ssh :secure shell,工作于tcp22号端口,有两个版本,sshv1和sshv2。常用的是sshv2。openssh是对ssh协议的一种应用实现,工作于tcp/ip的连接都可以通过ssh隧道加密后转发。windows下客户端常用的工具有xshell,secure crt,putty,pietty等,linux下官户端命令是ssh,服务端程序是sshd。默认系统已经安装了ssh。
客户端第一次发请求连接服务器时,客户机会向服务器要服务器端的身份信息,服务器端向客户端发送密钥指纹给客户端。这时客户端会验证服务器端是否为客户端想要连接的目标,如果客户端没有连接过,就需要用户手动确认。如果之前客户端连接过此服务器,客户端会保存一份指纹信息,下次再连接就会比对此指纹。如果不指纹不符合,会提示用户,且问用户是否连接。在linux下第一次连接其它主机时如下,此功能可以关闭:
在linux中,密钥信息保存在用户家目录的.ssh/known_hosts文件中,如下:
[root@localhost .ssh]# cat /root/.ssh/known_hosts
172.16.2.15 ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEA2kUBUM4qK5dmdhRrThd4YkqxffjxOBlxTr7/NPl++oenqctPj+fc8dO5S+LM6TNrtodTAbNoWDiGELGMWRyMf2q2lBKXRvW1xKIBds+mezjsYgseEsH7tOp0hwYNcuh/VJZJIkrYOnH1IjEyHX9nDUILYO/jP33jJF2nGRzEb4e6PGFRkw+H7CO8G+b5zN+7jdgyapMg1VwZcxdzwrzkcplNilYQ37mpRHjvNGk4h2qaj9b0/bx3ZoTbIw66EOa85DWT7KB+syIvdj47FDyspQ0cDAOwXyu8M/ctBZbfewSJ7l4Al6bT1qbzzecRZmb+nXbdb4o4xGEsSfZRZ2MJaw==
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ssh服务端程序的rpm包是:openssh-server-4.3p2-82.el5。版本可能不一样。
ssh客户端rpm包是:openssh-clients-4.3p2-82.el5
在centos6以下版本维护sshd服务,服务脚本配置文件在/etc/sysconfig/sshd
获取脚本配置文件/etc/sysconfig/sshd的帮助文档命令。
# man sshd_config
启动或关闭服务等
#service sshd {start|stop|restart|reload|force-reload|condrestart|try-restart|status}
# ss -tnlp | grep ':22' #查看sshd服务有没有启动
在centos7系统上维护sshd服务
# systemctl list-unit-files | grep '^sshd.service' #查看sshd服务开机是否自动启动,
sshd.service enabled #ebabled为开机自动启动disabled为禁用
# systemctl enable sshd.service #设置sshd服务开机自动启动
# systemctl disabled sshd.service #设置sshd服务开机禁止启动
# systemctl restart sshd.service #重新启动sshd服务
# systemctl stop sshd.service #停止sshd服务
# systemctl start sshd.service #启动sshd服务
# ss -tnlp | grep ':22' #查看sshd服务有没有启动
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
openssh的客户端组件
ssh命令使用格式
ssh [username@]hostname [command] :用户可有可无,如果没有指定用户名会以当前用户登陆。如果在主机后面跟上命令表示,登陆到目标主机执行所指定的命令,然后再本机显示。如下:
# ssh [email protected] hostname
[root@localhost /]# ssh [email protected] hostname
[email protected]'s password:
bogon
lastb:显示尝试使用ssh登陆本机的ip和时间。
scp:使用ssh协议在两台主机之间进行文件安装传输的工具。
-r :用来复制目录。
-q:静默模式,
-p :(小写)复制文件时保持文件的权限模型和时间戳。
-P:(大写)指定目标主机使用的tcp端口。
# scp /tmp/wukui.txt [email protected]/tmp/ :复制wukui.txt到172.16.2.15的/tmp下。如果复制多个文件目标必须为目录。
#scp [email protected]/etc/passwd ./ :把目标主机上的/etc/passwd文件复制到当前目录下。
sftp :基于ssh的ftp文件传输工具。比scp更灵活,可以到远程主机上查看文件名。centos默认此功能为开启。
子命令有
help:获取帮助
get :下载文件
put:上传文件
mkdir :在目标主机上创建目录。
lpwd:查看本机工作目录。
pwd:查看所在目标主机的目录
quit:退出sftp.
#put /etc/passwd /tmp :把本机passwd上传到目标主机的tmp下
ssh 服务端配置文件在/etc/ssh/sshd_config
ssh 客户端配置文件在/etc/ssh/ssh_config
日志文件记录在/var/log/secure中,只有管理员有权限访问。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
服务端配置文件配置,#为注释。以#开头后面跟一空格是的描述信息,以#开头后面直接是字符的是注释后配置选项,如果此选项没有指定,则默认为此注释表示的特性运行。
# $OpenBSD: sshd_config,v 1.80 2008/07/02 02:24:18 djm Exp $
# This is the sshd server system-wide configuration file. See
# sshd_config(5) for more information.
# This sshd was compiled with PATH=/usr/local/bin:/bin:/usr/bin
# The strategy used for options in the default sshd_config shipped with
# OpenSSH is to specify options with their default value where
# possible, but leave them commented. Uncommented options change a
# default value.
#Port 22 #此处指定sshd使用的tcp端口
#AddressFamily any #批定监听在那个版本的ip上(ipv4和ipv6),any表示所有
#ListenAddress 0.0.0.0 #sshd服务工作在那个ipv4的地址上。0.0.0.0表示监听本机所有地址
#ListenAddress :: #监听于那个ipv6地址,::表示监听所有ipv6地址。
# Disable legacy (protocol version 1) support in the server for new
# installations. In future the default will change to require explicit
# activation of protocol 1
Protocol 2 #使用那个版本的ssh协议,这里表示使用sshv2版本。
#DenyUsers #拒绝那些用记登陆,用户名写在此项后面
#AllowUsers #允许那此用户登陆。
#AllowGroups #允许那些组可以登陆。
# HostKey for protocol version 1
#HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_key #sshv1使用到的主机密钥,当客户端请求服务端时,服务端发给客户端的公钥。
# HostKeys for protocol version 2 #sshv2使用的主机密钥
#HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key #sshv2使用的rsa加密算法,rsa可以做加密解密,身份认证。一般都使用rsa。
#HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_dsa_key #sshv2使用的dsa加密算法,dsa只能做身份认证。
# Lifetime and size of ephemeral version 1 server key
#KeyRegenerationInterval 1h #双方通信时使用对衬加密,加密的密钥由双方协商(协商不需要用户参与,由客户端与服务端自动协商),这里指定协商频率。默认每隔1小时就换一次。
#ServerKeyBits 1024 #批定密钥的长度
# Logging
# obsoletes QuietMode and FascistLogging
#SyslogFacility AUTH
SyslogFacility AUTHPRIV #日志发送给那个程序。日志文件记录在/var/log/secure中
#LogLevel INFO
# Authentication:
#LoginGraceTime 2m #登陆宽限期,宽限期是指客户端连接服务端后,没有输入用户名或密码,而停在此处。 默认为2分钟。
#PermitRootLogin yes #是否允许管理员登陆,yes为允许,no为不允许管理员直接登陆,必须使用普通用户登陆,然后su到root用户上,no为安全的做法。
#StrictModes yes
#MaxAuthTries 6 #最大认证次数,最多允许输入多少次密码。到
#MaxSessions 10 #最大会话个数,此sshd服务最多允许多少个会话连接。
#RSAAuthentication yes #是否允许RSA机制认证。
#PubkeyAuthentication yes #是否允许基于公钥认证
#AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys #使用密钥认证时的密钥文件在那个文件中。用户家目录(.ssh/authorized_keys)
#AuthorizedKeysCommand none
#AuthorizedKeysCommandRunAs nobody
# For this to work you will also need host keys in /etc/ssh/ssh_known_hosts
#RhostsRSAAuthentication no
# similar for protocol version 2
#HostbasedAuthentication no
# Change to yes if you don't trust ~/.ssh/known_hosts for
# RhostsRSAAuthentication and HostbasedAuthentication
#IgnoreUserKnownHosts no
# Don't read the user's ~/.rhosts and ~/.shosts files
#IgnoreRhosts yes
# To disable tunneled clear text passwords, change to no here!
#PasswordAuthentication yes
#PermitEmptyPasswords no
PasswordAuthentication yes
# Change to no to disable s/key passwords
#ChallengeResponseAuthentication yes
ChallengeResponseAuthentication no
# Kerberos options
#KerberosAuthentication no
#KerberosOrLocalPasswd yes
#KerberosTicketCleanup yes
#KerberosGetAFSToken no
#KerberosUseKuserok yes
# GSSAPI options
#GSSAPIAuthentication no
GSSAPIAuthentication yes
#GSSAPICleanupCredentials yes
GSSAPICleanupCredentials yes
#GSSAPIStrictAcceptorCheck yes
#GSSAPIKeyExchange no
#UsePAM no
UsePAM yes
# Accept locale-related environment variables
AcceptEnv LANG LC_CTYPE LC_NUMERIC LC_TIME LC_COLLATE LC_MONETARY LC_MESSAGES
AcceptEnv LC_PAPER LC_NAME LC_ADDRESS LC_TELEPHONE LC_MEASUREMENT
AcceptEnv LC_IDENTIFICATION LC_ALL LANGUAGE
AcceptEnv XMODIFIERS
#AllowAgentForwarding yes
#AllowTcpForwarding yes
#GatewayPorts no
#X11Forwarding no
X11Forwarding yes
#X11DisplayOffset 10
#X11UseLocalhost yes
#PrintMotd yes
#PrintLastLog yes
#TCPKeepAlive yes
#UseLogin no
#UsePrivilegeSeparation yes
#PermitUserEnvironment no
#Compression delayed
#ClientAliveInterval 0 #设定会话超时时长,单位为秒。
#ClientAliveCountMax 3 #设定空闲最大计数。
#ShowPatchLevel no
#UseDNS yes
#PidFile /var/run/sshd.pid
#MaxStartups 10:30:100
#PermitTunnel no
#ChrootDirectory none
# no default banner path
#Banner none
# override default of no subsystems
Subsystem sftp /usr/libexec/openssh/sftp-server #是否启用sftp服务功能,注释了此行就是禁用sftp
# Example of overriding settings on a per-user basis
#Match User anoncvs
# X11Forwarding no
# AllowTcpForwarding no
# ForceCommand cvs server
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
客户配置文件
# $OpenBSD: ssh_config,v 1.25 2009/02/17 01:28:32 djm Exp $
# This is the ssh client system-wide configuration file. See
# ssh_config(5) for more information. This file provides defaults for
# users, and the values can be changed in per-user configuration files
# or on the command line.
# Configuration data is parsed as follows:
# 1. command line options
# 2. user-specific file
# 3. system-wide file
# Any configuration value is only changed the first time it is set.
# Thus, host-specific definitions should be at the beginning of the
# configuration file, and defaults at the end.
# Site-wide defaults for some commonly used options. For a comprehensive
# list of available options, their meanings and defaults, please see the
# ssh_config(5) man page.
# Host *
# ForwardAgent no
# ForwardX11 no
# RhostsRSAAuthentication no
# RSAAuthentication yes
# PasswordAuthentication yes
# HostbasedAuthentication no
# GSSAPIAuthentication no
# GSSAPIDelegateCredentials no
# GSSAPIKeyExchange no
# GSSAPITrustDNS no
# BatchMode no
# CheckHostIP yes
# AddressFamily any
# ConnectTimeout 0
# StrictHostKeyChecking ask
# IdentityFile ~/.ssh/identity
# IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa
# IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_dsa
# Port 22 #默认连接服务端使用的tcp端口
# Protocol 2,1 #最优先使用sshv2协议,如果不支持sshv2然后使用sshv1协议
# Cipher 3des #连接时使用3des实现对衬加密
# Ciphers aes128-ctr,aes192-ctr,aes256-ctr,arcfour256,arcfour128,aes128-cbc,3des-cbc #其它可选的加密
# MACs hmac-md5,hmac-sha1,[email protected],hmac-ripemd160 #支持那些消息验证协议
# EscapeChar ~
# Tunnel no
# TunnelDevice any:any
# PermitLocalCommand no
# VisualHostKey no
Host 172.16.2.10 #访问172.16.2.10主机时使用的特性
Port 22
Protocol 2,1
Host * #访问任意主机时定义的特性
GSSAPIAuthentication yes
# If this option is set to yes then remote X11 clients will have full access
# to the original X11 display. As virtually no X11 client supports the untrusted
# mode correctly we set this to yes.
ForwardX11Trusted yes
# Send locale-related environment variables
SendEnv LANG LC_CTYPE LC_NUMERIC LC_TIME LC_COLLATE LC_MONETARY LC_MESSAGES
SendEnv LC_PAPER LC_NAME LC_ADDRESS LC_TELEPHONE LC_MEASUREMENT
SendEnv LC_IDENTIFICATION LC_ALL LANGUAGE
SendEnv XMODIFIERS
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ssh认证方式
1,基于口令谁,就是使用用户名密码认证。
2,基于密钥认证,使用公钥认证。客户端需要把自己的公钥放到服务端定义的密钥文件中,客户端使用密钥连接服务器时,双方会相互验证客户端的私钥与服务端密钥文件中存储客户端的公钥能否配对。如果能配对直接登陆。
linux使用密钥连接linux方法
1,先在客户端生成私钥,然后从私钥中提取出公钥。私钥一般不应该给除属主以外其它人任何权限。
2,把提取出的公钥传到服务端,并把公钥导入到用户家目录下的.ssh/authorized_keys文件中。(为了安全 .ssh目录权限应当为700)
# ssh-keygen -t rsa #生成密钥
3,把公钥导入到服务端主机用户家目录下的.ssh/authorized_keys文件中。这个用户是以后使用密钥连接服务端时的用户身份。这里使用root身份登陆,如果使用其它用户需要把公钥导入到其它用户的.ssh/authorized_keys文件中。
# ssh-copy-id -i ./id_rsa.pub [email protected] [email protected]'s password: Now try logging into the machine, with "ssh '[email protected]'", and check in: .ssh/authorized_keys to make sure we haven't added extra keys that you weren't expecting. [root@localhost .ssh]# ssh 172.16.2.11 Last login: Sat Aug 2 14:30:25 2014 from 172.16.2.10 [root@7 ~]#
如果系统没有ssh-copy-id这个命令,需要手动拷贝。
# scp ./id_isa.pub [email protected]:/root/.ssh/ #把公钥上传到目标主机的用户家目录.ssh目录下
# cat id_isa.pub >> authorized_keys #到172.16.2.11主机上,cd到用户家目录下的.ssh目录下。然后把公钥内容追加到authorized_keys文件中。
# ssh [email protected] #回到本机上,然后再指定对方已导入公钥的用户连接,就直接连接上了。
在windows下使用xshell连接方法。
1,生成密钥,并导出公钥。
这里选择RSA算法,用此算法支持加密和身份认证。然后再下一步。设置用户名
这一步选择私钥的文件名,和密码,如果不选择,文件名为默认,密码为空。
这里选择使用的ssh协议版本。显示私钥的公钥,可以把把公钥保存到一个文件中
。
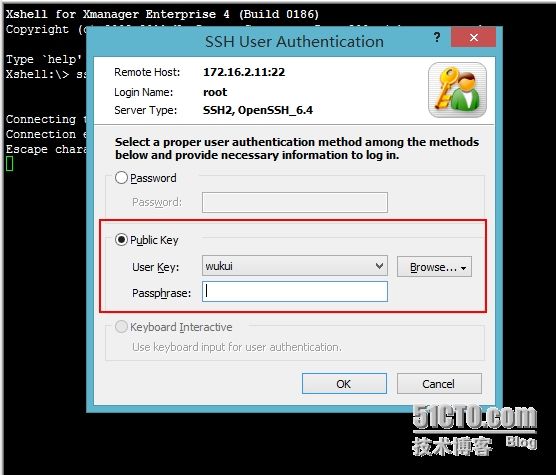
这里只要把生成的公钥导入到linux主机上的用户家目录下的.ssh/authorized_keys文件中。然后再使用xshell连接选择使用密钥认证就可以了。
ssh安全使用规则。
1,不使用默认22号端口
2,不使用sshv1协议
3,必要时设置黑名单,或白名单
4,不让root用户直接登陆,使用普通用户登陆后,su到root用户。
5,设定空闲会话超时时间。
6,在防火墙中设置策略,只允许指定的IP可以登陆。
7,只允许sshd服务只监听到本地特定Ip上,而非本机所有ip
8,使用强密码策略,密码组成尽可能复杂。
linux下生成随机密码:# tr -dc A-Za-z0-9_ < /dev/urandom | head -c 20 | xargs :head后面跟上要生成多少位的密码。
9,尽量使用密钥登陆系统。
10,禁止使用空密码
11,限制ssh使用频度
12,经常分析日志。
lastb :查看最近失败登陆的命令。