前端进阶(八)React16性能优化-实战
一、优化实践
从过往的经验和实践中,影响网页性能最大的因素就是浏览器的重绘和回流,React背后的虚拟DOM就是尽可能的减少浏览器的重绘和回流。以下都是实际使用中一些常见的优化实践。
1、{...this.props} (不要滥用,请只传递component需要的props,传得太多,或者层次传得太深,都会加重shouldComponentUpdate里面的数据比较负担,因此,请慎用spread attributes(
2、::this.handleChange()。(请将方法的bind一律置于constructor)
this.handleChange = this.handleChange.bind(this);3、复杂的页面不要在一个组件里面写完,对组件拆分粒度要小。
4、请尽量使用const element。
5、map里面添加key,并且key不要使用index(可变的)。具体可参考:使用Perf工具研究React Key对渲染的影响
6、尽量少用setTimeOut或不可控的refs、DOM操作,使用数据驱动,而不是操作DOM的方式。
7、props和state的数据尽可能简单明了,扁平化,如果不可避免的使用了多层数据结构,在复制时必须要用深拷贝方式重新生成新的对象或者数组,深拷贝可以使用lodash中的cloneDeep方法.
import { cloneDeep } from 'lodash';8、使用return null而不是CSS的display:none来控制节点的显示隐藏。保证同一时间页面的DOM节点尽可能的少。
9、和视图无关的数据变化不要放在state中,这样可以避免不必要的render操作。
二、React组件性能优化
1、react性能查看工具
(1)React官方提供的:React.addons.Perf
在chorme中先安装React Perf扩展,然后在入口文件或者redux的store.js中加入相应的代码即可。
import Perf from 're-addons-perfact';
const win = window;
win.perf = Perf;查看react加载组件时所耗费的时间的工具,在react 16版本之前我们可以使用React Perf来查看。从React16版本开始,我们可以直接在url后加上?react_pref,就可以在chrome浏览器的performance,我们可以查看User Timeing来查看组件的加载时间。
使用此工具的具体操作大家可以看下图所示:
(2)react-perf-tool
react-perf-tool为React应用提供了一种可视化的性能检测方案,该工程同样是基于React.addons,但是使用图表来显示结果,更加方便。
2、单个React组件性能优化
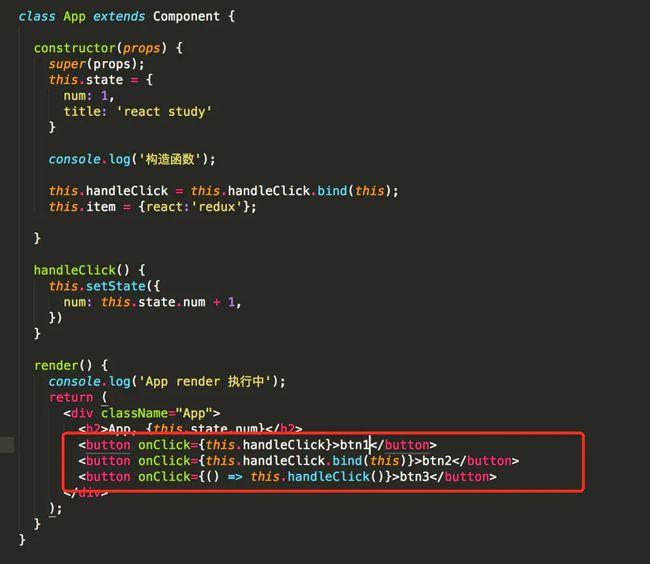
(1)render函数中尽量减少新建变量和bind函数,传递参数尽量传递最少的值
性能最好的是第一种。
第一种,构造函数每一次渲染的时候只会执行一遍;
而第二种方法,在每次render()的时候都会重新执行一遍函数;
第三种方法的话,每一次render()的时候,都会生成一个新的箭头函数,即使两个箭头函数的内容是一样的。
(2)定制shouldComponentUpdate函数
shouldComponentUpdate函数是决定React组件是否重新渲染的,返回结果是boolean类型。默认每次更新都要调用React所有生命周期函数,非常浪费。
shouldComponentUpdate函数参数(nextProps,nextState)中可以分别对两个参数中的数据项进行判断,如果想要实现在有些数据不变时不渲染,返回false即可。
如需要在props中的num和state中的flag数据项不变时不渲染,可采用如下代码:
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
if(nextProps.num === this.props.num || nextState.flag === this.state.flag){
return false;
}
return true;
}从React15.3后,react给我们提供了React.PureComponent,其源码也比较简单。这个类的用法很简单,如果你有些组件是纯组件,那么把继承类从 Component 换成 PureComponent 即可。当组件更新时,如果组件的 props 和 state 都没发生改变,render 方法就不会触发,省去 Virtual DOM 的生成和比对过程,达到提升性能的目的。
function ReactPureComponent(props, context, updater) {
// Duplicated from ReactComponent.
this.props = props;
this.context = context;
this.refs = emptyObject;
// We initialize the default updater but the real one gets injected by the
// renderer.
this.updater = updater || ReactNoopUpdateQueue;
}
function ComponentDummy() {}
ComponentDummy.prototype = ReactComponent.prototype;
ReactPureComponent.prototype = new ComponentDummy();
ReactPureComponent.prototype.constructor = ReactPureComponent;
// Avoid an extra prototype jump for these methods.
Object.assign(ReactPureComponent.prototype, ReactComponent.prototype);
ReactPureComponent.prototype.isPureReactComponent = true;官方也在早期提供了名为react-addons-pure-render-mixin插件来重新实现shouldComponentUpdate生命周期方法。
通过上述的方法的效果也是和我们定制shouldComponentUpdate的效果是一致的。
这里的PureComponent的render方法是浅比较的,因为深比较的场景是相当昂贵的。
所以我们要注意:不要直接为props设置对象或者数组、不要将方法直接绑定在元素上,因为其实函数也是对象。
(3)Immutable.js
Immutable 实现的原理是 Persistent Data Structure(持久化数据结构),也就是使用旧数据创建新数据时,要保证旧数据同时可用且不变。同时为了避免 deepCopy 把所有节点都复制一遍带来的性能损耗,Immutable 使用了 Structural Sharing(结构共享),即如果对象树中一个节点发生变化,只修改这个节点和受它影响的父节点,其它节点则进行共享。
Immutable 提供了简洁高效的判断数据是否变化的方法,只需 === 和 is 比较就能知道是否需要执行 render(),而这个操作几乎 0 成本,所以可以极大提高性能。
import React from 'react';
import {is} from 'immutable';
class App extends Component {
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps,nextState){
const thisProps = this.props || {};
const thisState = this.state || {};
if(Object.keys(thisProps).length !== Object.keys(nextProps.keys).length ||
Object.keys(thisProps).length !== Object.keys(nextProps.keys).length){
return true;
}
for(const key in nextProps){
if(nextProps.hasOwnProperty(key) && !is(thisProps[key],nextProps[key])){
return true;
}
}
for(const key in nextState){
if(nextState.hasOwnProperty(key) && !is(thisState[key],nextState[key])){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}(4)react-immutable-render-mixin
这是一个facebook/immutable-js的react pure render mixin 的库,可以简化很多写法。使用react-immutable-render-mixin可以实现装饰器的写法。
import React from 'react';
import { immutableRenderDecorator } from 'react-immutable-render-mixin';
@immutableRenderDecorator
class Test extends React.Component {
render() {
return ;
}
}具体使用可以参见:使用immutable优化React
3、多个react组件性能优化,key的优化
一个常见的错误就是,拿数组的的下标值去当做key,这个是很危险的,代码如下,我们一定要避免。
{
todos.map((item, index) => {
我们可以像下面这样用一个全局的localCounter变量来添加稳定唯一的key值。
var localCounter = 1;
this.data.forEach(el=>{
el.id = localCounter++;
});
//向数组中动态添加元素时,
function createUser(user) {
return {
...user,
id: localCounter++
}
}4、使用无状态组件(函数组件)代替类组件
这种组件没有生命周期,没有状态(16.7后引入hooks,变得有状态了)。对于只需要接收父组件传递的props的子组件可以改写成无状态组件,可以节省很多不必要的开销,性能也得到很大提升。
无状态组件
var Header = (props) = (
{props.xxx}
);有状态组件
class Home extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
};
//React生命周期函数定义
render() {
return (
5、高阶组件
使用高阶组件封装组件内部可复用的逻辑。
需要注意:
(1)官方推荐在高阶组件里尽量不要设置state值,传值的话可以用props的方法。
(2)尽量不去改变原始组件,而是通过组合的方式。
三、Redux性能优化
1、reselect(数据获取时优化)
在前面的优化过程中,我们都是优化渲染来提高性能的,既然react和redux都是通过数据驱动的的方式驱动渲染过程,那么处理优化渲染过程,获取数据的过程也是需要考虑的一个优化点。
//下面是redux中简单的一个筛选功能
const getVisibleTodos = (todos, filter) => {
switch (filter) {
case 'SHOW_ALL':
return todos
case 'SHOW_COMPLETED':
return todos.filter(t => t.completed)
case 'SHOW_ACTIVE':
return todos.filter(t => !t.completed)
}
}
const mapStateToProps = (state) => {
return {
todos: getVisibleTodos(state.todos, state.visibilityFilter)
}
}mapStateToProps函数作为redux store中获取数据的重要一环,当我们根据filter和todos来显示相应的待办事项的时候,我们都要遍历todos字段上的数组。
当数组比较大的时候,则会降低性能。
这个时候,reselect就应运而生了,它的动作原理:只要相关的状态没有改变,那么就直接使用上一次的缓存结果。
使用方法以及原理见:Redux的中间件-Reselect
2、Ramda
是一个由许多高阶函数组成、功能强大的函数库。换句话说,就是许多用于创建函数的函数。由于我们的映射函数也不过只是函数而已,所以我们可以利用 Ramda 方便地创建 selectors。Ramda 可以完成所有 selectors 可以完成的工作,而且还不止于此。Ramda cookbook 中介绍了一些 Ramda 的应用示例。
3、redux-saga
redux-saga是一个用于管理redux应用异步操作的中间件,redux-saga通过创建sagas将所有异步操作逻辑收集在一个地方集中处理,可以用来代替redux-thunk中间件。
四、参考资料
1、针对 Airbnb 清单页的 React 性能优化
2、Redux isn't slow, you're just doing it wrong - An optimization guide