Django REST framework之认证
文章目录
- 1. 自定义认证
- 2. 认证流程
- 3. 全局配置认证
- 4. 匿名用户配置
- 5. 内置基本认证
1. 自定义认证
有些API不需要用户登录就可以访问,但是有些需要用户登录才可以访问。Django REST framework中内置认证组件,可以实现需要用户登录才可以访问API的功能。借助内置认证组件,可以方便地自定义认证规则:
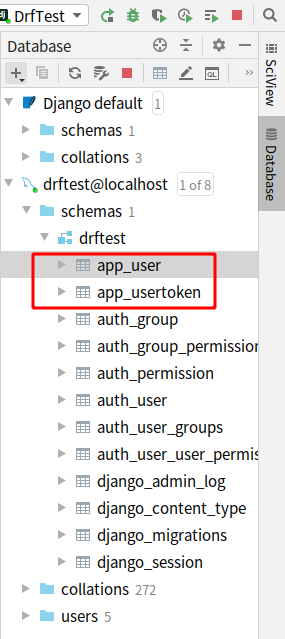
models.py
from django.db import models
# Create your models here.
class User(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32, unique=True)
pwd = models.CharField(max_length=64)
user_type_choices = (
(1, '普通用户'),
(2, 'VIP'),
(3, 'SVIP')
)
user_type = models.IntegerField(choices=user_type_choices)
class UserToken(models.Model):
token = models.CharField(max_length=64)
user = models.OneToOneField(to='User',on_delete=models.CASCADE)
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
'NAME': 'drftest',
'USER': 'root',
'PASSWORD': '123456',
'HOST': 'localhost',
'PORT': '3306'
},
'mysql': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.sqlite3',
'NAME': os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'db.sqlite3'),
}
}
views.py:
import hashlib, time
from rest_framework.views import APIView, exceptions
from .models import User, UserToken
from django.http import JsonResponse
# Create your views here.
def md5(name):
obj = hashlib.md5(bytes(name, encoding='utf-8'))
ctime = str(time.time())
obj.update(bytes(ctime, encoding='utf-8'))
return obj.hexdigest()
class Authenticate:
def authenticate(self, request):
token = request._request.GET.get('token')
print(token)
token_obj = UserToken.objects.filter(token=token).first()
if not token_obj:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed('用户认证失败!')
# 在rest framework内部会将整个两个字段赋值给request,共后续操作使用
# 有三种返回值,None:表示不管;异常:没有通过认证;元组:返回下面两个元素,一个给request.use,一个给request.auth
return (token_obj.user, token_obj) # (request.user,request.auth)
def authenticate_header(self, request):
pass
class AuthView(APIView):
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
用户登录成功后,返回根据时间辍生成的token,每次登录的时间不同,每次生成的token也不同,都被记录到token表中用于与每次请求带着的token进行对比。如果对比成功,则认证成功,是允许访问的。
:param request:
:param args:
:param kwargs:
:return:
"""
ret = {'code': 1000, 'msg': None}
try:
# 需要以form-data的方式提交
name = request._request.POST.get('name')
pwd = request._request.POST.get('pwd')
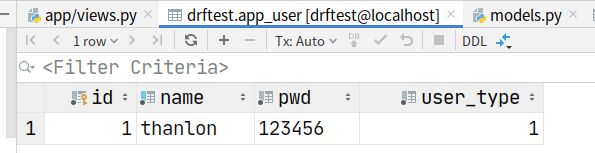
instance = User.objects.filter(name=name, pwd=pwd).first() # User object (1),
print(type(instance)) # ,加不加all()结果一样
print(instance) # User object (1),加不加all()结果一样
if not instance:
ret['code'] = 1001
ret['msg'] = '用户名或密码错误'
else:
token = md5(name=name)
UserToken.objects.update_or_create(user=instance, defaults={'token': token})
ret['token'] = token
except Exception as e:
ret['code'] = 1001
ret['msg'] = '请求异常'
return JsonResponse(ret)
class OrderView(APIView):
# 列表中有写认证类则需要认证,使用自定义的Authenticate类来认证
authentication_classes = [Authenticate, ]
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# request.user
# request.auth
self.dispatch
order_dict = {
1: {
'name': "thanlon",
'age': 24,
'gender': '男',
},
2: {
'name': "kiku",
'age': 26,
'gender': '女',
},
}
# token = request._request.GET.get('token')
ret = {'code': 1000, "msg": None, 'data': None}
try:
ret['data'] = order_dict
except Exception as e:
pass
return JsonResponse(ret)
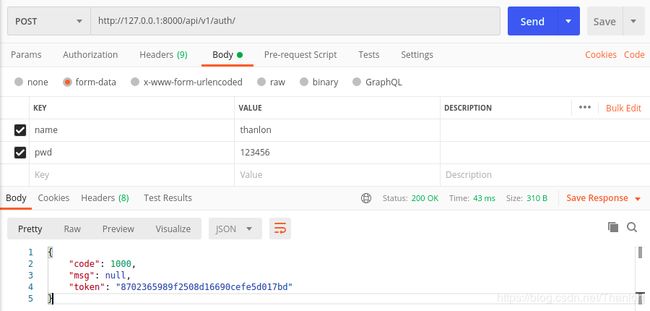
登录时生成的token:

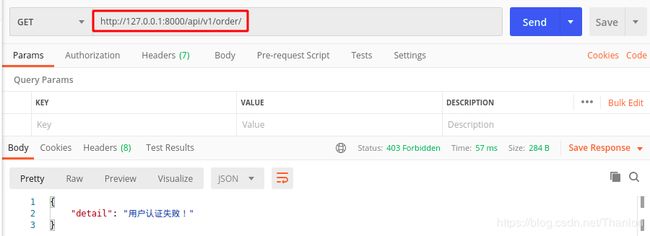
用于用户登录成功生成token的类AuthView不需要认证,OrderView类需要认证,如果不带token访问这个接口会返回失败的认证:
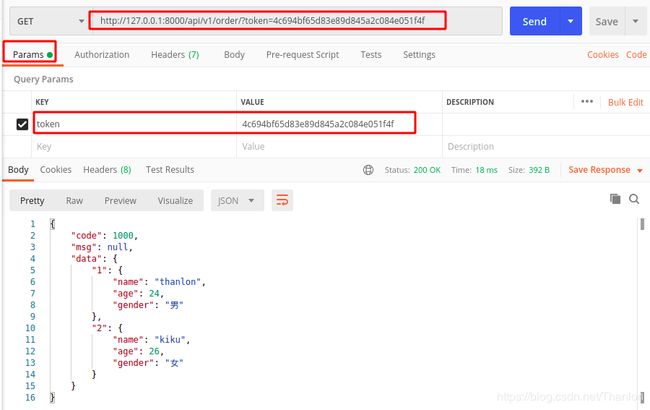
带着这token来访问这个接口,注意这里从url中获取的,要把token放在url上,不要放到请求头发送过去。结果发现可以访问到请求的数据:
也可以放到请求头中发过去,认证类获取token的时候要到请求头中获取。
2. 认证流程
想要更好地使用认证组件,不得不研究和学习下认证组件的实现原理:
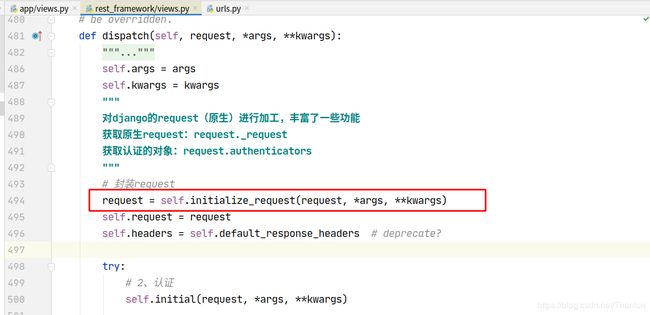
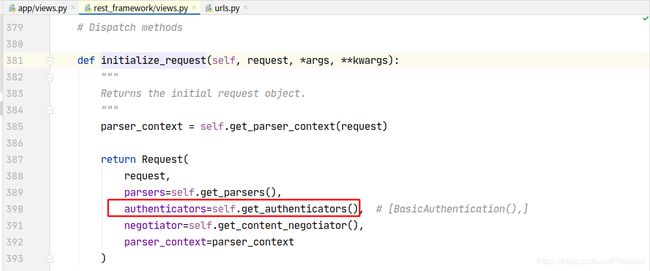
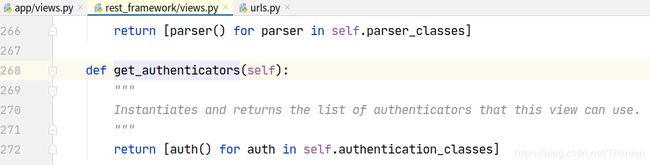
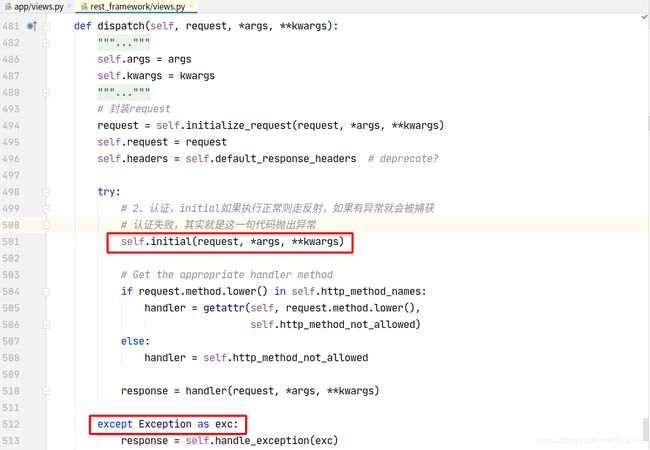
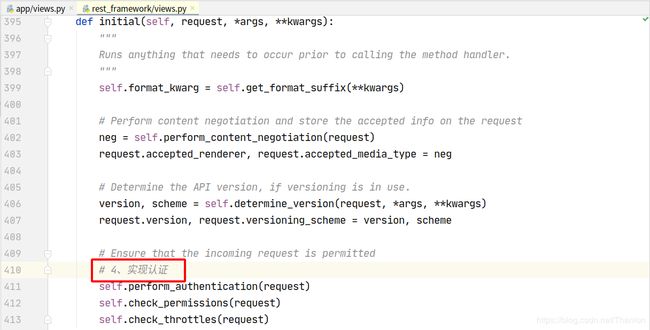
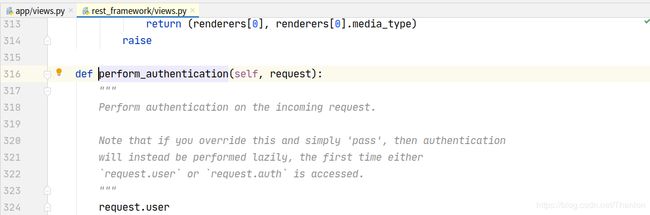
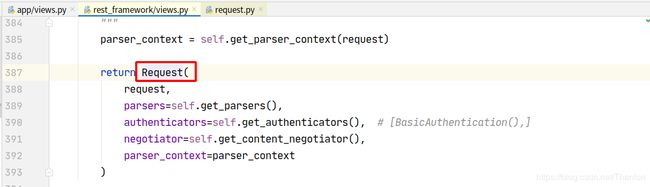
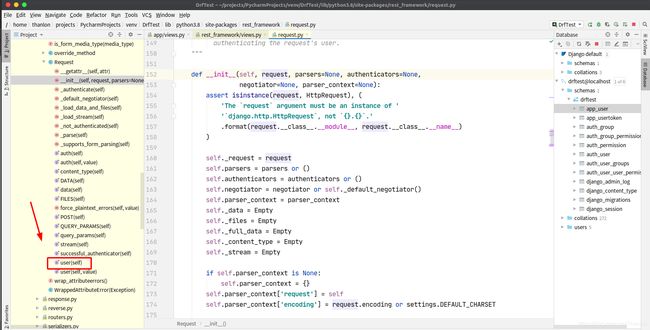
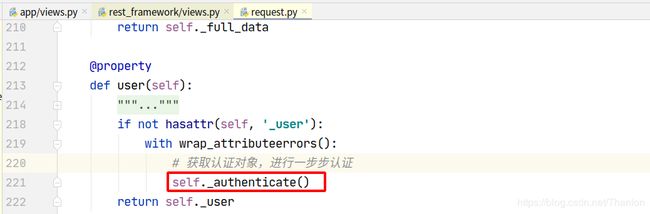
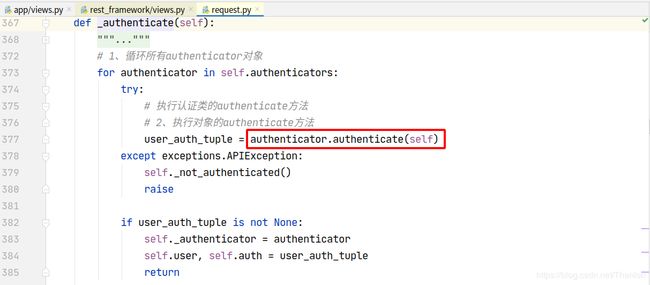
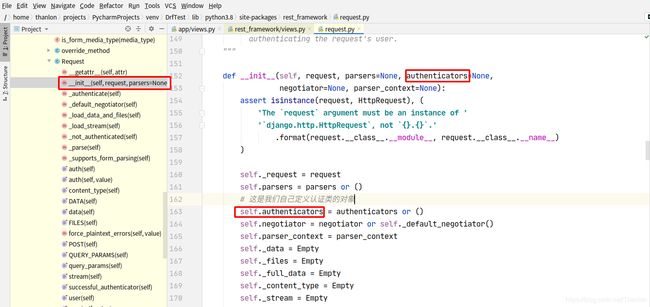
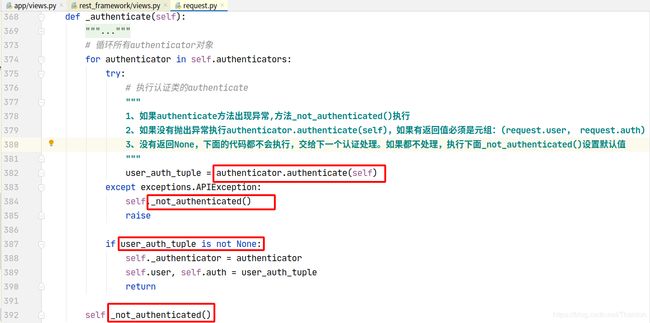

认证可以加多个,一般不会使用到多个认证。列表中的认证类中从第一个开始,如果第一个认证没有做处理,返回None,则交给下一个认证处理:
import hashlib, time
from rest_framework.views import APIView, exceptions
from .models import User, UserToken
from django.http import JsonResponse
# Create your views here.
def md5(name):
obj = hashlib.md5(bytes(name, encoding='utf-8'))
ctime = str(time.time())
obj.update(bytes(ctime, encoding='utf-8'))
return obj.hexdigest()
class Authenticate:
def authenticate(self, request):
token = request._request.GET.get('token')
print(token)
token_obj = UserToken.objects.filter(token=token).first()
if not token_obj:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed('用户认证失败!')
# 在rest framework内部会将整个两个字段赋值给request,共后续操作使用
return (token_obj.user, token_obj) # (request.name,request.auth)
def authenticate_header(self, request):
pass
class FirstAuthenticate:
def authenticate(self, request):
pass
def authenticate_header(self, request):
pass
class AuthView(APIView):
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
print(md5('thanlon'))
ret = {'code': 1000, 'msg': None}
try:
# 需要以form-data的方式提交
name = request._request.POST.get('name')
pwd = request._request.POST.get('pwd')
instance = User.objects.filter(name=name, pwd=pwd).first() # User object (1),
print(type(instance)) # ,加不加all()结果一样
print(instance) # User object (1),加不加all()结果一样
if not instance:
ret['code'] = 1001
ret['msg'] = '用户名或密码错误'
else:
token = md5(name=name)
UserToken.objects.update_or_create(user=instance, defaults={'token': token})
ret['token'] = token
except Exception as e:
ret['code'] = 1001
ret['msg'] = '请求异常'
return JsonResponse(ret)
class OrderView(APIView):
# 需要认证,使用自定义的Authenticate类来认证
authentication_classes = [FirstAuthenticate, Authenticate, ]
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# request.name
# request.auth
self.dispatch
order_dict = {
1: {
'name': "thanlon",
'age': 24,
'gender': '男',
},
2: {
'name': "kiku",
'age': 26,
'gender': '女',
},
}
# token = request._request.GET.get('token')
ret = {'code': 1000, "msg": None, 'data': None}
try:
ret['data'] = order_dict
except Exception as e:
pass
return JsonResponse(ret)
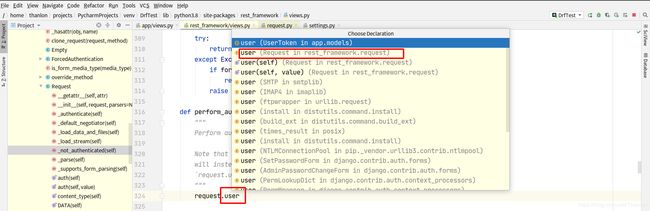
流程概述:
- dispatch
- 封装request
- 获取定义的认证类(全局或者局部),通过列表生成式创建对象
- initial
- perform_authentication
request.user
内部循环认证类执行authenticate方法
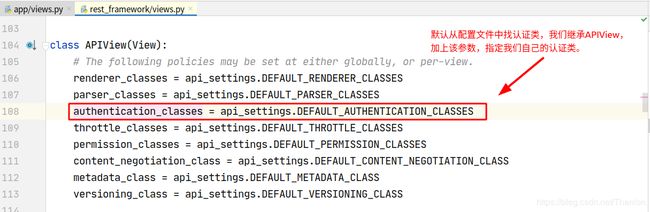
3. 全局配置认证
如果我们不使用自己的认证类,默认使用Django REST framework的认证类,路径在配置文件中。源码中有体现:
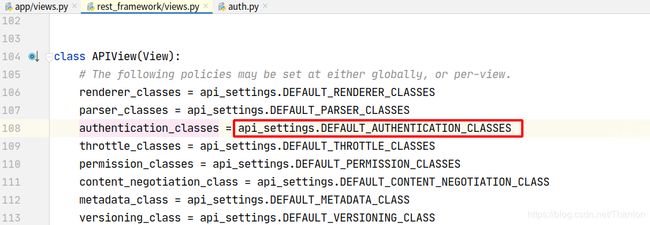
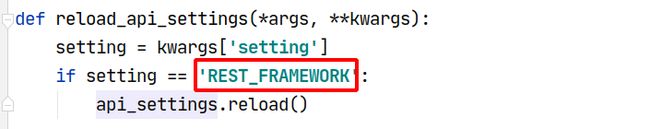
加下来可以这样来配置全局的认证类。在app目录下创建用于存放认证类的 auth,py 文件(认证的类不要写在views中,否则可能引用出现问题),然后在 settings.py 的认证配置项指向这个文件:
settings.py:
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': ['app.auth.FirstAuthenticate', 'app.auth.Authenticate', ]
}
auth.py:
from rest_framework.views import exceptions
from .models import UserToken
class FirstAuthenticate:
def authenticate(self, request):
pass
def authenticate_header(self, request):
pass
class Authenticate:
def authenticate(self, request):
token = request._request.GET.get('token')
print(token)
token_obj = UserToken.objects.filter(token=token).first()
if not token_obj:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed('用户认证失败!')
# 在rest framework内部会将整个两个字段赋值给request,共后续操作使用
return (token_obj.user, token_obj) # (request.name,request.auth)
def authenticate_header(self, request):
pass
这样配置之后全部请求的方法都需要认证,但是有些是需要认证的,比如登录的方法,也需要认证:
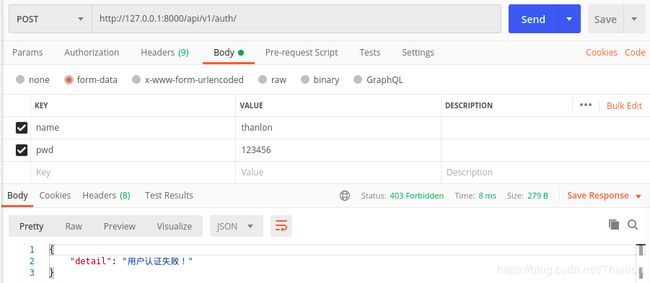
只需要在类中把authentication_classes设置为空列表即可:
class AuthView(APIView):
authentication_classes = []
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
print(md5('thanlon'))
ret = {'code': 1000, 'msg': None}
try:
# 需要以form-data的方式提交
name = request._request.POST.get('name')
pwd = request._request.POST.get('pwd')
instance = User.objects.filter(name=name, pwd=pwd).first() # User object (1),
print(type(instance)) # ,加不加all()结果一样
print(instance) # User object (1),加不加all()结果一样
if not instance:
ret['code'] = 1001
ret['msg'] = '用户名或密码错误'
else:
token = md5(name=name)
UserToken.objects.update_or_create(user=instance, defaults={'token': token})
ret['token'] = token
except Exception as e:
ret['code'] = 1001
ret['msg'] = '请求异常'
return JsonResponse(ret)
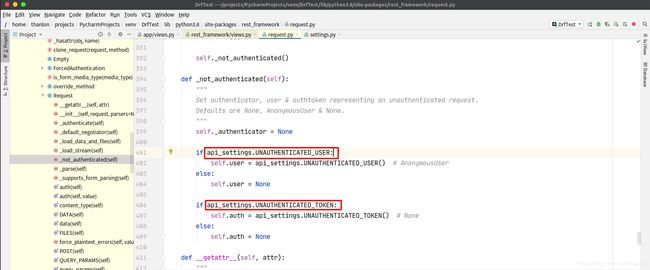
4. 匿名用户配置
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
# 'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': ['app.auth.FirstAuthenticate', 'app.auth.Authenticate', ]
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': ['app.auth.FirstAuthenticate', ], # FirstAuthenticate中什么也没有做
# 'UNAUTHENTICATED_USER': lambda x: '匿名用户',
'UNAUTHENTICATED_USER': None, # request.user = None,默认是AnonymousUser
'UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN': None # request.auth = None
}
5. 内置基本认证
Django REST framework中内置了很多内部认证类,
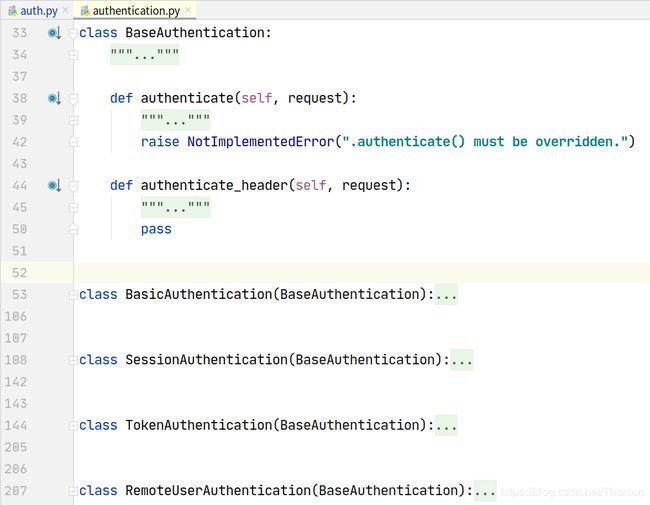
导入这些认证类的方式:
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication,BasicAuthentication, SessionAuthentication,TokenAuthentication, RemoteUserAuthentication
BaseAuthentication类有两种方法,所有的认证类必须继承这个类:
class BaseAuthentication:
"""
All authentication classes should extend BaseAuthentication.
"""
def authenticate(self, request):
"""
Authenticate the request and return a two-tuple of (user, token).
自定义认证操作的方法
"""
raise NotImplementedError(".authenticate() must be overridden.")
def authenticate_header(self, request):
"""
Return a string to be used as the value of the `WWW-Authenticate`
header in a `401 Unauthenticated` response, or `None` if the
authentication scheme should return `403 Permission Denied` responses.
认证失败之后给浏览器返回的响应头,
"""
pass
自定义认证类的时候,必须继承BaseAuthentication,其它的认证类中BasicAuthentication是浏览器对用户名和密码进行base64加密,
HTTP_AUTHORIZATION:basic base64(用户名和密码)
然后放到请求头里面发送给服务端。服务端接收数据后进行处理,之后做一系列的校验:
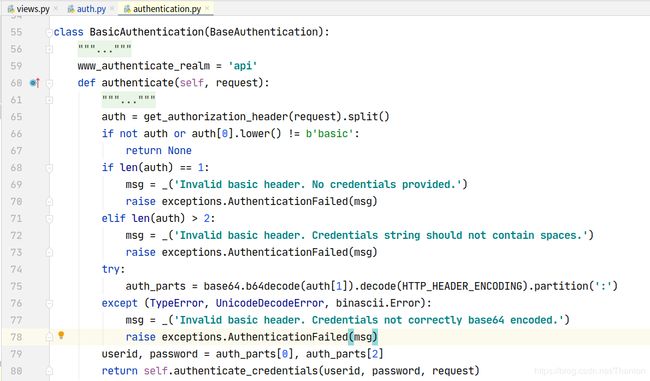
剩下的认证则是基于Django的session和token等实现的认证。