redis client
redis 服务器是典型的一对多的服务器应用程序:一个服务器可以与多个客户端连接,每个客户端可以向服务器发送命令请求,而服务器则接受并处理客户端发送的请求,并将处理结果返回给客户端。
通过使用I/O多路复用技术, redis 服务器使用单线程单进程的方式处理命令请求,并与多个客户端连接进行网络通讯。
客户端 redis-cli.c
根据 redis-cli.c 中main函数分析客户端的启动流程
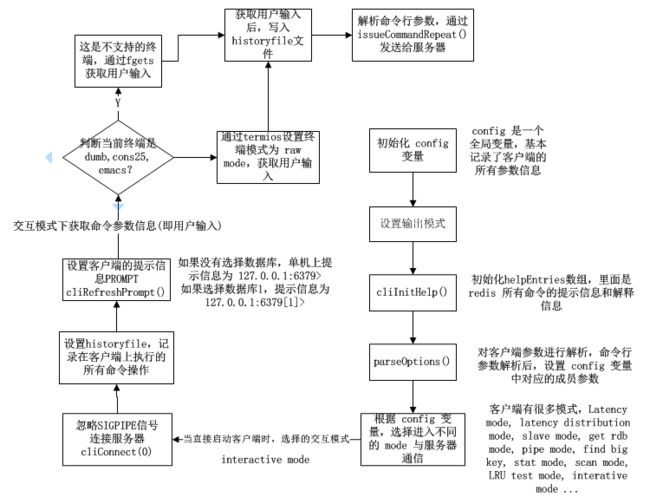
上图因为在 Visio 中画的,截图的时候图方便,看起来像然在一起。(:haha)
下面看一下客户端的两个重要的全局变量
static redisContext *context;
static struct config
- 1
- 2
- 3
启动客户端时,会初始化 config 全局变量,该变量记录了客户端几乎所有的配置参数信息,而 context 用于连接 redis 服务器。看一下 config 的结构
static struct config {
char *hostip; // IP
int hostport; //端口
char *hostsocket;
long repeat;
long interval;
int dbnum; //数据库编号,一般默认是0-15
int interactive; //交互模式
int shutdown;
int monitor_mode;
int pubsub_mode;
int latency_mode;
int latency_dist_mode;
int latency_history;
int lru_test_mode;
long long lru_test_sample_size;
int cluster_mode;
int cluster_reissue_command;
int slave_mode;
int pipe_mode;
int pipe_timeout;
int getrdb_mode;
int stat_mode;
int scan_mode;
int intrinsic_latency_mode;
int intrinsic_latency_duration;
char *pattern;
char *rdb_filename;
int bigkeys;
int stdinarg; /* get last arg from stdin. (-x option) */
char *auth;
int output; /* output mode, see OUTPUT_* defines */
sds mb_delim;
char prompt[128];
char *eval;
int last_cmd_type;
} config;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
客户端在 parseOptions() 中设置 config 变量参数
static int parseOptions(int argc, char **argv) {
int i;
for (i = 1; i < argc; i++) {
int lastarg = i==argc-1;
if (!strcmp(argv[i],"-h") && !lastarg) { //./redis-cli -h 10.255.245.41
sdsfree(config.hostip);
config.hostip = sdsnew(argv[++i]);
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"-h") && lastarg) { //./redis-cli -h
usage();
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--help")) { // ./redis-cli --help
usage();
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"-x")) { // ./redis-cli -x
config.stdinarg = 1;
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"-p") && !lastarg) { // ./redis-cli -p [PORT]
config.hostport = atoi(argv[++i]);
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"-s") && !lastarg) { // ./redis-cli -s
config.hostsocket = argv[++i];
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"-r") && !lastarg) { // ./redis-cli -r , execute specified command N times
config.repeat = strtoll(argv[++i],NULL,10);
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"-i") && !lastarg) { // ./redis-cli -i , used with -r
double seconds = atof(argv[++i]);
config.interval = seconds*1000000;
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"-n") && !lastarg) { // ./redis-cli -n
config.dbnum = atoi(argv[++i]);
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"-a") && !lastarg) { // ./redis-cli -a , connect to server with password
config.auth = argv[++i];
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--raw")) {
config.output = OUTPUT_RAW; // no formatted output
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--no-raw")) {
config.output = OUTPUT_STANDARD;
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--csv")) { //redis-cli --csv, output in csv format
config.output = OUTPUT_CSV;
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--latency")) {
config.latency_mode = 1;
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--latency-dist")) {
config.latency_dist_mode = 1;
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--mono")) {
spectrum_palette = spectrum_palette_mono;
spectrum_palette_size = spectrum_palette_mono_size;
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--latency-history")) {
config.latency_mode = 1;
config.latency_history = 1;
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--lru-test") && !lastarg) {
config.lru_test_mode = 1;
config.lru_test_sample_size = strtoll(argv[++i],NULL,10);
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--slave")) {
config.slave_mode = 1;
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--stat")) {
config.stat_mode = 1;
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--scan")) {
config.scan_mode = 1;
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--pattern") && !lastarg) {
config.pattern = argv[++i];
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--intrinsic-latency") && !lastarg) {
config.intrinsic_latency_mode = 1;
config.intrinsic_latency_duration = atoi(argv[++i]);
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--rdb") && !lastarg) { // redis-cli --rdb , transfer an rdb dump from remote server to local file
config.getrdb_mode = 1;
config.rdb_filename = argv[++i];
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--pipe")) {
config.pipe_mode = 1;
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--pipe-timeout") && !lastarg) {
config.pipe_timeout = atoi(argv[++i]);
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--bigkeys")) {
config.bigkeys = 1;
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"--eval") && !lastarg) {
config.eval = argv[++i];
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"-c")) {
config.cluster_mode = 1;
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"-d") && !lastarg) {
sdsfree(config.mb_delim);
config.mb_delim = sdsnew(argv[++i]);
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i],"-v") || !strcmp(argv[i], "--version")) {
sds version = cliVersion();
printf("redis-cli %s\n", version);
sdsfree(version);
exit(0);
} else {
if (argv[i][0] == '-') {
fprintf(stderr,
"Unrecognized option or bad number of args for: '%s'\n",
argv[i]);
exit(1);
} else {
/* Likely the command name, stop here. */
break;
}
}
}
return i;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
上述解析命令行参数的各个参数信息,在客户端,使用 --help 就能看到,
void usage(void) {
fprintf(stderr,"Usage: ./redis-server [/path/to/redis.conf] [options]\n");
fprintf(stderr," ./redis-server - (read config from stdin)\n");
fprintf(stderr," ./redis-server -v or --version\n");
fprintf(stderr," ./redis-server -h or --help\n");
fprintf(stderr," ./redis-server --test-memory \n\n");
fprintf(stderr,"Examples:\n");
fprintf(stderr," ./redis-server (run the server with default conf)\n");
fprintf(stderr," ./redis-server /etc/redis/6379.conf\n");
fprintf(stderr," ./redis-server --port 7777\n");
fprintf(stderr," ./redis-server --port 7777 --slaveof 127.0.0.1 8888\n");
fprintf(stderr," ./redis-server /etc/myredis.conf --loglevel verbose\n\n");
fprintf(stderr,"Sentinel mode:\n");
fprintf(stderr," ./redis-server /etc/sentinel.conf --sentinel\n");
exit(1);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
根据不同的参数,设置 config 的值,然后,根据命令行参数设定的值和模式(mode),选择进入不同的模式与 redis 服务器进行通讯。在本机上,直接启动 redis 客户端,比如 ./redis-cli ,这样客户端启动之后,进入的将是交互模式,config.interactive = 1,这种模式下,用户可以直接在客户端输入指令,并能立马得到服务器返回的信息。下面,主要介绍的就是交互模式。
交互模式下,首先,需要连接服务器,这时,需要用到 context 变量
/* Connect to the server. If force is not zero the connection is performed
* even if there is already a connected socket. */
static int cliConnect(int force) {
if (context == NULL || force) {
if (context != NULL)
redisFree(context);
if (config.hostsocket == NULL) {
context = redisConnect(config.hostip,config.hostport);
} else {
context = redisConnectUnix(config.hostsocket);
}
if (context->err) {
fprintf(stderr,"Could not connect to Redis at ");
if (config.hostsocket == NULL)
fprintf(stderr,"%s:%d: %s\n",config.hostip,config.hostport,context->errstr);
else
fprintf(stderr,"%s: %s\n",config.hostsocket,context->errstr);
redisFree(context);
context = NULL;
return REDIS_ERR;
}
/* Set aggressive KEEP_ALIVE socket option in the Redis context socket
* in order to prevent timeouts caused by the execution of long
* commands. At the same time this improves the detection of real
* errors. */
anetKeepAlive(NULL, context->fd, REDIS_CLI_KEEPALIVE_INTERVAL);
/* Do AUTH and select the right DB. */
if (cliAuth() != REDIS_OK)
return REDIS_ERR;
if (cliSelect() != REDIS_OK)
return REDIS_ERR;
}
return REDIS_OK;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
当服务器连接成功时,context 的 fd 为连接成功后的 sockfd,flags 设置为
REDIS_CONNECTED,redisContext 的结构如下
/* Context for a connection to Redis */
typedef struct redisContext {
int err; /* Error flags, 0 when there is no error */
char errstr[128]; /* String representation of error when applicable */
int fd;
int flags;
char *obuf; /* Write buffer */
redisReader *reader; /* Protocol reader */
} redisContext;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
当连接服务器或者命令发生错误时,err将设置为非0数字,errstr 中将记录错误信息,连接成功时,将 socket 套接字的文件描述符记录在 fd 中,同时 flags 设置为 REDIS_CONNECTED,obuf 为输出缓存,客户端发送给服务器的命令信息,解析后存放在 obuf 中,reader 作为协议解析器,用于读取和分析服务器返回的信息。
当客户端成功连接 redis 服务器之后,需要对客户端的身份进行验证(前提是服务器打开了验证的功能),cliAuth(),如果验证失败,出了 AUTH 操作之外, 服务器将决绝客户端发送的一切其他命令操作。
cliSelect(),用于客户端选择 redis 数据库,通过 select dbnum 的指令进行数据库选择。
服务器连接成功,进入到交互模式下,与服务器交互。但是在交互之前,还需要设置一下终端的模式。
客户端的交互模式
准备工作
客户端进入交互模式如下所示 
也就是说,在用户通过客户端与服务器交互之前,还需要一些准备工作。
redis 会将在客户端上操作的所有命令记录在一个历史文件中 historyfile,如果没有设置,一般默认为 $HOME/.rediscli_history 文件。同时,设置提示信息 config.prompt,如上图所示的提示信息为 “127.0.0.1:6379>”,这里默认的数据库编号为 0 ,所以没有显示出来,如果是非 0 的数据库,比如是 1,需要重新设置提示信息,为 “127.0.0.1:6379[1]>”。
在交互模式下获取用户输入
/* The high level function that is the main API of the linenoise library.
* This function checks if the terminal has basic capabilities, just checking
* for a blacklist of stupid terminals, and later either calls the line
* editing function or uses dummy fgets() so that you will be able to type
* something even in the most desperate of the conditions. */
char *linenoise(const char *prompt) {
char buf[LINENOISE_MAX_LINE];
int count;
if (isUnsupportedTerm()) { //not support these terms,such as dumb,cons25,emacs
size_t len;
printf("%s",prompt);
fflush(stdout);
if (fgets(buf,LINENOISE_MAX_LINE,stdin) == NULL) return NULL;
len = strlen(buf);
while(len && (buf[len-1] == '\n' || buf[len-1] == '\r')) {
len--;
buf[len] = '\0';
}
return strdup(buf); //should be free
} else {
count = linenoiseRaw(buf,LINENOISE_MAX_LINE,prompt);
if (count == -1) return NULL;
return strdup(buf);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
redis 通过上面的 linenoise() 函数获取用户输入,首先判断当前终端是不是 redis 所支持的终端类型(通过判断环境变量 TERM),如果不是,通过 fgets 函数获取用户输入;如果是支持的终端,那么首先通过 termios 相关的API,将 term 设置为 raw mode,该模式下,用户输入一个字符时,程序就会立即处理,类似于ncurses 中的 cbreak 模式,在 linenoiseEdit() 函数中,redis 对用户键盘的各种操作进行处理,并记录用户输入的有效字符
/* This function is the core of the line editing capability of linenoise.
* It expects 'fd' to be already in "raw mode" so that every key pressed
* will be returned ASAP to read().
*
* The resulting string is put into 'buf' when the user type enter, or
* when ctrl+d is typed.
*
* The function returns the length of the current buffer. */
static int linenoiseEdit(int stdin_fd, int stdout_fd, char *buf, size_t buflen, const char *prompt)
{
struct linenoiseState l;
/* Populate the linenoise state that we pass to functions implementing
* specific editing functionalities. */
l.ifd = stdin_fd;
l.ofd = stdout_fd;
l.buf = buf;
l.buflen = buflen;
l.prompt = prompt;
l.plen = strlen(prompt);
l.oldpos = l.pos = 0;
l.len = 0;
l.cols = getColumns(stdin_fd, stdout_fd);
l.maxrows = 0;
l.history_index = 0;
/* Buffer starts empty. */
l.buf[0] = '\0';
l.buflen--; /* Make sure there is always space for the nulterm */
/* The latest history entry is always our current buffer, that
* initially is just an empty string. */
linenoiseHistoryAdd("");
if (write(l.ofd,prompt,l.plen) == -1) return -1;
while(1) {
char c;
int nread;
char seq[3];
nread = read(l.ifd,&c,1);
if (nread <= 0) return l.len; //nread is 0, server may close the connect
/* Only autocomplete when the callback is set. It returns < 0 when
* there was an error reading from fd. Otherwise it will return the
* character that should be handled next. */
if (c == 9 && completionCallback != NULL) {
c = completeLine(&l);
/* Return on errors */
if (c < 0) return l.len;
/* Read next character when 0 */
if (c == 0) continue;
}
switch(c) {
case ENTER: /* enter */
history_len--;
free(history[history_len]);
if (mlmode) linenoiseEditMoveEnd(&l);
return (int)l.len;
case CTRL_C: /* ctrl-c */
errno = EAGAIN;
return -1;
case BACKSPACE: /* backspace */
case 8: /* ctrl-h */
linenoiseEditBackspace(&l);
break;
case CTRL_D: /* ctrl-d, remove char at right of cursor, or if the
line is empty, act as end-of-file. */
if (l.len > 0) {
linenoiseEditDelete(&l);
} else {
history_len--;
free(history[history_len]);
return -1;
}
break;
case CTRL_T: /* ctrl-t, swaps current character with previous. */
if (l.pos > 0 && l.pos < l.len) {
int aux = buf[l.pos-1];
buf[l.pos-1] = buf[l.pos];
buf[l.pos] = aux;
if (l.pos != l.len-1) l.pos++;
refreshLine(&l);
}
break;
case CTRL_B: /* ctrl-b */
linenoiseEditMoveLeft(&l);
break;
case CTRL_F: /* ctrl-f */
linenoiseEditMoveRight(&l);
break;
case CTRL_P: /* ctrl-p */
linenoiseEditHistoryNext(&l, LINENOISE_HISTORY_PREV);
break;
case CTRL_N: /* ctrl-n */
linenoiseEditHistoryNext(&l, LINENOISE_HISTORY_NEXT);
break;
case ESC: /* escape sequence */
/* Read the next two bytes representing the escape sequence.
* Use two calls to handle slow terminals returning the two
* chars at different times. */
if (read(l.ifd,seq,1) == -1) break;
if (read(l.ifd,seq+1,1) == -1) break;
/* ESC [ sequences. */
if (seq[0] == '[') {
if (seq[1] >= '0' && seq[1] <= '9') {
/* Extended escape, read additional byte. */
if (read(l.ifd,seq+2,1) == -1) break;
if (seq[2] == '~') {
switch(seq[1]) {
case '3': /* Delete key. */
linenoiseEditDelete(&l);
break;
}
}
} else {
switch(seq[1]) {
case 'A': /* Up */
linenoiseEditHistoryNext(&l, LINENOISE_HISTORY_PREV);
break;
case 'B': /* Down */
linenoiseEditHistoryNext(&l, LINENOISE_HISTORY_NEXT);
break;
case 'C': /* Right */
linenoiseEditMoveRight(&l);
break;
case 'D': /* Left */
linenoiseEditMoveLeft(&l);
break;
case 'H': /* Home */
linenoiseEditMoveHome(&l);
break;
case 'F': /* End*/
linenoiseEditMoveEnd(&l);
break;
}
}
}
/* ESC O sequences. */
else if (seq[0] == 'O') {
switch(seq[1]) {
case 'H': /* Home */
linenoiseEditMoveHome(&l);
break;
case 'F': /* End*/
linenoiseEditMoveEnd(&l);
break;
}
}
break;
default:
if (linenoiseEditInsert(&l,c)) return -1;
break;
case CTRL_U: /* Ctrl+u, delete the whole line. */
buf[0] = '\0';
l.pos = l.len = 0;
refreshLine(&l);
break;
case CTRL_K: /* Ctrl+k, delete from current to end of line. */
buf[l.pos] = '\0';
l.len = l.pos;
refreshLine(&l);
break;
case CTRL_A: /* Ctrl+a, go to the start of the line */
linenoiseEditMoveHome(&l);
break;
case CTRL_E: /* ctrl+e, go to the end of the line */
linenoiseEditMoveEnd(&l);
break;
case CTRL_L: /* ctrl+l, clear screen */
linenoiseClearScreen();
refreshLine(&l);
break;
case CTRL_W: /* ctrl+w, delete previous word */
linenoiseEditDeletePrevWord(&l);
break;
}
}
return l.len;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
获取用户输入之后,将用户输入写入到历史文件中 historyfile 中,并将用户输入的命令参数解析后,发送到服务器。
客户端发送消息到服务器
客户端获取用户输入的命令及参数之后
argv = sdssplitargs(line,&argc);
- 1
- 2
将命令参数放到 argv 数组中,通过 cliSendCommand() 发送给服务器
客户端发送命令和接受结果的函数调用关系如下:
cliSendCommand -> redisAppendCommandArgv -> redisFormatCommandArgv这是根据 redis 协议格式化输出,发送到服务器
cliSendCommand -> cliReadReply -> redisGetReply ->
redisBufferWrite 和 redisBufferRead 发送和接收
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
redis 协议格式
/* Format a command according to the Redis protocol. This function takes the
* number of arguments, an array with arguments and an array with their
* lengths. If the latter is set to NULL, strlen will be used to compute the
* argument lengths.
*/
int redisFormatCommandArgv(char **target, int argc, const char **argv, const size_t *argvlen) {
char *cmd = NULL; /* final command */
int pos; /* position in final command */
size_t len;
int totlen, j;
/* Calculate number of bytes needed for the command */
totlen = 1+intlen(argc)+2; //1长度表示开头*,2表示 \r\n,再加上 argc 转换成字符串后的长度
for (j = 0; j < argc; j++) {
len = argvlen ? argvlen[j] : strlen(argv[j]);
totlen += bulklen(len);
}
/* Build the command at protocol level */
cmd = malloc(totlen+1);
if (cmd == NULL)
return -1;
pos = sprintf(cmd,"*%d\r\n",argc);
for (j = 0; j < argc; j++) {
len = argvlen ? argvlen[j] : strlen(argv[j]);
pos += sprintf(cmd+pos,"$%zu\r\n",len);
memcpy(cmd+pos,argv[j],len);
pos += len;
cmd[pos++] = '\r';
cmd[pos++] = '\n';
}
assert(pos == totlen);
cmd[pos] = '\0';
*target = cmd;
return totlen;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
redisFormatCommandArgv 函数是将客户端输入的命令按照 redis protocol 格式化,然后发送给服务器。比如 SET NAME "redis",按照 Redis protocol 格式化成
*3\r\n$3\r\nSET\r\n$4\r\nNAME\r\n$5\r\nredis\r\n
- 1
- 2
每一个元素都是以 \r\n 分割,最前面 *3 表示该条命令有三个元素,后面 $3 表示当前元素的长度为3