Mybatis源码分析(5)---配置节点typeAliases源码解析
- 背景
在上篇Mybatis源码分析(4)—配置节点settings源码解析中,我们通过settings节点在于XMLConfigBuilder类中的settingsAsProperties(XNode context)、loadCustomVfs(Properties props)、loadCustomLogImpl(Properties props)以及settingsElement(Properties props)等方法源码分析,了解了mybatis的整个settings节点的源码解析过程。
今天接下来我们将对节点typeAliases进行源码分析,分析之前,依然先通过以下图来重温一下之前SqlSessionFactory对象创建的过程:

我们依然围绕着Demo工程mybatisCode对节点typeAliases进行深入的解析和测试 - 节点typeAliases介绍
顾名思义:typeAliases直译:类型别名,为Java 类型设置的一个短的名字,它只和 XML 配置有关,存在的意义仅在于用来减少类完全限定名的冗余(本介绍来源于mybatis官网)。
类型别名(typeAliases)在mybatis-config.xml中的配置的方式可以有两种,我们拿Demo工程mybatisCode中的配置来讲解:
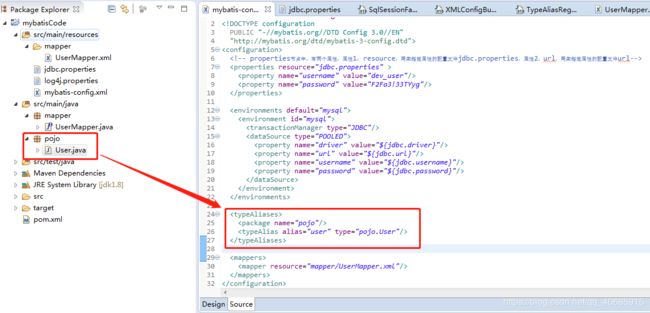
以上截图中,我可以看到,节点typeAliases可以不配置,但是如果配置的话,可以直接配置元素节点:package和typeAlias。package配置属性name为包路径,typeAlias配置的type为类完全限定名,alias为别名,
那么问题来了!
- 问题1:如果我们的mybatis-config.xml中不配置节点typeAliases,mybatis在解析配置文件的时候会做什么?
- 问题2:如果配置了节点typeAliases信息,解析节点元素package和typeAlias顺序和方式是什么?
带着上面两个问题,我们接下来就开始对节点typeAliases源码进行深入的分析!
- 节点typeAliases源码分析
- 节点typeAliases源码解析的位置在XMLConfigBuilder类中typeAliasesElement(XNode parent)方法中
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
/**************解析节点typeAliases**************/
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
private void typeAliasesElement(XNode parent) {
if (parent != null) {
//遍历节点typeAliases的所有子元素
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
//如果配置的子元素为package
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
//获取package的属性name中的包路径名
String typeAliasPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
//注册到全局配置类Configuration中的TypeAliasRegistry类别名容器中
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAliases(typeAliasPackage);
} else {
//如果配置的子元素是typeAlias,则获取alias别名和type类完全限定名
String alias = child.getStringAttribute("alias");
String type = child.getStringAttribute("type");
try {
//反射获取type的Class对象
Class<?> clazz = Resources.classForName(type);
//注册到全局配置类Configuration中的TypeAliasRegistry类别名容器中
if (alias == null) {
//如果alias没有配置
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(clazz);
} else {
//如果alias配置了
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(alias, clazz);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error registering typeAlias for '" + alias + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
我们通过上面源码剖析总结:
1.解析节点:typeAliases的子元素解析顺序可以说是先package后typeAlias;
2.typeAlias中alias别名可以配置或者不配置,两者区别是什么,接下来我们将继续分析;
3.不管是package还是typeAlias元素节点配置,最终均注册到mybatis的全局配置类Configuration中的TypeAliasRegistry容器中;
- package元素源码解析过程
通过源码解析分析上面我们知道typeAliases节点中元素package,最终获取到的属性name中的包路径,然后调用mybatis的全局配置类Configuration中的TypeAliasRegistry容器类的 registerAliases(String packageName)方法进行注册。接下来我们顺着源码的调用看看package元素中的包路径是怎么注册到TypeAliasRegistry容器中的;
public class TypeAliasRegistry {
private final Map<String, Class<?>> typeAliases = new HashMap<>();
public void registerAliases(String packageName) {
//实际调用的是registerAliases(String packageName, Class superType)
registerAliases(packageName, Object.class);
}
public void registerAliases(String packageName, Class<?> superType) {
ResolverUtil<Class<?>> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<>();
resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName);
Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> typeSet = resolverUtil.getClasses();
for (Class<?> type : typeSet) {
// Ignore inner classes and interfaces (including package-info.java)
// Skip also inner classes. See issue #6
if (!type.isAnonymousClass() && !type.isInterface() && !type.isMemberClass()) {
registerAlias(type);
}
}
}
public void registerAlias(Class<?> type) {
String alias = type.getSimpleName();
Alias aliasAnnotation = type.getAnnotation(Alias.class);
if (aliasAnnotation != null) {
alias = aliasAnnotation.value();
}
registerAlias(alias, type);
}
public void registerAlias(String alias, Class<?> value) {
if (alias == null) {
throw new TypeException("The parameter alias cannot be null");
}
// 把解析完后的包路径下的bean的首字母进行小写
String key = alias.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
if (typeAliases.containsKey(key) && typeAliases.get(key) != null && !typeAliases.get(key).equals(value)) {
throw new TypeException("The alias '" + alias + "' is already mapped to the value '" + typeAliases.get(key).getName() + "'.");
}
// 最终解析完之后包路径下的所有类的别名作为key,类的Class对象作为Value保存在TypeAliasRegistry容器中
//注意:typeAliases为一个HashMap集合
typeAliases.put(key, value);
}
}
上面的源码调用链路比较长,这里就不具体的一一解释,我们重点落在两个地方:
1.解析完后的包路径下的bean的首字母进行小写;
2.包路径下的所有类的别名作为key,类的Class对象作为Value保存在typeAliases中
总结:package元素解析,就是扫描包下的所有bean,然后默认别名为类名的首字母小写,最终注册到全局配置类Configuration中的TypeAliasRegistry容器类中,容器中实际使用的是HashMap来存储:bean的首字母小写为作为key,bean的Class对象为Value。
- typeAlias元素源码解析过程
public class TypeAliasRegistry {
public void registerAlias(Class<?> type) {
//获取类的简写名称(不包含包路径)
String alias = type.getSimpleName();
//如果类上面有注解@Alias则注解中的值作为类别名,否则类名默认为类的简写名称
Alias aliasAnnotation = type.getAnnotation(Alias.class);
if (aliasAnnotation != null) {
alias = aliasAnnotation.value();
}
registerAlias(alias, type);
}
public void registerAlias(String alias, Class<?> value) {
if (alias == null) {
throw new TypeException("The parameter alias cannot be null");
}
// 最终别名的命名规则都进行首字母小写
String key = alias.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
if (typeAliases.containsKey(key) && typeAliases.get(key) != null && !typeAliases.get(key).equals(value)) {
throw new TypeException("The alias '" + alias + "' is already mapped to the value '" + typeAliases.get(key).getName() + "'.");
}
// 最终解析完之后typeAlias中配置的类别名作为key,类的Class对象作为Value保存在TypeAliasRegistry容器中
typeAliases.put(key, value);
}
}
总结:
1.typeAlias中的属性type进行对bean反射获取它的Class对象
2.属性alias没配置,就使用bean本身的类的简写名称(不包含包路径),如果bean的类上面有注解@Alias(""),则以注解中的值作为类别名,别名都默认进行首字母小写。
3.最终注册到全局配置类Configuration中的TypeAliasRegistry容器类中,bean的别名首字母小写为作为key,bean的Class对象为Value;
4.源码分析到这里,我们解决了一开始提出的问题2:解析节点元素package和typeAlias顺序和方式是什么?那么问题1:如果不配置节点typeAliases的时候,mybatis自己会做些什么呢?接下来我们就开始寻找问题的答案;
- 无节点typeAliases配置源码分析
- 首先我们来回顾XMLConfigBuilder实例化时父类BaseBuilder中的全局配置类Configuration初始化的地方
public class XMLConfigBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) {
//初始化mybatis的全局配置类,调用的是无参构造方法
super(new Configuration());
ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration");
this.configuration.setVariables(props);
this.parsed = false;
this.environment = environment;
this.parser = parser;
}
}
- Configuration的无参构造方法
public class Configuration {
protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry = new TypeAliasRegistry();
public Configuration() {
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDBC", JdbcTransactionFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("MANAGED", ManagedTransactionFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JNDI", JndiDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("POOLED", PooledDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("UNPOOLED", UnpooledDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("PERPETUAL", PerpetualCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("FIFO", FifoCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LRU", LruCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("SOFT", SoftCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("WEAK", WeakCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("DB_VENDOR", VendorDatabaseIdProvider.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("XML", XMLLanguageDriver.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("RAW", RawLanguageDriver.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("SLF4J", Slf4jImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("COMMONS_LOGGING", JakartaCommonsLoggingImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LOG4J", Log4jImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LOG4J2", Log4j2Impl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDK_LOGGING", Jdk14LoggingImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("STDOUT_LOGGING", StdOutImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("NO_LOGGING", NoLoggingImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("CGLIB", CglibProxyFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JAVASSIST", JavassistProxyFactory.class);
languageRegistry.setDefaultDriverClass(XMLLanguageDriver.class);
languageRegistry.register(RawLanguageDriver.class);
}
}
看到这里我们知道了,mybatis在初始化全局配置类Configuration的时候在其无参构造方法,自动注册了一堆bean别名和他们的Class对象到typeAliasRegistry容器类中,而节点typeAliases配置的别名最终也是注册到typeAliasRegistry容器类中,为了方便后面直接获取调用;
当然事情还没结束,我们接着来窥探typeAliasRegistry类别名注册容器的内部。
public class TypeAliasRegistry {
private final Map<String, Class<?>> typeAliases = new HashMap<>();
public TypeAliasRegistry() {
registerAlias("string", String.class);
registerAlias("byte", Byte.class);
registerAlias("long", Long.class);
registerAlias("short", Short.class);
registerAlias("int", Integer.class);
registerAlias("integer", Integer.class);
registerAlias("double", Double.class);
registerAlias("float", Float.class);
registerAlias("boolean", Boolean.class);
registerAlias("byte[]", Byte[].class);
registerAlias("long[]", Long[].class);
registerAlias("short[]", Short[].class);
registerAlias("int[]", Integer[].class);
registerAlias("integer[]", Integer[].class);
registerAlias("double[]", Double[].class);
registerAlias("float[]", Float[].class);
registerAlias("boolean[]", Boolean[].class);
registerAlias("_byte", byte.class);
registerAlias("_long", long.class);
registerAlias("_short", short.class);
registerAlias("_int", int.class);
registerAlias("_integer", int.class);
registerAlias("_double", double.class);
registerAlias("_float", float.class);
registerAlias("_boolean", boolean.class);
registerAlias("_byte[]", byte[].class);
registerAlias("_long[]", long[].class);
registerAlias("_short[]", short[].class);
registerAlias("_int[]", int[].class);
registerAlias("_integer[]", int[].class);
registerAlias("_double[]", double[].class);
registerAlias("_float[]", float[].class);
registerAlias("_boolean[]", boolean[].class);
registerAlias("date", Date.class);
registerAlias("decimal", BigDecimal.class);
registerAlias("bigdecimal", BigDecimal.class);
registerAlias("biginteger", BigInteger.class);
registerAlias("object", Object.class);
registerAlias("date[]", Date[].class);
registerAlias("decimal[]", BigDecimal[].class);
registerAlias("bigdecimal[]", BigDecimal[].class);
registerAlias("biginteger[]", BigInteger[].class);
registerAlias("object[]", Object[].class);
registerAlias("map", Map.class);
registerAlias("hashmap", HashMap.class);
registerAlias("list", List.class);
registerAlias("arraylist", ArrayList.class);
registerAlias("collection", Collection.class);
registerAlias("iterator", Iterator.class);
registerAlias("ResultSet", ResultSet.class);
}
}
看到没有,TypeAliasRegistry 本身在初始化的时候,也会自动注册一些bean的别名和Class对象到自身最终存储HashMap中去,而这些大多是我们常常用到的基本类型的包装类和数组,字符串,集合等等,所以就算我们做相关的节点typeAliases配置,mybatis通过全局配置类Configuration,以其属性中的类别名注册容器TypeAliasRegistry为我们提前准备好了很多实用和常用的类别名,方便我们后期的调用。
