ARM 原生程序的生成过程
- Android 平台上的 ARM 原生程序是用 Android NDK 开发的,整个原生程序的编译生成工作由 Android NDK 提供的编译工具链完成
- Android NDK 目前提供了两套 ARM 编译器,分别是基于 GNU GCC 编译器的 gcc 编译器和基于LLVM 编译套件的 Clang 编译器
- Android NDK 打算从 r17 版本开始移除对 gcc 的支持,只提供 Clang 编译开发 Android 原生程序,但实际却是仍可用 gcc 开发
- 现在用 Android NDK 写一个 ARM 原生程序,然后分析编译器执行的每一步操作,从而了解原生程序的整个生成过程。代码如下:

- 系统:Ubuntu 18.04
- Android NDK 版本:r10e
- 用传统的 gcc 工具编译这段代码,只要执行
gcc hello.c -o hello 命令;用 Android NDK 要麻烦一些
- 在命令行下指定 CC 环境变量,用 arm-linux-androideabi-gcc 编译器单独编译代码时要指定 --sysroot 选项(官方解释)
- 执行如下命令,可在命令行下编译 hello.c 代码:
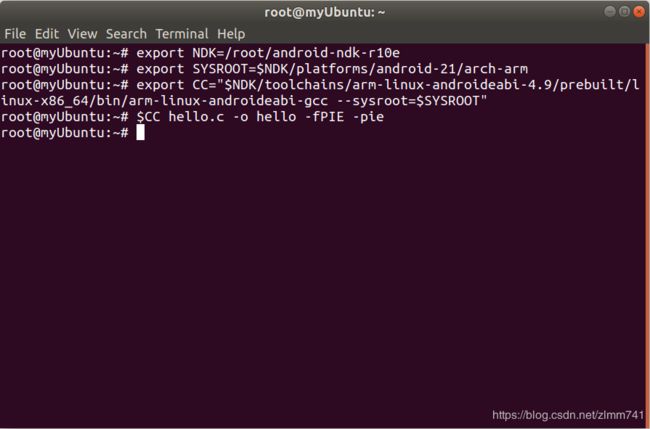
- 第一行:指定 Android NDK 的根目录,方便在下面的命令中引用
- 第二行:指定 SYSROOT 环境变量,arm-linux-androideabi-gcc 编译器在编译代码时会到此目录下查找头文件和库。此处使用的是 android-21,表示系统版本是 Android 5.0(这是第一个引入 arm64-v8a 架构的系统版本)
- 第三行:指定 CC 环境变量,指向具体的编译器路径
- 第四行:使用由 CC 环境变量指定的编译器编译代码。后面的
-fPIE -pie 参数,作用是生成与位置无关的代码,在 Android 5.0 及以上版本的系统中必须设置此参数,不然程序运行时会产生异常,提示信息为“error: only position independent executables (PIE) are supported”。编译成功后,会生成 hello 可执行文件
- 若是编译 C++ 代码,第四行命令可改为
export CXX="$NDK/toolchains/arm-linux-androideabi-4.9/prebuilt/linux-x86_64/bin/arm-linux-androideabi-g++ --sysroot=$SYSROOT"
- 直接执行 hello 程序会提示“该文件无法执行”

- 可将文件传入 Android 手机或模拟器执行,命令和输出如下:

- 上面用
$CC 编译的 Android 原生程序没指定 -march 参数,故默认的是 ARM 架构,对应的处理器是 armeabi,采用的指令集是 ARMv5TE
- 若想生成其他 ARM 架构的程序,如 ARMv7-A,可执行如下命令:
$CC -march=armv7-a hello.c -o hello
- 除了用 arm-linux-androideabi-gcc 编译器,还可用 Android NDK 提供的 Clang 编译器生成程序,二者只在指定编译工具链的环境变量设置上有所不同
- (本书成书时)Android NDK 提供的 LLVM 编译套件中虽有 Clang 前端,但没用于处理代码的后端工具,如汇编器 as 和链接器 ld。用 Clang 只能完成编译工作,要想完成汇编和链接工作,还得借助 gcc 的 arm-linux-androideabi-as 和 arm-linux-androideabi-ld。在设置 CC 环境变量时,指定
-gcc-toolchain 即可将后端部分传给 gcc。除此之外,用 Clang 编译器编译不同架构的代码应通过 -target 参数指定,而不应通过 gcc 的 -march。指定 -target 的值为“armv7-linux-androideabi”,表示生成 ARMv7-A 架构的程序。若没指定 -target 的值,默认情况下其值为当前编译系统平台架构的名称
- CC 环境变量的设置和 hello.c 的编译可执行如下命令:

- 无论 gcc 或 Clang,执行一次完整的编译工作通常分为预处理、编译、汇编、链接四个步骤,各步骤的工作细节有所不同
预处理
- 在预处理阶段,编译器将处理代码中的预处理指令。如,
#include 中包含的头文件会全部被编译出来,#define 预定义、#if 预条件处理等也都会被编译器处理。详细的输出信息可通过向编译器传递 -E 选项查看。以 hello.c 为例,gcc 和 Clang 都可执行 $CC -E -fPIE -pie hello.c -o hello.i 命令完成代码的预处理
- hello.i 内容如下:
# 1 "hello.c"
# 1 "" 1
# 1 "" 3
# 325 "" 3
# 1 "" 1
# 1 "" 2
# 1 "hello.c" 2
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/stdio.h" 1 3 4
# 49 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/sys/cdefs.h" 1 3 4
# 77 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/sys/cdefs.h" 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/sys/cdefs_elf.h" 1 3 4
# 78 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/sys/cdefs.h" 2 3 4
# 547 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/sys/cdefs.h" 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/android/api-level.h" 1 3 4
# 548 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/sys/cdefs.h" 2 3 4
# 50 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/sys/types.h" 1 3 4
# 31 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/sys/types.h" 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/toolchains/llvm-3.5/prebuilt/linux-x86_64/bin/../lib/clang/3.5/include/stddef.h" 1 3 4
# 47 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/toolchains/llvm-3.5/prebuilt/linux-x86_64/bin/../lib/clang/3.5/include/stddef.h" 3 4
typedef int ptrdiff_t;
# 58 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/toolchains/llvm-3.5/prebuilt/linux-x86_64/bin/../lib/clang/3.5/include/stddef.h" 3 4
typedef unsigned int size_t;
# 86 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/toolchains/llvm-3.5/prebuilt/linux-x86_64/bin/../lib/clang/3.5/include/stddef.h" 3 4
typedef unsigned int wchar_t;
# 32 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/sys/types.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/toolchains/llvm-3.5/prebuilt/linux-x86_64/bin/../lib/clang/3.5/include/stdint.h" 1 3 4
# 63 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/toolchains/llvm-3.5/prebuilt/linux-x86_64/bin/../lib/clang/3.5/include/stdint.h" 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/stdint.h" 1 3 4
# 32 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/stdint.h" 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/toolchains/llvm-3.5/prebuilt/linux-x86_64/bin/../lib/clang/3.5/include/stddef.h" 1 3 4
# 33 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/stdint.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/machine/wchar_limits.h" 1 3 4
# 34 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/stdint.h" 2 3 4
typedef signed char __int8_t;
typedef unsigned char __uint8_t;
typedef short __int16_t;
typedef unsigned short __uint16_t;
typedef int __int32_t;
typedef unsigned int __uint32_t;
typedef long long __int64_t;
typedef unsigned long long __uint64_t;
typedef int __intptr_t;
typedef unsigned int __uintptr_t;
typedef __int8_t int8_t;
typedef __uint8_t uint8_t;
typedef __int16_t int16_t;
typedef __uint16_t uint16_t;
typedef __int32_t int32_t;
typedef __uint32_t uint32_t;
typedef __int64_t int64_t;
typedef __uint64_t uint64_t;
typedef __intptr_t intptr_t;
typedef __uintptr_t uintptr_t;
typedef int8_t int_least8_t;
typedef uint8_t uint_least8_t;
typedef int16_t int_least16_t;
typedef uint16_t uint_least16_t;
typedef int32_t int_least32_t;
typedef uint32_t uint_least32_t;
typedef int64_t int_least64_t;
typedef uint64_t uint_least64_t;
typedef int8_t int_fast8_t;
typedef uint8_t uint_fast8_t;
typedef int64_t int_fast64_t;
typedef uint64_t uint_fast64_t;
typedef int32_t int_fast16_t;
typedef uint32_t uint_fast16_t;
typedef int32_t int_fast32_t;
typedef uint32_t uint_fast32_t;
typedef uint64_t uintmax_t;
typedef int64_t intmax_t;
# 64 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/toolchains/llvm-3.5/prebuilt/linux-x86_64/bin/../lib/clang/3.5/include/stdint.h" 2 3 4
# 33 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/sys/types.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/linux/types.h" 1 3 4
# 21 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/linux/types.h" 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm/types.h" 1 3 4
# 19 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm/types.h" 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm-generic/types.h" 1 3 4
# 21 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm-generic/types.h" 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm-generic/int-ll64.h" 1 3 4
# 21 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm-generic/int-ll64.h" 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm/bitsperlong.h" 1 3 4
# 19 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm/bitsperlong.h" 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm-generic/bitsperlong.h" 1 3 4
# 20 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm/bitsperlong.h" 2 3 4
# 22 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm-generic/int-ll64.h" 2 3 4
typedef __signed__ char __s8;
typedef unsigned char __u8;
typedef __signed__ short __s16;
typedef unsigned short __u16;
typedef __signed__ int __s32;
typedef unsigned int __u32;
__extension__ typedef __signed__ long long __s64;
__extension__ typedef unsigned long long __u64;
# 22 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm-generic/types.h" 2 3 4
# 20 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm/types.h" 2 3 4
# 22 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/linux/types.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/linux/posix_types.h" 1 3 4
# 21 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/linux/posix_types.h" 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/linux/stddef.h" 1 3 4
# 19 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/linux/stddef.h" 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/linux/compiler.h" 1 3 4
# 20 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/linux/stddef.h" 2 3 4
# 22 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/linux/posix_types.h" 2 3 4
typedef struct {
unsigned long fds_bits[1024 / (8 * sizeof(long))];
} __kernel_fd_set;
typedef void (*__kernel_sighandler_t)(int);
typedef int __kernel_key_t;
typedef int __kernel_mqd_t;
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm/posix_types.h" 1 3 4
# 21 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm/posix_types.h" 3 4
typedef unsigned short __kernel_mode_t;
typedef unsigned short __kernel_ipc_pid_t;
typedef unsigned short __kernel_uid_t;
typedef unsigned short __kernel_gid_t;
typedef unsigned short __kernel_old_dev_t;
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm-generic/posix_types.h" 1 3 4
# 21 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm-generic/posix_types.h" 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm/bitsperlong.h" 1 3 4
# 22 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm-generic/posix_types.h" 2 3 4
typedef long __kernel_long_t;
typedef unsigned long __kernel_ulong_t;
typedef __kernel_ulong_t __kernel_ino_t;
typedef int __kernel_pid_t;
# 49 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm-generic/posix_types.h" 3 4
typedef __kernel_long_t __kernel_suseconds_t;
typedef int __kernel_daddr_t;
typedef unsigned int __kernel_uid32_t;
typedef unsigned int __kernel_gid32_t;
typedef __kernel_uid_t __kernel_old_uid_t;
typedef __kernel_gid_t __kernel_old_gid_t;
# 71 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm-generic/posix_types.h" 3 4
typedef unsigned int __kernel_size_t;
typedef int __kernel_ssize_t;
typedef int __kernel_ptrdiff_t;
# 84 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm-generic/posix_types.h" 3 4
typedef struct {
int val[2];
} __kernel_fsid_t;
typedef __kernel_long_t __kernel_off_t;
typedef long long __kernel_loff_t;
typedef __kernel_long_t __kernel_time_t;
typedef __kernel_long_t __kernel_clock_t;
typedef int __kernel_timer_t;
typedef int __kernel_clockid_t;
typedef char * __kernel_caddr_t;
typedef unsigned short __kernel_uid16_t;
typedef unsigned short __kernel_gid16_t;
# 33 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/asm/posix_types.h" 2 3 4
# 33 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/linux/posix_types.h" 2 3 4
# 25 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/linux/types.h" 2 3 4
typedef __u16 __le16;
typedef __u16 __be16;
typedef __u32 __le32;
typedef __u32 __be32;
typedef __u64 __le64;
typedef __u64 __be64;
typedef __u16 __sum16;
typedef __u32 __wsum;
# 36 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/sys/types.h" 2 3 4
typedef __kernel_gid32_t __gid_t;
typedef __gid_t gid_t;
typedef __kernel_uid32_t __uid_t;
typedef __uid_t uid_t;
typedef __kernel_pid_t __pid_t;
typedef __pid_t pid_t;
typedef uint32_t __id_t;
typedef __id_t id_t;
typedef unsigned long blkcnt_t;
typedef unsigned long blksize_t;
typedef __kernel_caddr_t caddr_t;
typedef __kernel_clock_t clock_t;
typedef __kernel_clockid_t __clockid_t;
typedef __clockid_t clockid_t;
typedef __kernel_daddr_t daddr_t;
typedef unsigned long fsblkcnt_t;
typedef unsigned long fsfilcnt_t;
typedef __kernel_mode_t __mode_t;
typedef __mode_t mode_t;
typedef __kernel_key_t __key_t;
typedef __key_t key_t;
typedef __kernel_ino_t __ino_t;
typedef __ino_t ino_t;
typedef uint32_t __nlink_t;
typedef __nlink_t nlink_t;
typedef void* __timer_t;
typedef __timer_t timer_t;
typedef __kernel_suseconds_t __suseconds_t;
typedef __suseconds_t suseconds_t;
typedef uint32_t __useconds_t;
typedef __useconds_t useconds_t;
typedef uint32_t dev_t;
typedef __kernel_time_t __time_t;
typedef __time_t time_t;
typedef __kernel_off_t off_t;
typedef __kernel_loff_t loff_t;
typedef loff_t off64_t;
# 122 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/sys/types.h" 3 4
typedef int32_t __socklen_t;
typedef __socklen_t socklen_t;
typedef __builtin_va_list __va_list;
# 138 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/sys/types.h" 3 4
typedef __kernel_ssize_t ssize_t;
typedef unsigned int uint_t;
typedef unsigned int uint;
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/sys/sysmacros.h" 1 3 4
# 36 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/sys/sysmacros.h" 3 4
static __inline__ int major(dev_t _dev)
{
return (_dev >> 8) & 0xfff;
}
static __inline__ int minor(dev_t _dev)
{
return (_dev & 0xff) | ((_dev >> 12) & 0xfff00);
}
static __inline__ dev_t makedev(int __ma, int __mi)
{
return ((__ma & 0xfff) << 8) | (__mi & 0xff) | ((__mi & 0xfff00) << 12);
}
# 146 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/sys/types.h" 2 3 4
typedef unsigned char u_char;
typedef unsigned short u_short;
typedef unsigned int u_int;
typedef unsigned long u_long;
typedef uint32_t u_int32_t;
typedef uint16_t u_int16_t;
typedef uint8_t u_int8_t;
typedef uint64_t u_int64_t;
# 51 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/toolchains/llvm-3.5/prebuilt/linux-x86_64/bin/../lib/clang/3.5/include/stdarg.h" 1 3 4
# 30 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/toolchains/llvm-3.5/prebuilt/linux-x86_64/bin/../lib/clang/3.5/include/stdarg.h" 3 4
typedef __builtin_va_list va_list;
# 50 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/toolchains/llvm-3.5/prebuilt/linux-x86_64/bin/../lib/clang/3.5/include/stdarg.h" 3 4
typedef __builtin_va_list __gnuc_va_list;
# 53 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/toolchains/llvm-3.5/prebuilt/linux-x86_64/bin/../lib/clang/3.5/include/stddef.h" 1 3 4
# 54 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/toolchains/llvm-3.5/prebuilt/linux-x86_64/bin/../lib/clang/3.5/include/stddef.h" 1 3 4
# 57 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
typedef off_t fpos_t;
# 75 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
struct __sbuf {
unsigned char *_base;
int _size;
};
# 108 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
typedef struct __sFILE {
unsigned char *_p;
int _r;
int _w;
short _flags;
short _file;
struct __sbuf _bf;
int _lbfsize;
void *_cookie;
int (*_close)(void *);
int (*_read)(void *, char *, int);
fpos_t (*_seek)(void *, fpos_t, int);
int (*_write)(void *, const char *, int);
struct __sbuf _ext;
unsigned char *_up;
int _ur;
unsigned char _ubuf[3];
unsigned char _nbuf[1];
struct __sbuf _lb;
int _blksize;
fpos_t _offset;
} FILE;
extern FILE __sF[];
# 220 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
void clearerr(FILE *);
int fclose(FILE *);
int feof(FILE *);
int ferror(FILE *);
int fflush(FILE *);
int fgetc(FILE *);
char *fgets(char * __restrict, int, FILE * __restrict);
FILE *fopen(const char * __restrict , const char * __restrict);
int fprintf(FILE * __restrict , const char * __restrict, ...)
__attribute__((__format__(printf, 2, 3))) __attribute__((__nonnull__ (2)));
int fputc(int, FILE *);
int fputs(const char * __restrict, FILE * __restrict);
size_t fread(void * __restrict, size_t, size_t, FILE * __restrict);
FILE *freopen(const char * __restrict, const char * __restrict,
FILE * __restrict);
int fscanf(FILE * __restrict, const char * __restrict, ...)
__attribute__((__format__(scanf, 2, 3))) __attribute__((__nonnull__ (2)));
int fseek(FILE *, long, int);
long ftell(FILE *);
size_t fwrite(const void * __restrict, size_t, size_t, FILE * __restrict);
int getc(FILE *);
int getchar(void);
ssize_t getdelim(char ** __restrict, size_t * __restrict, int,
FILE * __restrict);
ssize_t getline(char ** __restrict, size_t * __restrict, FILE * __restrict);
void perror(const char *);
int printf(const char * __restrict, ...)
__attribute__((__format__(printf, 1, 2))) __attribute__((__nonnull__ (1)));
int putc(int, FILE *);
int putchar(int);
int puts(const char *);
int remove(const char *);
void rewind(FILE *);
int scanf(const char * __restrict, ...)
__attribute__((__format__(scanf, 1, 2))) __attribute__((__nonnull__ (1)));
void setbuf(FILE * __restrict, char * __restrict);
int setvbuf(FILE * __restrict, char * __restrict, int, size_t);
int sscanf(const char * __restrict, const char * __restrict, ...)
__attribute__((__format__(scanf, 2, 3))) __attribute__((__nonnull__ (2)));
FILE *tmpfile(void);
int ungetc(int, FILE *);
int vfprintf(FILE * __restrict, const char * __restrict, __va_list)
__attribute__((__format__(printf, 2, 0))) __attribute__((__nonnull__ (2)));
int vprintf(const char * __restrict, __va_list)
__attribute__((__format__(printf, 1, 0))) __attribute__((__nonnull__ (1)));
int dprintf(int, const char * __restrict, ...) __attribute__((__format__(printf, 2, 3))) __attribute__((__nonnull__ (2)));
int vdprintf(int, const char * __restrict, __va_list) __attribute__((__format__(printf, 2, 0))) __attribute__((__nonnull__ (2)));
char* gets(char*) ;
int sprintf(char* __restrict, const char* __restrict, ...)
__attribute__((__format__(printf, 2, 3))) __attribute__((__nonnull__ (2)));
char* tmpnam(char*) ;
int vsprintf(char* __restrict, const char* __restrict, __va_list)
__attribute__((__format__(printf, 2, 0))) __attribute__((__nonnull__ (2)));
char* tempnam(const char*, const char*)
;
extern int rename(const char*, const char*);
extern int renameat(int, const char*, int, const char*);
int fgetpos(FILE * __restrict, fpos_t * __restrict);
int fsetpos(FILE *, const fpos_t *);
int fseeko(FILE *, off_t, int);
off_t ftello(FILE *);
int snprintf(char * __restrict, size_t, const char * __restrict, ...)
__attribute__((__format__(printf, 3, 4))) __attribute__((__nonnull__ (3)));
int vfscanf(FILE * __restrict, const char * __restrict, __va_list)
__attribute__((__format__(scanf, 2, 0))) __attribute__((__nonnull__ (2)));
int vscanf(const char *, __va_list)
__attribute__((__format__(scanf, 1, 0))) __attribute__((__nonnull__ (1)));
int vsnprintf(char * __restrict, size_t, const char * __restrict, __va_list)
__attribute__((__format__(printf, 3, 0))) __attribute__((__nonnull__ (3)));
int vsscanf(const char * __restrict, const char * __restrict, __va_list)
__attribute__((__format__(scanf, 2, 0))) __attribute__((__nonnull__ (2)));
# 317 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
FILE *fdopen(int, const char *);
int fileno(FILE *);
int pclose(FILE *);
FILE *popen(const char *, const char *);
void flockfile(FILE *);
int ftrylockfile(FILE *);
void funlockfile(FILE *);
int getc_unlocked(FILE *);
int getchar_unlocked(void);
int putc_unlocked(int, FILE *);
int putchar_unlocked(int);
# 349 "/root/android-ndk-r10e/platforms/android-21/arch-arm/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
int asprintf(char ** __restrict, const char * __restrict, ...)
__attribute__((__format__(printf, 2, 3))) __attribute__((__nonnull__ (2)));
char *fgetln(FILE * __restrict, size_t * __restrict);
int fpurge(FILE *);
void setbuffer(FILE *, char *, int);
int setlinebuf(FILE *);
int vasprintf(char ** __restrict, const char * __restrict,
__va_list)
__attribute__((__format__(printf, 2, 0))) __attribute__((__nonnull__ (2)));
FILE *funopen(const void *,
int (*)(void *, char *, int),
int (*)(void *, const char *, int),
fpos_t (*)(void *, fpos_t, int),
int (*)(void *));
# 2 "hello.c" 2
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
printf("Hello ARM!\n");
return 0;
}
- 预处理阶段 gcc 和 Clang 所做的工作差不多
编译
- 在编译阶段,编译器首先检查代码的规范性,及其中是否存在语法错误等,以确定代码实际要做的工作。确认无误后,编译器把代码翻译成 ARM 汇编语言的代码,输出信息可通过向编译器传递
-S 选项查看
- 以 hello.c 为例,执行
$CC hello.i -S -fPIE -o hello.s 命令后会生成 hello.s 汇编文件,根据 CC 环境变量指定编译器的不同,生成的汇编代码也会不同
- gcc 生成的代码如下:
.arch armv5te
.fpu softvfp
.eabi_attribute 20, 1
.eabi_attribute 21, 1
.eabi_attribute 23, 3
.eabi_attribute 24, 1
.eabi_attribute 25, 1
.eabi_attribute 26, 2
.eabi_attribute 30, 6
.eabi_attribute 34, 0
.eabi_attribute 18, 4
.file "hello.c"
.section .rodata
.align 2
.LC0:
.ascii "Hello ARM!\000"
.text
.align 2
.global main
.type main, %function
main:
@ args = 0, pretend = 0, frame = 8
@ frame_needed = 1, uses_anonymous_args = 0
stmfd sp!, {fp, lr}
add fp, sp, #4
sub sp, sp, #8
str r0, [fp, #-8]
str r1, [fp, #-12]
ldr r3, .L3
.LPIC0:
add r3, pc, r3
mov r0, r3
bl puts(PLT)
mov r3, #0
mov r0, r3
sub sp, fp, #4
@ sp needed
ldmfd sp!, {fp, pc}
.L4:
.align 2
.L3:
.word .LC0-(.LPIC0+8)
.size main, .-main
.ident "GCC: (GNU) 4.9 20140827 (prerelease)"
.section .note.GNU-stack,"",%progbits
- hello.s 展示了一个 ARM 汇编程序源文件的完整结构
. 开头的汇编指令是汇编器提供的伪指令,不同的伪指令描述了汇编程序的不同部分
.arch:指定汇编程序使用的处理器架构,默认情况下,armeabi 指定的处理器架构为 ARMv5TE.section:声明一个段.ascii:声明一个字符串
- 将 CC 环境变量定义为 Clang,并将
-target 设置为 armv5te-linux-androideabi,生成 hello.s

- hello.s 内容如下:
.text
.syntax unified
.cpu arm1022e
.eabi_attribute 6, 4 @ Tag_CPU_arch
.eabi_attribute 8, 1 @ Tag_ARM_ISA_use
.eabi_attribute 15, 1 @ Tag_ABI_PCS_RW_data
.eabi_attribute 16, 1 @ Tag_ABI_PCS_RO_data
.eabi_attribute 17, 2 @ Tag_ABI_PCS_GOT_use
.eabi_attribute 20, 1 @ Tag_ABI_FP_denormal
.eabi_attribute 21, 1 @ Tag_ABI_FP_exceptions
.eabi_attribute 23, 3 @ Tag_ABI_FP_number_model
.eabi_attribute 24, 1 @ Tag_ABI_align_needed
.eabi_attribute 25, 1 @ Tag_ABI_align_preserved
.eabi_attribute 18, 4 @ Tag_ABI_PCS_wchar_t
.eabi_attribute 26, 2 @ Tag_ABI_enum_size
.file "hello.i"
.globl main
.align 2
.type main,%function
main: @ @main
.fnstart
.Leh_func_begin0:
@ BB#0: @ %entry
.save {r11, lr}
push {r11, lr}
.setfp r11, sp
mov r11, sp
.pad #16
sub sp, sp, #16
ldr r2, .LCPI0_2
.LPC0_0:
add r2, pc, r2
ldr r3, .LCPI0_1
add r2, r3, r2
ldr r3, .LCPI0_0
str r3, [r11, #-4]
str r0, [sp, #8]
str r1, [sp, #4]
mov r0, r2
bl printf(PLT)
ldr r1, .LCPI0_0
str r0, [sp] @ 4-byte Spill
mov r0, r1
mov sp, r11
pop {r11, pc}
.align 2
@ BB#1:
.LCPI0_0:
.long 0 @ 0x0
.LCPI0_1:
.long .L.str(GOTOFF)
.LCPI0_2:
.long _GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_-(.LPC0_0+8)
.Ltmp0:
.size main, .Ltmp0-main
.cantunwind
.fnend
.type .L.str,%object @ @.str
.section .rodata.str1.1,"aMS",%progbits,1
.L.str:
.asciz "Hello ARM!\n"
.size .L.str, 12
.ident "clang version 3.5 "
- 可看出,Clang 用的指令集为 arm1022e,生成的汇编代码也与 gcc 不同
- Clang 在生成 hello.s 期间还做了许多内部转换工作。Clang 作为 LLVM 套件的 C 语言编译器前端,在生成汇编代码前会将代码转换成 LLVM 特有的中间代码 Bitcode 字节码,然后将 Bitcode 字节码转换成与机器相关的汇编指令
- 要想生成 Bitcode 字节码,可在调用 Clang 时使用
-emit-llvm 参数
- hello.c 可执行如下命令生成 hello.bc:

- Bitcode 是 LLVM IR(一种程序代码的中间语法表达)的表现形式,它即可存在于二进制格式的
.bc 文件中,也可存在于可读的文本格式的 .ll 文件中。可用 llvm-dis 命令将 .bc 文件转换成可读的 .ll 文件,也可用 llvm-as 命令将 .ll 转换为 .bc

- hello.ll 的内容如下:
; ModuleID = 'hello.bc'
target datalayout = "e-m:e-p:32:32-i64:64-v128:64:128-n32-S64"
target triple = "armv5e--linux-androideabi"
@.str = private unnamed_addr constant [12 x i8] c"Hello ARM!\0A\00", align 1
; Function Attrs: nounwind
define i32 @main(i32 %argc, i8** %argv) #0 {
entry:
%retval = alloca i32, align 4
%argc.addr = alloca i32, align 4
%argv.addr = alloca i8**, align 4
store i32 0, i32* %retval
store i32 %argc, i32* %argc.addr, align 4
store i8** %argv, i8*** %argv.addr, align 4
%call = call i32 (i8*, ...)* @printf(i8* getelementptr inbounds ([12 x i8]* @.str, i32 0, i32 0))
ret i32 0
}
declare i32 @printf(i8*, ...) #1
attributes #0 = { nounwind "less-precise-fpmad"="false" "no-frame-pointer-elim"="true" "no-frame-pointer-elim-non-leaf" "no-infs-fp-math"="false" "no-nans-fp-math"="false" "stack-protector-buffer-size"="8" "unsafe-fp-math"="false" "use-soft-float"="true" }
attributes #1 = { "less-precise-fpmad"="false" "no-frame-pointer-elim"="true" "no-frame-pointer-elim-non-leaf" "no-infs-fp-math"="false" "no-nans-fp-math"="false" "stack-protector-buffer-size"="8" "unsafe-fp-math"="false" "use-soft-float"="true" }
!llvm.module.flags = !{!0, !1}
!llvm.ident = !{!2}
!0 = metadata !{i32 1, metadata !"wchar_size", i32 4}
!1 = metadata !{i32 1, metadata !"min_enum_size", i32 4}
!2 = metadata !{metadata !"clang version 3.5 "}
- 将 hello.bc 转换为 hello.s:

- 这和之前生成的 hello.s 是一样的
汇编
- 汇编阶段,执行如下命令,生成 hello.o:
$CC -c hello.s -o hello.o
- 它的内部环境变量 CC 将汇编文件传给汇编器生成目标文件
- arm-linux-androideabi-gcc 用的汇编器是 arm-linux-androideabi-as,用的汇编格式为 GNU ARM,它有自己的语法结构
- Clang 是 LLVM 的一部分,目前(成书时)Clang 在编译时用的汇编器仍是 arm-linux-androideabi-as。因此,无论是 gcc 还是 Clang,汇编工作统一由 arm-linux-androideabi-as 完成,实际上它完成了如下工作:

链接
- 最后一步为链接,即将所有的目标合并,生成最终的可执行程序或动态库,命令如下:
$CC hello.o -fPIE -pie -o hello
- 在它的内部,其实是由 CC 指定的编译器将目标文件传给链接器,从而完成链接工作的
- 注意:除了在编译时要指定
-fPIE,链接时也要指定
- Clang 没有自己的链接器,两个编译器都是调用 arm-linux-androideabi-ld 完成链接工作。因此,实际是进行了如下操作:

-xxx:指额外的链接参数,如库的路径与引用的库,具体的参数可通过如下命令看到:
$CC hello.o -o hello -v










