow(point.x()-nowPoint.x(), 2)+Math.pow(point.y()-nowPoint.y(), 2);
nextBearing = nowBearing;
nextPoint = point;
}
}
if(minPoint.equals(nextPoint)) //再次遇到最左下角的点,退出循环
{
break;
}
nowPoint = nextPoint;
preBearing += nextBearing;
shellPoint.add(nextPoint);
}
}
return shellPoint;
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("implement me!");
}
}
3.2.6 Problem 8: Personal art

代码如下:
public static void drawPersonalArt(Turtle turtle) {
try {
for(int i=0; i<360; i++) {
turtle.forward(i);
if(i<36)
turtle.color(PenColor.BLACK);
else if(i<72)
turtle.color(PenColor.BLUE);
else if(i<108)
turtle.color(PenColor.CYAN);
else if(i<144)
turtle.color(PenColor.GRAY);
else if(i<180)
turtle.color(PenColor.GREEN);
else if(i<216)
turtle.color(PenColor.MAGENTA);
else if(i<252)
turtle.color(PenColor.ORANGE);
else if(i<288)
turtle.color(PenColor.PINK);
else if(i<324)
turtle.color(PenColor.RED);
else
turtle.color(PenColor.YELLOW);
turtle.turn(170);
}
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("implement me!");
}
}
main函数:
public static void main(String args[]) {
DrawableTurtle turtle = new DrawableTurtle();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
double angle;
int x,y,input;
int sides;
do {
System.out.println("1.画一个正方形。\n2.输入边数,计算对应的多边形的内角度数。");
System.out.println("3.输入一个度数(内角),计算相应的多边形的边数");
System.out.println("4.绘制一个多边形。\n5.计算轴承。\n6.计算凸包。\n7.绘制艺术图案。");
System.out.println("请输入你的选择,执行相应的功能:");
input = sc.nextInt();
switch (input) {
case 1:
drawSquare(turtle, 40);
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("请输入边数:");
sides = sc.nextInt();
angle = calculateRegularPolygonAngle(sides);
System.out.println(sides + "条边的多边形的内角的度数为:" + angle);
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("请输入一个角度");
angle = sc.nextDouble();
sides = calculatePolygonSidesFromAngle(angle);
System.out.println("边数为:" + sides);
break;
case 4:
int sideLength;
System.out.println("请输入要绘制的多边形的边数及长度:");
sides = sc.nextInt();
sideLength = sc.nextInt();
drawRegularPolygon(turtle, sides, sideLength);
break;
case 5:
int currentX, currentY;
int targetX, targetY;
int nextInput;
System.out.println("请输入要计算的轴承的点的数量(大于等于2)");
nextInput = sc.nextInt();
if(nextInput == 2) {
System.out.println("请输入起点坐标(空格隔开):");
currentX = sc.nextInt();
currentY = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入起点偏角:");
double currentBearing = sc.nextDouble();
System.out.println("请输入终点坐标(空格隔开):");
targetX = sc.nextInt();
targetY = sc.nextInt();
double BearingToPoint = calculateBearingToPoint(currentBearing,currentX,currentY,
targetX,targetY);
System.out.println("轴承为:" + BearingToPoint);
}else if(nextInput > 2) {
List<Integer> xCoords = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> yCoords = new ArrayList<>();
List<Double> Bearings = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=1; i<=nextInput; i++) {
System.out.println("请输入第" + i + "个点的坐标(空格隔开):");
x = sc.nextInt();
y = sc.nextInt();
xCoords.add(x);
yCoords.add(y);
}
Bearings = calculateBearings(xCoords,yCoords);
System.out.println("点的轴承为:");
for(int i=0; i<Bearings.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(Bearings.get(i) + " ");
}
}else {
System.out.println("输入错误");
}
break;
case 6:
Set<Point> points = new HashSet<Point>();
Set<Point> convexHull = new HashSet<Point>();
int pointNum;
System.out.println("请输入点的个数");
pointNum = sc.nextInt();
for(int i=1; i<=pointNum; i++) {
System.out.println("请输入第" + i + "个点的坐标(空格隔开):");
x = sc.nextInt();
y = sc.nextInt();
Point p = new Point(x, y);
points.add(p);
}
convexHull = convexHull(points);
Iterator<Point> it = convexHull.iterator();
System.out.println("凸包的点的坐标为:");
while(it.hasNext()) {
Point p = it.next();
System.out.print("(" + p.x() + "," + p.y() + ")");
}
break;
case 7:
drawPersonalArt(turtle);
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入错误,请重新输入");
break;
}
if(input==1 || input==4 || input==7) {
// draw the window
turtle.draw();
}
}while(input != -1);
sc.close();
}
3.3 Social Network
该任务要求实现一个社交网络图,该图是无向图,并且可以被扩展为有向图。图中,如果A和B认识,则A与B之间就会有一条连线,同时要求该图可以扩展,可以不断的加入顶点,加入边,并且能计算出图中任意两点间的最短距离,也要求能够处理一些特殊情况,诸如不同的人有相同的名字,图中两点之间不存在路径,以及所求最小距离的两个点是同一个点。
3.3.1 设计/实现FriendshipGraph类
函数public boolean addVertex(Person name),往图中加点
//添加联系人
public boolean addVertex(Person name)
{
if(getPosition(name)!=-1)
{
System.out.println("This name has already exist!");
return false;
}
else {
this.adjGraph.VertexCount++;
this.adjGraph.VertexList.add(name);
return true;
}
}
函数public boolean addEdge(Person name1,Person name2)在两人之间建立联系
//在两个联系人之间添加边
public boolean addEdge(Person name1,Person name2)
{
int name1position=getPosition(name1);
int name2position=getPosition(name2);
if(name1position==name2position) //两人为同一人
{
System.out.println(name1 + " and " + name2 + " are the same people,Not leagle!");
return false;
}
if(name1position==-1||name2position==-1) //查无此人
{
System.out.println(name1 + " or " + name2 + "not exist!");
return false;
}
if(name1.edgeExist(name1position)&&name2.edgeExist(name2position))
{
System.out.println("Has exist!");
return false;
}
else {
this.adjGraph.EdgeCount++;
name1.linkListAdd(name2position);
return true;
}
}
public int getDistance,计算两人之间的距离,这里采用的是广度优先搜索的方法
如果注释掉实验报告中的第十行,输出的是-1,-1,0,-1
//获得两个联系人之间的距离
public int getDistance(Person name1,Person name2)
{
return BFS(this.adjGraph,name1,name2);
}
//用广度搜索算法来和队列结构来计算
public int BFS(adjGraph graph,Person name1,Person name2)
{
Map<Integer, Integer> routeMap = new HashMap<>();
int start = getPosition(name1);
int end = getPosition(name2);
if (start == end)
return 0;
else if ((start == -1) || (end == -1)) {
System.out.printf("The Person doesn't exist");
return -1;
}
boolean visited[] = new boolean[graph.VertexCount];
for(int i = 0; i < visited.length; i++)
visited[i] = false;
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
visited[start] = true;
queue.add(start);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int curValue = queue.remove();//获取队顶数据并出队
int next=0;
for ( next = 0; next < graph.VertexList.get(curValue).netWorkSize(); next++) {
int curvisit = graph.VertexList.get(curValue).getSocial(next);//获取每一个人在curvalue的社会位置
if (!visited[curvisit]) {
visited[curvisit] = true;
routeMap.put(curvisit, curValue);
queue.add(curvisit);//入队
}
}
}
int i=0;
int distence;
for (i = 0, distence = 1; i < routeMap.keySet().size(); i++, distence++) {
if (!routeMap.containsKey(end))
return -1;
if (routeMap.get(end) == start)
return distence;
end = routeMap.get(end);
}
return -1;
}
3.3.2 设计/实现Person类
Person方法将名字赋给类中的name
linkListAdd在SocialList中添加一个联系人
netWorkSize获取联系人的大小
edgeExist判断边是否存在
getSocial判断联系人的社会位置
public final class Person {//一些辅助方法
private String name;
private LinkedList<Integer> SocialList = new LinkedList<>();
public Person(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public void linkListAdd(int personPosition) //在SocialList中添加联系人
{
this.SocialList.add(personPosition);
}
public int netWorkSize() //获取联系人的数量
{
return this.SocialList.size();
}
public boolean edgeExist(int personPosition) //判断边是否存在
{
if (this.SocialList.contains(personPosition))
return true;
return false;
}
public int getSocial(int position) //获取联系人在关系网中的位置
{
return this.SocialList.get(position);
}
}
3.3.3 设计/实现客户端代码main()
main()函数使用了实验报告给的例子,没有做添加有其他的功能:
public static void main(String[] args) {
FriendshipGraph graph = new FriendshipGraph();
Person rachel = new Person("rachel");
Person ross = new Person("ross");
Person ben = new Person("ben");
Person kramer = new Person("kramer");
graph.addVertex(rachel);
graph.addVertex(ross);
graph.addVertex(ben);
graph.addVertex(kramer);
graph.addEdge(rachel, ross);
graph.addEdge(ross, rachel);
graph.addEdge(ross, ben);
graph.addEdge(ben, ross);
System.out.println(graph.getDistance(rachel,ross));
System.out.println(graph.getDistance(rachel,ben));
System.out.println(graph.getDistance(rachel,rachel));
System.out.println(graph.getDistance(rachel,kramer));
}
3.3.4 设计/实现测试用例
验证图中点的存在:
@Test
public void addVertex() {
FriendshipGraph graph = new FriendshipGraph();
Person rachel = new Person("rachel");
Person ross = new Person("ross");
Person ben = new Person("ben");
Person kramer = new Person("kramer");
Person jake = new Person("jake");
graph.addVertex(rachel);
graph.addVertex(ross);
graph.addVertex(ben);
graph.addVertex(kramer);
graph.addEdge(rachel, ross);
graph.addEdge(ross, rachel);
graph.addEdge(ross, ben);
graph.addEdge(ben, ross);
assertTrue(graph.addVertex(rachel));
assertTrue(graph.addVertex(ross));
assertTrue(graph.addVertex(ben));
assertTrue(graph.addVertex(kramer));
assertFalse(graph.addVertex(jake));
}
测试两点之间是否直接相连,即两点之间是否有边
@Test
public void addEdge() { //测试两点之间是否直接相连,即两点之间是否有边
FriendshipGraph graph = new FriendshipGraph();
Person rachel = new Person("rachel");
Person ross = new Person("ross");
Person ben = new Person("ben");
Person kramer = new Person("kramer");
graph.addVertex(rachel);
graph.addVertex(ross);
graph.addVertex(ben);
graph.addVertex(kramer);
graph.addEdge(rachel, ross);
graph.addEdge(ross, rachel);
graph.addEdge(ross, ben);
graph.addEdge(ben, ross);
assertTrue(graph.addEdge(rachel,ross));
assertTrue(graph.addEdge(ben,ross));
assertFalse(graph.addEdge(rachel,kramer));
}
测试两点之间的距离:
@Test
public void getDistance() { //测试两点之间的距离:
FriendshipGraph graph = new FriendshipGraph();
Person rachel = new Person("rachel");
Person ross = new Person("ross");
Person ben = new Person("ben");
Person kramer = new Person("kramer");
graph.addVertex(rachel);
graph.addVertex(ross);
graph.addVertex(ben);
graph.addVertex(kramer);
graph.addEdge(rachel, ross);
graph.addEdge(ross, rachel);
graph.addEdge(ross, ben);
graph.addEdge(ben, ross);
assertEquals(1,graph.getDistance(rachel,ross));
assertEquals(2,graph.getDistance(rachel,ben));
assertEquals(0,graph.getDistance(rachel,rachel));
assertEquals(-1,graph.getDistance(rachel,kramer));
}