python 多进程 —— multiprocessing.Process
由于Python是跨平台的,自然也应该提供一个跨平台的多进程支持。
multiprocessing模块就是跨平台版本的多进程模块。
multiprocessing模块提供了一个Process类来代表一个进程对象。
创建子进程时,只需要传入一个执行函数和函数的参数,创建一个Process实例
start()方法启动,这样创建进程比fork()还要简单。
join()方法可以等待子进程结束后再继续往下运行,通常用于进程间的同步。
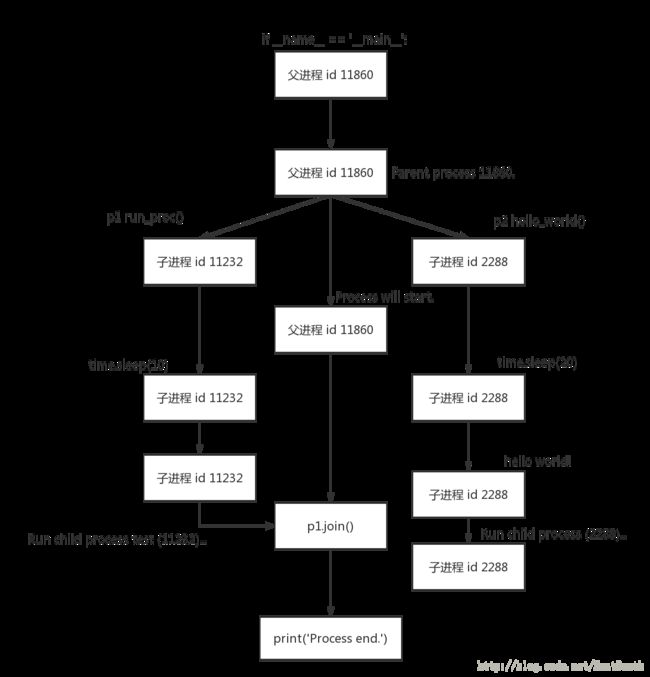
使用 join()
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from multiprocessing import Process
import os
import time
def run_proc(name):
time.sleep(10)
print('Run child process %s (%s)...' % (name, os.getpid()))
def hello_world():
# time.sleep(5)
time.sleep(20)
print('hello world!')
print('Run child process (%s)...' % (os.getpid()))
if __name__ == '__main__':
print ('Parent process %s.' % os.getpid())
p1 = Process(target=run_proc, args=('test',))
p2 = Process(target=hello_world)
print 'Process will start.'
p1.start()
p2.start()
p1.join()
print('Process end.')输出:
Parent process 11860.
Process will start.
Run child process test (11232)...
Process end.
hello world!
Run child process (2288)...
Process finished with exit code 0子进程的开始时间
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from multiprocessing import Process
import os
import time
def run_proc(name):
print(time.time())
time.sleep(10)
print('Run child process %s (%s)...' % (name, os.getpid()))
def hello_world():
print(time.time())
# time.sleep(5)
time.sleep(20)
print('hello world!')
print('Run child process (%s)...' % (os.getpid()))
if __name__ == '__main__':
print ('Parent process %s.' % os.getpid())
p1 = Process(target=run_proc, args=('test',))
p2 = Process(target=hello_world)
print 'Process will start.'
p1.start()
p2.start()
p1.join()
print('Process end.')输出:
Parent process 7220.
Process will start.
1496374096.56
1496374096.56
Run child process test (2196)...
Process end.
hello world!
Run child process (832)...
Process finished with exit code 0可以认为 子进程 p1 与 子进程 p2 同时开始
去掉 join(),使用 map
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from multiprocessing import Process
import os
import time
def run_proc(name):
print(time.time())
time.sleep(10)
print('Run child process %s (%s)...' % (name, os.getpid()))
def hello_world():
print(time.time())
# time.sleep(5)
time.sleep(20)
print('hello world!')
print('Run child process (%s)...' % (os.getpid()))
if __name__ == '__main__':
print ('Parent process %s.' % os.getpid())
p1 = Process(target=run_proc, args=('test',))
p2 = Process(target=hello_world)
print 'Process will start.'
# p1.start()
# p2.start()
# p1.join()
p_list = (p1, p2)
map(Process.start, p_list)
print('Process end.')输出:
Parent process 8580.
Process will start.
Process end.
1496374397.24
1496374397.24
Run child process test (7148)...
hello world!
Run child process (8348)...
Process finished with exit code 0