C++STL学习(9)仿函数(function objects, functor)
注:博客内容均来自于对《C++标准库》侯捷,华中科技大学出版社一书的笔记。转载请注明出处。
所有例程在Red Hat Linux 3.2.2-5版本上编译运行,g++的版本是 g++ (GCC) 3.2.2 20030222。
1、仿函数
仿函数(functor),就是使一个类的使用看上去象一个函数。其实现就是类中实现一个operator(),这个类就有了类似函数的行为,就是一个仿函数类了。例如:
class FunctorType
{
public:
void operator() ()
{
//...
}
};
在调用的时候可以:
FunctorType fo;
fo();
或者是直接使用FunctorType()的方式来进行调用。
相比一般的函数,仿函数的形式显然很复杂。但是仿函数相比普通函数也是有优势的:
1> 仿函数比普通函数更灵活。它可以有很多“状态”(后面举例说明),这是因为仿函数是在类的内部实现的,类中的成员变量可以表示对象的不同状态,这就使得仿函数有了不同的状态。
2> 每个仿函数都有自己的型别。因此可以将仿函数的型别当做template参数来传递,从而指定某种行为模式。
容器型别也会因为仿函数的不同而不同。
3> 在执行的速度上,仿函数通常比函数指针要快。
2、仿函数使用
A> 仿函数当做排序准则
这个其实是前面已经举过的例子,利用自定义排序规则对容器类元素进行排序。
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(string a,string b) :
strFirstname(a),strLastname(b)
{}
public:
string firstname() const
{
return strFirstname;
}
string lastname() const
{
return strLastname;
}
private:
const string strFirstname;
const string strLastname;
};
//仿函数实现自定义排序
class PersonSortCriterion
{
public :
//仿函数
//排序规则为:按照lastname升序排列,lastname相同时按firstname升序排列
bool operator()(const Person &p1, const Person &p2)
{
return (p1.lastname() < p2.lastname() ||
(!(p2.lastname() < p1.lastname()) &&
p1.firstname() < p2.firstname()));
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//类型重定义,并指定排序规则
typedef set PersonSet;
PersonSet col1;
//创建元素,并添加到容器
Person p1("Jay", "Chou");
Person p2("Robin", "Chou");
Person p3("Robin", "Lee");
Person p4("Bob", "Smith");
//向容器中插入元素
col1.insert(p1);
col1.insert(p2);
col1.insert(p3);
col1.insert(p4);
PersonSet::iterator pos;
//输出PersonSet中的所有元素
for(pos = col1.begin(); pos != col1.end(); ++pos)
{
cout<firstname()<< " " << pos->lastname() << endl;
}
cout< B> 有多种状态的仿函数
#include
#icnlude
#icnlude
#icnlude "print.h"
using namespace std;
class IntSequence
{
private:
int value; //记录内部状态的成员变量
public:
IntSequence (int initialValue) : value(initialValue)
{
}
//仿函数
int operator()()
{
return value++;
}
};
int main()
{
list col1;
//产生长度为9的序列,依次插值到col1容器的尾部
generate_n(back_inserter(col1),
9,
IntSequence(1));
//1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
PRINT_ELEMENTS(col1);
//替换col1容器中第2个到倒数第2个,从42开始
generate(++col1.begin(),
--col1.end(),
IntSequence(42));
//1 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 9
PRINT_ELEMENTS(col1);
return 0;
}
特别注意:
仿函数都是传值,而不是传址的。因此算法并不会改变随参数而来的仿函数的状态。
比如:IntSequence seq(1); //从1开始的序列
//从1开始向容器col1中插入9个元素
generate_n(back_inserter(col1), 9, seq);
//仍然从1开始向容器col1中插入9个元素
generate_n(back_inserter(col1), 9, seq);
当然,也有方法来解决上述使仿函数内部状态改变的问题。方法有两种:
1、以引用的方式传递仿函数;
2、运用for_each()算法的返回值。
因为for_each()算法它返回其仿函数。也就是说,我们可以通过返回值可以取得仿函数的状态。
下面来分别举例说明:
A> 以引用的方式传递仿函数
#include
#include
#include
#include "print.h"
using namespace std;
class IntSequence
{
private:
int value;
public:
IntSequence(int initValue) : value(initValue)
{}
int operator()()
{
return value++;
}
};
int main()
{
list col1;
IntSequence seq(1);
//采用引用类型
generate_n >,
int, IntSequence&>(back_inserter(col1),
4,
seq);
//1 2 3 4;
PRINT_ELEMENTS(col1);
//相当于重新构建一个对象从42开始插入4个元素
generate_n(back_inserter(col1),
4,
IntSequence(42));
//1 2 3 4; 42 43 44 45
PRINT_ELEMENTS(col1);
//前面使用的是引用类型,所以seq的内部状态已经被改变了
//插值从上次完成后的5开始
//注意:这次调用仍然使用的是传值类型
generate_n(back_inserter(col1),
4,
seq);
//1 2 3 4; 42 43 44 45; 5 6 7 8
PRINT_ELEMENTS(col1);
//上一次调用使用的是传值类型,所以这次还是从5开始插值
generate_n(back_inserter(col1),
4,
seq);
//1 2 3 4; 42 43 44 45; 5 6 7 8; 5 6 7 8
PRINT_ELEMENTS(col1);
return 0;
}
B> 运用for_each()算法的返回值
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class MeanValue
{
private:
long num;
long sum;
public:
MeanValue(): num(0), sum(0)
{}
void operator() (int elem)
{
num++;
sum += elem;
}
double value()
{
return static_cast(sum) / static_cast(num);
}
};
int main()
{
vector col1;
for(int i=1; i<=8; ++i)
{
col1.push_back(i);
}
MeanValue mv = for_each(col1.begin(), col1.end(), MeanValue());
cout<< "Mean Value: " << mv.value() << endl
return 0;
}
C> 判断式与仿函数
判断式就是返回布尔型的函数或者仿函数。对于STL而言,并非所有返回布尔值的函数都是合法的判断式。这可能会导致很多出人意料的行为,比如下例:#include
#include
#include
#include "print.h"
using namespace std;
class Nth
{
private:
int nth;
int count;
public:
Nth(int n): nth(n), count(0)
{
}
bool operator() (int)
{
return ++count == nth;
}
};
int main()
{
list col1;
for(int i=1; i<=9; ++i)
{
col1.push_back(i);
}
//1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
PRINT_ELEMENTS(col1);
list::iterator pos;
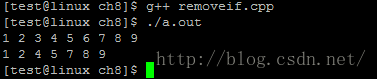
pos = remove_if(col1.begin(), col1.end(), Nth(3));
col1.erase(pos,col1.end());
PRINT_ELEMENTS(col1);
}
这个就和remove_if的实现有关系,remove_if一般的实现方法如下:
template
ForwIter std::remove_if(ForwIter beg, ForwIter end,
Predicate op)
{
beg = find_if(beg, end, op);
if(beg == end) return beg;
else
{
ForwIter next = beg;
return remove_copy_if(++next, end, beg, op);
}
}
这个算法使用find_if()来搜寻应被删除的第一个元素。然而,接下来它使用传进来的判断式op的副本去处理剩余的元素。这时原始状态下的Nth再一次被使用,因此会删除剩余元素中的第3个元素,也就是第6个元素。
使用的时候要尽量避免这种问题的出现。为了获得C++ STL 的保证行为,不应该传递一个“行为取决于拷贝次数或被调用次数”的仿函数。
3、预定义仿函数
STL中已经预定义好了很多仿函数。这些仿函数都包含在头文件如下表所示:
3.1 函数配接器
函数配接器:能够将仿函数和另一个仿函数(或某个值,或某个一般函数)结合起来的仿函数。函数配接器包含在头文件
函数配接器本身也是仿函数,所以函数配接器介意结合仿函数以形成更强大(复杂)的表达式。
下面来看着几种情况:
A> 针对成员函数设计的函数配接器

举例如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
//针对成员函数设计的函数配接器
class Person
{
private:
string name;
public:
Person(){}
Person(string str): name(str)
{}
//输出name
void print() const
{
cout << name << endl;
}
//输出name 和 prefix
void PrintWithPrefix(string prefix) const
{
cout << prefix << name << endl;
}
};
void foo(const vector& col1)
{
//对容器中的每一个元素执行仿函数mem_fun_ref(&Person::print)
for_each(col1.begin(), col1.end(),
mem_fun_ref(&Person::print));
//对容器中的每一个元素执行仿函数bind2nd(mem_fun_ref(&Person::PrintWithPrefix)
for_each(colq.begin(), col1.end(),
bind2nd(mem_fun_ref(&Person::PrintWithPrefix),"Person: "));
}
int main()
{
vector col1;
Person p1("Robin");
Person p2("Romio");
col1.push_back(p1);
col2.push_back(p2);
foo(col1);
return 0;
}
B> 针对一般函数设计的函数配接器
举例如下:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
//针对一般函数设计的函数配接器
bool isThree(int em)
{
if(em == 3)
{
cout<< em << "is 3" < col1;
for(int i=0;i<9;++i)
{
col1.push_back(i);
}
for_each(col1.begin(), col1.end(), not1(ptr_fun(isThree))); //将一般函数isThree转换成仿函数
cout< C> 自定义仿函数使用函数配接器
#ifndef __FOPOW_H
#define __FOPOW_H
#include
#include
template
struct fopow : public std::binary_function
{
T1 operator() (T1 base, T2 exp) const
{
return std::pow(base, exp);
}
};
#endif //__FOPOW_H #include
#include
#include
#include
#include "fopow.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector col1;
for(int i=1; i<=9; ++i)
{
col1.push_back(i);
}
transform(col1.begin(), col1.end(),
ostream_iterator(cout, " "),
bind1st(fopow(), 3));
cout<(cout, " "),
bind2nd(fopow(), 3));
cout< 4、组合型仿函数
仿函数的组合能力非常重要,我们可以使用简单的仿函数来构建出复杂的仿函数。4.1一元组合函数配接器
举一例子:
#ifndef __COMPOSE_H
#define __COMPOSE_H
#include
template
class compose_f_gx_t
: public std::unary_function
{
private:
OP1 op1;
OP2 op2;
public:
compose_f_gx_t(const OP1& o1, const OP2& o2)
: op1(o1), op2(o2)
{}
typename OP1::result_type
operator() (const typename OP2::argument_type& x) const
{
return op1(op2(x));
}
};
template
inline compose_f_gx_t
compose_f_gx(const OP1& o1, const OP2& o2)
{
return compose_f_gx_t(o1, o2);
}
#endif //__COMPOSE_H
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "print.h"
#include "compose11.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector col1;
for(int i=1; i<=9; ++i)
{
col1.push_back(i);
}
PRINT_ELEMENTS(col1);
transform(col1.begin(), col1.end(),
ostream_iterator(cout, " "),
compose_f_gx(bind2nd(multiplies(),5),
bind2nd(plus(),10)));
cout< 第二例:
#ifndef __COMPOSE_H
#define __COMPOSE_H
#include
template
class compose_f_gx_hx_t
: public std::unary_function
{
private:
OP1 op1;
OP2 op2;
OP3 op3;
public:
compose_f_gx_hx_t(const OP1& o1, const OP2& o2,const OP3& o3)
: op1(o1), op2(o2), op3(o3)
{}
typename OP1::result_type
operator() (const typename OP2::argument_type& x) const
{
return op1(op2(x), op3(x));
}
};
template
inline compose_f_gx_hx_t
compose_f_gx_hx(const OP1& o1, const OP2& o2, const OP3& o3)
{
return compose_f_gx_hx_t(o1, o2, o3);
}
#endif //__COMPOSE_H
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "print.h"
#include "compose21.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector col1;
for(int i=1; i<=9; ++i)
{
col1.push_back(i);
}
PRINT_ELEMENTS(col1);
vector::iterator pos;
pos = remove_if(col1.begin(), col1.end(),
compose_f_gx_hx(logical_and(),
bind2nd(greater(), 4),
bind2nd(less(), 7)));
col1.erase(pos, col1.end());
PRINT_ELEMENTS(col1);
cout< 4.2 二元组合函数配接器
#ifndef __COMPOSE_H
#define __COMPOSE_H
#include
template
class compose_f_gx_hy_t
: public std::binary_function
{
private:
OP1 op1; //op1(op2(x),op3(y))
OP2 op2;
OP3 op3;
public:
compose_f_gx_hy_t(const OP1& o1, const OP2& o2, const OP3& o3)
: op1(o1), op2(o2), op3(o3)
{
}
typename OP1::result_type
operator()(const typename OP2::argument_type& x,
const typename OP3::argument_type& y) const
{
return op1(op2(x), op3(y));
}
};
template
inline compose_f_gx_hy_t
compose_f_gx_hy(const OP1& o1, const OP2& o2, const OP3& o3)
{
return compose_f_gx_hy_t(o1, o2, o3);
}
#endif //__COMPOSE_H
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "compose22.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("Internationalization");
string sub("Nation");
string::iterator pos;
pos = search(s.begin(), s.end(),
sub.begin(), sub.end(),
compose_f_gx_hy(equal_to(),
ptr_fun(::toupper),
ptr_fun(::toupper)));
if(pos != s.end())
{
cout<< "\"" << sub << "\" is a part of \"" << s << "\"" << endl;
}
//int sum = compose_f_gx_hy(plus(),20,30);
return 0;
}