Mybatis源码笔记之浅析ParameterHandler
目录
- 概念
- 职责
- 类图
- 源码
- ParameterHandler对象创建
- ParameterHandler解析参数
- 总结
概念
职责
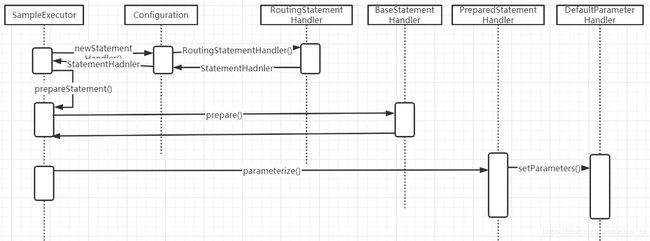
ParameterHandler是用来设置参数规则的。StatementHandler中介绍到,其SimpleExecutor中调用prepare()方法之后,接下来StatementHandler就是使用parameterize来设置参数。以SampleExecutor为例,具体代码如下:
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
//解析并设置参数
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
@Override
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);
}
类图
进入源码,该接口很简单,且只有一个默认实现类DefaultParameterHandler
public interface ParameterHandler {
Object getParameterObject();
void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps)
throws SQLException;
}
源码
ParameterHandler对象创建
对于ParameterHandler对象的创建过程,首先抛出结论:该对象是在创建StatementHandler对象的同时被创建完成。StatementHandler文章中我们谈论到其依赖ParameterHandler和ResultSetHandler,下面我们进入正题。
上面谈到了该对象在StatementHandler对象创建时被创建,所以我们从StatementHandler对象位置开始跟踪:
- SimpleExecutor
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// 获取环境配置
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
//Configuration中获取StatementHandler,跟进去
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
- Configuration
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
//创建StatementHandler
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
跟进RoutingStatementHandler,我们以SimpleStatementHandler为例,其余*StatementHandler对象创建一样,调用其父类BaseStatementHandler构造方法,所以我们跟踪到其父类的构造方法中。
- SimpleStatementHandler
public SimpleStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
super(executor, mappedStatement, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
}
- BaseStatementHandler
protected BaseStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
this.configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration();
this.executor = executor;
this.mappedStatement = mappedStatement;
this.rowBounds = rowBounds;
this.typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
this.objectFactory = configuration.getObjectFactory();
if (boundSql == null) { // issue #435, get the key before calculating the statement
generateKeys(parameterObject);
boundSql = mappedStatement.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
}
this.boundSql = boundSql;
// 创建参数处理器
this.parameterHandler = configuration.newParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
// 创建结果映射器
this.resultSetHandler = configuration.newResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, rowBounds, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql);
}
从代码注释上,我们可以清晰看到parameterHandler 和resultSetHandler 对象的创建交给Configuration类操作;
从上面几步源码的跟踪:Configuration类依次完成了StatementHandler、parameterHandler 、resultSetHandler 对象的创建过程。
那么继续回归到Configuration中。
- Configuration
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
ParameterHandler解析参数
上面完成了StatementHandler,ParameterHandler和ResultSetHandler对象的创建,基本工作已准备完成,下面继续回归到SimpleExecutor#prepareStatement()
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// 获取环境配置
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
//Configuration中获取StatementHandler
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
//准备Statement对象
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
- PrepareStatementHandler
@Override
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);
}
代码里看到是parameterHandler对象调用,上面我们了解到ParameterHandler接口仅有一个实现类即DefaultParameterHandler,因此Debug进去。
- DefaultParameterHandler
@Override
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
// parameterMappings 就是对 #{} 或者 ${} 里面参数的封装
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
// 如果是参数化的SQL,便需要循环取出并设置参数的值
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
// 如果参数类型不是 OUT ,这个类型与 CallableStatementHandler 有关
// 因为存储过程不存在输出参数,所以参数不是输出参数的时候,就需要设置。
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
// 得到#{} 中的属性名
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
// 如果 propertyName 是 Map 中的key
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params
// 通过key 来得到 additionalParameter 中的value值
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
// 如果不是 additionalParameters 中的key,而且传入参数是 null, 则value 就是null
value = null;
}
// 如果 typeHandlerRegistry 中已经注册了这个参数的 Class对象,即它是Primitive 或者是String 的话
else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
// 否则就是 Map
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
// 在通过SqlSource 的parse 方法得到parameterMappings 的具体实现中,我们会得到parameterMappings的typeHandler
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
// 获取typeHandler 的jdbc type
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}