【leetcode】Python实现-111.二叉树的最小深度
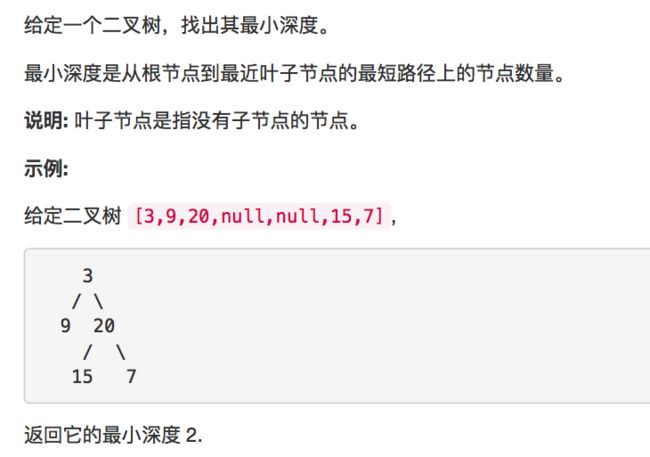
111.二叉树的最小深度
if root is None:
return 0
p = [root]
current_level_num = 1
next_level_num = 0
i = 1
while p:
current = p.pop(0)
current_level_num-=1
if current.left is None and current.right is None:
return i
if current.left:
next_level_num+=1
p.append(current.left)
if current.right:
next_level_num+=1
p.append(current.right)
if current_level_num == 0:
i += 1
current_level_num = next_level_num
next_level_num = 0我采用的方法是层次遍历,按层次打印结点的,将其稍做修改。用变量i记录当前层数,当遇到叶子结点时则返回当前层数。代码还可以进行优化。待我第二遍再来优化吧,现在需要加快进度。
别人采用递归实现:
if root is None:
return 0
if root.left is None and root.right is None:
return 1
elif root.left is None:
return 1 + self.minDepth(root.right)
elif root.right is None:
return 1 + self.minDepth(root.left)
else:
return 1 + min([self.minDepth(root.left), self.minDepth(root.right)])递归有以下几种情况:
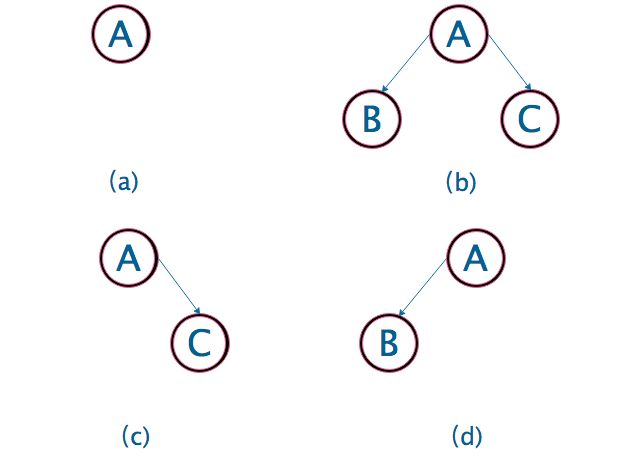
1.根节点为空,深度为0
2.只有一个根节点。深度为1
3.左右子树皆不空,则返回1+左右子树中最小的深度。
4.左子树为空,则返回1+右子树深度。这里可能有点难以理解,可以想象成此时只有根节点a,以及其右子树b,此时最小深度为2。
5.右子树为空,则返回1+左子树深度。同上分析。