python学习笔记第十七天------------MySQL数据库
文章目录
- 1. 数据库简介
- 1.1 RDBMS
- 1.2 SQL
- 1.3 MySQL 简介
- 2. 数据完整性
- 3. 数据库的指令
- 4. 数据表的指令
- 5. 增删改查(curd)
- 6. 数据库设计
- 7. MySQL-基本使用
- 7.1 MySQL-查询
- 7.1.1 创建数据库、数据表
- 7.1.2 准备数据
- 7.1.3 消除重复行
- 7.2 条件
- 7.2.1 比较运算符
- 7.2.2 逻辑运算符
- 7.2.3 模糊查询
- 7.2.4 范围查询
- 7.2.5 空判断
- 7.2.6 优先级
- 7.3 排序
- 7.3.1 语法
- 7.3.2 说明
- 7.4 聚合函数
- 7.4.1 总数
- 7.4.2 最大值
- 7.4.3 最小值
- 7.4.4 求和
- 7.4.5 平均值
- 7.5 分组
- 7.5.1 group by
- 7.5.2 group by + group_concat()
- 7.5.3 group by + 集合函数
- 7.5.4 group by + having
- 7.5.5 group by + with rollup
- 7.6 分页
- 7.7 连接查询
- 7.8 自关联
- 7.9 子查询
- 7.9.1 子查询
- 7.9.2 主查询
- 7.9.3 主查询和子查询的关系
- 7.9.4 子查询分类
- 7.9.5 标量子查询
- 7.9.6 列级子查询
- 7.9.7 行级子查询
- 7.9.8 子查询中特定关键字使用
- 7.10 总结
- 8. MySQL与Python交互
- 8.1 准备数据
- 8.1.1 创建数据表
- 8.1.2 插入数据
- 8.2 SQL演练
- 8.2.1 SQL语句的强化
- 8.2.2 创建 "商品分类"" 表
- 8.2.3 同步表数据
- 8.2.4 创建 "商品品牌表" 表
- 8.2.5 同步数据
- 8.2.6 修改表结构
- 8.2.7 外键
- 8.3 数据库的设计
- 8.3.1 创建 "商品分类" 表
- 8.3.2 创建 "商品品牌" 表
- 8.3.3 创建 "商品" 表
- 8.3.4 创建 "顾客" 表
- 8.3.5 创建 "订单" 表
- 8.3.6 创建 "订单详情" 表
- 8.4 Python 中操作 MySQL 步骤
- 8.4.1 引入模块
- 8.4.2 Connection 对象
- 8.4.3 Cursor对象
- 8.5 增删改
- 8.6 查询一行数据
- 8.7 查询多行数据
- 8.8 参数化
- 9. MySQL高级
- 9.1 视图
- 9.1.1 问题
- 9.1.2 视图是什么
- 9.1.3 定义视图
- 9.1.4 查看视图
- 9.1.5 使用视图
- 9.1.6 删除视图
- 9.1.7 视图demo
- 9.1.8 视图的作用
- 9.2 事务
- 9.2.1 为什么要有事务
- 9.2.2 事务四大特性(简称ACID)
- 9.2.3 事务命令
- 9.3 提交
- 9.3.1 step1:连接
- 9.3.2 step2:增加数据
- 9.3.3 step3:查询
- 9.3.4 step4:提交
- 9.3.5 step5:查询
- 9.4 回滚
- 9.4.1 step1:连接
- 9.4.2 step2:增加数据
- 9.4.3 step3:查询
- 9.4.4 step4:回滚
- 9.4.5 step5:查询
- 9.5 索引
- 9.5.1 索引是什么
- 9.5.2 索引目的
- 9.5.3 索引原理
- 9.5.4 索引的使用
- 9.5.5 索引demo
- 9.5.5.1 创建测试表testindex
- 9.5.5.2 使用python程序(ipython也可以)通过pymsql模块 向表中加入十万条数据
- 9.5.5.3 查询
- 9.5.6 注意
1. 数据库简介
关系型数据库核心元素
- 数据行(记录)
- 数据列(字段)
- 数据表(数据行的集合)
- 数据库(数据表的集合)
1.1 RDBMS
Relational Database Management System
通过表来表示关系型
- 当前主要使用两种类型的数据库:关系型数据库、非关系型数据库,本部分主要讨论关系型数据库,对于非关系型数据库会在后面学习
- 所谓的关系型数据库RDBMS,是建立在关系模型基础上的数据库,借助于集合代数等数学概念和方法来处理数据库中的数据
- 查看数据库排名:https://db-engines.com/en/ranking
- 关系型数据库的主要产品:
- oracle:在以前的大型项目中使用,银行,电信等项目
- mysql:web时代使用最广泛的关系型数据库
- ms sql server:在微软的项目中使用
- sqlite:轻量级数据库,主要应用在移动平台
RDBMS和数据库的关系
1.2 SQL
Structured Query Language
SQL是结构化查询语言,是一种用来操作RDBMS的数据库语言,当前关系型数据库都支持使用SQL语言进行操作,也就是说可以通过 SQL 操作 oracle,sql server,mysql,sqlite 等等所有的关系型的数据库
- SQL语句主要分为:
- DQL:数据查询语言,用于对数据进行查询,如select
- DML:数据操作语言,对数据进行增加、修改、删除,如insert、udpate、delete
- TPL:事务处理语言,对事务进行处理,包括begin transaction、commit、rollback
- DCL:数据控制语言,进行授权与权限回收,如grant、revoke
- DDL:数据定义语言,进行数据库、表的管理等,如create、drop
- CCL:指针控制语言,通过控制指针完成表的操作,如declare cursor
- 对于web程序员来讲,重点是数据的crud(增删改查),必须熟练编写DQL、DML,能够编写DDL完成数据库、表的操作,其它语言如TPL、DCL、CCL了解即可
- SQL 是一门特殊的语言,专门用来操作关系数据库
- 不区分大小写
学习要求
- 熟练掌握数据增删改查相关的 SQL 语句编写
- 在 Python代码中操作数据就是通过 SQL 语句来操作数据
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='mysql', database='python1', charset='utf8')
# 得Cursor对象
cs = conn.cursor()
# 更新
# sql = 'update students set name="刘邦" where id=6'
# 删除
# sql = 'delete from students where id=6'
# 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询一条学生数据
sql = 'select id,name from students where id = 7'
# sql = 'SELECT id,name FROM students WHERE id = 7'
count=cs.execute(sql)
# 打印受影响的行数
print(count)
1.3 MySQL 简介
- 点击查看MySQL官方网站
- MySQL是一个关系型数据库管理系统,由瑞典MySQL AB公司开发,后来被Sun公司收购,Sun公司后来又被Oracle公司收购,目前属于Oracle旗下产品
特点
- 使用C和C++编写,并使用了多种编译器进行测试,保证源代码的可移植性
- 支持多种操作系统,如Linux、Windows、AIX、FreeBSD、HP-UX、MacOS、NovellNetware、OpenBSD、OS/2 Wrap、Solaris等
- 为多种编程语言提供了API,如C、C++、Python、Java、Perl、PHP、Eiffel、Ruby等
- 支持多线程,充分利用CPU资源
- 优化的SQL查询算法,有效地提高查询速度
- 提供多语言支持,常见的编码如GB2312、BIG5、UTF8
- 提供TCP/IP、ODBC和JDBC等多种数据库连接途径
- 提供用于管理、检查、优化数据库操作的管理工具
- 大型的数据库。可以处理拥有上千万条记录的大型数据库
- 支持多种存储引擎
- MySQL 软件采用了双授权政策,它分为社区版和商业版,由于其体积小、速度快、总体拥有成本低,尤其是开放源码这一特点,一般中小型网站的开发都选择MySQL作为网站数据库
- MySQL使用标准的SQL数据语言形式
- Mysql是可以定制的,采用了GPL协议,你可以修改源码来开发自己的Mysql系统
- 在线DDL更改功能
- 复制全局事务标识
- 复制无崩溃从机
- 复制多线程从机
开源 免费 不要钱 使用范围广,跨平台支持性好,提供了多种语言调用的 API
是学习数据库开发的首选
2. 数据完整性
- 一个数据库就是一个完整的业务单元,可以包含多张表,数据被存储在表中
- 在表中为了更加准确的存储数据,保证数据的正确有效,可以在创建表的时候,为表添加一些强制性的验证,包括数据字段的类型、约束
数据类型
- 可以通过查看帮助文档查阅所有支持的数据类型
- 使用数据类型的原则是:够用就行,尽量使用取值范围小的,而不用大的,这样可以更多的节省存储空间
- 常用数据类型如下:
- 整数:int,bit
- 小数:decimal
- 字符串:varchar,char
- 日期时间: date, time, datetime
- 枚举类型(enum)
- 特别说明的类型如下:
- decimal表示浮点数,如decimal(5,2)表示共存5位数,小数占2位
- char表示固定长度的字符串,如char(3),如果填充’ab’时会补一个空格为
'ab ' - varchar表示可变长度的字符串,如varchar(3),填充’ab’时就会存储’ab’
- 字符串text表示存储大文本,当字符大于4000时推荐使用
- 对于图片、音频、视频等文件,不存储在数据库中,而是上传到某个服务器上,然后在表中存储这个文件的保存路径
- 更全的数据类型可以参考http://blog.csdn.net/anxpp/article/details/51284106
约束
- 主键primary key:物理上存储的顺序
- 非空not null:此字段不允许填写空值
- 惟一unique:此字段的值不允许重复
- 默认default:当不填写此值时会使用默认值,如果填写时以填写为准
- 外键foreign key:对关系字段进行约束,当为关系字段填写值时,会到关联的表中查询此值是否存在,如果存在则填写成功,如果不存在则填写失败并抛出异常
- 说明:虽然外键约束可以保证数据的有效性,但是在进行数据的crud(增加、修改、删除、查询)时,都会降低数据库的性能,所以不推荐使用,那么数据的有效性怎么保证呢?答:可以在逻辑层进行控制
数值类型(常用)
| 类型 | 字节大小 | 有符号范围(Signed) | 无符号范围(Unsigned) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TINYINT | 1 | -128 ~ 127 | 0 ~ 255 |
| SMALLINT | 2 | -32768 ~ 32767 | 0 ~ 65535 |
| MEDIUMINT | 3 | -8388608 ~ 8388607 | 0 ~ 16777215 |
| INT/INTEGER | 4 | -2147483648 ~2147483647 | 0 ~ 4294967295 |
| BIGINT | 8 | -9223372036854775808 ~ 9223372036854775807 | 0 ~ 18446744073709551615 |
字符串
| 类型 | 字节大小 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| CHAR | 0-255 | 类型:char(3) 输入 ‘ab’, 实际存储为’ab ‘, 输入’abcd’ 实际存储为 ‘abc’ |
| VARCHAR | 0-255 | 类型:varchar(3) 输 ‘ab’,实际存储为’ab’, 输入’abcd’,实际存储为’abc’ |
| TEXT | 0-65535 | 大文本 |
日期时间类型
| 类型 | 字节大小 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| DATE | 4 | ‘2020-01-01’ |
| TIME | 3 | ‘12:29:59’ |
| DATETIME | 8 | ‘2020-01-01 12:29:59’ |
| YEAR | 1 | ‘2017’ |
| TIMESTAMP | 4 | ‘1970-01-01 00:00:01’ UTC ~ ‘2038-01-01 00:00:01’ UTC |
3. 数据库的指令
- 查看所有数据库
show databases;
- 使用数据库
use 数据库名;
- 查看当前使用的数据库
select database();
- 创建数据库
create database 数据库名 charset=utf8;
例:
create database python charset=utf8;
- 删除数据库
drop database 数据库名;
例:
drop database python;
4. 数据表的指令
- 查看当前数据库中所有表
show tables;
- 查看表结构
desc 表名;
- 创建表
- auto_increment表示自动增长
CREATE TABLE table_name(
column1 datatype contrai,
column2 datatype,
column3 datatype,
.....
columnN datatype,
PRIMARY KEY(one or more columns)
);
例:创建班级表
create table classes(
id int unsigned auto_increment primary key not null,
name varchar(10)
);
例:创建学生表
create table students(
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment not null,
name varchar(20) default '',
age tinyint unsigned default 0,
height decimal(5,2),
gender enum('男','女','人妖','保密'),
cls_id int unsigned default 0
)
- 修改表-添加字段
alter table 表名 add 列名 类型;
例:
alter table students add birthday datetime;
- 修改表-修改字段:重命名版
alter table 表名 change 原名 新名 类型及约束;
例:
alter table students change birthday birth datetime not null;
- 修改表-修改字段:不重命名版
alter table 表名 modify 列名 类型及约束;
例:
alter table students modify birth date not null;
- 修改表-删除字段
alter table 表名 drop 列名;
例:
alter table students drop birthday;
- 删除表
drop table 表名;
例:
drop table students;
- 查看表的创建语句
show create table 表名;
例:
show create table classes;
5. 增删改查(curd)
curd的解释: 代表创建(Create)、更新(Update)、读取(Retrieve)和删除(Delete)
查询基本使用
- 查询所有列
select * from 表名;
例:
select * from classes;
- 查询指定列
- 可以使用as为列或表指定别名
select 列1,列2,... from 表名;
例:
select id,name from classes;
增加
格式:INSERT [INTO] tb**name [(col**name,…)] {VALUES | VALUE} ({expr | DEFAULT},…),(…),…
- 说明:主键列是自动增长,但是在全列插入时需要占位,通常使用0或者 default 或者 null 来占位,插入成功后以实际数据为准
- 全列插入:值的顺序与表中字段的顺序对应
insert into 表名 values(...)
例:
insert into students values(0,’郭靖‘,1,'蒙古','2016-1-2');
- 部分列插入:值的顺序与给出的列顺序对应
insert into 表名(列1,...) values(值1,...)
例:
insert into students(name,hometown,birthday) values('黄蓉','桃花岛','2016-3-2');
- 上面的语句一次可以向表中插入一行数据,还可以一次性插入多行数据,这样可以减少与数据库的通信
- 全列多行插入:值的顺序与给出的列顺序对应
insert into 表名 values(...),(...)...;
例:
insert into classes values(0,'python1'),(0,'python2');
insert into 表名(列1,...) values(值1,...),(值1,...)...;
例:
insert into students(name) values('杨康'),('杨过'),('小龙女');
修改
格式: UPDATE *tbname* SET col1={expr1|DEFAULT} [,col2={expr2|default}]…[where 条件判断]
update 表名 set 列1=值1,列2=值2... where 条件
例:
update students set gender=0,hometown='北京' where id=5;
删除
DELETE FROM tbname [where 条件判断]
delete from 表名 where 条件
例:
delete from students where id=5;
- 逻辑删除,本质就是修改操作
update students set isdelete=1 where id=1;
备份
- 运行mysqldump命令
mysqldump –uroot –p 数据库名 > python.sql;
# 按提示输入mysql的密码
恢复
- 连接mysql,创建新的数据库
- 退出连接,执行如下命令
mysql -uroot –p 新数据库名 < python.sql
# 根据提示输入mysql密码
6. 数据库设计
- 关系型数据库建议在E-R模型的基础上,我们需要根据产品经理的设计策划,抽取出来模型与关系,制定出表结构,这是项目开始的第一步
- 在开发中有很多设计数据库的软件,常用的如power designer,db desinger等,这些软件可以直观的看到实体及实体间的关系
- 设计数据库,可能是由专门的数据库设计人员完成,也可能是由开发组成员完成,一般是项目经理带领组员来完成
- 现阶段不需要独立完成数据库设计,但是要注意积累一些这方面的经验
三范式
-
经过研究和对使用中问题的总结,对于设计数据库提出了一些规范,这些规范被称为范式(Normal Form)
-
目前有迹可寻的共有8种范式,一般需要遵守3范式即可
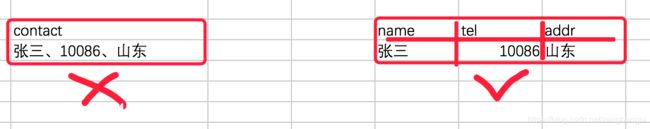
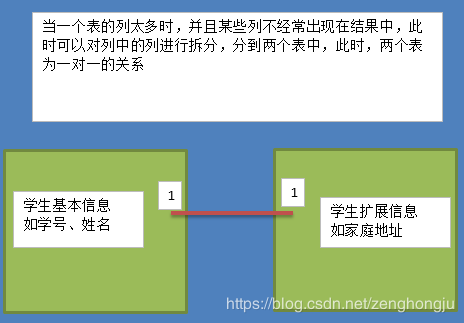
◆ 第一范式(1NF):强调的是列的原子性,即列不能够再分成其他几列。
考虑这样一个表:【联系人】(姓名,性别,电话) 如果在实际场景中,一个联系人有家庭电话和公司电话,那么这种表结构设计就没有达到 1NF。要符合 1NF 我们只需把列(电话)拆分,即:【联系人】(姓名,性别,家庭电话,公司电话)。1NF 很好辨别,但是 2NF 和 3NF 就容易搞混淆。
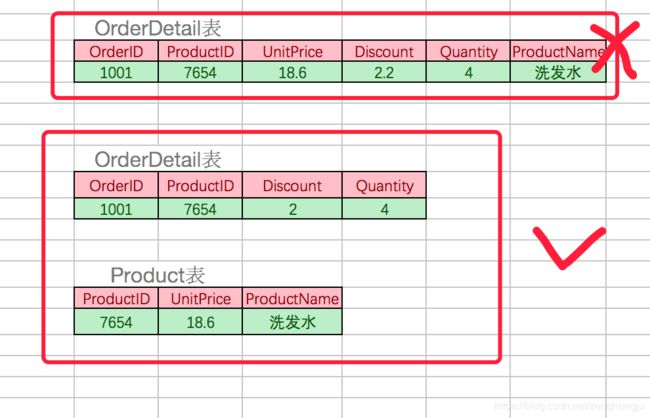
◆ 第二范式(2NF):首先是 1NF,另外包含两部分内容,一是表必须有一个主键;二是没有包含在主键中的列必须完全依赖于主键,而不能只依赖于主键的一部分。
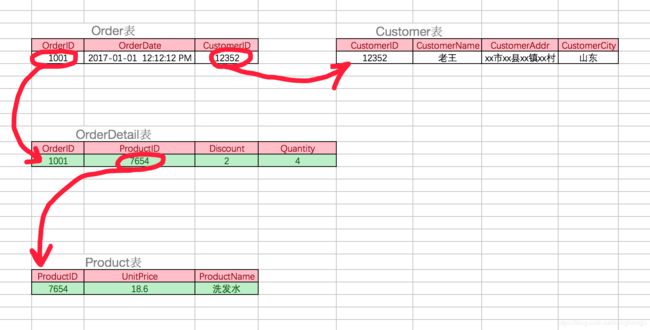
考虑一个订单明细表:【OrderDetail】(OrderID,ProductID,UnitPrice,Discount,Quantity,ProductName)。 因为我们知道在一个订单中可以订购多种产品,所以单单一个 OrderID 是不足以成为主键的,主键应该是(OrderID,ProductID)。显而易见 Discount(折扣),Quantity(数量)完全依赖(取决)于主键(OderID,ProductID),而 UnitPrice,ProductName 只依赖于 ProductID。所以 OrderDetail 表不符合 2NF。不符合 2NF 的设计容易产生冗余数据。
可以把【OrderDetail】表拆分为【OrderDetail】(OrderID,ProductID,Discount,Quantity)和【Product】(ProductID,UnitPrice,ProductName)来消除原订单表中UnitPrice,ProductName多次重复的情况。
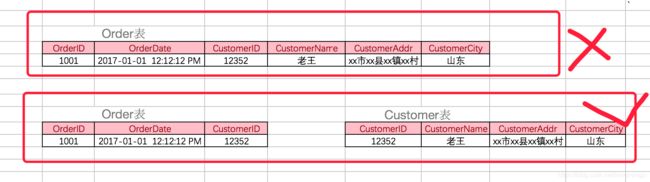
◆ 第三范式(3NF):首先是 2NF,另外非主键列必须直接依赖于主键,不能存在传递依赖。即不能存在:非主键列 A 依赖于非主键列 B,非主键列 B 依赖于主键的情况。
考虑一个订单表【Order】(OrderID,OrderDate,CustomerID,CustomerName,CustomerAddr,CustomerCity)主键是(OrderID)。 其中 OrderDate,CustomerID,CustomerName,CustomerAddr,CustomerCity 等非主键列都完全依赖于主键(OrderID),所以符合 2NF。不过问题是 CustomerName,CustomerAddr,CustomerCity 直接依赖的是 CustomerID(非主键列),而不是直接依赖于主键,它是通过传递才依赖于主键,所以不符合 3NF。 通过拆分【Order】为【Order】(OrderID,OrderDate,CustomerID)和【Customer】(CustomerID,CustomerName,CustomerAddr,CustomerCity)从而达到 3NF。 *第二范式(2NF)和第三范式(3NF)的概念很容易混淆,区分它们的关键点在于,2NF:非主键列是否完全依赖于主键,还是依赖于主键的一部分;3NF:非主键列是直接依赖于主键,还是直接依赖于非主键列。
不遵循1NF
不遵循2NF
不遵循3NF
最终表
E-R模型
- E表示entry,实体,设计实体就像定义一个类一样,指定从哪些方面描述对象,一个实体转换为数据库中的一个表
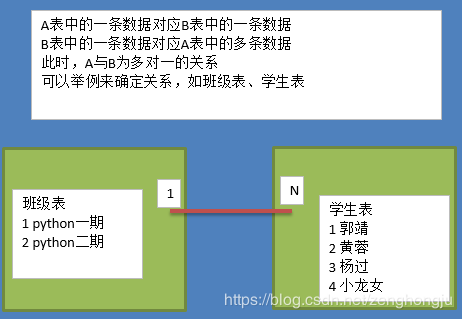
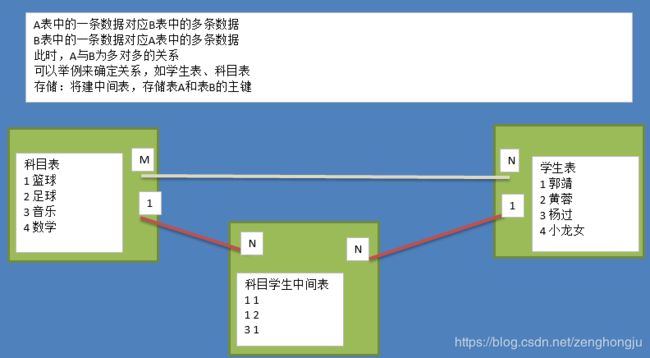
- R表示relationship,关系,关系描述两个实体之间的对应规则,关系的类型包括包括一对一、一对多、多对多
- 关系也是一种数据,需要通过一个字段存储在表中
- 实体A对实体B为1对1,则在表A或表B中创建一个字段,存储另一个表的主键值
- 实体A对实体B为1对多:在表B中创建一个字段,存储表A的主键值
- 实体A对实体B为多对多:新建一张表C,这个表只有两个字段,一个用于存储A的主键值,一个用于存储B的主键值
逻辑删除
- 对于重要数据,并不希望物理删除,一旦删除,数据无法找回
- 删除方案:设置isDelete的列,类型为bit,表示逻辑删除,默认值为0
- 对于非重要数据,可以进行物理删除
- 数据的重要性,要根据实际开发决定
示例
- 设计两张表:班级表、学生表
- 班级表classes
- id
- name
- isdelete
- 学生表students
- id
- name
- birthday
- gender
- clsid
- isdelete
扩展阅读
- 58到家数据库30条军规解读
7. MySQL-基本使用
7.1 MySQL-查询
7.1.1 创建数据库、数据表
-- 创建数据库
create database python_test_1 charset=utf8;
-- 使用数据库
use python_test_1;
-- students表
create table students(
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment not null,
name varchar(20) default '',
age tinyint unsigned default 0,
height decimal(5,2),
gender enum('男','女','中性','保密') default '保密',
cls_id int unsigned default 0,
is_delete bit default 0
);
-- classes表
create table classes (
id int unsigned auto_increment primary key not null,
name varchar(30) not null
);
7.1.2 准备数据
-- 向students表中插入数据
insert into students values
(0,'小明',18,180.00,2,1,0),
(0,'小月月',18,180.00,2,2,1),
(0,'彭于晏',29,185.00,1,1,0),
(0,'刘德华',59,175.00,1,2,1),
(0,'黄蓉',38,160.00,2,1,0),
(0,'凤姐',28,150.00,4,2,1),
(0,'王祖贤',18,172.00,2,1,1),
(0,'周杰伦',36,NULL,1,1,0),
(0,'程坤',27,181.00,1,2,0),
(0,'刘亦菲',25,166.00,2,2,0),
(0,'金星',33,162.00,3,3,1),
(0,'静香',12,180.00,2,4,0),
(0,'郭靖',12,170.00,1,4,0),
(0,'周杰',34,176.00,2,5,0);
-- 向classes表中插入数据
insert into classes values (0, "python_01期"), (0, "python_02期");
- 查询所有字段
select * from 表名;
例:
select * from students;
- 查询指定字段
select 列1,列2,... from 表名;
例:
select name from students;
- 使用 as 给字段起别名
select id as 序号, name as 名字, gender as 性别 from students;
- 可以通过 as 给表起别名
-- 如果是单表查询 可以省略表明
select id, name, gender from students;
-- 表名.字段名
select students.id,students.name,students.gender from students;
-- 可以通过 as 给表起别名
select s.id,s.name,s.gender from students as s;
7.1.3 消除重复行
- 在select后面列前使用distinct可以消除重复的行
select distinct 列1,... from 表名;
例:
select distinct gender from students;
7.2 条件
使用where子句对表中的数据筛选,结果为true的行会出现在结果集中
- 语法如下:
select * from 表名 where 条件;
例:
select * from students where id=1;
- where后面支持多种运算符,进行条件的处理
- 比较运算符
- 逻辑运算符
- 模糊查询
- 范围查询
- 空判断
7.2.1 比较运算符
- 等于: =
- 大于: >
- 大于等于: >=
- 小于: <
- 小于等于: <=
- 不等于: != 或 <>
例:查询编号大于3的学生
select * from students where id > 3;
例:查询编号不大于4的学生
select * from students where id <= 4;
例:查询姓名不是“黄蓉”的学生
select * from students where name != '黄蓉';
例:查询没被删除的学生
select * from students where is_delete=0;
7.2.2 逻辑运算符
- and
- or
- not
例:查询编号大于3的女同学
select * from students where id > 3 and gender=0;
例:查询编号小于4或没被删除的学生
select * from students where id < 4 or is_delete=0;
7.2.3 模糊查询
- like
- %表示任意多个任意字符
- _表示一个任意字符
例:查询姓黄的学生
select * from students where name like '黄%';
例:查询姓黄并且“名”是一个字的学生
select * from students where name like '黄_';
例:查询姓黄或叫靖的学生
select * from students where name like '黄%' or name like '%靖';
7.2.4 范围查询
- in表示在一个非连续的范围内
例:查询编号是1或3或8的学生
select * from students where id in(1,3,8);
- between … and …表示在一个连续的范围内
例:查询编号为3至8的学生
select * from students where id between 3 and 8;
例:查询编号是3至8的男生
select * from students where (id between 3 and 8) and gender=1;
7.2.5 空判断
- 注意:null与’'是不同的
- 判空is null
例:查询没有填写身高的学生
select * from students where height is null;
- 判非空is not null
例:查询填写了身高的学生
select * from students where height is not null;
例:查询填写了身高的男生
select * from students where height is not null and gender=1;
7.2.6 优先级
- 优先级由高到低的顺序为:小括号,not,比较运算符,逻辑运算符
- and比or先运算,如果同时出现并希望先算or,需要结合()使用
7.3 排序
为了方便查看数据,可以对数据进行排序
7.3.1 语法
select * from 表名 order by 列1 asc|desc [,列2 asc|desc,...]
7.3.2 说明
- 将行数据按照列1进行排序,如果某些行列1的值相同时,则按照列2排序,以此类推
- 默认按照列值从小到大排列(asc)
- asc从小到大排列,即升序
- desc从大到小排序,即降序
例1:查询未删除男生信息,按学号降序
select * from students where gender=1 and is_delete=0 order by id desc;
例2:查询未删除学生信息,按名称升序
select * from students where is_delete=0 order by name;
例3:显示所有的学生信息,先按照年龄从大–>小排序,当年龄相同时 按照身高从高–>矮排序
select * from students order by age desc,height desc;
7.4 聚合函数
为了快速得到统计数据,经常会用到如下5个聚合函数
7.4.1 总数
- count(*)表示计算总行数,括号中写星与列名,结果是相同的
例1:查询学生总数
select count(*) from students;
7.4.2 最大值
- max(列)表示求此列的最大值
例2:查询女生的编号最大值
select max(id) from students where gender=2;
7.4.3 最小值
- min(列)表示求此列的最小值
例3:查询未删除的学生最小编号
select min(id) from students where is_delete=0;
7.4.4 求和
- sum(列)表示求此列的和
例4:查询男生的总年龄
select sum(age) from students where gender=1;
-- 平均年龄
select sum(age)/count(*) from students where gender=1;
7.4.5 平均值
- avg(列)表示求此列的平均值
例5:查询未删除女生的编号平均值
select avg(id) from students where is_delete=0 and gender=2;
7.5 分组
7.5.1 group by
- group by的含义:将查询结果按照1个或多个字段进行分组,字段值相同的为一组
- group by可用于单个字段分组,也可用于多个字段分组
select * from students;
+----+-----------+------+--------+--------+--------+-----------+
| id | name | age | height | gender | cls_id | is_delete |
+----+-----------+------+--------+--------+--------+-----------+
| 1 | 小明 | 18 | 180.00 | 女 | 1 | |
| 2 | 小月月 | 18 | 180.00 | 女 | 2 | |
| 3 | 彭于晏 | 29 | 185.00 | 男 | 1 | |
| 4 | 刘德华 | 59 | 175.00 | 男 | 2 | |
| 5 | 黄蓉 | 38 | 160.00 | 女 | 1 | |
| 6 | 凤姐 | 28 | 150.00 | 保密 | 2 | |
| 7 | 王祖贤 | 18 | 172.00 | 女 | 1 | |
| 8 | 周杰伦 | 36 | NULL | 男 | 1 | |
| 9 | 程坤 | 27 | 181.00 | 男 | 2 | |
| 10 | 刘亦菲 | 25 | 166.00 | 女 | 2 | |
| 11 | 金星 | 33 | 162.00 | 中性 | 3 | |
| 12 | 静香 | 12 | 180.00 | 女 | 4 | |
| 13 | 周杰 | 34 | 176.00 | 女 | 5 | |
| 14 | 郭靖 | 12 | 170.00 | 男 | 4 | |
+----+-----------+------+--------+--------+--------+-----------+
select gender from students group by gender;
+--------+
| gender |
+--------+
| 男 |
| 女 |
| 中性 |
| 保密 |
+--------+
根据gender字段来分组,gender字段的全部值有4个’男’,‘女’,‘中性’,‘保密’,所以分为了4组 当group by单独使用时,只显示出每组的第一条记录, 所以group by单独使用时的实际意义不大
7.5.2 group by + group_concat()
- group_concat(字段名)可以作为一个输出字段来使用,
- 表示分组之后,根据分组结果,使用group_concat()来放置每一组的某字段的值的集合
select gender from students group by gender;
+--------+
| gender |
+--------+
| 男 |
| 女 |
| 中性 |
| 保密 |
+--------+
select gender,group_concat(name) from students group by gender;
+--------+-----------------------------------------------------------+
| gender | group_concat(name) |
+--------+-----------------------------------------------------------+
| 男 | 彭于晏,刘德华,周杰伦,程坤,郭靖 |
| 女 | 小明,小月月,黄蓉,王祖贤,刘亦菲,静香,周杰 |
| 中性 | 金星 |
| 保密 | 凤姐 |
+--------+-----------------------------------------------------------+
select gender,group_concat(id) from students group by gender;
+--------+------------------+
| gender | group_concat(id) |
+--------+------------------+
| 男 | 3,4,8,9,14 |
| 女 | 1,2,5,7,10,12,13 |
| 中性 | 11 |
| 保密 | 6 |
+--------+------------------+
7.5.3 group by + 集合函数
- 通过group_concat()的启发,我们既然可以统计出每个分组的某字段的值的集合,那么我们也可以通过集合函数来对这个
值的集合做一些操作
select gender,group_concat(age) from students group by gender;
+--------+----------------------+
| gender | group_concat(age) |
+--------+----------------------+
| 男 | 29,59,36,27,12 |
| 女 | 18,18,38,18,25,12,34 |
| 中性 | 33 |
| 保密 | 28 |
+--------+----------------------+
分别统计性别为男/女的人年龄平均值
select gender,avg(age) from students group by gender;
+--------+----------+
| gender | avg(age) |
+--------+----------+
| 男 | 32.6000 |
| 女 | 23.2857 |
| 中性 | 33.0000 |
| 保密 | 28.0000 |
+--------+----------+
分别统计性别为男/女的人的个数
select gender,count(*) from students group by gender;
+--------+----------+
| gender | count(*) |
+--------+----------+
| 男 | 5 |
| 女 | 7 |
| 中性 | 1 |
| 保密 | 1 |
+--------+----------+
7.5.4 group by + having
- having 条件表达式:用来分组查询后指定一些条件来输出查询结果
- having作用和where一样,但having只能用于group by
select gender,count(*) from students group by gender having count(*)>2;
+--------+----------+
| gender | count(*) |
+--------+----------+
| 男 | 5 |
| 女 | 7 |
+--------+----------+
7.5.5 group by + with rollup
- with rollup的作用是:在最后新增一行,来记录当前列里所有记录的总和
select gender,count(*) from students group by gender with rollup;
+--------+----------+
| gender | count(*) |
+--------+----------+
| 男 | 5 |
| 女 | 7 |
| 中性 | 1 |
| 保密 | 1 |
| NULL | 14 |
+--------+----------+
select gender,group_concat(age) from students group by gender with rollup;
+--------+-------------------------------------------+
| gender | group_concat(age) |
+--------+-------------------------------------------+
| 男 | 29,59,36,27,12 |
| 女 | 18,18,38,18,25,12,34 |
| 中性 | 33 |
| 保密 | 28 |
| NULL | 29,59,36,27,12,18,18,38,18,25,12,34,33,28 |
+--------+-------------------------------------------+
7.6 分页
当数据量过大时,在一页中查看数据是一件非常麻烦的事情
语法
select * from 表名 limit start,count
说明
- 从start开始,获取count条数据
例1:查询前3行男生信息
select * from students where gender=1 limit 0,3;
示例:分页
- 已知:每页显示m条数据,当前显示第n页
- 求总页数:此段逻辑后面会在python中实现
- 查询总条数p1
- 使用p1除以m得到p2
- 如果整除则p2为总数页
- 如果不整除则p2+1为总页数
- 求第n页的数据
select * from students where is_delete=0 limit (n-1)*m,m
7.7 连接查询
当查询结果的列来源于多张表时,需要将多张表连接成一个大的数据集,再选择合适的列返回
mysql支持三种类型的连接查询,分别为:
- 左连接查询:查询的结果为两个表匹配到的数据,左表特有的数据,对于右表中不存在的数据使用null填充
语法
select * from 表1 inner或left或right join 表2 on 表1.列 = 表2.列
例1:使用内连接查询班级表与学生表
select * from students inner join classes on students.cls_id = classes.id;
例2:使用左连接查询班级表与学生表
- 此处使用了as为表起别名,目的是编写简单
select * from students as s left join classes as c on s.cls_id = c.id;
例3:使用右连接查询班级表与学生表
select * from students as s right join classes as c on s.cls_id = c.id;
例4:查询学生姓名及班级名称
select s.name,c.name from students as s inner join classes as c on s.cls_id = c.id;
7.8 自关联
- 设计省信息的表结构provinces
- id
- ptitle
- 设计市信息的表结构citys
- id
- ctitle
- proid
- citys表的proid表示城市所属的省,对应着provinces表的id值
问题:
能不能将两个表合成一张表呢?
思考:
观察两张表发现,citys表比provinces表多一个列proid,其它列的类型都是一样的
意义:
存储的都是地区信息,而且每种信息的数据量有限,没必要增加一个新表,或者将来还要存储区、乡镇信息,都增加新表的开销太大
答案:
定义表areas,结构如下
- id
- atitle
- pid
说明:
- 因为省没有所属的省份,所以可以填写为null
- 城市所属的省份pid,填写省所对应的编号id
- 这就是自关联,表中的某一列,关联了这个表中的另外一列,但是它们的业务逻辑含义是不一样的,城市信息的pid引用的是省信息的id
- 在这个表中,结构不变,可以添加区县、乡镇街道、村社区等信息
创建areas表的语句如下:
create table areas(
aid int primary key,
atitle varchar(20),
pid int
);
- 从sql文件中导入数据
source areas.sql;
- 查询一共有多少个省
select count(*) from areas where pid is null;
- 例1:查询省的名称为“山西省”的所有城市
select city.* from areas as city
inner join areas as province on city.pid=province.aid
where province.atitle='山西省';
- 例2:查询市的名称为“广州市”的所有区县
select dis.* from areas as dis
inner join areas as city on city.aid=dis.pid
where city.atitle='广州市';
7.9 子查询
7.9.1 子查询
在一个 select 语句中,嵌入了另外一个 select 语句, 那么被嵌入的 select 语句称之为子查询语句
7.9.2 主查询
主要查询的对象,第一条 select 语句
7.9.3 主查询和子查询的关系
- 子查询是嵌入到主查询中
- 子查询是辅助主查询的,要么充当条件,要么充当数据源
- 子查询是可以独立存在的语句,是一条完整的 select 语句
7.9.4 子查询分类
- 标量子查询: 子查询返回的结果是一个数据(一行一列)
- 列子查询: 返回的结果是一列(一列多行)
- 行子查询: 返回的结果是一行(一行多列)
7.9.5 标量子查询
- 查询班级学生平均年龄
- 查询大于平均年龄的学生
查询班级学生的平均身高
select * from students where age > (select avg(age) from students);
7.9.6 列级子查询
- 查询还有学生在班的所有班级名字
-
- 找出学生表中所有的班级 id
- 找出班级表中对应的名字
select name from classes where id in (select cls_id from students);
7.9.7 行级子查询
- 需求: 查找班级年龄最大,身高最高的学生
- 行元素: 将多个字段合成一个行元素,在行级子查询中会使用到行元素
select * from students where (height,age) = (select max(height),max(age) from students);
7.9.8 子查询中特定关键字使用
- in 范围
- 格式: 主查询 where 条件 in (列子查询)
7.10 总结
查询的完整格式
SELECT select_expr [,select_expr,...] [
FROM tb_name
[WHERE 条件判断]
[GROUP BY {col_name | postion} [ASC | DESC], ...]
[HAVING WHERE 条件判断]
[ORDER BY {col_name|expr|postion} [ASC | DESC], ...]
[ LIMIT {[offset,]rowcount | row_count OFFSET offset}]
]
- 完整的select语句
select distinct *
from 表名
where ....
group by ... having ...
order by ...
limit start,count
- 执行顺序为:
- from 表名
- where …
- group by …
- select distinct *
- having …
- order by …
- limit start,count
- 实际使用中,只是语句中某些部分的组合,而不是全部
8. MySQL与Python交互
8.1 准备数据
8.1.1 创建数据表
-- 创建 "京东" 数据库
create database jing_dong charset=utf8;
-- 使用 "京东" 数据库
use jing_dong;
-- 创建一个商品goods数据表
create table goods(
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment not null,
name varchar(150) not null,
cate_name varchar(40) not null,
brand_name varchar(40) not null,
price decimal(10,3) not null default 0,
is_show bit not null default 1,
is_saleoff bit not null default 0
);
8.1.2 插入数据
-- 向goods表中插入数据
insert into goods values(0,'r510vc 15.6英寸笔记本','笔记本','华硕','3399',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'y400n 14.0英寸笔记本电脑','笔记本','联想','4999',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'g150th 15.6英寸游戏本','游戏本','雷神','8499',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'x550cc 15.6英寸笔记本','笔记本','华硕','2799',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'x240 超极本','超级本','联想','4880',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'u330p 13.3英寸超极本','超级本','联想','4299',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'svp13226scb 触控超极本','超级本','索尼','7999',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'ipad mini 7.9英寸平板电脑','平板电脑','苹果','1998',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'ipad air 9.7英寸平板电脑','平板电脑','苹果','3388',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'ipad mini 配备 retina 显示屏','平板电脑','苹果','2788',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'ideacentre c340 20英寸一体电脑 ','台式机','联想','3499',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'vostro 3800-r1206 台式电脑','台式机','戴尔','2899',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'imac me086ch/a 21.5英寸一体电脑','台式机','苹果','9188',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'at7-7414lp 台式电脑 linux )','台式机','宏碁','3699',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'z220sff f4f06pa工作站','服务器/工作站','惠普','4288',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'poweredge ii服务器','服务器/工作站','戴尔','5388',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'mac pro专业级台式电脑','服务器/工作站','苹果','28888',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'hmz-t3w 头戴显示设备','笔记本配件','索尼','6999',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'商务双肩背包','笔记本配件','索尼','99',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'x3250 m4机架式服务器','服务器/工作站','ibm','6888',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'商务双肩背包','笔记本配件','索尼','99',default,default);
8.2 SQL演练
8.2.1 SQL语句的强化
- 查询类型cate_name为 ‘超极本’ 的商品名称、价格
select name,price from goods where cate_name = '超级本';
- 显示商品的种类
select cate_name from goods group by cate_name;
- 求所有电脑产品的平均价格,并且保留两位小数
select round(avg(price),2) as avg_price from goods;
- 显示每种商品的平均价格
select cate_name,avg(price) from goods group by cate_name;
- 查询每种类型的商品中 最贵、最便宜、平均价、数量
select cate_name,max(price),min(price),avg(price),count(*) from goods group by cate_name;
- 查询所有价格大于平均价格的商品,并且按价格降序排序
select id,name,price from goods
where price > (select round(avg(price),2) as avg_price from goods)
order by price desc;
- 查询每种类型中最贵的电脑信息
select * from goods
inner join
(
select
cate_name,
max(price) as max_price,
min(price) as min_price,
avg(price) as avg_price,
count(*) from goods group by cate_name
) as goods_new_info
on goods.cate_name=goods_new_info.cate_name and goods.price=goods_new_info.max_price;
8.2.2 创建 “商品分类”" 表
-- 创建商品分类表
create table if not exists goods_cates(
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(40) not null
);
- 查询goods表中商品的种类
select cate_name from goods group by cate_name;
- 将分组结果写入到goods_cates数据表
insert into goods_cates (name) select cate_name from goods group by cate_name;
8.2.3 同步表数据
- 通过goods_cates数据表来更新goods表
update goods as g inner join goods_cates as c on g.cate_name=c.name set g.cate_name=c.id;
8.2.4 创建 “商品品牌表” 表
- 通过create…select来创建数据表并且同时写入记录,一步到位
-- select brand_name from goods group by brand_name;
-- 在创建数据表的时候一起插入数据
-- 注意: 需要对brand_name 用as起别名,否则name字段就没有值
create table goods_brands (
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(40) not null) select brand_name as name from goods group by brand_name;
8.2.5 同步数据
- 通过goods_brands数据表来更新goods数据表
update goods as g inner join goods_brands as b on g.brand_name=b.name set g.brand_name=b.id;
8.2.6 修改表结构
- 查看 goods 的数据表结构,会发现 cate_name 和 brand_name对应的类型为
varchar但是存储的都是数字
desc goods;
- 通过alter table语句修改表结构
alter table goods
change cate_name cate_id int unsigned not null,
change brand_name brand_id int unsigned not null;
8.2.7 外键
- 分别在 goods_cates 和 goods_brands表中插入记录
insert into goods_cates(name) values ('路由器'),('交换机'),('网卡');
insert into goods_brands(name) values ('海尔'),('清华同方'),('神舟');
- 在 goods 数据表中写入任意记录
insert into goods (name,cate_id,brand_id,price)
values('LaserJet Pro P1606dn 黑白激光打印机', 12, 4,'1849');
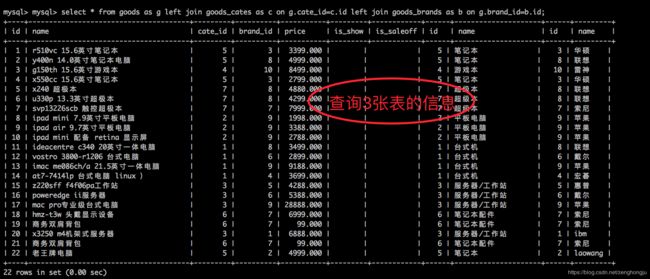
- 查询所有商品的详细信息 (通过内连接)
select g.id,g.name,c.name,b.name,g.price from goods as g
inner join goods_cates as c on g.cate_id=c.id
inner join goods_brands as b on g.brand_id=b.id;
- 查询所有商品的详细信息 (通过左连接)
select g.id,g.name,c.name,b.name,g.price from goods as g
left join goods_cates as c on g.cate_id=c.id
left join goods_brands as b on g.brand_id=b.id;
- 如何防止无效信息的插入,就是可以在插入前判断类型或者品牌名称是否存在呢? 可以使用之前讲过的外键来解决
- 外键约束:对数据的有效性进行验证
- 关键字: foreign key,只有 innodb数据库引擎 支持外键约束
- 对于已经存在的数据表 如何更新外键约束
-- 给brand_id 添加外键约束成功
alter table goods add foreign key (brand_id) references goods_brands(id);
-- 给cate_id 添加外键失败
-- 会出现1452错误
-- 错误原因:已经添加了一个不存在的cate_id值12,因此需要先删除
alter table goods add foreign key (cate_id) references goods_cates(id);
- 如何在创建数据表的时候就设置外键约束呢?
- 注意: goods 中的 cate_id 的类型一定要和 goods_cates 表中的 id 类型一致
create table goods(
id int primary key auto_increment not null,
name varchar(40) default '',
price decimal(5,2),
cate_id int unsigned,
brand_id int unsigned,
is_show bit default 1,
is_saleoff bit default 0,
foreign key(cate_id) references goods_cates(id),
foreign key(brand_id) references goods_brands(id)
);
- 如何取消外键约束
-- 需要先获取外键约束名称,该名称系统会自动生成,可以通过查看表创建语句来获取名称
show create table goods;
-- 获取名称之后就可以根据名称来删除外键约束
alter table goods drop foreign key 外键名称;
- 在实际开发中,很少会使用到外键约束,会极大的降低表更新的效率
8.3 数据库的设计
8.3.1 创建 “商品分类” 表
create table goods_cates(
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment not null,
name varchar(40) not null
);
8.3.2 创建 “商品品牌” 表
create table goods_brands (
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment not null,
name varchar(40) not null
);
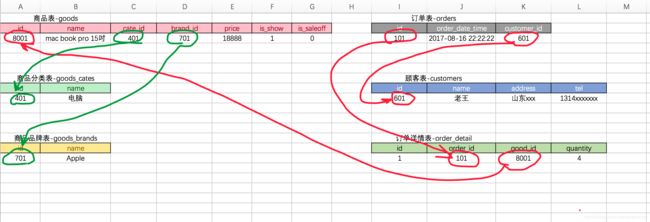
8.3.3 创建 “商品” 表
create table goods(
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment not null,
name varchar(40) default '',
price decimal(5,2),
cate_id int unsigned,
brand_id int unsigned,
is_show bit default 1,
is_saleoff bit default 0,
foreign key(cate_id) references goods_cates(id),
foreign key(brand_id) references goods_brands(id)
);
8.3.4 创建 “顾客” 表
create table customer(
id int unsigned auto_increment primary key not null,
name varchar(30) not null,
addr varchar(100),
tel varchar(11) not null
);
8.3.5 创建 “订单” 表
create table orders(
id int unsigned auto_increment primary key not null,
order_date_time datetime not null,
customer_id int unsigned,
foreign key(customer_id) references customer(id)
);
8.3.6 创建 “订单详情” 表
create table order_detail(
id int unsigned auto_increment primary key not null,
order_id int unsigned not null,
goods_id int unsigned not null,
quantity tinyint unsigned not null,
foreign key(order_id) references orders(id),
foreign key(goods_id) references goods(id)
);
说明
- 以上创建表的顺序是有要求的,即如果goods表中的外键约束用的是goods_cates或者是goods_brands,那么就应该先创建这2个表,否则创建goods会失败
- 创建外键时,一定要注意类型要相同,否则失败
8.4 Python 中操作 MySQL 步骤
8.4.1 引入模块
- 在py文件中引入pymysql模块
from pymysql import *
8.4.2 Connection 对象
- 用于建立与数据库的连接
- 创建对象:调用connect()方法
conn=connect(参数列表)
- 参数host:连接的mysql主机,如果本机是’localhost’
- 参数port:连接的mysql主机的端口,默认是3306
- 参数database:数据库的名称
- 参数user:连接的用户名
- 参数password:连接的密码
- 参数charset:通信采用的编码方式,推荐使用utf8
对象的方法
- close()关闭连接
- commit()提交
- cursor()返回Cursor对象,用于执行sql语句并获得结果
8.4.3 Cursor对象
- 用于执行sql语句,使用频度最高的语句为select、insert、update、delete
- 获取Cursor对象:调用Connection对象的cursor()方法
cs1=conn.cursor()
对象的方法
- close()关闭
- execute(operation [, parameters ])执行语句,返回受影响的行数,主要用于执行insert、update、delete语句,也可以执行create、alter、drop等语句
- fetchone()执行查询语句时,获取查询结果集的第一个行数据,返回一个元组
- fetchall()执行查询时,获取结果集的所有行,一行构成一个元组,再将这些元组装入一个元组返回
对象的属性
- rowcount只读属性,表示最近一次execute()执行后受影响的行数
- connection获得当前连接对象
8.5 增删改
from pymysql import *
def main():
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,database='jing_dong',user='root',password='mysql',charset='utf8')
# 获得Cursor对象
cs1 = conn.cursor()
# 执行insert语句,并返回受影响的行数:添加一条数据
# 增加
count = cs1.execute('insert into goods_cates(name) values("硬盘")')
#打印受影响的行数
print(count)
count = cs1.execute('insert into goods_cates(name) values("光盘")')
print(count)
# # 更新
# count = cs1.execute('update goods_cates set name="机械硬盘" where name="硬盘"')
# # 删除
# count = cs1.execute('delete from goods_cates where id=6')
# 提交之前的操作,如果之前已经之执行过多次的execute,那么就都进行提交
conn.commit()
# 关闭Cursor对象
cs1.close()
# 关闭Connection对象
conn.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
8.6 查询一行数据
from pymysql import *
def main():
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,user='root',password='mysql',database='jing_dong',charset='utf8')
# 获得Cursor对象
cs1 = conn.cursor()
# 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询一条数据
count = cs1.execute('select id,name from goods where id>=4')
# 打印受影响的行数
print("查询到%d条数据:" % count)
for i in range(count):
# 获取查询的结果
result = cs1.fetchone()
# 打印查询的结果
print(result)
# 获取查询的结果
# 关闭Cursor对象
cs1.close()
conn.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
8.7 查询多行数据
from pymysql import *
def main():
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,user='root',password='mysql',database='jing_dong',charset='utf8')
# 获得Cursor对象
cs1 = conn.cursor()
# 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询一条数据
count = cs1.execute('select id,name from goods where id>=4')
# 打印受影响的行数
print("查询到%d条数据:" % count)
# for i in range(count):
# # 获取查询的结果
# result = cs1.fetchone()
# # 打印查询的结果
# print(result)
# # 获取查询的结果
result = cs1.fetchall()
print(result)
# 关闭Cursor对象
cs1.close()
conn.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
8.8 参数化
- sql语句的参数化,可以有效防止sql注入
- 注意:此处不同于python的字符串格式化,全部使用%s占位
from pymysql import *
def main():
find_name = input("请输入物品名称:")
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,user='root',password='mysql',database='jing_dong',charset='utf8')
# 获得Cursor对象
cs1 = conn.cursor()
# # 非安全的方式
# # 输入 " or 1=1 or " (双引号也要输入)
# sql = 'select * from goods where name="%s"' % find_name
# print("""sql===>%s<====""" % sql)
# # 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询所有数据
# count = cs1.execute(sql)
# 安全的方式
# 构造参数列表
params = [find_name]
# 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询所有数据
count = cs1.execute('select * from goods where name=%s', params)
# 注意:
# 如果要是有多个参数,需要进行参数化
# 那么params = [数值1, 数值2....],此时sql语句中有多个%s即可
# 打印受影响的行数
print(count)
# 获取查询的结果
# result = cs1.fetchone()
result = cs1.fetchall()
# 打印查询的结果
print(result)
# 关闭Cursor对象
cs1.close()
# 关闭Connection对象
conn.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
9. MySQL高级
9.1 视图
9.1.1 问题
对于复杂的查询,往往是有多个数据表进行关联查询而得到,如果数据库因为需求等原因发生了改变,为了保证查询出来的数据与之前相同,则需要在多个地方进行修改,维护起来非常麻烦
解决办法:定义视图
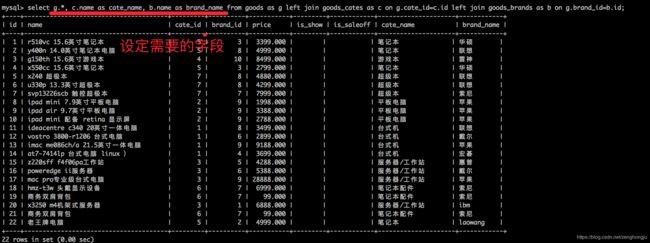
9.1.2 视图是什么
通俗的讲,视图就是一条SELECT语句执行后返回的结果集。所以我们在创建视图的时候,主要的工作就落在创建这条SQL查询语句上。
视图是对若干张基本表的引用,一张虚表,查询语句执行的结果,不存储具体的数据(基本表数据发生了改变,视图也会跟着改变);
方便操作,特别是查询操作,减少复杂的SQL语句,增强可读性;
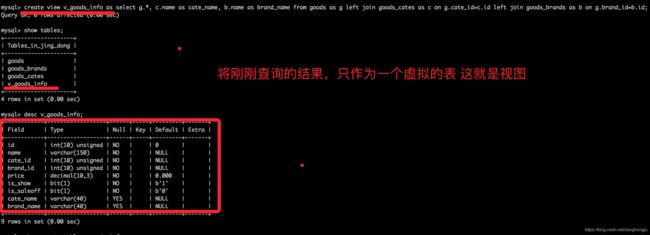
9.1.3 定义视图
建议以v_开头
create view 视图名称 as select语句;
9.1.4 查看视图
查看表会将所有的视图也列出来
show tables;
9.1.5 使用视图
视图的用途就是查询
select * from v_stu_score;
9.1.6 删除视图
drop view 视图名称;
例:
drop view v_stu_sco;
9.1.7 视图demo
9.1.8 视图的作用
- 提高了重用性,就像一个函数
- 对数据库重构,却不影响程序的运行
- 提高了安全性能,可以对不同的用户
- 让数据更加清晰
9.2 事务
9.2.1 为什么要有事务
事务广泛的运用于订单系统、银行系统等多种场景
例如:
A用户和B用户是银行的储户,现在A要给B转账500元,那么需要做以下几件事:
- 检查A的账户余额>500元;
- A 账户中扣除500元;
- B 账户中增加500元;
正常的流程走下来,A账户扣了500,B账户加了500,皆大欢喜。
那如果A账户扣了钱之后,系统出故障了呢?A白白损失了500,而B也没有收到本该属于他的500。
以上的案例中,隐藏着一个前提条件:A扣钱和B加钱,要么同时成功,要么同时失败。事务的需求就在于此
所谓事务,它是一个操作序列,这些操作要么都执行,要么都不执行,它是一个不可分割的工作单位。
例如,银行转帐工作:从一个帐号扣款并使另一个帐号增款,这两个操作要么都执行,要么都不执行。所以,应该把他们看成一个事务。事务是数据库维护数据一致性的单位,在每个事务结束时,都能保持数据一致性
9.2.2 事务四大特性(简称ACID)
- 原子性(Atomicity)
- 一致性(Consistency)
- 隔离性(Isolation)
- 持久性(Durability)
以下内容出自《高性能MySQL》第三版,了解事务的ACID及四种隔离级有助于我们更好的理解事务运作。
下面举一个银行应用是解释事务必要性的一个经典例子。假如一个银行的数据库有两张表:支票表(checking)和储蓄表(savings)。现在要从用户Jane的支票账户转移200美元到她的储蓄账户,那么至少需要三个步骤:
- 检查支票账户的余额高于或者等于200美元。
- 从支票账户余额中减去200美元。
- 在储蓄帐户余额中增加200美元。
上述三个步骤的操作必须打包在一个事务中,任何一个步骤失败,则必须回滚所有的步骤。
可以用START TRANSACTION语句开始一个事务,然后要么使用COMMIT提交将修改的数据持久保存,要么使用ROLLBACK撤销所有的修改。事务SQL的样本如下:
- start transaction;
- select balance from checking where customer_id = 10233276;
- update checking set balance = balance - 200.00 where customer_id = 10233276;
- update savings set balance = balance + 200.00 where customer_id = 10233276;
- commit;
一个很好的事务处理系统,必须具备这些标准特性:
- 原子性(atomicity)
一个事务必须被视为一个不可分割的最小工作单元,整个事务中的所有操作要么全部提交成功,要么全部失败回滚,对于一个事务来说,不可能只执行其中的一部分操作,这就是事务的原子性
- 一致性(consistency)
数据库总是从一个一致性的状态转换到另一个一致性的状态。(在前面的例子中,一致性确保了,即使在执行第三、四条语句之间时系统崩溃,支票账户中也不会损失200美元,因为事务最终没有提交,所以事务中所做的修改也不会保存到数据库中。)
- 隔离性(isolation)
通常来说,一个事务所做的修改在最终提交以前,对其他事务是不可见的。(在前面的例子中,当执行完第三条语句、第四条语句还未开始时,此时有另外的一个账户汇总程序开始运行,则其看到支票帐户的余额并没有被减去200美元。)
- 持久性(durability)
一旦事务提交,则其所做的修改会永久保存到数据库。(此时即使系统崩溃,修改的数据也不会丢失。)
9.2.3 事务命令
表的引擎类型必须是innodb类型才可以使用事务,这是mysql表的默认引擎
查看表的创建语句,可以看到engine=innodb
-- 选择数据库
use jing_dong;
-- 查看goods表
show create table goods;
开启事务,命令如下:
- 开启事务后执行修改命令,变更会维护到本地缓存中,而不维护到物理表中
begin;
或者
start transaction;
提交事务,命令如下
- 将缓存中的数据变更维护到物理表中
commit;
回滚事务,命令如下:
- 放弃缓存中变更的数据
rollback;
注意
- 修改数据的命令会自动的触发事务,包括insert、update、delete
- 而在SQL语句中有手动开启事务的原因是:可以进行多次数据的修改,如果成功一起成功,否则一起会滚到之前的数据
9.3 提交
- 为了演示效果,需要打开两个终端窗口,使用同一个数据库,操作同一张表(用到之前的jing_dong数据,可以回到mysql第3天中查看)
9.3.1 step1:连接
- 终端1:查询商品分类信息
select * from goods_cates;
9.3.2 step2:增加数据
- 终端2:开启事务,插入数据
begin;
insert into goods_cates(name) values('小霸王游戏机');
- 终端2:查询数据,此时有新增的数据
select * from goods_cates;
9.3.3 step3:查询
- 终端1:查询数据,发现并没有新增的数据
select * from goods_cates;
9.3.4 step4:提交
- 终端2:完成提交
commit;
9.3.5 step5:查询
- 终端1:查询,发现有新增的数据
select * from goods_cates;
9.4 回滚
- 为了演示效果,需要打开两个终端窗口,使用同一个数据库,操作同一张表
9.4.1 step1:连接
- 终端1
select * from goods_cates;
9.4.2 step2:增加数据
- 终端2:开启事务,插入数据
begin;
insert into goods_cates(name) values('小霸王游戏机');
- 终端2:查询数据,此时有新增的数据
select * from goods_cates;
9.4.3 step3:查询
- 终端1:查询数据,发现并没有新增的数据
select * from goods_cates;
9.4.4 step4:回滚
- 终端2:完成回滚
rollback;
9.4.5 step5:查询
- 终端1:查询数据,发现没有新增的数据
select * from goods_cates;
9.5 索引
9.5.1 索引是什么
索引是一种特殊的文件(InnoDB数据表上的索引是表空间的一个组成部分),它们包含着对数据表里所有记录的引用指针。
更通俗的说,数据库索引好比是一本书前面的目录,能加快数据库的查询速度
9.5.2 索引目的
索引的目的在于提高查询效率,可以类比字典,如果要查“mysql”这个单词,我们肯定需要定位到m字母,然后从下往下找到y字母,再找到剩下的sql。如果没有索引,那么你可能需要把所有单词看一遍才能找到你想要的,如果我想找到m开头的单词呢?或者ze开头的单词呢?是不是觉得如果没有索引,这个事情根本无法完成?
9.5.3 索引原理
除了词典,生活中随处可见索引的例子,如火车站的车次表、图书的目录等。它们的原理都是一样的,通过不断的缩小想要获得数据的范围来筛选出最终想要的结果,同时把随机的事件变成顺序的事件,也就是我们总是通过同一种查找方式来锁定数据。
数据库也是一样,但显然要复杂许多,因为不仅面临着等值查询,还有范围查询(>、<、between、in)、模糊查询(like)、并集查询(or)等等。数据库应该选择怎么样的方式来应对所有的问题呢?我们回想字典的例子,能不能把数据分成段,然后分段查询呢?最简单的如果1000条数据,1到100分成第一段,101到200分成第二段,201到300分成第三段……这样查第250条数据,只要找第三段就可以了,一下子去除了90%的无效数据。
9.5.4 索引的使用
- 查看索引
show index from 表名;
- 创建索引
- 如果指定字段是字符串,需要指定长度,建议长度与定义字段时的长度一致
- 字段类型如果不是字符串,可以不填写长度部分
create index 索引名称 on 表名(字段名称(长度))
- 删除索引:
drop index 索引名称 on 表名;
9.5.5 索引demo
9.5.5.1 创建测试表testindex
create table test_index(title varchar(10));
9.5.5.2 使用python程序(ipython也可以)通过pymsql模块 向表中加入十万条数据
from pymysql import connect
def main():
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,database='jing_dong',user='root',password='mysql',charset='utf8')
# 获得Cursor对象
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 插入10万次数据
for i in range(100000):
cursor.execute("insert into test_index values('ha-%d')" % i)
# 提交数据
conn.commit()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
9.5.5.3 查询
- 开启运行时间监测:
set profiling=1;
- 查找第1万条数据ha-99999
select * from test_index where title='ha-99999';
- 查看执行的时间:
show profiles;
- 为表title_index的title列创建索引:
create index title_index on test_index(title(10));
- 执行查询语句:
select * from test_index where title='ha-99999';
- 再次查看执行的时间
show profiles;
9.5.6 注意
要注意的是,建立太多的索引将会影响更新和插入的速度,因为它需要同样更新每个索引文件。对于一个经常需要更新和插入的表格,就没有必要为一个很少使用的where字句单独建立索引了,对于比较小的表,排序的开销不会很大,也没有必要建立另外的索引。
索引是一种特殊的文件(InnoDB数据表上的索引是表空间的一个组成部分),它们包含着对数据表里所有记录的引用指针。
更通俗的说,数据库索引好比是一本书前面的目录,能加快数据库的查询速度