※数据结构※→☆非线性结构(tree)☆============哈夫曼树 顺序存储结构(tree Huffman sequence)(二十二)
哈夫曼树 (Huffman Tree)
给定n个权值作为n个叶子结点,构造一棵二叉树,若带权路径长度达到最小,称这样的二叉树为最优二叉树,也称为哈夫曼树(Huffman tree)。
哈夫曼树(霍夫曼树)又称为最优树.
1、路径和路径长度
在一棵树中,从一个结点往下可以达到的孩子或孙子结点之间的通路,称为路径。通路中分支的数目称为路径长度。若规定根结点的层数为1,则从根结点到第L层结点的路径长度为L-1。
2、结点的权及带权路径长度
若将树中结点赋给一个有着某种含义的数值,则这个数值称为该结点的权。结点的带权路径长度为:从根结点到该结点之间的路径长度与该结点的权的乘积。
3、树的带权路径长度
树的带权路径长度规定为所有叶子结点的带权路径长度之和,记为WPL。
哈夫曼树构造过程
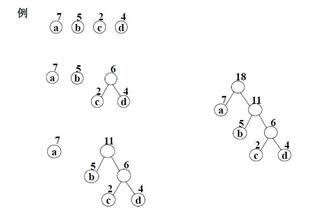
假设有n个权值,则构造出的哈夫曼树有n个叶子结点。 n个权值分别设为 w1、w2、…、wn,则哈夫曼树的构造规则为:
- (1) 将w1、w2、…,wn看成是有n 棵树的森林(每棵树仅有一个结点);
- (2) 在森林中选出两个根结点的权值最小的树合并,作为一棵新树的左、右子树,且新树的根结点权值为其左、右子树根结点权值之和;
- (3)从森林中删除选取的两棵树,并将新树加入森林;
- (4)重复(2)、(3)步,直到森林中只剩一棵树为止,该树即为所求得的哈夫曼树。
优点:使用仿函数就像使用一个普通的函数一样,但是它的实现可以访问仿函数中所有的成员变量来进行通行;而普通函数若要通信就只能依靠全局变量了。
函数对象顾名思义,就是在某种方式上表现的象一个函数的对象。典型的,它是指一个类的实例,这个类定义了应用操作符operator()。
函数对象是比函数更加通用的概念,因为函数对象可以定义跨越多次调用的可持久的部分(类似静态局部变量),同时又能从对象的外面进行初始化和检查(和静态局部变量不同)
/**
* ConvertToHuffman
*
* @param
* @return BOOL
* @note Convert current binary tree to Huffman tree (binary tree)
Suppose there are n weights, then construct a Huffman tree with n leaf nodes. n-weights are set to w1, w2, ..., wn, the Huffman tree structure rules:
(1) The w1, w2, ..., wn as a forest tree with n (each tree has only one node);
(2) in the forest root weights elect two smallest tree merge as a new tree in the left and right sub-tree, and the new root of the tree weight of its left and right sub-tree root node weights sum;
(3) Delete selected from the forest two trees and new trees added to the forest;
(4) Repeat (2), (3) step until only one tree in the forest until the tree is that obtained from Huffman tree.
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeHuffmanSeq::ConvertToHuffman()
{
if (TRUE == IsEmpty()) {
return FALSE;
}
if (NULL == m_pRootNode) {
return FALSE;
}
//Get Descendant node
//(1) The w1, w2, ..., wn as a forest tree with n (each tree has only one node);
AL_ListSeq*> listTreeNodeDescendant;
if (FALSE == m_pRootNode->GetDescendant(listTreeNodeDescendant)) {
return FALSE;
}
AL_QueuePrioritySeq*, AL_TreeNodeBinSeq > cQueuePrioritySeq;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pTreeNodeDescendant = NULL;
m_pRootNode->SetLevel(0x00);
m_pRootNode->RemoveParent();
m_pRootNode->RemoveLeft();
m_pRootNode->RemoveRight();
cQueuePrioritySeq.Push(m_pRootNode);
for (DWORD dwDescendantCnt=0x00; dwDescendantCntSetLevel(0x00);
pTreeNodeDescendant->RemoveParent();
pTreeNodeDescendant->RemoveLeft();
pTreeNodeDescendant->RemoveRight();
cQueuePrioritySeq.Push(pTreeNodeDescendant);
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
//Rebuilt Huffman Tree
m_dwDegree = 0x00;
m_dwHeight = TREEHUFFMANSEQ_HEIGHTINVALID;
m_pRootNode = NULL;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pTreeNodeSmallest = NULL;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pTreeNodeSmaller = NULL;
while (0x01 < cQueuePrioritySeq.Size()) {
//loop all, until only one tree in the priority queue
//(2) in the forest root weights elect two smallest tree merge as a new tree in the left and right sub-tree, and the new root of the tree weight of its left and right sub-tree root node weights sum;
if (TRUE == cQueuePrioritySeq.Pop(pTreeNodeSmallest) && TRUE == cQueuePrioritySeq.Pop(pTreeNodeSmaller)){
if (NULL != pTreeNodeSmallest && NULL != pTreeNodeSmaller) {
//rebuilt the root node
m_pTreeNode[m_dwUsed].SetLevel(0x00);
m_pTreeNode[m_dwUsed].SetWeight(pTreeNodeSmallest->GetWeight() + pTreeNodeSmaller->GetWeight());
m_pRootNode = &m_pTreeNode[m_dwUsed];
if (TRUE == m_pRootNode->InsertLeft(pTreeNodeSmallest)
&& TRUE == m_pRootNode->InsertRight(pTreeNodeSmaller)) {
//(3) Delete selected from the forest two trees and new trees added to the forest;
m_dwUsed++;
m_dwNumNodes++;
cQueuePrioritySeq.Push(m_pRootNode);
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
else{
return FALSE;
}
//(4) Repeat (2), (3) step until only one tree in the forest until the tree is that obtained from Huffman tree.
}
if (FALSE == RecalcDegreeHeight()) {
return FALSE;
}
return TRUE;
}
知识扩展
多叉哈夫曼树
哈夫曼树也可以是k叉的,只是在构造k叉哈夫曼树时需要先进行一些调整。构造哈夫曼树的思想是每次选k个权重最小的元素来合成一个新的元素,该元素权重为k个元素权重之和。但是当k大于2时,按照这个步骤做下去可能到最后剩下的元素少于k个。解决这个问题的办法是假设已经有了一棵哈夫曼树(且为一棵满k叉树),则可以计算出其叶节点数目为(k-1)nk+1,式子中的nk表示子节点数目为k的节点数目。于是对给定的n个权值构造k叉哈夫曼树时,可以先考虑增加一些权值为0的叶子节点,使得叶子节点总数为(k-1)nk+1这种形式,然后再按照哈夫曼树的方法进行构造即可。
哈夫曼树应用
1、哈夫曼编码
在数据通信中,需要将传送的文字转换成二进制的字符串,用0,1码的不同排列来表示字符。例如,需传送的报文为“AFTER DATA EAR ARE ART AREA”,这里用到的字符集为“A,E,R,T,F,D”,各字母出现的次数为{8,4,5,3,1,1}。现要求为这些字母设计编码。要区别6个字母,最简单的二进制编码方式是等长编码,固定采用3位二进制,可分别用000、001、010、011、100、101对“A,E,R,T,F,D”进行编码发送,当对方接收报文时再按照三位一分进行译码。显然编码的长度取决报文中不同字符的个数。若报文中可能出现26个不同字符,则固定编码长度为5。然而,传送报文时总是希望总长度尽可能短。在实际应用中,各个字符的出现频度或使用次数是不相同的,如A、B、C的使用频率远远高于X、Y、Z,自然会想到设计编码时,让使用频率高的用短码,使用频率低的用长码,以优化整个报文编码。
为使不等长编码为前缀编码(即要求一个字符的编码不能是另一个字符编码的前缀),可用字符集中的每个字符作为叶子结点生成一棵编码二叉树,为了获得传送报文的最短长度,可将每个字符的出现频率作为字符结点的权值赋予该结点上,显然字使用频率越小权值越小,权值越小叶子就越靠下,于是频率小编码长,频率高编码短,这样就保证了此树的最小带权路径长度效果上就是传送报文的最短长度。因此,求传送报文的最短长度问题转化为求由字符集中的所有字符作为叶子结点,由字符出现频率作为其权值所产生的哈夫曼树的问题。利用哈夫曼树来设计二进制的前缀编码,既满足前缀编码的条件,又保证报文编码总长最短。
哈夫曼静态编码:它对需要编码的数据进行两遍扫描:第一遍统计原数据中各字符出现的频率,利用得到的频率值创建哈夫曼树,并必须把树的信息保存起来,即把字符0-255(2^8=256)的频率值以2-4BYTES的长度顺序存储起来,(用4Bytes的长度存储频率值,频率值的表示范围为0--2^32-1,这已足够表示大文件中字符出现的频率了)以便解压时创建同样的哈夫曼树进行解压;第二遍则根据第一遍扫描得到的哈夫曼树进行编码,并把编码后得到的码字存储起来。
哈夫曼动态编码:动态哈夫曼编码使用一棵动态变化的哈夫曼树,对第t+1个字符的编码是根据原始数据中前t个字符得到的哈夫曼树来进行的,编码和解码使用相同的初始哈夫曼树,每处理完一个字符,编码和解码使用相同的方法修改哈夫曼树,所以没有必要为解码而保存哈夫曼树的信息。编码和解码一个字符所需的时间与该字符的编码长度成正比,所以动态哈夫曼编码可实时进行。
2、哈夫曼译码
在通信中,若将字符用哈夫曼编码形式发送出去,对方接收到编码后,将编码还原成字符的过程,称为哈夫曼译码。
======================================================================================================
二叉树
在计算机科学中,二叉树是每个结点最多有两个子树的有序树。通常子树的根被称作“左子树”(left subtree)和“右子树”(right subtree)。二叉树常被用作二叉查找树和二叉堆或是二叉排序树。二叉树的每个结点至多只有二棵子树(不存在出度大于2的结点),二叉树的子树有左右之分,次序不能颠倒。二叉树的第i层至多有2的 i -1次方个结点;深度为k的二叉树至多有2^(k) -1个结点;对任何一棵二叉树T,如果其终端结点数(即叶子结点数)为,出度为2的结点数为,则=+ 1。
基本形态
二叉树也是递归定义的,其结点有左右子树之分,逻辑上二叉树有五种基本形态:
(1)空二叉树——(a);
(2)只有一个根结点的二叉树——(b);
(3)只有左子树——(c);
(4)只有右子树——(d);
(5)完全二叉树——(e)
注意:尽管二叉树与树有许多相似之处,但二叉树不是树的特殊情形。
重要概念
(1)完全二叉树——若设二叉树的高度为h,除第 h 层外,其它各层 (1~h-1) 的结点数都达到最大个数,第 h 层有叶子结点,并且叶子结点都是从左到右依次排布,这就是完全二叉树。
(2)满二叉树——除了叶结点外每一个结点都有左右子叶且叶子结点都处在最底层的二叉树。
(3)深度——二叉树的层数,就是高度。
性质
(1) 在二叉树中,第i层的结点总数不超过2^(i-1);
(2) 深度为h的二叉树最多有2^h-1个结点(h>=1),最少有h个结点;
(3) 对于任意一棵二叉树,如果其叶结点数为N0,而度数为2的结点总数为N2,则N0=N2+1;
(4) 具有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度为int(log2n)+1
(5)有N个结点的完全二叉树各结点如果用顺序方式存储,则结点之间有如下关系:
若I为结点编号则 如果I>1,则其父结点的编号为I/2;
如果2*I<=N,则其左儿子(即左子树的根结点)的编号为2*I;若2*I>N,则无左儿子;
如果2*I+1<=N,则其右儿子的结点编号为2*I+1;若2*I+1>N,则无右儿子。
(6)给定N个节点,能构成h(N)种不同的二叉树。
h(N)为卡特兰数的第N项。h(n)=C(n,2*n)/(n+1)。
(7)设有i个枝点,I为所有枝点的道路长度总和,J为叶的道路长度总和J=I+2i
1.完全二叉树 (Complete Binary Tree)
若设二叉树的高度为h,除第 h 层外,其它各层 (1~h-1) 的结点数都达到最大个数,第 h 层从右向左连续缺若干结点,这就是完全二叉树。
2.满二叉树 (Full Binary Tree)
一个高度为h的二叉树包含正是2^h-1元素称为满二叉树。
二叉树四种遍历
1.先序遍历 (仅二叉树)
指先访问根,然后访问孩子的遍历方式
非递归实现
利用栈实现,先取根节点,处理节点,然后依次遍历左节点,遇到有右节点压入栈,向左走到尽头。然后从栈中取出右节点,处理右子树。
/*** PreOrderTraversal
*
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return BOOL
* @note Pre-order traversal
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::PreOrderTraversal(AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const
{
if (NULL == m_pRootNode) {
return FALSE;
}
listOrder.Clear();
//Recursion Traversal
PreOrderTraversal(m_pRootNode, listOrder);
return TRUE;
//Not Recursion Traversal
AL_StackSeq*> cStack;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pTreeNode = m_pRootNode;
while (TRUE != cStack.IsEmpty() || NULL != pTreeNode) {
while (NULL != pTreeNode) {
listOrder.InsertEnd(pTreeNode->GetData());
if (NULL != pTreeNode->GetChildRight()) {
//push the child right to stack
cStack.Push(pTreeNode->GetChildRight());
}
pTreeNode = pTreeNode->GetChildLeft();
}
if (TRUE == cStack.Pop(pTreeNode)) {
if (NULL == pTreeNode) {
return FALSE;
}
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
递归实现
/**
* PreOrderTraversal
*
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return VOID
* @note Pre-order traversal
* @attention Recursion Traversal
*/
template VOID
AL_TreeBinSeq::PreOrderTraversal(const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode, AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const
{
if (NULL == pCurTreeNode) {
return;
}
//Do Something with root
listOrder.InsertEnd(pCurTreeNode->GetData());
if(NULL != pCurTreeNode->GetChildLeft()) {
PreOrderTraversal(pCurTreeNode->GetChildLeft(), listOrder);
}
if(NULL != pCurTreeNode->GetChildRight()) {
PreOrderTraversal(pCurTreeNode->GetChildRight(), listOrder);
}
} 2.中序遍历(仅二叉树)
指先访问左(右)孩子,然后访问根,最后访问右(左)孩子的遍历方式
非递归实现
利用栈实现,先取根节点,然后依次遍历左节点,将左节点压入栈,向左走到尽头。然后从栈中取出左节点,处理节点。然后处理其右子树。
/**
* InOrderTraversal
*
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return BOOL
* @note In-order traversal
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::InOrderTraversal(AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const
{
if (NULL == m_pRootNode) {
return FALSE;
}
listOrder.Clear();
//Recursion Traversal
InOrderTraversal(m_pRootNode, listOrder);
return TRUE;
//Not Recursion Traversal
AL_StackSeq*> cStack;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pTreeNode = m_pRootNode;
while (TRUE != cStack.IsEmpty() || NULL != pTreeNode) {
while (NULL != pTreeNode) {
cStack.Push(pTreeNode);
pTreeNode = pTreeNode->GetChildLeft();
}
if (TRUE == cStack.Pop(pTreeNode)) {
if (NULL != pTreeNode) {
listOrder.InsertEnd(pTreeNode->GetData());
if (NULL != pTreeNode->GetChildRight()){
//child right exist, push the node, and loop it's left child to push
pTreeNode = pTreeNode->GetChildRight();
}
else {
//to pop the node in the stack
pTreeNode = NULL;
}
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
递归实现
/**
* InOrderTraversal
*
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return VOID
* @note In-order traversal
* @attention Recursion Traversal
*/
template VOID
AL_TreeBinSeq::InOrderTraversal(const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode, AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const
{
if (NULL == pCurTreeNode) {
return;
}
if(NULL != pCurTreeNode->GetChildLeft()) {
InOrderTraversal(pCurTreeNode->GetChildLeft(), listOrder);
}
//Do Something with root
listOrder.InsertEnd(pCurTreeNode->GetData());
if(NULL != pCurTreeNode->GetChildRight()) {
InOrderTraversal(pCurTreeNode->GetChildRight(), listOrder);
}
}
3.后序遍历(仅二叉树)
指先访问孩子,然后访问根的遍历方式
非递归实现
利用栈实现,先取根节点,然后依次遍历左节点,将左节点压入栈,向左走到尽头。然后从栈中取出左节点,处理节点。处理其右节点,还需要记录已经使用过的节点,比较麻烦和复杂。大致思路如下:
- 1.找到最左边的子节点
- 2.如果最左边的子节点有右节点,处理右节点(类似1)
- 3.从栈里弹出节点处理
- 3.当碰到左右节点都存在的节点时,需要进行记录了回归节点了。然后以当前节点的右子树进行处理
- 4.碰到回归节点时,把当前的最后一个元素消除(因为后面还会回归到这个点的)。
/**
* PostOrderTraversal
*
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return BOOL
* @note Post-order traversal
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::PostOrderTraversal(AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const
{
if (NULL == m_pRootNode) {
return FALSE;
}
listOrder.Clear();
//Recursion Traversal
PostOrderTraversal(m_pRootNode, listOrder);
return TRUE;
//Not Recursion Traversal
AL_StackSeq*> cStack;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pTreeNode = m_pRootNode;
AL_StackSeq*> cStackReturn;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pTreeNodeReturn = NULL;
while (TRUE != cStack.IsEmpty() || NULL != pTreeNode) {
while (NULL != pTreeNode) {
cStack.Push(pTreeNode);
if (NULL != pTreeNode->GetChildLeft()) {
pTreeNode = pTreeNode->GetChildLeft();
}
else {
//has not left child, get the right child
pTreeNode = pTreeNode->GetChildRight();
}
}
if (TRUE == cStack.Pop(pTreeNode)) {
if (NULL != pTreeNode) {
listOrder.InsertEnd(pTreeNode->GetData());
if (NULL != pTreeNode->GetChildLeft() && NULL != pTreeNode->GetChildRight()){
//child right exist
cStackReturn.Top(pTreeNodeReturn);
if (pTreeNodeReturn != pTreeNode) {
listOrder.RemoveAt(listOrder.Length()-1);
cStack.Push(pTreeNode);
cStackReturn.Push(pTreeNode);
pTreeNode = pTreeNode->GetChildRight();
}
else {
//to pop the node in the stack
cStackReturn.Pop(pTreeNodeReturn);
pTreeNode = NULL;
}
}
else {
//to pop the node in the stack
pTreeNode = NULL;
}
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
} 递归实现
/**
* PostOrderTraversal
*
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return VOID
* @note Post-order traversal
* @attention Recursion Traversal
*/
template VOID
AL_TreeBinSeq::PostOrderTraversal(const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode, AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const
{
if (NULL == pCurTreeNode) {
return;
}
if(NULL != pCurTreeNode->GetChildLeft()) {
PostOrderTraversal(pCurTreeNode->GetChildLeft(), listOrder);
}
if(NULL != pCurTreeNode->GetChildRight()) {
PostOrderTraversal(pCurTreeNode->GetChildRight(), listOrder);
}
//Do Something with root
listOrder.InsertEnd(pCurTreeNode->GetData());
} 4.层次遍历
一层一层的访问,所以一般用广度优先遍历。
非递归实现
利用链表或者队列均可实现,先取根节点压入链表或者队列,依次从左往右体访问子节点,压入链表或者队列。直至处理完所有节点。
/**
* LevelOrderTraversal
*
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return BOOL
* @note Level-order traversal
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::LevelOrderTraversal(AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const
{
if (TRUE == IsEmpty()) {
return FALSE;
}
if (NULL == m_pRootNode) {
return FALSE;
}
listOrder.Clear();
/*
AL_ListSeq*> listNodeOrder;
listNodeOrder.InsertEnd(m_pRootNode);
//loop the all node
DWORD dwNodeOrderLoop = 0x00;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pNodeOrderLoop = NULL;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pNodeOrderChild = NULL;
while (TRUE == listNodeOrder.Get(pNodeOrderLoop, dwNodeOrderLoop)) {
dwNodeOrderLoop++;
if (NULL != pNodeOrderLoop) {
listOrder.InsertEnd(pNodeOrderLoop->GetData());
pNodeOrderChild = pNodeOrderLoop->GetChildLeft();
if (NULL != pNodeOrderChild) {
queueOrder.Push(pNodeOrderChild);
}
pNodeOrderChild = pNodeOrderLoop->GetChildRight();
if (NULL != pNodeOrderChild) {
queueOrder.Push(pNodeOrderChild);
}
}
else {
//error
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
*/
AL_QueueSeq*> queueOrder;
queueOrder.Push(m_pRootNode);
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pNodeOrderLoop = NULL;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pNodeOrderChild = NULL;
while (FALSE == queueOrder.IsEmpty()) {
if (TRUE == queueOrder.Pop(pNodeOrderLoop)) {
if (NULL != pNodeOrderLoop) {
listOrder.InsertEnd(pNodeOrderLoop->GetData());
pNodeOrderChild = pNodeOrderLoop->GetChildLeft();
if (NULL != pNodeOrderChild) {
queueOrder.Push(pNodeOrderChild);
}
pNodeOrderChild = pNodeOrderLoop->GetChildRight();
if (NULL != pNodeOrderChild) {
queueOrder.Push(pNodeOrderChild);
}
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
} 递归实现 (无)
======================================================================================================
树(tree)
树(tree)是包含n(n>0)个结点的有穷集合,其中:
- 每个元素称为结点(node);
- 有一个特定的结点被称为根结点或树根(root)。
- 除根结点之外的其余数据元素被分为m(m≥0)个互不相交的集合T1,T2,……Tm-1,其中每一个集合Ti(1<=i<=m)本身也是一棵树,被称作原树的子树(subtree)。
树也可以这样定义:树是由根结点和若干颗子树构成的。树是由一个集合以及在该集合上定义的一种关系构成的。集合中的元素称为树的结点,所定义的关系称为父子关系。父子关系在树的结点之间建立了一个层次结构。在这种层次结构中有一个结点具有特殊的地位,这个结点称为该树的根结点,或称为树根。
我们可以形式地给出树的递归定义如下:
- 单个结点是一棵树,树根就是该结点本身。
- 设T1,T2,..,Tk是树,它们的根结点分别为n1,n2,..,nk。用一个新结点n作为n1,n2,..,nk的父亲,则得到一棵新树,结点n就是新树的根。我们称n1,n2,..,nk为一组兄弟结点,它们都是结点n的子结点。我们还称n1,n2,..,nk为结点n的子树。
- 空集合也是树,称为空树。空树中没有结点。
![]()
树的四种遍历
1.先序遍历 (仅二叉树)
指先访问根,然后访问孩子的遍历方式
2.中序遍历(仅二叉树)
指先访问左(右)孩子,然后访问根,最后访问右(左)孩子的遍历方式
3.后序遍历(仅二叉树)
指先访问孩子,然后访问根的遍历方式
4.层次遍历
一层一层的访问,所以一般用广度优先遍历。
======================================================================================================
树结点 顺序存储结构(tree node sequence)
结点:
包括一个数据元素及若干个指向其它子树的分支;例如,A,B,C,D等。在数据结构的图形表示中,对于数据集合中的每一个数据元素用中间标有元素值的方框表示,一般称之为数据结点,简称结点。
在C语言中,链表中每一个元素称为“结点”,每个结点都应包括两个部分:一为用户需要用的实际数据;二为下一个结点的地址,即指针域和数据域。
数据结构中的每一个数据结点对应于一个储存单元,这种储存单元称为储存结点,也可简称结点
树结点(树节点):
![]()
树节点相关术语:
- 节点的度:一个节点含有的子树的个数称为该节点的度;
- 叶节点或终端节点:度为0的节点称为叶节点;
- 非终端节点或分支节点:度不为0的节点;
- 双亲节点或父节点:若一个结点含有子节点,则这个节点称为其子节点的父节点;
- 孩子节点或子节点:一个节点含有的子树的根节点称为该节点的子节点;
- 兄弟节点:具有相同父节点的节点互称为兄弟节点;
- 节点的层次:从根开始定义起,根为第1层,根的子结点为第2层,以此类推;
- 堂兄弟节点:双亲在同一层的节点互为堂兄弟;
- 节点的祖先:从根到该节点所经分支上的所有节点;
- 子孙:以某节点为根的子树中任一节点都称为该节点的子孙。
根据树结点的相关定义,采用“双亲孩子表示法”。其属性如下:
DWORD m_dwLevel; //Node levels: starting from the root to start defining the root of the first layer, the root node is a sub-layer 2, and so on;
T m_data; //the friend class can use it directly
AL_TreeNodeSeq* m_pParent; //Parent position
AL_ListSeq*> m_listChild; //All Child tree node 树的几种表示法
在实际中,可使用多种形式的存储结构来表示树,既可以采用顺序存储结构,也可以采用链式存储结构,但无论采用何种存储方式,都要求存储结构不但能存储各结点本身的数据信息,还要能唯一地反映树中各结点之间的逻辑关系。
1.双亲表示法
由于树中的每个结点都有唯一的一个双亲结点,所以可用一组连续的存储空间(一维数组)存储树中的各个结点,数组中的一个元素表示树中的一个结点,每个结点含两个域,数据域存放结点本身信息,双亲域指示本结点的双亲结点在数组中位置。
![]()
2.孩子表示法
1.多重链表:每个结点有多个指针域,分别指向其子树的根
1)结点同构:结点的指针个数相等,为树的度k,这样n个结点度为k的树必有n(k-1)+1个空链域.
![]()
2)结点不同构:结点指针个数不等,为该结点的度d
![]()
2.孩子链表:每个结点的孩子结点用单链表存储,再用含n个元素的结构数组指向每个孩子链表
![]()
3.双亲孩子表示法
1.双亲表示法,PARENT(T,x)可以在常量时间内完成,但是求结点的孩子时需要遍历整个结构。
2.孩子链表表示法,适于那些涉及孩子的操作,却不适于PARENT(T,x)操作。
3.将双亲表示法和孩子链表表示法合在一起,可以发挥以上两种存储结构的优势,称为带双亲的孩子链表表示法
![]()
4.双亲孩子兄弟表示法 (二叉树专用)
又称为二叉树表示法,以二叉链表作为树的存储结构。
![]()
![]()
顺序存储结构
在计算机中用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表的各个数据元素,称作线性表的顺序存储结构.
顺序存储结构是存储结构类型中的一种,该结构是把逻辑上相邻的节点存储在物理位置上相邻的存储单元中,结点之间的逻辑关系由存储单元的邻接关系来体现。由此得到的存储结构为顺序存储结构,通常顺序存储结构是借助于计算机程序设计语言(例如c/c++)的数组来描述的。
顺序存储结构的主要优点是节省存储空间,因为分配给数据的存储单元全用存放结点的数据(不考虑c/c++语言中数组需指定大小的情况),结点之间的逻辑关系没有占用额外的存储空间。采用这种方法时,可实现对结点的随机存取,即每一个结点对应一个序号,由该序号可以直接计算出来结点的存储地址。但顺序存储方法的主要缺点是不便于修改,对结点的插入、删除运算时,可能要移动一系列的结点。
优点:
随机存取表中元素。缺点:插入和删除操作需要移动元素。
本代码默认list可以容纳的item数目为100个,用户可以自行设置item数目。当list饱和时,由于Tree是非线性结构,动态扩展内存相当麻烦。因此示例中的Demo及代码将不会动态扩展内存。
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
以后的笔记潇汀会尽量详细讲解一些相关知识的,希望大家继续关注我的博客。
本节笔记到这里就结束了。
潇汀一有时间就会把自己的学习心得,觉得比较好的知识点写出来和大家一起分享。
编程开发的路很长很长,非常希望能和大家一起交流,共同学习,共同进步。
如果文章中有什么疏漏的地方,也请大家指正。也希望大家可以多留言来和我探讨编程相关的问题。
最后,谢谢你们一直的支持~~~
C++完整个代码示例(代码在VS2005下测试可运行)

AL_TreeNodeBinSeq.h
/**
@(#)$Id: AL_TreeNodeBinSeq.h 56 2013-09-24 08:47:13Z xiaoting $
@brief Each of the data structure corresponds to a data node storage unit, this storage unit is called storage node, the node can
also be referred to.
The related concepts of tree node
1.degree degree node: A node of the subtree containing the number is called the node degree;
2.leaf leaf nodes or terminal nodes: degree 0 are called leaf nodes;
3.branch non-terminal node or branch node: node degree is not 0;
4.parent parent node or the parent node: If a node contains a child node, this node is called its child node's parent;
5.child child node or child node: A node subtree containing the root node is called the node's children;
6.slibing sibling nodes: nodes with the same parent node is called mutual sibling;
7.ancestor ancestor node: from the root to the node through all the nodes on the branch;
8.descendant descendant nodes: a node in the subtree rooted at any node is called the node's descendants.
////////////////////////////////Binary Tree//////////////////////////////////////////
In computer science, a binary tree is that each node has at most two sub-trees ordered tree. Usually the root of the subtree is
called "left subtree" (left subtree) and the "right subtree" (right subtree). Binary tree is often used as a binary search tree
and binary heap or a binary sort tree. Binary tree each node has at most two sub-tree (does not exist a degree greater than two
nodes), left and right sub-tree binary tree of the points, the order can not be reversed. Binary i-th layer of at most 2 power
nodes i -1; binary tree of depth k at most 2 ^ (k) -1 nodes; for any binary tree T, if it is the terminal nodes (i.e. leaf nodes)
is, the nodes of degree 2 is, then = + 1.
////////////////////////////////Sequential storage structure//////////////////////////////////////////
Using a set of addresses in the computer storage unit sequentially stores continuous linear form of individual data elements, called
the linear order of the table storage structure.
Sequential storage structure is a type of a storage structure, the structure is the logically adjacent nodes stored in the physical
location of the adjacent memory cells, the logical relationship between nodes from the storage unit to reflect the adjacency.
Storage structure thus obtained is stored in order structure, usually by means of sequential storage structure computer programming
language (e.g., c / c) of the array to describe.
The main advantage of the storage structure in order to save storage space, because the allocation to the data storage unit storing
all nodes with data (without regard to c / c language in the array size required for the case), the logical relationship between
the nodes does not take additional storage space. In this method, the node can be realized on a random access, that is, each node
corresponds to a number, the number can be calculated directly from the node out of the memory address. However, the main
disadvantage of sequential storage method is easy to modify the node insert, delete operations, may have to move a series of nodes.
Benefits:
Random Access table elements.
Disadvantages:
insert and delete operations need to move elements.
@Author $Author: xiaoting $
@Date $Date: 2013-09-24 16:47:13 +0800 (周二, 24 九月 2013) $
@Revision $Revision: 56 $
@URL $URL: https://svn.code.sf.net/p/xiaoting/game/trunk/MyProject/AL_DataStructure/groupinc/AL_TreeNodeBinSeq.h $
@Header $Header: https://svn.code.sf.net/p/xiaoting/game/trunk/MyProject/AL_DataStructure/groupinc/AL_TreeNodeBinSeq.h 56 2013-09-24 08:47:13Z xiaoting $
*/
#ifndef CXX_AL_TREENODEBINSEQ_H
#define CXX_AL_TREENODEBINSEQ_H
#ifndef CXX_AL_LISTSEQ_H
#include "AL_ListSeq.h"
#endif
#ifndef CXX_AL_QUEUESEQ_H
#include "AL_QueueSeq.h"
#endif
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// AL_TreeNodeBinSeq
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
template class AL_TreeBinSeq;
template
class AL_TreeNodeBinSeq
{
public:
/**
* Destruction
*
* @param
* @return
* @note
* @attention
*/
~AL_TreeNodeBinSeq();
/**
* GetLevel
*
* @param
* @return DWORD
* @note Node levels: starting from the root to start defining the root of the first layer, the root node is a sub-layer 2, and so on;
* @attention
*/
DWORD GetLevel() const;
/**
* SetLevel
*
* @param DWORD dwLevel
* @return
* @note Node levels: starting from the root to start defining the root of the first layer, the root node is a sub-layer 2, and so on;
* @attention
*/
VOID SetLevel(DWORD dwLevel);
/**
* GetData
*
* @param
* @return T
* @note
* @attention
*/
T GetData() const;
/**
* SetData
*
* @param const T& tTemplate
* @return
* @note
* @attention
*/
VOID SetData(const T& tTemplate);
/**
* GetParent
*
* @param
* @return AL_TreeNodeBinSeq*
* @note parent node pointer, not to manager memory
* @attention
*/
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* GetParent() const;
/**
* SetParent
*
* @param DWORD dwIndex
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pParent
* @return BOOL
* @note parent node pointer, not to manager memory
* @attention as the child to set the parent at the index (from the left of parent's child ) [0x00: left child, 0x01: right child]
*/
BOOL SetParent(DWORD dwIndex, AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pParent);
/**
* SetParentLeft
*
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pParent
* @return BOOL
* @note parent node pointer, not to manager memory
* @attention as the child to set the parent at the left (from the left of parent's child )
*/
BOOL SetParentLeft(AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pParent);
/**
* SetParentRight
*
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pParent
* @return BOOL
* @note parent node pointer, not to manager memory
* @attention as the child to set the parent at the right (from the right of parent's child )
*/
BOOL SetParentRight(AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pParent);
/**
* Insert
*
* @param DWORD dwIndex
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pInsertChild
* @return BOOL
* @note inset the const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* into the child notes at the position [0x00: left child, 0x01: right child]
* @attention
*/
BOOL Insert(DWORD dwIndex, AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pInsertChild);
/**
* InsertLeft
*
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pInsertChild
* @return BOOL
* @note inset the const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* into the child notes at the left
* @attention
*/
BOOL InsertLeft(AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pInsertChild);
/**
* InsertRight
*
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pInsertChild
* @return BOOL
* @note inset the const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* into the child notes at the right
* @attention
*/
BOOL InsertRight(AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pInsertChild);
/**
* Remove
*
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pRemoveChild
* @return BOOL
* @note remove the notes in the child
* @attention
*/
BOOL Remove(AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pRemoveChild);
/**
* Remove
*
* @param DWORD dwIndex
* @return BOOL
* @note remove the child notes at the position [0x00: left child, 0x01: right child]
* @attention
*/
BOOL Remove(DWORD dwIndex);
/**
* RemoveLeft
*
* @param
* @return BOOL
* @note remove the child notes at the left
* @attention
*/
BOOL RemoveLeft();
/**
* RemoveRight
*
* @param
* @return BOOL
* @note remove the child notes at the right
* @attention
*/
BOOL RemoveRight();
/**
* GetChildLeft
*
* @param
* @return AL_TreeNodeBinSeq*
* @note
* @attention
*/
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* GetChildLeft() const;
/**
* GetChildRight
*
* @param
* @return AL_TreeNodeBinSeq*
* @note
* @attention
*/
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* GetChildRight() const;
/**
* GetDegree
*
* @param
* @return DWORD
* @note degree node: A node of the subtree containing the number is called the node degree;
* @attention
*/
DWORD GetDegree() const;
/**
* IsLeaf
*
* @param
* @return BOOL
* @note leaf nodes or terminal nodes: degree 0 are called leaf nodes;
* @attention
*/
BOOL IsLeaf() const;
/**
* IsBranch
*
* @param
* @return BOOL
* @note non-terminal node or branch node: node degree is not 0;
* @attention
*/
BOOL IsBranch() const;
/**
* IsParent
*
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pChild
* @return BOOL
* @note parent node or the parent node: If a node contains a child node, this node is called its child
* @attention
*/
BOOL IsParent(const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pChild) const;
/**
* GetSibling
*
* @param AL_ListSeq*>& listSibling
* @return BOOL
* @note sibling nodes: nodes with the same parent node is called mutual sibling;
* @attention
*/
BOOL GetSibling(AL_ListSeq*>& listSibling) const;
/**
* GetAncestor
*
* @param AL_ListSeq*>& listAncestor
* @return BOOL
* @note ancestor node: from the root to the node through all the nodes on the branch;
* @attention
*/
BOOL GetAncestor(AL_ListSeq*>& listAncestor) const;
/**
* GetDescendant
*
* @param AL_ListSeq*>& listDescendant
* @return BOOL
* @note ancestor node: from the root to the node through all the nodes on the branch;
* @attention
*/
BOOL GetDescendant(AL_ListSeq*>& listDescendant) const;
protected:
public:
friend class AL_TreeBinSeq;
/**
* Construction
*
* @param
* @return
* @note private the Construction, avoid the others use it
* @attention
*/
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq();
/**
* Construction
*
* @param const T& tTemplate
* @return
* @note
* @attention private the Construction, avoid the others use it
*/
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq(const T& tTemplate);
/**
*Copy Construct
*
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq& cAL_TreeNodeBinSeq
* @return
*/
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq(const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq& cAL_TreeNodeBinSeq);
/**
*Assignment
*
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq& cAL_TreeNodeBinSeq
* @return AL_TreeNodeBinSeq&
*/
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq& operator = (const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq& cAL_TreeNodeBinSeq);
public:
protected:
private:
DWORD m_dwLevel; //Node levels: starting from the root to start defining the root of the first layer, the root node is a sub-layer 2, and so on;
T m_data; //the friend class can use it directly
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* m_pParent; //Parent position
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* m_pChildLeft; //Child tree node left
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* m_pChildRight; //Child tree node right
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// AL_TreeNodeBinSeq
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Construction
*
* @param
* @return
* @note private the Construction, avoid the others use it
* @attention
*/
template
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::AL_TreeNodeBinSeq():
m_dwLevel(0x00),
m_pParent(NULL),
m_pChildLeft(NULL),
m_pChildRight(NULL)
{
}
/**
* Construction
*
* @param const T& tTemplate
* @return
* @note
* @attention private the Construction, avoid the others use it
*/
template
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::AL_TreeNodeBinSeq(const T& tTemplate):
m_dwLevel(0x00),
m_data(tTemplate),
m_pParent(NULL),
m_pChildLeft(NULL),
m_pChildRight(NULL)
{
}
/**
* Destruction
*
* @param
* @return
* @note
* @attention
*/
template
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::~AL_TreeNodeBinSeq()
{
//it doesn't matter to clear the pointer or not.
m_dwLevel = 0x00;
m_pParent = NULL;
m_pChildLeft = NULL;
m_pChildRight = NULL;
}
/**
* GetLevel
*
* @param
* @return DWORD
* @note Node levels: starting from the root to start defining the root of the first layer, the root node is a sub-layer 2, and so on;
* @attention
*/
template DWORD
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::GetLevel() const
{
return m_dwLevel;
}
/**
* SetLevel
*
* @param DWORD dwLevel
* @return
* @note Node levels: starting from the root to start defining the root of the first layer, the root node is a sub-layer 2, and so on;
* @attention
*/
template VOID
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::SetLevel(DWORD dwLevel)
{
m_dwLevel = dwLevel;
}
/**
* GetData
*
* @param
* @return T
* @note
* @attention
*/
template T
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::GetData() const
{
return m_data;
}
/**
* SetData
*
* @param const T& tTemplate
* @return
* @note
* @attention
*/
template VOID
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::SetData(const T& tTemplate)
{
m_data = tTemplate;
}
/**
* GetParent
*
* @param
* @return AL_TreeNodeBinSeq*
* @note parent node pointer, not to manager memory
* @attention
*/
template AL_TreeNodeBinSeq*
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::GetParent() const
{
return m_pParent;
}
/**
* SetParent
*
* @param DWORD dwIndex
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pParent
* @return BOOL
* @note parent node pointer, not to manager memory
* @attention as the child to set the parent at the index (from the left of parent's child ) [0x00: left child, 0x01: right child]
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::SetParent(DWORD dwIndex, AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pParent)
{
if (NULL == pParent) {
return FALSE;
}
BOOL bSetParent = FALSE;
bSetParent = pParent->Insert(dwIndex, this);
if (TRUE == bSetParent) {
//current node insert to the parent successfully
if (NULL != m_pParent) {
//current node has parent
m_pParent->Remove(this);
}
m_pParent = pParent;
}
return bSetParent;
}
/**
* SetParentLeft
*
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pParent
* @return
* @note parent node pointer, not to manager memory
* @attention as the child to set the parent at the left (from the left of parent's child )
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::SetParentLeft(AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pParent)
{
return SetParent(0x00, pParent);
}
/**
* SetParentRight
*
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pParent
* @return
* @note parent node pointer, not to manager memory
* @attention as the child to set the parent at the right (from the right of parent's child )
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::SetParentRight(AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pParent)
{
return SetParent(0x01, pParent);
}
/**
* Insert
*
* @param DWORD dwIndex
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pInsertChild
* @return BOOL
* @note inset the const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* into the child notes at the position [0x00: left child, 0x01: right child]
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::Insert(DWORD dwIndex, AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pInsertChild)
{
if (0x01 < dwIndex || NULL == pInsertChild) {
return FALSE;
}
BOOL bInsert = FALSE;
if (0x00 == dwIndex && NULL == m_pChildLeft) {
//left and the child left not exist
m_pChildLeft = pInsertChild;
bInsert = TRUE;
}
else if (0x01 == dwIndex && NULL == m_pChildRight) {
//right and the child right not exist
m_pChildRight = pInsertChild;
bInsert = TRUE;
}
else {
//no case
bInsert = FALSE;
}
if (TRUE == bInsert) {
if (GetLevel()+1 != pInsertChild->GetLevel()) {
//deal with the child level
INT iLevelDiff = pInsertChild->GetLevel() - GetLevel();
AL_ListSeq*> listDescendant;
if (FALSE == GetDescendant(listDescendant)) {
return FALSE;
}
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pDescendant = NULL;
for (DWORD dwCnt=0; dwCntSetLevel(pDescendant->GetLevel()-iLevelDiff+1);
}
else {
//error
return FALSE;
}
}
else {
//error
return FALSE;
}
}
}
//child node insert to the current successfully
pInsertChild->m_pParent = this;
}
return bInsert;
}
/**
* InsertLeft
*
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pInsertChild
* @return BOOL
* @note inset the const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* into the child notes at the left
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::InsertLeft(AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pInsertChild)
{
return Insert(0x00, pInsertChild);
}
/**
* InsertRight
*
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pInsertChild
* @return BOOL
* @note inset the const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* into the child notes at the right
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::InsertRight(AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pInsertChild)
{
return Insert(0x01, pInsertChild);
}
/**
* Remove
*
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pRemoveChild
* @return BOOL
* @note remove the notes in the child
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::Remove(AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pRemoveChild)
{
BOOL bRemove = FALSE;
if (m_pChildLeft == pRemoveChild) {
m_pChildLeft = NULL;
bRemove = TRUE;
}
else if (m_pChildRight == pRemoveChild) {
m_pChildRight = NULL;
bRemove = TRUE;
}
else {
bRemove = FALSE;
}
return bRemove;
}
/**
* Remove
*
* @param DWORD dwIndex
* @return BOOL
* @note remove the child notes at the position [0x00: left child, 0x01: right child]
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::Remove(DWORD dwIndex)
{
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pRemoveChild = NULL;
if (0x00 == dwIndex) {
pRemoveChild = m_pChildLeft;
}
else if (0x01 == dwIndex) {
pRemoveChild = m_pChildRight;
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
return Remove(pRemoveChild);
}
/**
* RemoveLeft
*
* @param
* @return BOOL
* @note remove the child notes at the left
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::RemoveLeft()
{
return Remove(m_pChildLeft);
}
/**
* RemoveRight
*
* @param
* @return BOOL
* @note remove the child notes at the right
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::RemoveRight()
{
return Remove(m_pChildRight);
}
/**
* GetChildLeft
*
* @param
* @return AL_TreeNodeBinSeq*
* @note
* @attention
*/
template AL_TreeNodeBinSeq*
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::GetChildLeft() const
{
return m_pChildLeft;
}
/**
* GetChildRight
*
* @param
* @return AL_TreeNodeBinSeq*
* @note
* @attention
*/
template AL_TreeNodeBinSeq*
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::GetChildRight() const
{
return m_pChildRight;
}
/**
* GetDegree
*
* @param
* @return DWORD
* @note degree node: A node of the subtree containing the number is called the node degree;
* @attention
*/
template DWORD
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::GetDegree() const
{
DWORD dwDegree = 0x00;
if (NULL != m_pChildLeft) {
dwDegree++;
}
if (NULL != m_pChildRight) {
dwDegree++;
}
return dwDegree;
}
/**
* IsLeaf
*
* @param
* @return BOOL
* @note leaf nodes or terminal nodes: degree 0 are called leaf nodes;
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::IsLeaf() const
{
return (0x00 == GetDegree()) ? TRUE:FALSE;
}
/**
* IsBranch
*
* @param
* @return BOOL
* @note non-terminal node or branch node: node degree is not 0;
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::IsBranch() const
{
return (0x00 != GetDegree()) ? TRUE:FALSE;
}
/**
* IsParent
*
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pChild
* @return BOOL
* @note parent node or the parent node: If a node contains a child node, this node is called its child
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::IsParent(const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pChild) const
{
if (NULL == pChild) {
return FALSE;
}
// AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCompare = NULL;
// for (DWORD dwCnt=0; dwCntm_pParent) {
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
/**
* GetSibling
*
* @param AL_ListSeq*>& listSibling
* @return BOOL
* @note sibling nodes: nodes with the same parent node is called mutual sibling;
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::GetSibling(AL_ListSeq*>& listSibling) const
{
BOOL bSibling = FALSE;
if (NULL == m_pParent) {
//not parent node
return bSibling;
}
listSibling.Clear();
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pParentChild = GetChildLeft();
if (NULL != pParentChild) {
if (pParentChild != this) {
//not itself
listSibling.InsertEnd(pParentChild);
bSibling = TRUE;
}
}
pParentChild = GetChildRight();
if (NULL != pParentChild) {
if (pParentChild != this) {
//not itself
listSibling.InsertEnd(pParentChild);
bSibling = TRUE;
}
}
return bSibling;
}
/**
* GetAncestor
*
* @param AL_ListSeq*>& listAncestor
* @return BOOL
* @note ancestor node: from the root to the node through all the nodes on the branch;
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::GetAncestor(AL_ListSeq*>& listAncestor) const
{
if (NULL == m_pParent) {
//not parent node
return FALSE;
}
listAncestor.Clear();
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pParent = m_pParent;
while (NULL != pParent) {
listAncestor.InsertEnd(pParent);
pParent = pParent->m_pParent;
}
return TRUE;
}
/**
* GetDescendant
*
* @param AL_ListSeq*>& listDescendant
* @return BOOL
* @note ancestor node: from the root to the node through all the nodes on the branch;
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::GetDescendant(AL_ListSeq*>& listDescendant) const
{
if (TRUE == IsLeaf()) {
//child node
return FALSE;
}
listDescendant.Clear();
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pDescendant = GetChildLeft();
if (NULL != pDescendant) {
listDescendant.InsertEnd(pDescendant);
}
pDescendant = GetChildRight();
if (NULL != pDescendant) {
listDescendant.InsertEnd(pDescendant);
}
//loop the all node in listDescendant
DWORD dwDescendantLoop = 0x00;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pDescendantLoop = NULL;
while (TRUE == listDescendant.Get(pDescendant, dwDescendantLoop)) {
dwDescendantLoop++;
if (NULL != pDescendant) {
pDescendantLoop = pDescendant->GetChildLeft();
if (NULL != pDescendantLoop) {
listDescendant.InsertEnd(pDescendantLoop);
}
pDescendantLoop = pDescendant->GetChildRight();
if (NULL != pDescendantLoop) {
listDescendant.InsertEnd(pDescendantLoop);
}
}
else {
//error
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
/**
*Assignment
*
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq& cAL_TreeNodeBinSeq
* @return AL_TreeNodeBinSeq&
*/
template AL_TreeNodeBinSeq&
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq::operator = (const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq& cAL_TreeNodeBinSeq)
{
m_dwLevel = cAL_TreeNodeBinSeq.m_dwLevel;
m_data = cAL_TreeNodeBinSeq.m_data;
m_pParent = cAL_TreeNodeBinSeq.m_pParent;
m_pChildLeft = cAL_TreeNodeBinSeq.m_pChildLeft;
m_pChildRight = cAL_TreeNodeBinSeq.m_pChildRight;
return *this;
}
#endif // CXX_AL_TREENODEBINSEQ_H
/* EOF */
AL_TreeBinSeq.h
/**
@(#)$Id: AL_TreeBinSeq.h 55 2013-09-24 06:58:07Z xiaoting $
@brief Tree (tree) that contains n (n> 0) nodes of a finite set, where:
(1) Each element is called node (node);
(2) there is a particular node is called the root node or root (root).
(3) In addition to the remaining data elements other than the root node is divided into m (m ≥ 0) disjoint set of T1, T2, ......
Tm-1, wherein each set of Ti (1 <= i <= m ) itself is a tree, the original tree is called a subtree (subtree).
Trees can also be defined as: the tree is a root node and several sub-tree consisting of stars. And a tree is a set defined on the
set consisting of a relationship. Elements in the collection known as a tree of nodes, the defined relationship is called
parent-child relationship. Parent-child relationship between the nodes of the tree establishes a hierarchy. In this there is a
hierarchy node has a special status, this node is called the root of the tree, otherwise known as root.
We can give form to the tree recursively defined as follows:
Single node is a tree, the roots is the node itself.
Let T1, T2, .., Tk is a tree, the root node are respectively n1, n2, .., nk. With a new node n as n1, n2, .., nk's father, then
get a new tree node n is the new root of the tree. We call n1, n2, .., nk is a group of siblings, they are sub-node n junction.
We also said that n1, n2, .., nk is the sub-tree node n.
Empty tree is also called the empty tree. Air no node in the tree.
The related concepts of tree
1. Degree of tree: a tree, the maximum degree of the node of the tree is called degree;
2. Height or depth of the tree: the maximum level of nodes in the tree;
3. Forests: the m (m> = 0) disjoint trees set of trees called forest;
The related concepts of tree node
1.degree degree node: A node of the subtree containing the number is called the node degree;
2.leaf leaf nodes or terminal nodes: degree 0 are called leaf nodes;
3.branch non-terminal node or branch node: node degree is not 0;
4.parent parent node or the parent node: If a node contains a child node, this node is called its child node's parent;
5.child child node or child node: A node subtree containing the root node is called the node's children;
6.slibing sibling nodes: nodes with the same parent node is called mutual sibling;
7.ancestor ancestor node: from the root to the node through all the nodes on the branch;
8.descendant descendant nodes: a node in the subtree rooted at any node is called the node's descendants.
////////////////////////////////Binary Tree//////////////////////////////////////////
In computer science, a binary tree is that each node has at most two sub-trees ordered tree. Usually the root of the subtree is
called "left subtree" (left subtree) and the "right subtree" (right subtree). Binary tree is often used as a binary search tree
and binary heap or a binary sort tree. Binary tree each node has at most two sub-tree (does not exist a degree greater than two
nodes), left and right sub-tree binary tree of the points, the order can not be reversed. Binary i-th layer of at most 2 power
nodes i -1; binary tree of depth k at most 2 ^ (k) -1 nodes; for any binary tree T, if it is the terminal nodes (i.e. leaf nodes)
is, the nodes of degree 2 is, then = + 1.
////////////////////////////////Complete Binary Tree//////////////////////////////////////////
If set binary height of h, the h layer in addition, the other layers (1 ~ h-1) has reached the maximum number of nodes, right to
left, the h-layer node number of consecutive missing, this is a complete binary tree .
////////////////////////////////Full Binary Tree//////////////////////////////////////////
A binary tree of height h is 2 ^ h-1 element is called a full binary tree.
////////////////////////////////Sequential storage structure//////////////////////////////////////////
Using a set of addresses in the computer storage unit sequentially stores continuous linear form of individual data elements, called
the linear order of the table storage structure.
Sequential storage structure is a type of a storage structure, the structure is the logically adjacent nodes stored in the physical
location of the adjacent memory cells, the logical relationship between nodes from the storage unit to reflect the adjacency.
Storage structure thus obtained is stored in order structure, usually by means of sequential storage structure computer programming
language (e.g., c / c) of the array to describe.
The main advantage of the storage structure in order to save storage space, because the allocation to the data storage unit storing
all nodes with data (without regard to c / c language in the array size required for the case), the logical relationship between
the nodes does not take additional storage space. In this method, the node can be realized on a random access, that is, each node
corresponds to a number, the number can be calculated directly from the node out of the memory address. However, the main
disadvantage of sequential storage method is easy to modify the node insert, delete operations, may have to move a series of nodes.
Benefits:
Random Access table elements.
Disadvantages:
insert and delete operations need to move elements.
@Author $Author: xiaoting $
@Date $Date: 2013-09-24 14:58:07 +0800 (周二, 24 九月 2013) $
@Revision $Revision: 55 $
@URL $URL: https://svn.code.sf.net/p/xiaoting/game/trunk/MyProject/AL_DataStructure/groupinc/AL_TreeBinSeq.h $
@Header $Header: https://svn.code.sf.net/p/xiaoting/game/trunk/MyProject/AL_DataStructure/groupinc/AL_TreeBinSeq.h 55 2013-09-24 06:58:07Z xiaoting $
*/
#ifndef CXX_AL_TREEBINSEQ_H
#define CXX_AL_TREEBINSEQ_H
#ifndef CXX_AL_LISTSEQ_H
#include "AL_ListSeq.h"
#endif
#ifndef CXX_AL_QUEUESEQ_H
#include "AL_QueueSeq.h"
#endif
#ifndef CXX_AL_TREENODEBINSEQ_H
#include "AL_TreeNodeBinSeq.h"
#endif
#ifndef CXX_AL_STACKSEQ_H
#include "AL_StackSeq.h"
#endif
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// AL_TreeBinSeq
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
template
class AL_TreeBinSeq
{
public:
static const DWORD TREESEQ_DEFAULTSIZE = 100;
static const DWORD TREESEQ_MAXSIZE = 0xffffffff;
/**
* Construction
*
* @param DWORD dwSize (default value: TREESEQ_DEFAULTSIZE)
* @return
* @note
* @attention
*/
AL_TreeBinSeq(DWORD dwSize = TREESEQ_DEFAULTSIZE);
/**
* Destruction
*
* @param
* @return
* @note
* @attention
*/
~AL_TreeBinSeq();
/**
* IsEmpty
*
* @param VOID
* @return BOOL
* @note the tree has data?
* @attention
*/
BOOL IsEmpty() const;
/**
* GetRootNode
*
* @param
* @return const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq*
* @note Get the root data
* @attention
*/
const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* GetRootNode() const;
/**
* GetDegree
*
* @param
* @return DWORD
* @note Degree of tree: a tree, the maximum degree of the node of the tree is called degree;
* @attention
*/
DWORD GetDegree() const;
/**
* GetHeight
*
* @param
* @return DWORD
* @note Height or depth of the tree: the maximum level of nodes in the tree;
* @attention
*/
DWORD GetHeight() const;
/**
* GetNodesNum
*
* @param
* @return DWORD
* @note get the notes number of the tree
* @attention
*/
DWORD GetNodesNum() const;
/**
* Clear
*
* @param
* @return
* @note
* @attention
*/
VOID Clear();
/**
* PreOrderTraversal
*
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return BOOL
* @note Pre-order traversal
* @attention
*/
BOOL PreOrderTraversal(AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const;
/**
* InOrderTraversal
*
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return BOOL
* @note In-order traversal
* @attention
*/
BOOL InOrderTraversal(AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const;
/**
* PostOrderTraversal
*
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return BOOL
* @note Post-order traversal
* @attention
*/
BOOL PostOrderTraversal(AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const;
/**
* LevelOrderTraversal
*
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return BOOL
* @note Level-order traversal
* @attention
*/
BOOL LevelOrderTraversal(AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const;
/**
* GetSiblingAtNode
*
* @param AL_ListSeq& listSibling
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @return BOOL
* @note sibling nodes: nodes with the same parent node is called mutual sibling;
* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree
*/
BOOL GetSiblingAtNode(AL_ListSeq& listSibling, const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode) const;
/**
* GetAncestorAtNode
*
* @param AL_ListSeq& listAncestor
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @return BOOL
* @note ancestor node: from the root to the node through all the nodes on the branch;
* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree
*/
BOOL GetAncestorAtNode(AL_ListSeq& listAncestor, const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode) const;
/**
* GetDescendantAtNode
*
* @param AL_ListSeq& listDescendant
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @return BOOL
* @note ancestor node: from the root to the node through all the nodes on the branch;
* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree
*/
BOOL GetDescendantAtNode(AL_ListSeq& listDescendant, const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode) const;
/**
* InsertRoot
*
* @param const T& tTemplate
* @return BOOL
* @note
* @attention
*/
BOOL InsertRoot(const T& tTemplate);
/**
* InsertLeftAtNode
*
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @param const T& tTemplate
* @return BOOL
* @note insert the tTemplate as child tree node to the current tree node (pCurTreeNode) at the position (left)
* @attention if NULL == pCurTreeNode, it will be insert as root tree node, the current tree node must be in the tree
*/
BOOL InsertLeftAtNode(AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode, const T& tTemplate);
/**
* InsertRightAtNode
*
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @param const T& tTemplate
* @return BOOL
* @note insert the tTemplate as child tree node to the current tree node (pCurTreeNode) at the position (right)
* @attention if NULL == pCurTreeNode, it will be insert as root tree node, the current tree node must be in the tree
*/
BOOL InsertRightAtNode(AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode, const T& tTemplate);
/**
* RemoveNode
*
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @return BOOL
* @note
* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree
*/
BOOL RemoveNode(AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode);
/**
* GetChildNodeLeftAtNode
*
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @return const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq*
* @note get the current tree node (pCurTreeNode)'s child node at the position (left)
* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree
*/
const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* GetChildNodeLeftAtNode(const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode) const;
/**
* GetChildNodeRightAtNode
*
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @return const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq*
* @note get the current tree node (pCurTreeNode)'s child node at the position (right)
* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree
*/
const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* GetChildNodeRightAtNode(const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode) const;
/**
* IsCompleteTreeBin
*
* @param
* @return BOOL
* @note Is Complete Binary Tree
* @attention If set binary height of h, the h layer in addition, the other layers (1 ~ h-1) has reached the maximum number of
nodes, right to left, the h-layer node number of consecutive missing, this is a complete binary tree .
*/
BOOL IsCompleteTreeBin() const;
/**
* IsFullTreeBin
*
* @param
* @return BOOL
* @note Is Full Binary Tree
* @attention A binary tree of height h is 2 ^ h-1 element is called a full binary tree.
*/
BOOL IsFullTreeBin() const;
protected:
private:
/**
* InsertAtNode
*
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @param DWORD dwIndex
* @param const T& tTemplate
* @return BOOL
* @note insert the tTemplate as child tree node to the current tree node (pCurTreeNode) at the position (dwIndex)
* @attention if NULL == pCurTreeNode, it will be insert as root tree node, the current tree node must be in the tree
*/
BOOL InsertAtNode(AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode, DWORD dwIndex, const T& tTemplate);
/**
* PreOrderTraversal
*
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return VOID
* @note Pre-order traversal
* @attention Recursion Traversal
*/
VOID PreOrderTraversal(const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode, AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const;
/**
* InOrderTraversal
*
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return VOID
* @note In-order traversal
* @attention Recursion Traversal
*/
VOID InOrderTraversal(const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode, AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const;
/**
* PostOrderTraversal
*
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return VOID
* @note Post-order traversal
* @attention Recursion Traversal
*/
VOID PostOrderTraversal(const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode, AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const;
/**
* GetBuffer
*
* @param VOID
* @return VOID
* @note get the work buffer
* @attention when the buffer is not enough, it will become to double
*/
VOID GetBuffer();
/**
* IsFull
*
* @param VOID
* @return BOOL
* @note the buffer is full?
* @attention
*/
BOOL IsFull() const;
/**
*Copy Construct
*
* @param const AL_TreeBinSeq& cAL_TreeBinSeq
* @return
*/
AL_TreeBinSeq(const AL_TreeBinSeq& cAL_TreeBinSeq);
/**
*Assignment
*
* @param const AL_TreeBinSeq& cAL_TreeBinSeq
* @return AL_TreeBinSeq&
*/
AL_TreeBinSeq& operator = (const AL_TreeBinSeq& cAL_TreeBinSeq);
public:
protected:
private:
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* m_pTreeNode;
DWORD m_dwMaxSize;
DWORD m_dwUsed;
DWORD m_dwDegree;
DWORD m_dwHeight;
DWORD m_dwNumNodes;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* m_pRootNode;
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// AL_TreeBinSeq
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Construction
*
* @param DWORD dwSize (default value: TREESEQ_DEFAULTSIZE)
* @return
* @note
* @attention
*/
template
AL_TreeBinSeq::AL_TreeBinSeq(DWORD dwSize):
m_pTreeNode(NULL),
m_dwMaxSize(dwSize),
m_dwUsed(0x00),
m_dwDegree(0xffffffff),
m_dwHeight(0x00),
m_dwNumNodes(0x00),
m_pRootNode(NULL)
{
if (0x00 == m_dwMaxSize) {
//for memory deal
m_dwMaxSize = 1;
}
GetBuffer();
}
/**
* Destruction
*
* @param
* @return
* @note
* @attention
*/
template
AL_TreeBinSeq::~AL_TreeBinSeq()
{
if (NULL != m_pTreeNode) {
delete[] m_pTreeNode;
m_pTreeNode = NULL;
}
m_dwMaxSize = 0x00;
m_dwUsed = 0x00;
m_dwDegree = 0xffffffff;
m_dwHeight = 0x00;
m_dwNumNodes = 0x00;
m_pRootNode = NULL;
}
/**
* IsEmpty
*
* @param VOID
* @return BOOL
* @note the tree has data?
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::IsEmpty() const
{
return (0x00 == m_dwNumNodes) ? TRUE:FALSE;
}
/**
* GetRootNode
*
* @param
* @return const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq*
* @note Get the root data
* @attention
*/
template const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq*
AL_TreeBinSeq::GetRootNode() const
{
return m_pRootNode;
}
/**
* GetDegree
*
* @param
* @return DWORD
* @note Degree of tree: a tree, the maximum degree of the node of the tree is called degree;
* @attention
*/
template DWORD
AL_TreeBinSeq::GetDegree() const
{
return m_dwDegree;
}
/**
* GetHeight
*
* @param
* @return DWORD
* @note Height or depth of the tree: the maximum level of nodes in the tree;
* @attention
*/
template DWORD
AL_TreeBinSeq::GetHeight() const
{
return m_dwHeight;
}
/**
* GetNodesNum
*
* @param
* @return DWORD
* @note get the notes number of the tree
* @attention
*/
template DWORD
AL_TreeBinSeq::GetNodesNum() const
{
return m_dwNumNodes;
}
/**
* Clear
*
* @param
* @return
* @note
* @attention
*/
template VOID
AL_TreeBinSeq::Clear()
{
m_dwUsed = 0x00;
m_dwDegree = 0xffffffff;
m_dwHeight = 0x00;
m_dwNumNodes = 0x00;
m_pRootNode = NULL;
}
/**
* PreOrderTraversal
*
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return BOOL
* @note Pre-order traversal
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::PreOrderTraversal(AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const
{
if (NULL == m_pRootNode) {
return FALSE;
}
listOrder.Clear();
//Recursion Traversal
PreOrderTraversal(m_pRootNode, listOrder);
return TRUE;
//Not Recursion Traversal
AL_StackSeq*> cStack;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pTreeNode = m_pRootNode;
while (TRUE != cStack.IsEmpty() || NULL != pTreeNode) {
while (NULL != pTreeNode) {
listOrder.InsertEnd(pTreeNode->GetData());
if (NULL != pTreeNode->GetChildRight()) {
//push the child right to stack
cStack.Push(pTreeNode->GetChildRight());
}
pTreeNode = pTreeNode->GetChildLeft();
}
if (TRUE == cStack.Pop(pTreeNode)) {
if (NULL == pTreeNode) {
return FALSE;
}
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
/**
* InOrderTraversal
*
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return BOOL
* @note In-order traversal
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::InOrderTraversal(AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const
{
if (NULL == m_pRootNode) {
return FALSE;
}
listOrder.Clear();
//Recursion Traversal
InOrderTraversal(m_pRootNode, listOrder);
return TRUE;
//Not Recursion Traversal
AL_StackSeq*> cStack;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pTreeNode = m_pRootNode;
while (TRUE != cStack.IsEmpty() || NULL != pTreeNode) {
while (NULL != pTreeNode) {
cStack.Push(pTreeNode);
pTreeNode = pTreeNode->GetChildLeft();
}
if (TRUE == cStack.Pop(pTreeNode)) {
if (NULL != pTreeNode) {
listOrder.InsertEnd(pTreeNode->GetData());
if (NULL != pTreeNode->GetChildRight()){
//child right exist, push the node, and loop it's left child to push
pTreeNode = pTreeNode->GetChildRight();
}
else {
//to pop the node in the stack
pTreeNode = NULL;
}
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
/**
* PostOrderTraversal
*
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return BOOL
* @note Post-order traversal
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::PostOrderTraversal(AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const
{
if (NULL == m_pRootNode) {
return FALSE;
}
listOrder.Clear();
//Recursion Traversal
PostOrderTraversal(m_pRootNode, listOrder);
return TRUE;
//Not Recursion Traversal
AL_StackSeq*> cStack;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pTreeNode = m_pRootNode;
AL_StackSeq*> cStackReturn;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pTreeNodeReturn = NULL;
while (TRUE != cStack.IsEmpty() || NULL != pTreeNode) {
while (NULL != pTreeNode) {
cStack.Push(pTreeNode);
if (NULL != pTreeNode->GetChildLeft()) {
pTreeNode = pTreeNode->GetChildLeft();
}
else {
//has not left child, get the right child
pTreeNode = pTreeNode->GetChildRight();
}
}
if (TRUE == cStack.Pop(pTreeNode)) {
if (NULL != pTreeNode) {
listOrder.InsertEnd(pTreeNode->GetData());
if (NULL != pTreeNode->GetChildLeft() && NULL != pTreeNode->GetChildRight()){
//child right exist
cStackReturn.Top(pTreeNodeReturn);
if (pTreeNodeReturn != pTreeNode) {
listOrder.RemoveAt(listOrder.Length()-1);
cStack.Push(pTreeNode);
cStackReturn.Push(pTreeNode);
pTreeNode = pTreeNode->GetChildRight();
}
else {
//to pop the node in the stack
cStackReturn.Pop(pTreeNodeReturn);
pTreeNode = NULL;
}
}
else {
//to pop the node in the stack
pTreeNode = NULL;
}
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
/**
* LevelOrderTraversal
*
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return BOOL
* @note Level-order traversal
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::LevelOrderTraversal(AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const
{
if (TRUE == IsEmpty()) {
return FALSE;
}
if (NULL == m_pRootNode) {
return FALSE;
}
listOrder.Clear();
/*
AL_ListSeq*> listNodeOrder;
listNodeOrder.InsertEnd(m_pRootNode);
//loop the all node
DWORD dwNodeOrderLoop = 0x00;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pNodeOrderLoop = NULL;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pNodeOrderChild = NULL;
while (TRUE == listNodeOrder.Get(pNodeOrderLoop, dwNodeOrderLoop)) {
dwNodeOrderLoop++;
if (NULL != pNodeOrderLoop) {
listOrder.InsertEnd(pNodeOrderLoop->GetData());
pNodeOrderChild = pNodeOrderLoop->GetChildLeft();
if (NULL != pNodeOrderChild) {
queueOrder.Push(pNodeOrderChild);
}
pNodeOrderChild = pNodeOrderLoop->GetChildRight();
if (NULL != pNodeOrderChild) {
queueOrder.Push(pNodeOrderChild);
}
}
else {
//error
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
*/
AL_QueueSeq*> queueOrder;
queueOrder.Push(m_pRootNode);
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pNodeOrderLoop = NULL;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pNodeOrderChild = NULL;
while (FALSE == queueOrder.IsEmpty()) {
if (TRUE == queueOrder.Pop(pNodeOrderLoop)) {
if (NULL != pNodeOrderLoop) {
listOrder.InsertEnd(pNodeOrderLoop->GetData());
pNodeOrderChild = pNodeOrderLoop->GetChildLeft();
if (NULL != pNodeOrderChild) {
queueOrder.Push(pNodeOrderChild);
}
pNodeOrderChild = pNodeOrderLoop->GetChildRight();
if (NULL != pNodeOrderChild) {
queueOrder.Push(pNodeOrderChild);
}
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
/**
* GetSiblingAtNode
*
* @param AL_ListSeq& listSibling
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @return BOOL
* @note sibling nodes: nodes with the same parent node is called mutual sibling;
* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::GetSiblingAtNode(AL_ListSeq& listSibling, const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode) const
{
if (NULL == pCurTreeNode) {
return FALSE;
}
AL_ListSeq*> listTreeNodeSibling;
if (FALSE == pCurTreeNode->GetSibling(listTreeNodeSibling)) {
return FALSE;
}
//clear listSibling
listSibling.Clear();
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pTreeNodeSibling = NULL;
for (DWORD dwCnt=0; dwCntGetData());
}
else {
//error
return FALSE;
}
}
else {
//error
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
/**
* GetAncestorAtNode
*
* @param AL_ListSeq& listAncestor
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @return BOOL
* @note ancestor node: from the root to the node through all the nodes on the branch;
* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::GetAncestorAtNode(AL_ListSeq& listAncestor, const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode) const
{
if (NULL == pCurTreeNode) {
return FALSE;
}
AL_ListSeq*> listTreeNodeAncestor;
if (FALSE == pCurTreeNode->GetAncestor(listTreeNodeAncestor)) {
return FALSE;
}
//clear listAncestor
listAncestor.Clear();
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pTreeNodeAncestor = NULL;
for (DWORD dwCnt=0; dwCntGetData());
}
else {
//error
return FALSE;
}
}
else {
//error
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
/**
* GetDescendantAtNode
*
* @param AL_ListSeq& listDescendant
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @return BOOL
* @note ancestor node: from the root to the node through all the nodes on the branch;
* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::GetDescendantAtNode(AL_ListSeq& listDescendant, const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode) const
{
if (NULL == pCurTreeNode) {
return FALSE;
}
AL_ListSeq*> listTreeNodeDescendant;
if (FALSE == pCurTreeNode->GetDescendant(listTreeNodeDescendant)) {
return FALSE;
}
//clear listAncestor
listDescendant.Clear();
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pTreeNodeDescendant = NULL;
for (DWORD dwCnt=0; dwCntGetData());
}
else {
//error
return FALSE;
}
}
else {
//error
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
/**
* InsertRoot
*
* @param const T& tTemplate
* @return BOOL
* @note
* @attention
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::InsertRoot(const T& tTemplate)
{
return InsertAtNode(NULL, 0x00, tTemplate);
}
/**
* InsertLeftAtNode
*
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @param const T& tTemplate
* @return BOOL
* @note insert the tTemplate as child tree node to the current tree node (pCurTreeNode) at the position (left)
* @attention if NULL == pCurTreeNode, it will be insert as root tree node, the current tree node must be in the tree
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::InsertLeftAtNode(AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode, const T& tTemplate)
{
return InsertAtNode(pCurTreeNode, 0x00, tTemplate);
}
/**
* InsertRightAtNode
*
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @param const T& tTemplate
* @return BOOL
* @note insert the tTemplate as child tree node to the current tree node (pCurTreeNode) at the position (right)
* @attention if NULL == pCurTreeNode, it will be insert as root tree node, the current tree node must be in the tree
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::InsertRightAtNode(AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode, const T& tTemplate)
{
return InsertAtNode(pCurTreeNode, 0x01, tTemplate);
}
/**
* RemoveNode
*
* @param AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @return BOOL
* @note
* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::RemoveNode(AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode)
{
IsFullTreeBin();
if (NULL == pCurTreeNode) {
return FALSE;
}
AL_ListSeq*> listTreeNodeDescendant;
if (FALSE == pCurTreeNode->GetDescendant(listTreeNodeDescendant)) {
return FALSE;
}
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pTreeNodeDescendant = NULL;
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pNodeParent = pCurTreeNode->GetParent();
if (NULL == pNodeParent && m_pRootNode != pNodeParent) {
//not root node and has no parent node
return FALSE;
}
pNodeParent->Remove(pCurTreeNode);
m_dwNumNodes -= (listTreeNodeDescendant.Length() + 1);
//loop all the node
listTreeNodeDescendant.Clear();
if (FALSE == m_pRootNode->GetDescendant(listTreeNodeDescendant)) {
return FALSE;
}
m_dwDegree = m_pRootNode->GetDegree();
m_dwHeight = m_pRootNode->GetLevel();
for (DWORD dwLoopCnt=0; dwLoopCntGetDegree()) {
m_dwDegree = pTreeNodeDescendant->GetDegree();
}
if (m_dwHeight < pTreeNodeDescendant->GetLevel()) {
m_dwHeight = pTreeNodeDescendant->GetLevel();
}
}
else {
//error
return FALSE;
}
}
else {
//error
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
/**
* GetChildNodeLeftAtNode
*
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @return const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq*
* @note get the current tree node (pCurTreeNode)'s child node at the position (left)
* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree
*/
template const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq*
AL_TreeBinSeq::GetChildNodeLeftAtNode(const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode) const
{
if (NULL == pCurTreeNode) {
return FALSE;
}
return pCurTreeNode->GetChildLeft();
}
/**
* GetChildNodeRightAtNode
*
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @return const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq*
* @note get the current tree node (pCurTreeNode)'s child node at the position (right)
* @attention
*/
template const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq*
AL_TreeBinSeq::GetChildNodeRightAtNode(const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode) const
{
if (NULL == pCurTreeNode) {
return FALSE;
}
return pCurTreeNode->GetChildRight();
}
/**
* IsCompleteTreeBin
*
* @param
* @return BOOL
* @note Is Complete Binary Tree
* @attention If set binary height of h, the h layer in addition, the other layers (1 ~ h-1) has reached the maximum number of
nodes, right to left, the h-layer node number of consecutive missing, this is a complete binary tree .
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::IsCompleteTreeBin() const
{
if (TRUE == IsEmpty()) {
return FALSE;
}
if (NULL == m_pRootNode) {
return FALSE;
}
AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pTreeNode;
AL_ListSeq*>& listDescendant;
m_pRootNode->GetDescendant(listDescendant);
BOOL bMissing = FALSE;
for (DWORD dwCnt=0x00; dwCntLength(); dwCnt++) {
if (TRUE == listDescendant.Get(pTreeNode, dwCnt)) {
if (NULL != pTreeNode) {
if (m_dwHeight > pTreeNode->GetLevel()) {
//the other layers (1 ~ h-1)
if (NULL == pTreeNode->GetChildLeft() || NULL == pTreeNode->GetChildRight()) {
//left or right child not exist!
return FALSE
}
}
else {
//the h-layer
if (TRUE == bMissing) {
//node number of consecutive missing
if (NULL == pTreeNode->GetChildLeft() || NULL == pTreeNode->GetChildRight()) {
//left or right child not exist!
return FALSE
}
}
if (NULL == pTreeNode->GetChildLeft()) {
//left child not exist!
bMissing = TRUE;
if (NULL != pTreeNode->GetChildRight()) {
//right child exist!
return FALSE;
}
}
else {
//left child exist!
if (NULL == pTreeNode->GetChildRight()) {
//right child not exist!
bMissing = TRUE;
}
}
}
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
/**
* IsFullTreeBin
*
* @param
* @return BOOL
* @note Is Full Binary Tree
* @attention A binary tree of height h is 2 ^ h-1 element is called a full binary tree.
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::IsFullTreeBin() const
{
if (TRUE == IsEmpty()) {
return FALSE;
}
DWORD dwTwo = 2;
DWORD dwFullTreeBinNum = 1;
for (DWORD dwFull=0x00; dwFull* pCurTreeNode
* @param DWORD dwIndex
* @param const T& tTemplate
* @return BOOL
* @note insert the tTemplate as child tree node to the current tree node (pCurTreeNode) at the position (dwIndex)
* @attention if NULL == pCurTreeNode, it will be insert as root tree node, the current tree node must be in the tree
*/
template BOOL
AL_TreeBinSeq::InsertAtNode(AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode, DWORD dwIndex, const T& tTemplate)
{
if (TRUE == IsEmpty()) {
if (NULL != pCurTreeNode) {
//error can not insert to the current node pCurTreeNode, is not exist in the tree
return FALSE;
}
else {
m_pTreeNode[m_dwUsed].SetData(tTemplate);
m_pTreeNode[m_dwUsed].SetLevel(0x00);
m_pRootNode = &m_pTreeNode[m_dwUsed];
m_dwUsed++;
m_dwDegree = 0x00;
m_dwHeight = 0x00; //empty tree 0xffffffff (-1)
m_dwNumNodes++;
return TRUE;
}
}
if (NULL == pCurTreeNode) {
return FALSE;
}
if (TRUE == IsFull()) {
// full, need to get more work buffer
//can not support Dynamic Expansion
return FALSE;
GetBuffer();
}
//inset to the current tree node
m_pTreeNode[m_dwUsed].SetData(tTemplate);
m_pTreeNode[m_dwUsed].SetLevel(pCurTreeNode->GetLevel() + 1);
if (FALSE == pCurTreeNode->Insert(dwIndex, &m_pTreeNode[m_dwUsed])) {
return FALSE;
}
DWORD dwCurNodeDegree = 0x00;
//loop all node to get the current node degree
if (pCurTreeNode->GetDegree() > m_dwDegree) {
m_dwDegree = pCurTreeNode->GetDegree();
}
if (m_pTreeNode[m_dwUsed].GetLevel() > m_dwHeight) {
m_dwHeight = m_pTreeNode[m_dwUsed].GetLevel();
}
m_dwUsed++;
m_dwNumNodes++;
return TRUE;
}
/**
* PreOrderTraversal
*
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return VOID
* @note Pre-order traversal
* @attention Recursion Traversal
*/
template VOID
AL_TreeBinSeq::PreOrderTraversal(const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode, AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const
{
if (NULL == pCurTreeNode) {
return;
}
//Do Something with root
listOrder.InsertEnd(pCurTreeNode->GetData());
if(NULL != pCurTreeNode->GetChildLeft()) {
PreOrderTraversal(pCurTreeNode->GetChildLeft(), listOrder);
}
if(NULL != pCurTreeNode->GetChildRight()) {
PreOrderTraversal(pCurTreeNode->GetChildRight(), listOrder);
}
}
/**
* InOrderTraversal
*
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder
* @return VOID
* @note In-order traversal
* @attention Recursion Traversal
*/
template VOID
AL_TreeBinSeq::InOrderTraversal(const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode, AL_ListSeq& listOrder) const
{
if (NULL == pCurTreeNode) {
return;
}
if(NULL != pCurTreeNode->GetChildLeft()) {
InOrderTraversal(pCurTreeNode->GetChildLeft(), listOrder);
}
//Do Something with root
listOrder.InsertEnd(pCurTreeNode->GetData());
if(NULL != pCurTreeNode->GetChildRight()) {
InOrderTraversal(pCurTreeNode->GetChildRight(), listOrder);
}
}
/**
* PostOrderTraversal
*
* @param const AL_TreeNodeBinSeq* pCurTreeNode
* @param AL_ListSeq& listOrder