最大流算法
目录
- 最大流算法
- 网络流基础概念
- 网络流
- 可行流
- 最大流
- 求解最大流算法
- 反向边
- 增广路经
- EK算法
- Dinic算法
最大流算法
网络流基础概念
网络流
在一个有向图 G = ( V , E ) G= (V,E) G=(V,E)中:
- 有一个唯一的源点S(入度为 0 0 0:出发点)
- 有一个唯一的汇点T(出度为 0 0 0:结束点)
- 图中的每一条边都一个非负的权值,这个权值叫做容量 c ( u , v ) c(u, v) c(u,v)
满足上述条件的图 G G G称为网络流图,记为 G = ( V , E , C ) G= (V,E,C) G=(V,E,C)
可以想象成,如果把每条边都看成一个管道,可以看成是水从源点S出发经过这些管道,最终流向汇点T,而每条管道有最大的容量。
可行流
流量:每条弧上给定一个实数 f ( u , v ) f(u,v) f(u,v),满足 0 ≤ f ( u , v ) ≤ c ( u , v ) 0 \leq f(u,v) \leq c(u,v) 0≤f(u,v)≤c(u,v)
可行流满足:
- 源点S:流出量 = 整个网络的流量
- 汇点T:流入量 = 整个网络的流量
- 中间的点:总流入量 = 总流出量,同时 0 ≤ f ( u , v ) ≤ c ( u , v ) 0 \leq f(u,v) \leq c(u,v) 0≤f(u,v)≤c(u,v)
这样的在整个网络中的流量就是可行流,可行流有多个
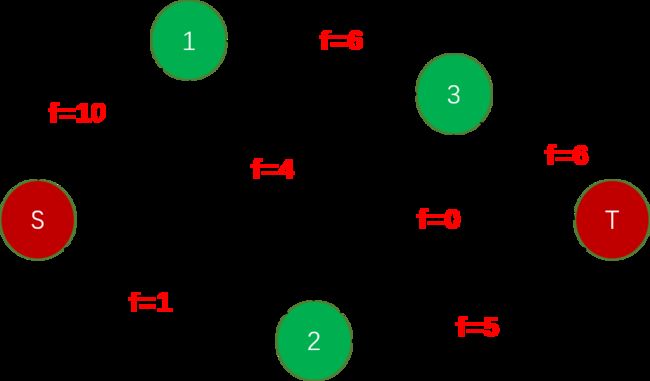
红色的部分表示流量,黑色的表示容量。可行流就是7
最大流
- 所有可行流中流量最大的流量
- 最大流可能不止一个
最大流为11
求解最大流算法
反向边
- 首先要明白一点,在一条从 S S S到 T T T的路径中,能够带来的最大流量取决于这条路径上的最小容量。
对于下面这张图 1 1 1是源点, 4 4 4是汇点
如果我们使用搜索算法找一条从1到4的路径,并且这条路径能够带来的流量是这条路径上边的容量的最小值,
假设我们找到的路径是 1 − > 2 − > 3 − > 4 1->2->3->4 1−>2−>3−>4,现在的流量是 1 1 1,因为这条路已经使用过了,把这条路径上的每条边减 1 1 1,再次找从1到4的路径,发现找不到了,因此得到的答案为1,但是正确的答案应该是 2 2 2。即 1 − > 2 − > 4 1->2->4 1−>2−>4、 1 − > 3 − > 4 1->3->4 1−>3−>4
这个时候,为了能够继续找到路径,必须要反向建立边,把当前路径反向建边,边的权值就是这条路径的流量
如图
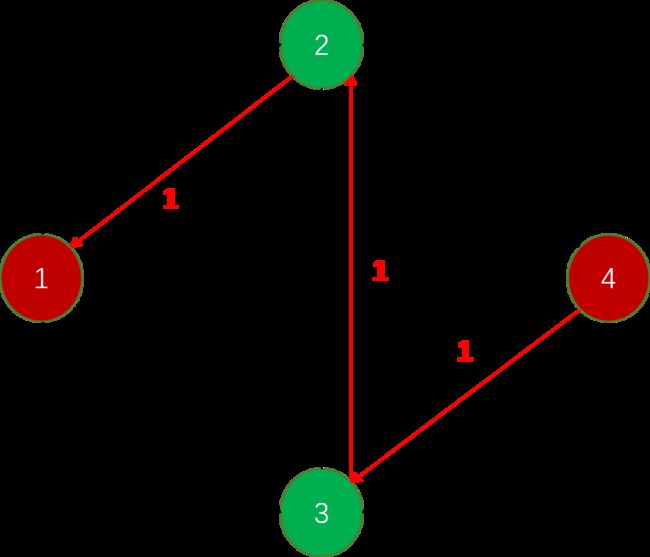
其中红色的边就是反向建立的,这个时候继续寻找一条路径,发现可以走 1 − > 3 − > 2 − > 4 1->3->2->4 1−>3−>2−>4,带来的流量是 1 1 1,然后继续找寻路径,发现没有可达的路径了,因此最大流是 1 + 1 = 2 1+1=2 1+1=2。
为什么要反向建边呢,仔细想想应该能够明白,反向建立边的作用相当于让之前的路径有可以反悔的余地。这样即使一开始走错也没有关系,因为可以通过反向边来反悔,最终一定能得到正确答案
增广路经
明白了反向建边后,来看什么是增广路经?
如果一个可行流不是最大流,那么当前网络中一定存在一条增广路经。
从源点 S S S到汇点 T T T的一条路径中,如果边 ( u , v ) (u,v) (u,v)与该路径的方向一致就称为正向边,否则就记为逆向边,如果在这条路径上的所有边满足
- 正向边 f ( u , v ) < c ( u , v ) f(u,v) <c(u,v) f(u,v)<c(u,v)
- 逆向边 f ( u , v ) > 0 f(u, v) > 0 f(u,v)>0
则该路径是增广路径
其实增广路径就是通过这样一条路径,来增加到达汇点的流量,而路径中的流量没到达容量。
(在上图中,其实每次找到的一条从 1 1 1到 4 4 4的路径都是一条增广路径)
沿这条增广路改进可行流的操作称为增广.所有可能的增广路径放在一起就构成了残余网络
以下这 2 2 2个算法,都是基于不断找增广路经来实现的
EK算法
复杂度: O ( n m 2 ) O(nm^2) O(nm2), n n n是点数, m m m是边数
首先要考虑的是怎么找增广路径,之前说用搜索算法,可以用 b f s bfs bfs也可以用 d f s dfs dfs,但是 b f s bfs bfs的好处在于能够在残余网络中每一次找到最短的一条增广路径。因此在 E K EK EK算法是基于 b f s bfs bfs来找增广路经, b f s bfs bfs每执行一次,就找出一条增广路径来,然后把这条路径上的权值进行修改,同时反向建边。直到找不到增广路径为止,算法就结束了(代码注释写的很详细)
步骤
- 利用 b f s bfs bfs找到一条最短增广路径,记录该路径的最小流量
- 利用一个数组把这个路径上的流量更新
- 不断重复 1 , 2 1,2 1,2直到没有增广路径为止
具体实现:
POJ 1273(模板题)题目链接
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#define N 205
#define INF 0x7fffffff
#define ll long long
ll min(ll a, ll b) {
return a > b ? b : a;
}
using namespace std;
// Ek 找最大流,其中源点是1,汇点是n
ll g[N][N], pre[N], dis[N]; //g用来存图,pre[i]表示当前节点i的前一个节点,dis[i]表示从源点到i点的路径上的最小流量
ll n, m, s, t, ans;
queue <ll> q;
ll bfs () { //找到一条增广路经, 返回这条路径的流量
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) pre[i] = -1;
while(!q.empty()) q.pop();
q.push(s);
dis[s] = INF;
while (!q.empty()) {
ll x = q.front();
q.pop();
if(x == t) break; //找到了汇点
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(pre[i] == -1 && g[x][i]) { //找到一个没有被访问且还有容量的点
pre[i] = x;
dis[i] = min(dis[x], g[x][i]); //更新增广路径上的最小流量
q.push(i);
}
}
}
if(pre[t] == -1) return -1; //说明没有增广路径了,因此才走不到汇点
else return dis[t];
}
void EK () { //更新残余网络的流量
ll inc;
while (1) {
inc = bfs();
if(inc == -1) break; //没有增广路径了,算法结束
ll k = t;
while (k != s) {
g[k][pre[k]] += inc; //建立反向弧
g[pre[k]][k] -= inc; //正向容量减去流量
k = pre[k];
}
ans += inc;
}
}
int main () {
ll u, v, cost;
while(scanf("%lld %lld", &m, &n) != EOF) { //读入数据,记得初始化
memset(dis, 0, sizeof(dis));
memset(g, 0, sizeof(g));
ans = 0;
s = 1, t = n;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
scanf("%lld %lld %lld", &u, &v, &cost);
g[u][v] += cost;
}
EK();
printf("%lld\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
Dinic算法
复杂度: O ( V 2 E ) O(V^2E) O(V2E)
E K EK EK算法找增广路径是基于 b f s bfs bfs来进行的, b f s bfs bfs会把周围能够扩展的点全部扩展进来,直到找到汇点为止,相当于每找一次增广路径都要搜索大量的点。 D i n i c Dinic Dinic算法实际上是对 E K EK EK的优化
D i n i c Dinic Dinic算法利用 b f s bfs bfs建立分层网络 (所谓分层网络,就是按照每一个点到源点的距离,分层,方便后面的 d f s dfs dfs)。然后基于这个分层网络,使用 d f s dfs dfs找到当前分层网络下的所有增广路径,并且做好相应的修改。然后不断重复这两个过程,直到无法分层为止,这样做只需要一次 b f s bfs bfs就可以找到多条增广路径。
(PS:分层网络,就是利用 b f s bfs bfs特性,源点为起点,一直扩散出去,每一个点都打一个标记,标记到源点的路径所经过的最少的弧的数量,假设用 d i s [ i ] dis[i] dis[i]表示 i i i到源点S的最少经过的弧的数量,这样就可以将整个网络分层,基于这个分层网络, d f s dfs dfs找增广路径的时候,就可以找到最短的增广路径。如果当前点是 x x x, d f s dfs dfs搜到下一个点 i i i,一定要满足 d i s [ i ] = d i s [ x ] + 1 dis[i] = dis[x] +1 dis[i]=dis[x]+1,这样才是最短增广路径,效率才是最高的。)
步骤
- 利用 b f s bfs bfs建立分层网络(记录每个节点的深度)
- 按照当前分层网络进行 d f s dfs dfs(一层一层找),找到所有该分层网络下的增广路径,并更新残余网络
- 重复 1 、 2 1、2 1、2直到无法建立分层网络为止
邻接矩阵实现
POJ 1273(模板题)题目链接
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#define N 205
#define INF 0x7fffffff
#define min(a,b) a>b?b:a
using namespace std;
int n, m, s, t, maxflow;
int deep[N], g[N][N]; // deep 表示从源点到当前节点的深度
queue <int> q;
bool bfs () { //建立分层网络
while(!q.empty()) q.pop();
memset(deep, -1, sizeof(deep));
deep[s] = 0; // 源点的深度为0
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(g[x][i] > 0 && deep[i] == -1) {// 如果有容量能够到达i,并且i节点的深度未被标记
deep[i] = deep[x] + 1;
q.push(i);
}
}
}
if(deep[n] > 0) return true; //能够建立分层图
else return false; //不存在分层网络时,算法结束
}
//基于当前分层图,找到所有增广路径
int dfs (int x, int mx) { //表示当前节点x,以及这条增广路经上的最小流量
int a;
if(x == t) return mx;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if( g[x][i] > 0 && deep[i] == deep[x] + 1 && (a = dfs(i, min(mx, g[x][i]))) ) {//找到x能流通过去的的相邻顶点i
g[x][i] -= a; //更新残余网络
g[i][x] += a;
return a;
}
}
return 0;
}
void dinic () {
while(bfs())
maxflow += dfs(s, INF);
}
int main () {
int u, v, cost;
while(scanf("%d %d", &m, &n) != EOF) {
s = 1, t = n;
memset(g, 0, sizeof(g));
maxflow = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
scanf("%d %d %d", &u, &v, &cost);
g[u][v] += cost;
}
dinic();
printf("%d\n", maxflow);
}
return 0;
}
链式前向星实现(内存小)
其中需要注意的细节:
-
存边的时候反边的容量设置为0;
-
假设 d f s dfs dfs在递归回来的时候找到了这条增广路径的流量为 f l o w flow flow,需要更新正反边
- 正边: e d g e [ i ] . c a p − = f l o w edge[i].cap \,\,\,\,-= \,\,\,\,flow edge[i].cap−=flow
- 反边: e d g e [ i ^ 1 ] . c a p + = f l o w edge[i \hat{} 1].cap\,\,\,\, +=\,\,\,\, flow edge[i^1].cap+=flow
- 其中 ^ \hat{} ^表示按位异或,如果 i i i是偶数则 i ^ 1 = i + 1 i \hat{} 1 = i+1 i^1=i+1,如果 i i i是奇数则 i ^ 1 = i − 1 i \hat{} 1 = i -1 i^1=i−1,为什么反边就是 i ^ 1 i \hat{} 1 i^1呢。因此在存边的时候,是先存的正边,然后 + + c n t ++cnt ++cnt后存反边,正反边差 1 1 1个,为了保证正边的编号是偶数,反边是奇数, c n t cnt cnt初始化为 − 1 -1 −1(因为我的习惯是写 + + c n t ++cnt ++cnt)
洛谷 网络最大流(题目链接)
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#define INF 0x7fffffff
#define N 10001
#define M 100005
using namespace std;
struct flow {
int to, next, cap;
}edge[M * 4];
int n, m, s, t, maxflow;
int cnt = -1;
int head[N], dep[N]; //其中dep[i]表示i的深度,也就是到源点的最小边数
queue <int> q;
inline void addEdge (int u, int v, int cost) {
edge[++cnt].to = v;
edge[cnt].cap = cost;
edge[cnt].next = head[u];
head[u] = cnt;
//反向建边,容量为0
edge[++cnt].to = u;
edge[cnt].cap = 0;
edge[cnt].next = head[v];
head[v] = cnt;
}
bool bfs () { //建立分层网络
while(!q.empty()) q.pop();
memset(dep, -1, sizeof(dep));
dep[s] = 0;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front(); q.pop();
for(int i = head[x]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next) {
int u = edge[i].to;
int cap = edge[i].cap;
if(cap > 0 && dep[u] == -1) {
dep[u] = dep[x] + 1;
q.push(u);
}
}
}
if(dep[t] == -1) return 0;
else return 1;
}
int dfs (int x, int mx) {
int a;
if(x == t) return mx; //找到汇点,返回
for(int i = head[x]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next) {
int u = edge[i].to;
int cap = edge[i].cap;
if(cap > 0 && dep[u] == dep[x] + 1 && (a = dfs(u, min(cap, mx))) ) {
edge[i].cap -= a;
edge[i^1].cap += a; //反向边
return a;
}
}
return 0; //搜不到增广路经了就返回0
}
void dinic () {
int res;
while ( bfs() ) //当前网络下,搜索所有的增广路径
while (1) {
res = dfs(s, INF); //加上该路径能带来的流量
if(!res) break;
maxflow += res;
}
}
int main () {
int u, v, cost;
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
scanf("%d %d %d %d", &n, &m, &s, &t);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
scanf("%d %d %d", &u, &v, &cost);
addEdge(u, v, cost);
}
dinic();
printf("%d", maxflow);
return 0;
}
算法还可以优化,加入一个 c u r cur cur数组。
首先要明白在 d f s dfs dfs找增广路径的时候,一定是完全增广的,也就是说这条路径使用过后,下一次不必再次检查这条路径了。直接从下一条边开使找,加入这个优化,算法能快不少
int cur[N];
bool bfs () {
while(!q.empty()) q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++) cur[i] = head[i]; //复制head数组
memset(dep, -1, sizeof(dep));
dep[s] = 0;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front(); q.pop();
for(int i = head[x]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next) {
int u = edge[i].to;
int cap = edge[i].cap;
if(cap > 0 && dep[u] == -1) {
dep[u] = dep[x] + 1;
q.push(u);
}
}
}
if(dep[t] == -1) return 0;
else return 1;
}
int dfs (int x, int mx) {
int a;
if(x == t) return mx;
for(int i = cur[x]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next) {
cur[x] = i; //避免了搜寻已经增广过的路径
int u = edge[i].to;
int cap = edge[i].cap;
if(cap > 0 && dep[u] == dep[x] + 1 && (a = dfs(u, min(cap, mx))) ) {
edge[i].cap -= a;
edge[i^1].cap += a; //反向边
return a;
}
}
return 0; //搜不到增广路经了就返回0
}