使用 CXF 开发 SOAP 服务
选框架犹如选媳妇,选来选去,最后我还是选了“丑媳妇(CXF)”,为什么是它?因为 CXF 是 Apache 旗下的一款非常优秀的 WS 开源框架,具备轻量级的特性,而且能无缝整合到 Spring 中。
其实 CXF 是两个开源框架的整合,它们分别是:Celtix 与 XFire,前者是一款 ESB 框架,后者是一款 WS 框架。话说早在 2007 年 5 月,当 XFire 发展到了它的鼎盛时期(最终版本是 1.2.6),突然对业界宣布了一个令人震惊的消息:“XFire is now CXF”,随后 CXF 2.0 诞生了,直到 2014 年 5 月,CXF 3.0 降临了。真是 7 年磨一剑啊!CXF 终于长大了,相信在不久的将来,一定会取代 Java 界 WS 龙头老大 Axis 的江湖地位,貌似 Axis 自从 2012 年 4 月以后就没有升级了,这是要告别 Java 界的节奏吗?还是后面有更大的动作?
如何使用 CXF 开发基于 SOAP 的 WS 呢?
这就是我今天要与您分享的内容,重点是在 Web 容器中发布与调用 WS,这样也更加贴近我们实际工作的场景。
在 CXF 这个主角正是登台之前,我想先请出今天的配角 Oracle JAX-WS RI,简称:RI(日),全称:Reference Implementation,它是 Java 官方提供的 JAX-WS 规范的具体实现。
先让 RI 来跑跑龙套,先来看看如何使用 RI 发布 WS 吧!
1. 使用 RI 发布 WS
第一步:整合 Tomcat 与 RI
这一步稍微有一点点繁琐,不过也很容易做到。首先您需要通过以下地址,下载一份 RI 的程序包:
https://jax-ws.java.net/2.2.8/
下载完毕后,只需解压即可,假设解压到 D:/Tool/jaxws-ri 目录下。随后需要对 Tomcat 的config/catalina.properties 文件进行配置:
common.loader=${catalina.base}/lib,${catalina.base}/lib/*.jar,${catalina.home}/lib,${catalina.home}/lib/*.jar,D:/Tool/jaxws-ri/lib/*.jar
注意:以上配置中的最后一部分,其实就是在 Tomcat 中添加一系列关于 RI 的 jar 包。
看起来并不复杂哦,只是对现有的 Tomcat 有所改造而已,当然,您将这些 jar 包全部放入自己应用的 WEB-INF/lib 目录中也是可行的。
第二步:编写 WS 接口及其实现
接口部分:
package demo.ws.soap_jaxws;
import javax.jws.WebService;
@WebService
public interface HelloService {
String say(String name);
}
实现部分:
package demo.ws.soap_jaxws;
import javax.jws.WebService;
@WebService(
serviceName = "HelloService",
portName = "HelloServicePort",
endpointInterface = "demo.ws.soap_jaxws.HelloService"
)
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
public String say(String name) {
return "hello " + name;
}
}
注意:接口与实现类上都标注 javax.jws.WebService 注解,可在实现类的注解中添加一些关于 WS 的相关信息,例如:serviceName、portName 等,当然这是可选的,为了让生成的 WSDL 的可读性更加强而已。
第三步:在 WEB-INF 下添加 sun-jaxws.xml 文件
就是在这个 sun-jaxws.xml 文件里配置需要发布的 WS,其内容如下:
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<endpoints xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/jax-ws/ri/runtime" version="2.0">
<endpoint name="HelloService"
implementation="demo.ws.soap_jaxws.HelloServiceImpl"
url-pattern="/ws/soap/hello"/>
endpoints>
这里仅发布一个 endpoint,并配置三个属性:WS 的名称、实现类、URL 模式。正是通过这个“URL 模式”来访问 WSDL 的,马上您就可以看到。
第四步:部署应用并启动 Tomcat
当 Tomcat 启动成功后,会在控制台上看到如下信息:
2014-7-2 13:39:31 com.sun.xml.ws.transport.http.servlet.WSServletDelegate <init>
信息: WSSERVLET14: JAX-WS servlet 正在初始化
2014-7-2 13:39:31 com.sun.xml.ws.transport.http.servlet.WSServletContextListener contextInitialized
信息: WSSERVLET12: JAX-WS 上下文监听程序正在初始化
哎呦,不错哦!还是中文的。
随后,立马打开您的浏览器,输入以下地址:
http://localhost:8080/ws/soap/hello
如果不出意外的话,您现在应该可以看到如下界面了:
看起来这应该是一个 WS 控制台,方便我们查看发布了哪些 WS,可以点击上面的 WSDL 链接可查看具体信息。
看起来 RI 确实挺好的!不仅仅有一个控制台,而且还能与 Tomcat 无缝整合。但 RI 似乎与 Spring 的整合能力并不是太强,也许是因为 Oracle 是 EJB 拥护者吧。
那么,CXF 也具备 RI 这样的特性吗?并且能够与 Spring 很好地集成吗?
CXF 不仅可以将 WS 发布在任何的 Web 容器中,而且还提供了一个便于测试的 Web 环境,实际上它内置了一个 Jetty。
我们先看看如何启动 Jetty 发布 WS,再来演示如何在 Spring 容器中整合 CXF。
2. 使用 CXF 内置的 Jetty 发布 WS
第一步:配置 Maven 依赖
如果您是一位 Maven 用户,那么下面这段配置相信一定不会陌生:
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>demo.wsgroupId>
<artifactId>soap_cxfartifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8project.build.sourceEncoding>
<cxf.version>3.0.0cxf.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cxfgroupId>
<artifactId>cxf-rt-frontend-jaxwsartifactId>
<version>${cxf.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cxfgroupId>
<artifactId>cxf-rt-transports-http-jettyartifactId>
<version>${cxf.version}version>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
如果您目前还没有使用 Maven,那么就需要从以下地址下载 CXF 的相关 jar 包,并将其放入应用中。
http://cxf.apache.org/download.html
第二步:写一个 WS 接口及其实现
接口部分:
package demo.ws.soap_cxf;
import javax.jws.WebService;
@WebService
public interface HelloService {
String say(String name);
}
实现部分:
package demo.ws.soap_cxf;
import javax.jws.WebService;
@WebService
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
public String say(String name) {
return "hello " + name;
}
}
这里简化了实现类上的 WebService 注解的配置,让 CXF 自动为我们取默认值即可。
第三步:写一个 JaxWsServer 类来发布 WS
package demo.ws.soap_cxf;
import org.apache.cxf.jaxws.JaxWsServerFactoryBean;
public class JaxWsServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JaxWsServerFactoryBean factory = new JaxWsServerFactoryBean();
factory.setAddress("http://localhost:8080/ws/soap/hello");
factory.setServiceClass(HelloService.class);
factory.setServiceBean(new HelloServiceImpl());
factory.create();
System.out.println("soap ws is published");
}
}
发布 WS 除了以上这种基于 JAX-WS 的方式以外,CXF 还提供了另一种选择,名为 simple 方式。
通过 simple 方式发布 WS 的代码如下:
package demo.ws.soap_cxf;
import org.apache.cxf.frontend.ServerFactoryBean;
public class SimpleServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerFactoryBean factory = new ServerFactoryBean();
factory.setAddress("http://localhost:8080/ws/soap/hello");
factory.setServiceClass(HelloService.class);
factory.setServiceBean(new HelloServiceImpl());
factory.create();
System.out.println("soap ws is published");
}
}
注意:以 simple 方式发布的 WS,不能通过 JAX-WS 方式来调用,只能通过 simple 方式的客户端来调用,下文会展示 simple 方式的客户端代码。
第四步:运行 JaxWsServer 类
当 JaxWsServer 启动后,在控制台中会看到打印出来的一句提示。随后,在浏览器中输入以下 WSDL 地址:
http://localhost:8080/ws/soap/hello?wsdl
注意:通过 CXF 内置的 Jetty 发布的 WS,仅能查看 WSDL,却没有像 RI 那样的 WS 控制台。
可见,这种方式非常容易测试与调试,大大节省了我们的开发效率,但这种方式并不适合于生产环境,我们还是需要依靠于 Tomcat 与 Spring。
那么,CXF 在实战中是如何集成在 Spring 容器中的呢?见证奇迹的时候到了!
3. 在 Web 容器中使用 Spring + CXF 发布 WS
Tomcat + Spring + CXF,这个场景应该更加接近我们的实际工作情况,开发过程也是非常自然。
第一步:配置 Maven 依赖
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>demo.wsgroupId>
<artifactId>soap_spring_cxfartifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
<packaging>warpackaging>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8project.build.sourceEncoding>
<spring.version>4.0.5.RELEASEspring.version>
<cxf.version>3.0.0cxf.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-contextartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-webartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cxfgroupId>
<artifactId>cxf-rt-frontend-jaxwsartifactId>
<version>${cxf.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cxfgroupId>
<artifactId>cxf-rt-transports-httpartifactId>
<version>${cxf.version}version>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
第二步:写一个 WS 接口及其实现
接口部分:
package demo.ws.soap_spring_cxf;
import javax.jws.WebService;
@WebService
public interface HelloService {
String say(String name);
}
实现部分:
package demo.ws.soap_spring_cxf;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@WebService
@Component
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
public String say(String name) {
return "hello " + name;
}
}
需要在实现类上添加 Spring 的 org.springframework.stereotype.Component 注解,这样才能被 Spring IOC 容器扫描到,认为它是一个 Spring Bean,可以根据 Bean ID(这里是 helloServiceImpl)来获取 Bean 实例。
第三步:配置 web.xml
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd"
version="3.0">
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring.xmlparam-value>
context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListenerlistener-class>
listener>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>cxfservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.apache.cxf.transport.servlet.CXFServletservlet-class>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>cxfservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/ws/*url-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
web-app>
所有带有 /ws 前缀的请求,将会交给被 CXFServlet 进行处理,也就是处理 WS 请求了。目前主要使用了 Spring IOC 的特性,利用了 ContextLoaderListener 加载 Spring 配置文件,即这里定义的 spring.xml 文件。
第四步:配置 Spring
配置 spring.xml:
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="demo.ws"/>
<import resource="spring-cxf.xml"/>
beans>
以上配置做了两件事情:
- 定义 IOC 容器扫描路径,即这里定义的
demo.ws,在这个包下面(包括所有子包)凡是带有Component的类都会扫描到 Spring IOC 容器中。 - 引入
spring-cxf.xml文件,用于编写 CXF 相关配置。将配置文件分离,是一种很好的开发方式。
第五步:配置 CXF
配置 spring-cxf.xml:
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:jaxws="http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/jaxws.xsd">
<jaxws:server id="helloService" address="/soap/hello">
<jaxws:serviceBean>
<ref bean="helloServiceImpl"/>
jaxws:serviceBean>
jaxws:server>
beans>
通过 CXF 提供的 Spring 命名空间,即 jaxws:server,来发布 WS。其中,最重要的是 address 属性,以及通过jaxws:serviceBean 配置的 Spring Bean。
可见,在 Spring 中集成 CXF 比想象的更加简单,此外,还有一种更简单的配置方法,那就是使用 CXF 提供的endpoint 方式,配置如下:
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:jaxws="http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/jaxws.xsd">
<jaxws:endpoint id="helloService" implementor="#helloServiceImpl" address="/soap/hello"/>
beans>
使用 jaxws:endpoint 可以简化 WS 发布的配置,与 jaxws:server 相比,确实是一种进步。
注意:这里的 implementor 属性值是 #helloServiceImpl,这是 CXF 特有的简写方式,并非是 Spring 的规范,意思是通过 Spring 的 Bean ID 获取 Bean 实例。
同样,也可以在 Spring 中使用 simple 方式来发布 WS,配置如下:
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:simple="http://cxf.apache.org/simple"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://cxf.apache.org/simple http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/simple.xsd">
<simple:server id="helloService" serviceClass="#helloService" address="/soap/hello">
<simple:serviceBean>
<ref bean="#helloServiceImpl"/>
simple:serviceBean>
simple:server>
beans>
可见,simple:server 与 jaxws:server 的配置方式类似,都需要配置一个 serviceBean。
比较以上这三种方式,我个人更加喜欢第二种,也就是 endpoint 方式,因为它够简单!
至于为什么 CXF 要提供如此之多的 WS 发布方式?我个人认为,CXF 为了满足广大开发者的喜好,也是为了向前兼容,所以这些方案全部保留下来了。
第六步:启动 Tomcat
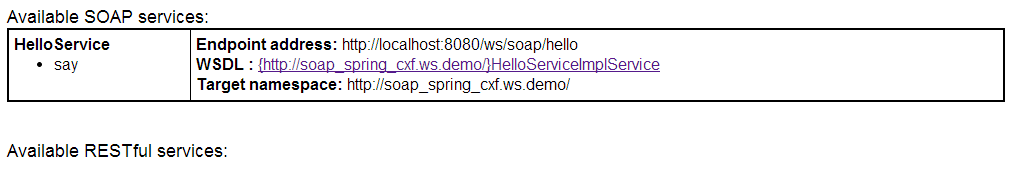
将应用部署到 Tomcat 中,在浏览器中输入以下地址可进入 CXF 控制台:
http://localhost:8080/ws
通过以上过程,可以看出 CXF 完全具备 RI 的易用性,并且与 Spring 有很好的可集成性,而且配置也非常简单。
同样通过这个地址可以查看 WSDL:
http://localhost:8080/ws/soap/hello?wsdl
注意:紧接在 /ws 前缀后面的 /soap/hello,其实是在 address="/soap/hello" 中配置的。
现在已经成功地通过 CXF 对外发布了 WS,下面要做的事情就是用 WS 客户端来调用这些 endpoint 了。
您可以不再使用 JDK 内置的 WS 客户端,也不必通过 WSDL 打客户端 jar 包,因为 CXF 已经为您提供了多种 WS 客户端解决方案,根据您的口味自行选择吧!
4. 关于 CXF 提供的 WS 客户端
方案一:静态代理客户端
package demo.ws.soap_cxf;
import org.apache.cxf.jaxws.JaxWsProxyFactoryBean;
public class JaxWsClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JaxWsProxyFactoryBean factory = new JaxWsProxyFactoryBean();
factory.setAddress("http://localhost:8080/ws/soap/hello");
factory.setServiceClass(HelloService.class);
HelloService helloService = factory.create(HelloService.class);
String result = helloService.say("world");
System.out.println(result);
}
}
这种方案需要自行通过 WSDL 打客户端 jar 包,通过静态代理的方式来调用 WS。这种做法最为原始,下面的方案更有特色。
方案二:动态代理客户端
package demo.ws.soap_cxf;
import org.apache.cxf.endpoint.Client;
import org.apache.cxf.jaxws.endpoint.dynamic.JaxWsDynamicClientFactory;
public class JaxWsDynamicClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JaxWsDynamicClientFactory factory = JaxWsDynamicClientFactory.newInstance();
Client client = factory.createClient("http://localhost:8080/ws/soap/hello?wsdl");
try {
Object[] results = client.invoke("say", "world");
System.out.println(results[0]);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这种方案无需通过 WSDL 打客户端 jar 包,底层实际上通过 JDK 的动态代理特性完成的,CXF 实际上做了一个简单的封装。与 JDK 动态客户端不一样的是,此时无需使用 HelloService 接口,可以说是货真价实的 WS 动态客户端。
方案三:通用动态代理客户端
package demo.ws.soap_cxf;
import org.apache.cxf.endpoint.Client;
import org.apache.cxf.endpoint.dynamic.DynamicClientFactory;
public class DynamicClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DynamicClientFactory factory = DynamicClientFactory.newInstance();
Client client = factory.createClient("http://localhost:8080/ws/soap/hello?wsdl");
try {
Object[] results = client.invoke("say", "world");
System.out.println(results[0]);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这种方案与“方案三”类似,但不同的是,它不仅用于调用 JAX-WS 方式发布的 WS,也用于使用 simple 方式发布的 WS,更加智能了。
方案四:基于 CXF simple 方式的客户端
package demo.ws.soap_cxf;
import org.apache.cxf.frontend.ClientProxyFactoryBean;
public class SimpleClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClientProxyFactoryBean factory = new ClientProxyFactoryBean();
factory.setAddress("http://localhost:8080/ws/soap/hello");
factory.setServiceClass(HelloService.class);
HelloService helloService = factory.create(HelloService.class);
String result = helloService.say("world");
System.out.println(result);
}
}
这种方式仅用于调用 simple 方式发布的 WS,不能调用 JAX-WS 方式发布的 WS,这是需要注意的。
方案五:基于 Spring 的客户端
方法一:使用 JaxWsProxyFactoryBean
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd">
<bean id="factoryBean" class="org.apache.cxf.jaxws.JaxWsProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="serviceClass" value="demo.ws.soap_spring_cxf.HelloService"/>
<property name="address" value="http://localhost:8080/ws/soap/hello"/>
bean>
<bean id="helloService" factory-bean="factoryBean" factory-method="create"/>
beans>
方法二:使用 jaxws:client(推荐)
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:jaxws="http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/jaxws.xsd">
<jaxws:client id="helloService"
serviceClass="demo.ws.soap_spring_cxf.HelloService"
address="http://localhost:8080/ws/soap/hello"/>
beans>
客户端代码:
package demo.ws.soap_spring_cxf;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-client.xml");
HelloService helloService = context.getBean("helloService", HelloService.class);
String result = helloService.say("world");
System.out.println(result);
}
}
谈不上那种方案更加优秀,建议根据您的实际场景选择最为合适的方案。
5. 总结
通过阅读本文,相信您已经大致了解了 CXF 的基本用法。可独立使用,也可与 Spring 集成;可面向 API 来编程,也可使用 Spring 配置;发布 WS 的方式有多种,调用 WS 的方式同样也有多种。
尤其是 Spring + CXF 这对搭档,让发布 WS 更加简单,只需以下四个步骤:
- 配置 web.xml
- 编写 WS 接口及其实现
- 配置 CXF 的 endpoint
- 启动 Web 容器