VINS-Mono 代码详细解读——feature_manager.cpp
LZ发现estimator.cpp中关键函数为processImage(),里面包含了IMU预积分、图像处理特征点跟踪等一系列流程,上一节中对processIMU()以及预积分的integrationBase类进行解读,本节继续做基础储备,对与estimator.cpp中的feature_manager.cpp进行详细介绍,主要是对特征点管理。特征点管理器主要就是FeatureManager类
目录
一、FeatureManager、FeaturePerId、FeaturePerFrame
1、三者关系
2、FeaturePerId,某feature_id下的所有FeaturePerFrame
3、FeaturePerFrame
二、主要函数
1、endFrame()
2、getFeatureCount()
3、addFeatureCheckParallax()
1、关键帧选取:
2、代码
4、compensatedParallax2()
5、getCorresponding()
6、setDepth()
7、trangulate()
8、三个边缘化函数
removeBackShiftDepth()
removeBack()
removeFront()
涉及到的类的成员函数
| 函数名 | 功能 |
| FeaturePerId::endFrame() | 返回最后一个观测到这个特征点的图像帧ID |
| FeatureManager()::getFeatureCount() | 窗口中被跟踪的特征点数量 |
| FeatureManager()::addFeatureCheckParallax() | 特征点进入时检查视差,是否为关键帧 |
| FeatureManager()::getCorresponding() | 前后两帧之间匹配特征点3D坐标 |
| FeatureManager()::setDepth() | 设置特征点逆深度 |
| FeatureManager()::triangulate() | 特征点三角化求深度(SVD分解) |
| FeatureManager()::removeOutlier() | 移除外点 |
| FeatureManager()::removeBackShiftDepth() | |
| FeatureManager()::removeBack() | 边缘化最老帧,直接将特征点保存的帧号前移 |
| FeatureManager()::removeFront() | 边缘化次新帧,对特征点在次新帧的信息移除 |
一、FeatureManager、FeaturePerId、FeaturePerFrame
1、三者关系
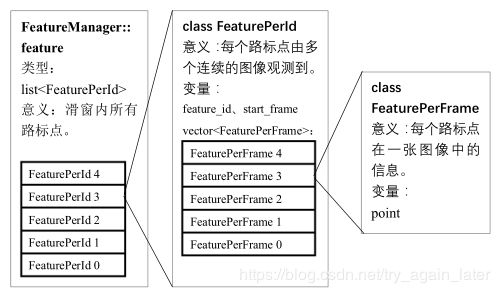
f_manager是特征管理器类的对象
FeatureManager f_manager;//特征管理器类这里f_mangager.feature主要指的是一个list容器
feature_manager.h主要三个类:
FeatureManager管理所有特征点,通过list容器存储特征点属性
FeaturePerId指的是某feature_id下的所有FeaturePerFrame。常用feature_id和观测第一帧start_frame、最后一帧endFrame()
FeaturePerFrame指的是每帧基本的数据:特征点[x,y,z,u,v,vx,vy]和td IMU与cam同步时间差
![]()
2、FeaturePerId,某feature_id下的所有FeaturePerFrame
feature_id 特征点ID、start_frame 出现该角点的第一帧的id--start_frame
class FeaturePerId
{
public:
const int feature_id;// 特征点ID索引
int start_frame;// 首次被观测到时,该帧的索引
vector feature_per_frame; // 能够观测到某个特征点的所有相关帧
int used_num;// 该特征出现的次数
bool is_outlier;// 是否外点
bool is_margin;// 是否Marg边缘化
double estimated_depth; // 估计的逆深度
int solve_flag; // 求解器 0 haven't solve yet; 1 solve succ; 2 solve fail;
Vector3d gt_p; // ???
FeaturePerId(int _feature_id, int _start_frame)
: feature_id(_feature_id), start_frame(_start_frame),
used_num(0), estimated_depth(-1.0), solve_flag(0)
{
}
int endFrame();// 返回最后一次观测到这个特征点的帧数ID
};
3、FeaturePerFrame
_point 每帧的特征点[x,y,z,u,v,vx,vy], td IMU和cam同步时间差
class FeaturePerFrame
{
public:
FeaturePerFrame(const Eigen::Matrix &_point, double td)
{
point.x() = _point(0);
point.y() = _point(1);
point.z() = _point(2);
uv.x() = _point(3);
uv.y() = _point(4);
velocity.x() = _point(5);
velocity.y() = _point(6);
cur_td = td;
}
double cur_td;
Vector3d point;
Vector2d uv;
Vector2d velocity;
double z; // 特征点的深度
bool is_used;// 是否被用了
double parallax;// 视差
MatrixXd A; //变换矩阵
VectorXd b;
double dep_gradient; // ???
}; 三者串联最好的例子是:从f_manager到it_per_id再到底层的it_per_frame,就可以得到基本数据point了
for (auto &it_per_id : f_manager.feature)
{
......
for (auto &it_per_frame : it_per_id.feature_per_frame)
{
Vector3d pts_j = it_per_frame.point;// 3D特征点坐标
}
}class FeatureManager中 list
feature;// 重要!! 通过FeatureManager可以得到滑动窗口内所有的角点信息 class FeaturePerId中 vector
feature_per_frame; // 能够观测到某个特征点的所有相关帧
二、主要函数
| 函数名 | 功能 |
| FeaturePerId::endFrame() | 返回最后一个观测到这个特征点的图像帧ID |
| FeatureManager()::getFeatureCount() | 窗口中被跟踪的特征点数量 |
| FeatureManager()::addFeatureCheckParallax() | 特征点进入时检查视差,是否为关键帧 |
| FeatureManager()::getCorresponding() | 前后两帧之间匹配特征点3D坐标 |
| FeatureManager()::setDepth() | 设置特征点逆深度 |
| FeatureManager()::triangulate() | 特征点三角化求深度(SVD分解) |
| FeatureManager()::removeOutlier() | 移除外点 |
| FeatureManager()::removeBackShiftDepth() | |
| FeatureManager()::removeBack() | 边缘化最老帧,直接将特征点保存的帧号前移 |
| FeatureManager()::removeFront() | 边缘化次新帧,对特征点在次新帧的信息移除 |
1、endFrame()
返回最后一个观测到这个特征点的图像帧ID
int FeaturePerId::endFrame()
{
return start_frame + feature_per_frame.size() - 1;
}其中,feature_per_frame的数量为vector容器中,FeaturePerFrame基本类的数量。代表能够观测到某个特征点的所有帧。
vector feature_per_frame; // 能够观测到某个特征点的所有相关帧 2、getFeatureCount()
窗口中被跟踪特征点的数量。
标准:该特征点被两帧以上观测到了,且第一次观测到的帧数不是在最后面。
int FeatureManager::getFeatureCount()
{
int cnt = 0;
for (auto &it : feature)// 遍历feature
{
it.used_num = it.feature_per_frame.size(); // 所有特征点被观测到的帧数
// 如果该特征点有两帧以上观测到了 且第一次观测到帧数不是在最后
if (it.used_num >= 2 && it.start_frame < WINDOW_SIZE - 2)
{
cnt++;// 这个特征点是有效的
}
}
return cnt;
}3、addFeatureCheckParallax()
为什么要检查视差?
VINS中为了控制优化计算量,只对当前帧之前某一部分帧进行优化,而不是全部历史帧,局部优化帧数量的大小就是窗口大小。
为了维持窗口大小,需要去除旧帧添加新帧,也就是边缘化Marginalization。到底是删去最旧的帧(MARGIN_OLD)还是删去刚刚进来窗口倒数第二帧(MARGIN_SECOND_NEW),就需要对当前帧与之前帧进行视差比较,如果是当前帧变化很小,就会删去倒数第二帧,如果变化很大,就删去最旧的帧。
通过检测两帧之间的视差以及特征点数量决定 次新帧是否作为关键帧
1、关键帧选取:
1、当前帧相对最近的关键帧的特征平均视差大于一个阈值就为关键帧(因为视差可以根据平移和旋转共同得到,而纯旋转则导致不能三角化成功,所以这一步需要IMU预积分进行补偿)
2、当前帧跟踪到的特征点数量小于阈值视为关键帧;
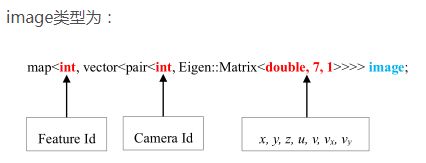
输入的是特征点,但是会把能观测到这个特征点的所有帧也都放进去,第一个索引是特征点ID,第二个索引是观测到该特征点的相机帧 ID。
先把特征点从image放入feature的list容器中,计算每一个点跟踪次数小于阈值 和 它在次新帧和次次新帧间所有特征点的平均视差大于阈值,返回是否是关键帧
2、代码
bool FeatureManager::addFeatureCheckParallax(int frame_count, const map>>> &image, double td)
{
ROS_DEBUG("input feature: %d", (int)image.size());// 特征点数量
ROS_DEBUG("num of feature: %d", getFeatureCount()); // 能够作为特征点的数量
double parallax_sum = 0;// 所有特征点视差总和
int parallax_num = 0;
last_track_num = 0;// 被跟踪的个数
// 1. 把image map中的所有特征点放入feature list容器中
// 遍历特征点,看该特征点是否在特征点的列表中,如果没在,则将存入到Feature列表中;否则统计数目
for (auto &id_pts : image)// 遍历所有特征点
{
FeaturePerFrame f_per_fra(id_pts.second[0].second, td);// _point 每帧的特征点[x,y,z,u,v,vx,vy]和td IMU和cam同步时间差
// 1.1迭代器寻找feature list中是否有这feature_id
int feature_id = id_pts.first;// 特征点ID
// 第三个参数是 Lambda表达式
auto it = find_if(feature.begin(), feature.end(), [feature_id](const FeaturePerId &it)
{
return it.feature_id == feature_id;
});
// 1.2 如果没有则新建一个,并在feature管理器的list容器最后添加:FeaturePerId、FeaturePerFrame
if (it == feature.end())
{
feature.push_back(FeaturePerId(feature_id, frame_count));// (特征点ID,首次观测到特征点的图像帧ID)
feature.back().feature_per_frame.push_back(f_per_fra);
}
// 1.3 之前有的话在FeaturePerFrame添加此特征点在此帧的位置和其他信息,并统计数目。
else if (it->feature_id == feature_id)
{
it->feature_per_frame.push_back(f_per_fra);
last_track_num++; // 此帧有多少相同特征点被跟踪
}
}
// 2. 追踪次数小于20或者窗口内帧的数目小于2,是关键帧
if (frame_count < 2 || last_track_num < 20)
return true;
// 3.计算每个特征在次新帧和次次新帧中的视差
for (auto &it_per_id : feature)
{
// 观测该特征点的:起始帧小于倒数第三帧,终止帧要大于倒数第二帧,保证至少有两帧能观测到。
if (it_per_id.start_frame <= frame_count - 2 &&
it_per_id.start_frame + int(it_per_id.feature_per_frame.size()) - 1 >= frame_count - 1)
{
// 总视差:该特征点在两帧的归一化平面上的坐标点的距离ans
parallax_sum += compensatedParallax2(it_per_id, frame_count);
parallax_num++;// 个数
}
}
// 4.1 第一次加进去的,是关键帧
if (parallax_num == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
ROS_DEBUG("parallax_sum: %lf, parallax_num: %d", parallax_sum, parallax_num);
ROS_DEBUG("current parallax: %lf", parallax_sum / parallax_num * FOCAL_LENGTH);
// 4.2 平均视差大于阈值的是关键帧
return parallax_sum / parallax_num >= MIN_PARALLAX;
}
} 其中,find_if函数可以参考 C++ STL find和find_if。意为:遍历feature list 容器看看之前是否出现过当前的feature_id
4、compensatedParallax2()
计算某个特征点it_per_id在次新帧和次次新帧的视差ans
判断观测到该特征点的frame中倒数第二帧和倒数第三帧的共视关系 实际是求取该特征点在两帧的归一化平面上的坐标点的距离ans
double FeatureManager::compensatedParallax2(const FeaturePerId &it_per_id, int frame_count)
{
//check the second last frame is keyframe or not
//parallax betwwen seconde last frame and third last frame
const FeaturePerFrame &frame_i = it_per_id.feature_per_frame[frame_count - 2 - it_per_id.start_frame];// 倒数第三帧
const FeaturePerFrame &frame_j = it_per_id.feature_per_frame[frame_count - 1 - it_per_id.start_frame];// 倒数第二帧
double ans = 0;
Vector3d p_j = frame_j.point;// 3D路标点(倒数第二帧j)
double u_j = p_j(0);
double v_j = p_j(1);
Vector3d p_i = frame_i.point;// 3D路标点(倒数第三帧i)
Vector3d p_i_comp;
//int r_i = frame_count - 2;
//int r_j = frame_count - 1;
//p_i_comp = ric[camera_id_j].transpose() * Rs[r_j].transpose() * Rs[r_i] * ric[camera_id_i] * p_i;
p_i_comp = p_i;
double dep_i = p_i(2);
double u_i = p_i(0) / dep_i;
double v_i = p_i(1) / dep_i;
double du = u_i - u_j, dv = v_i - v_j;
double dep_i_comp = p_i_comp(2);
double u_i_comp = p_i_comp(0) / dep_i_comp;
double v_i_comp = p_i_comp(1) / dep_i_comp;
double du_comp = u_i_comp - u_j, dv_comp = v_i_comp - v_j;
// 算斜边
ans = max(ans, sqrt(min(du * du + dv * dv, du_comp * du_comp + dv_comp * dv_comp)));
return ans;
}其中,获取倒数第三帧方式为:
const FeaturePerFrame &frame_i = it_per_id.feature_per_frame[frame_count - 2 - it_per_id.start_frame];// 倒数第三帧
5、getCorresponding()
得到给定两帧之间的对应特征点3D坐标
vector> FeatureManager::getCorresponding(int frame_count_l, int frame_count_r)
{
vector> corres;
for (auto &it : feature)// 遍历feature的list容器
{
// 要找特征点的两帧在窗口范围内,可以直接取。窗口为:观测到当前特征点的所有图像帧
if (it.start_frame <= frame_count_l && it.endFrame() >= frame_count_r)
{
Vector3d a = Vector3d::Zero(), b = Vector3d::Zero();
int idx_l = frame_count_l - it.start_frame;// 当前帧-第一次观测到特征点的帧数
int idx_r = frame_count_r - it.start_frame;
a = it.feature_per_frame[idx_l].point;
b = it.feature_per_frame[idx_r].point;
corres.push_back(make_pair(a, b));
}
}
return corres;
} 6、setDepth()
设置特征点的逆深度估计值
void FeatureManager::setDepth(const VectorXd &x)
{
int feature_index = -1;// 先给feature ID赋值-1
for (auto &it_per_id : feature)// 遍历所有特征点
{
// 至少两帧观测得到这个特征点 且 首次观测到该特征点的图像帧在滑动窗范围内
it_per_id.used_num = it_per_id.feature_per_frame.size();// 能够观测到某个特征点的所有相关帧数目
if (!(it_per_id.used_num >= 2 && it_per_id.start_frame < WINDOW_SIZE - 2))
continue;
// 求解逆深度
it_per_id.estimated_depth = 1.0 / x(++feature_index);
//ROS_INFO("feature id %d , start_frame %d, depth %f ", it_per_id->feature_id, it_per_id-> start_frame, it_per_id->estimated_depth);
// 深度小于0估计失败
if (it_per_id.estimated_depth < 0)
{
it_per_id.solve_flag = 2;//失败估计
}
else
it_per_id.solve_flag = 1;//成功估计
}
}问题:
// 求解逆深度
it_per_id.estimated_depth = 1.0 / x(++feature_index);
最后乘上的(++feature_index)是做什么用的?
7、trangulate()
对特征点进行三角化求深度(SVD分解)
void FeatureManager::triangulate(Vector3d Ps[], Vector3d tic[], Matrix3d ric[])
{
for (auto &it_per_id : feature)
{
// 需要至少两帧观测到该特征点 且 首次观测到特征点的帧不是倒数第三帧
it_per_id.used_num = it_per_id.feature_per_frame.size();
if (!(it_per_id.used_num >= 2 && it_per_id.start_frame < WINDOW_SIZE - 2))
continue;
if (it_per_id.estimated_depth > 0)
continue;
int imu_i = it_per_id.start_frame, imu_j = imu_i - 1;
ROS_ASSERT(NUM_OF_CAM == 1);
Eigen::MatrixXd svd_A(2 * it_per_id.feature_per_frame.size(), 4);
int svd_idx = 0;
//R0 t0为第i帧相机坐标系到世界坐标系的变换矩阵Rwc
Eigen::Matrix P0;
Eigen::Vector3d t0 = Ps[imu_i] + Rs[imu_i] * tic[0];
Eigen::Matrix3d R0 = Rs[imu_i] * ric[0];
P0.leftCols<3>() = Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity();
P0.rightCols<1>() = Eigen::Vector3d::Zero();
for (auto &it_per_frame : it_per_id.feature_per_frame)//遍历
{
imu_j++;
//R t为第j帧相机坐标系到第i帧相机坐标系的变换矩阵,P为i到j的变换矩阵
Eigen::Vector3d t1 = Ps[imu_j] + Rs[imu_j] * tic[0];
Eigen::Matrix3d R1 = Rs[imu_j] * ric[0];
Eigen::Vector3d t = R0.transpose() * (t1 - t0);
Eigen::Matrix3d R = R0.transpose() * R1;
Eigen::Matrix P;
P.leftCols<3>() = R.transpose();
P.rightCols<1>() = -R.transpose() * t;
Eigen::Vector3d f = it_per_frame.point.normalized();
//P = [P1 P2 P3]^T
//AX=0 A = [A(2*i) A(2*i+1) A(2*i+2) A(2*i+3) ...]^T
//A(2*i) = x(i) * P3 - z(i) * P1
//A(2*i+1) = y(i) * P3 - z(i) * P2
svd_A.row(svd_idx++) = f[0] * P.row(2) - f[2] * P.row(0);
svd_A.row(svd_idx++) = f[1] * P.row(2) - f[2] * P.row(1);
if (imu_i == imu_j)
continue;
}
//对A的SVD分解得到其最小奇异值对应的单位奇异向量(x,y,z,w),深度为z/w
ROS_ASSERT(svd_idx == svd_A.rows());
Eigen::Vector4d svd_V = Eigen::JacobiSVD(svd_A, Eigen::ComputeThinV).matrixV().rightCols<1>();
double svd_method = svd_V[2] / svd_V[3];
//it_per_id->estimated_depth = -b / A;
//it_per_id->estimated_depth = svd_V[2] / svd_V[3];
it_per_id.estimated_depth = svd_method;
//it_per_id->estimated_depth = INIT_DEPTH;
if (it_per_id.estimated_depth < 0.1)
{
it_per_id.estimated_depth = INIT_DEPTH;
}
}
} 8、三个边缘化函数
removeBackShiftDepth()
边缘化最老帧时,处理特征点保存的帧号,将起始帧是最老帧的特征点的深度值进行转移
//marg_R、marg_P为被边缘化的位姿,new_R、new_P为在这下一帧的位姿
void FeatureManager::removeBackShiftDepth(Eigen::Matrix3d marg_R, Eigen::Vector3d marg_P, Eigen::Matrix3d new_R, Eigen::Vector3d new_P)
{
for (auto it = feature.begin(), it_next = feature.begin();
it != feature.end(); it = it_next)
{
it_next++;
//特征点起始帧不是最老帧则将帧号减一
if (it->start_frame != 0)
it->start_frame--;
else
{
//特征点起始帧是最老帧
Eigen::Vector3d uv_i = it->feature_per_frame[0].point;
it->feature_per_frame.erase(it->feature_per_frame.begin());
//特征点只在最老帧被观测则直接移除
if (it->feature_per_frame.size() < 2)
{
feature.erase(it);
continue;
}
else
{
//pts_i为特征点在最老帧坐标系下的三维坐标
//w_pts_i为特征点在世界坐标系下的三维坐标
//将其转换到在下一帧坐标系下的坐标pts_j
Eigen::Vector3d pts_i = uv_i * it->estimated_depth;
Eigen::Vector3d w_pts_i = marg_R * pts_i + marg_P;
Eigen::Vector3d pts_j = new_R.transpose() * (w_pts_i - new_P);
double dep_j = pts_j(2);
if (dep_j > 0)
it->estimated_depth = dep_j;
else
it->estimated_depth = INIT_DEPTH;
}
}
// remove tracking-lost feature after marginalize
/*
if (it->endFrame() < WINDOW_SIZE - 1)
{
feature.erase(it);
}
*/
}
}removeBack()
边缘化最老帧时,直接将特征点所保存的帧号向前滑动
void FeatureManager::removeBack()
{
for (auto it = feature.begin(), it_next = feature.begin();
it != feature.end(); it = it_next)
{
it_next++;
//如果特征点起始帧号start_frame不为零则减一
if (it->start_frame != 0)
it->start_frame--;
//如果start_frame为0则直接移除feature_per_frame的第0帧FeaturePerFrame
//如果feature_per_frame为空则直接删除特征点
else
{
it->feature_per_frame.erase(it->feature_per_frame.begin());
if (it->feature_per_frame.size() == 0)
feature.erase(it);
}
}
}removeFront()
边缘化次新帧时,对特征点在次新帧的信息进行移除处理
void FeatureManager::removeFront(int frame_count)
{
for (auto it = feature.begin(), it_next = feature.begin(); it != feature.end(); it = it_next)
{
it_next++;
//起始帧为最新帧的滑动成次新帧
if (it->start_frame == frame_count)
{
it->start_frame--;
}
else
{
int j = WINDOW_SIZE - 1 - it->start_frame;
//如果次新帧之前已经跟踪结束则什么都不做
if (it->endFrame() < frame_count - 1)
continue;
//如果在次新帧仍被跟踪,则删除feature_per_frame中次新帧对应的FeaturePerFrame
//如果feature_per_frame为空则直接删除特征点
it->feature_per_frame.erase(it->feature_per_frame.begin() + j);
if (it->feature_per_frame.size() == 0)
feature.erase(it);
}
}
}