贪心算法--Dijkstra算法(单源最短路径算法)
其实网上有很多写Dijkstra算法的前辈们,我只是分享一下我自己写的一点心得,还有希望前辈来可以知道自己的错误。其实自己在写的过程中,发现你写一个算法,关键看您对于它了解有多少?你的理解是透彻清楚的吗?还有自己得认真去回味它一步一步是如何得到的,又是怎样的过程,问题就是这样解决的。
我自己写的Dijkstra算发的复杂度高于网上前辈写的,但我要是学会自我思考、自我认知、自我寻找之精神。我乐于思考、乐于探索,而非一步就去窥探别人,那非自我思考。Dijkstra算法:
1、找出起点附近最短的距离:纪录该点,以及到下一点最短距离;
2、到达下一点:该点到其他点距离,还有起点到该点的距离,如果是起点到该点下一点有直达的,那样考虑它们之间的大小,取小进行,再次计算该点到附近点的最短距离(保证取下一点不能是上一个已经走过的点上);
3、循环1-2保证所有点找到或是已经不能走通了。
实现的代码为:
#include
using namespace std;
#define MaxLine 9999
struct Node{
int node;
int value;
Node*next;
};
#define InISize 20
#define AppSize 50
typedef struct Stack{
int Capacity;
Node*base;
Node*top;
}Stack;
typedef struct queue{
Node *rear;
Node *front;
int size;
}Queue;
void IniStack(Stack *s)
{
s->base=(Node*)malloc(InISize*sizeof(Node));
if(!s->base)
return ;
s->top=s->base;
s->Capacity=InISize;
}
int StackSize(Stack *s)
{
return (int)(s->top-s->base);
}
int EmptyStack(Stack *s)
{
if(s->base==s->top)
{
return 1;
}
else
return 2;
}
void ClearStack(Stack *s)
{
s->top=s->base;
}
void Push(Stack *s,Node d)
{
if(s->top-s->base>=s->Capacity)
{
s->base=(Node *)realloc(s->base,AppSize*sizeof(Node));
if(!s->base)
return ;
s->top=s->base+s->Capacity;
s->Capacity=AppSize+InISize;
}
*(s->top)=d;
s->top++;
}
bool searchIn(const int &j,Stack s)
{
bool res=false;
while(s.base!=s.top)
{
if(s.base->node==j)
{
res=true;
break;
}
s.base++;
}
return res;
}
void DijkstraAlgorithm(Stack *s)
{
int n;
cout<<"the amount of node:";
cin>>n;
int **a=new int * [n+1];
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)
a[i]=new int [n+1];
cout<<"specific data:(as -1 is on behalf of ending)"<<endl;
for(int i=1;i
{
for(int j=1;j
a[i][j]=MaxLine;
}
int i,j,k;
while(cin>>i>>j>>k)
{
if(i>n||j>n)
break;
if((i>0&&i<=n)&&(j>0&&j<=n))
{
a[i][j]=k;
}
if(i==-1||j==-1)
break;
}
int start;
cout<<"the starting node:";
cin>>start;
int temp=start;
int value=MaxLine;
Node *l=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
l->node=start;
l->value=value;
Push(s, *l);
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(a[temp][j]!=MaxLine-1)
if(value>a[start][j])
{
value=a[start][j];
temp=j;
}
//
}
Node *lose=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
lose->node=temp;
lose->value=value;
Push(s, *lose);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(a[temp][i]==MaxLine)
cout<<"not ";
else
cout<<" "<
}
cout<<endl;
while(StackSize(s)!=n){
value=MaxLine;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(i==temp)
{
if(a[temp][j]!=MaxLine&&a[start][i]!=MaxLine)
{
if(a[temp][j]+a[start][i]
{
a[temp][j]=a[temp][j]+a[start][i];
}
else
{
a[temp][j]=a[start][j];
}
}
if(a[temp][j]==MaxLine&&a[start][i]!=MaxLine)
{
a[temp][j]=a[start][j];
}
}
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(a[temp][i]==MaxLine)
cout<<"not";
else
cout<<" "<
}
cout<<endl;
start=temp;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(a[start][j]!=MaxLine&&!searchIn(j, *s))
if(value>a[start][j])
{
value=a[start][j];
temp=j;
}
//
}
Node *lose=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
lose->node=temp;
lose->value=value;
Push(s, *lose);
}
}
void showLink(Stack *s)
{
Node *h=s->base;
Node *p=s->base;
while(h!=s->top)
{
cout<<" "<
h++;
}
cout<<endl;
while(p!=s->top)
{
cout<<" "<
p++;
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
// insert code here...
std::cout << "Hello, World!\n";
Stack S;
IniStack(&S);
DijkstraAlgorithm(&S);
cout<<StackSize(&S)<<endl;
showLink(&S);
return 0;
}
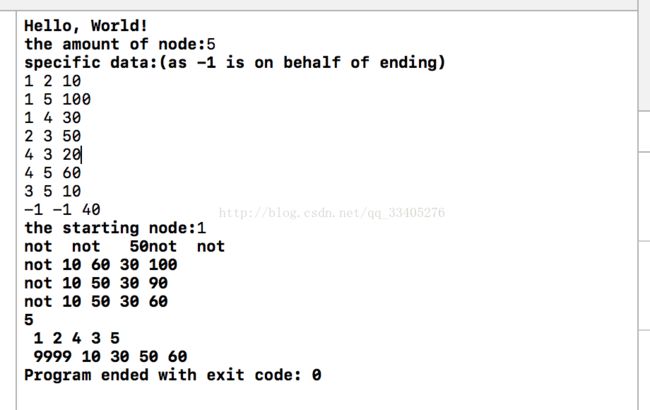
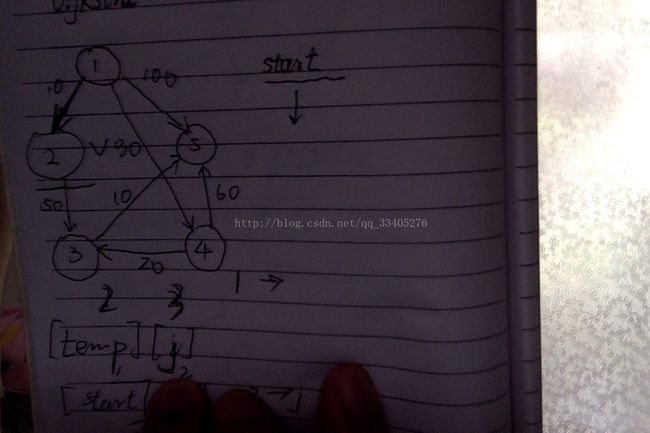
测试用例为: