在cmd、C#中使用命令为PostgreSQL创建数据库、登录角色,并对数据库进行备份和恢复
在cmd中执行时,由于需要用到的工具都在PostgreSQL的安装目录下的bin文件夹中,所以首先要进入到此目录中。例如,我的安装路径为D:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\9.5\bin,因此要先进入D盘,然后进入此目录(所有图片点击放大查看看得更清楚):
我在Krpano学习:C#操作命令提示符(cmd),在C#中生成全景中写过如何在C#中操作cmd,此处再重新写出代码:
using System.Diagnostics; //一定要引用这个命名空间
private Process theProcess = new Process();
string arguments = ""; //cmd中执行的语句
theProcess.StartInfo.FileName = "***.exe"; //cmd中执行命令的应用程序的完整路径
theProcess.StartInfo.Arguments = arguments;
theProcess.EnableRaisingEvents = true;//为true时为进程终止时激发System.Diagnostics.Process.Exited事件,默认为false
//进程退出时执行
theProcess.Exited += (object sender, EventArgs args) => //Lambda表达式
{
//执行内容
……
};
theProcess.Start();//启动程序
theProcess.WaitForExit();//等待进程退出
在MSDN上有对Process这个类的详细解说和例子。
当进程结束后不执行任何操作则不需要theProcess.EnableRaisingEvents、theProcess.Exited和theProcess.WaitForExit()。
一、创建登录角色
PostgreSQL中有两个创建角色的方法,分别为"CREATE USER"和"CREATE ROLE",它们的区别在于前者带有LOGIN属性,可以登录数据库,而后者不可以。具体看PostgreSQL角色与用户管理介绍。
以我们常用的"CREATE USER"为例:
1、在cmd中创建数登录角色
在安装目录下有一个应用程序:createuser.exe,这是专门用来创建用户的,首先看帮助了解它的用法:
createuser.exe --help
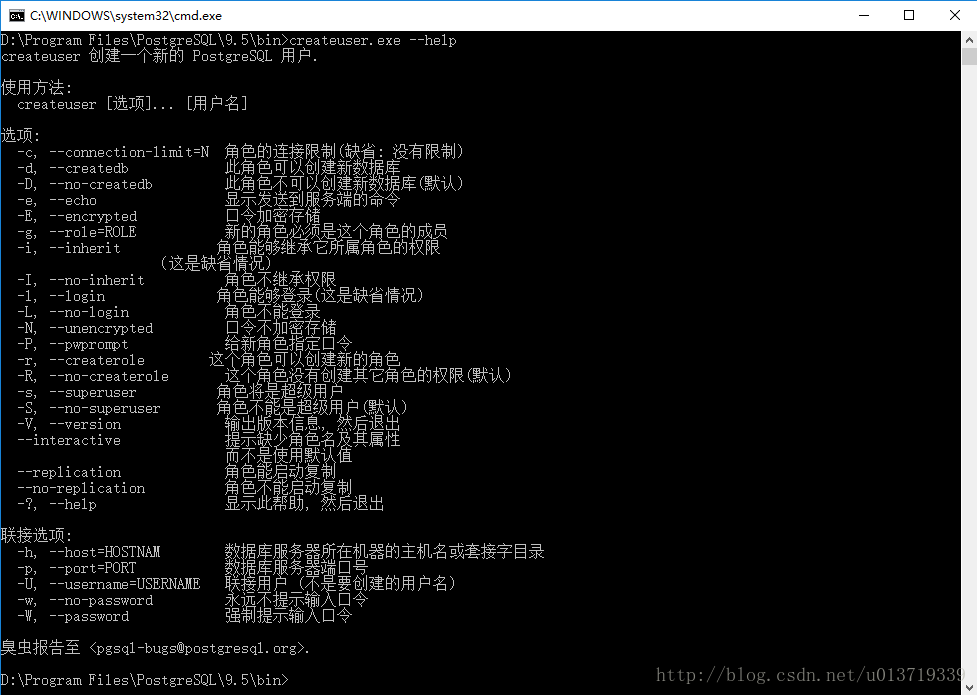
上面图片中,-c是缩写,–connection-limit是全称,=N表示也可以用N表示这个功能。
图片下面的联接选项表示要联接的PostgreSQL服务器属性,如果不填则默认为本机服务器(即-h localhost -p 5432),但是默认的username并不是服务器自己建立的postgres,而是电脑用户名(即windows用户名),因此,在输入命令时一定要指定username,当没有要特定指出的username时就用postgres(这是一个superuser,不用键入密码)。
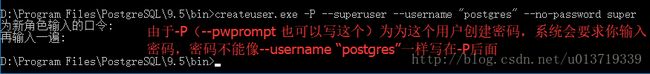
(1)根据使用方法创建一个超级用户superuser(命令执行后如果成功不会有任何反应):
// --superuser表示这是一个超级用户
// --username "postgres"表示连接数据库的用户为postgres
// --no-password表示不提示输入口令(postgres没有密码,因而不用提示输入口令)
createuser.exe --superuser --username "postgres" --no-password superuser
(2)根据使用方法创建一个有密码的超级用户super:
// -P(也可以用--pwprompt)表示这个用户有密码,系统随后会提示输入并确认口令,口令(密码)输入时不会显示
createuser.exe -P --superuser --username "postgres" --no-password super
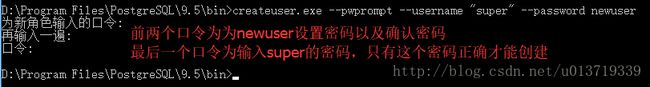
(3)根据刚刚创建的super创建一个有密码的普通用户newuser:
createuser.exe --pwprompt --username "super" --password newuser
2、在C#中创建登录角色
根据最上面的代码,可以看到只要给arguments和FileName赋对应的值就可以了,所以创建superuser的代码为(在C#中,两对双引号代表字符串中为双引号):
private Process theProcess = new Process();
string arguments = @"--superuser --username ""postgres"" --no-password superuser";
theProcess.StartInfo.FileName = @"D:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\9.5\bin\createuser.exe";
theProcess.StartInfo.Arguments = arguments;
theProcess.Start();//启动程序
二、创建数据库
1、在cmd中创建数据库
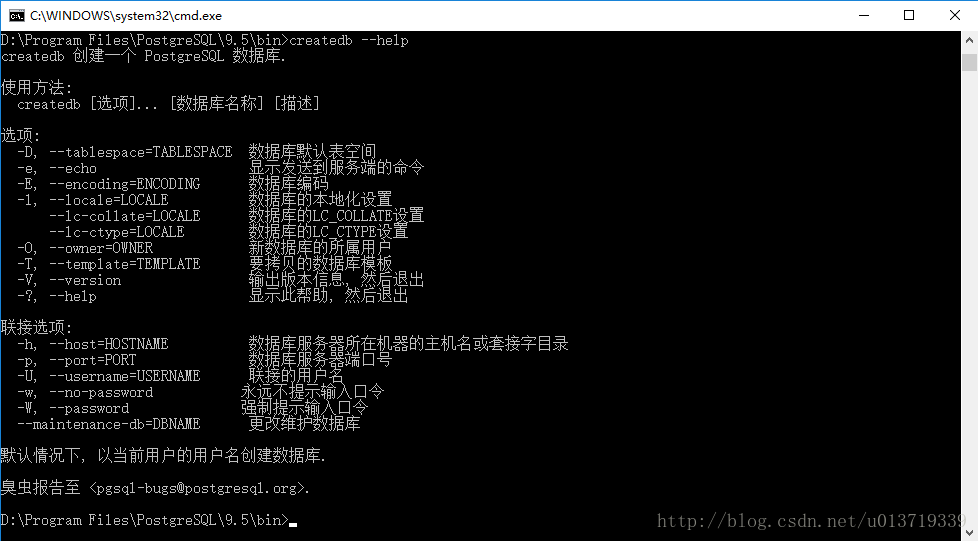
在安装目录下有一个应用程序:createdb.exe,这是专门用来创建用户的,首先看帮助了解它的用法:
createdb.exe --help
(1)根据使用方法创建一个数据库datatb(命令执行后如果成功不会有任何反应):
// 这个数据库属于postgres
// 使用postgres连接PostgreSQL服务器(这个用户没有密码)
createdb.exe --owner "postgres" --username "postgres" --no-password datatb
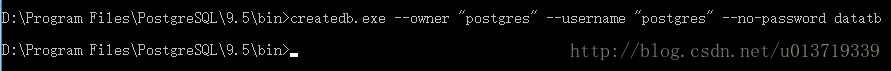
创建数据库的时间比创建用户的时间要长一点,需要稍等片刻才能成功。
2、在C#中创建数据库
private Process theProcess = new Process();
string arguments = @"--owner ""postgres"" --username ""postgres"" --no-password datatb";
theProcess.StartInfo.FileName = @"D:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\9.5\bin\createdb.exe";
theProcess.StartInfo.Arguments = arguments;
theProcess.Start();//启动程序
三、数据库备份
在数据库中进行可视化备份时,在最上方可以看到执行的备份语句。将这句话直接复制下来,在cmd中就可以执行(注意不要重名)。
1、在cmd中进行数据库备份
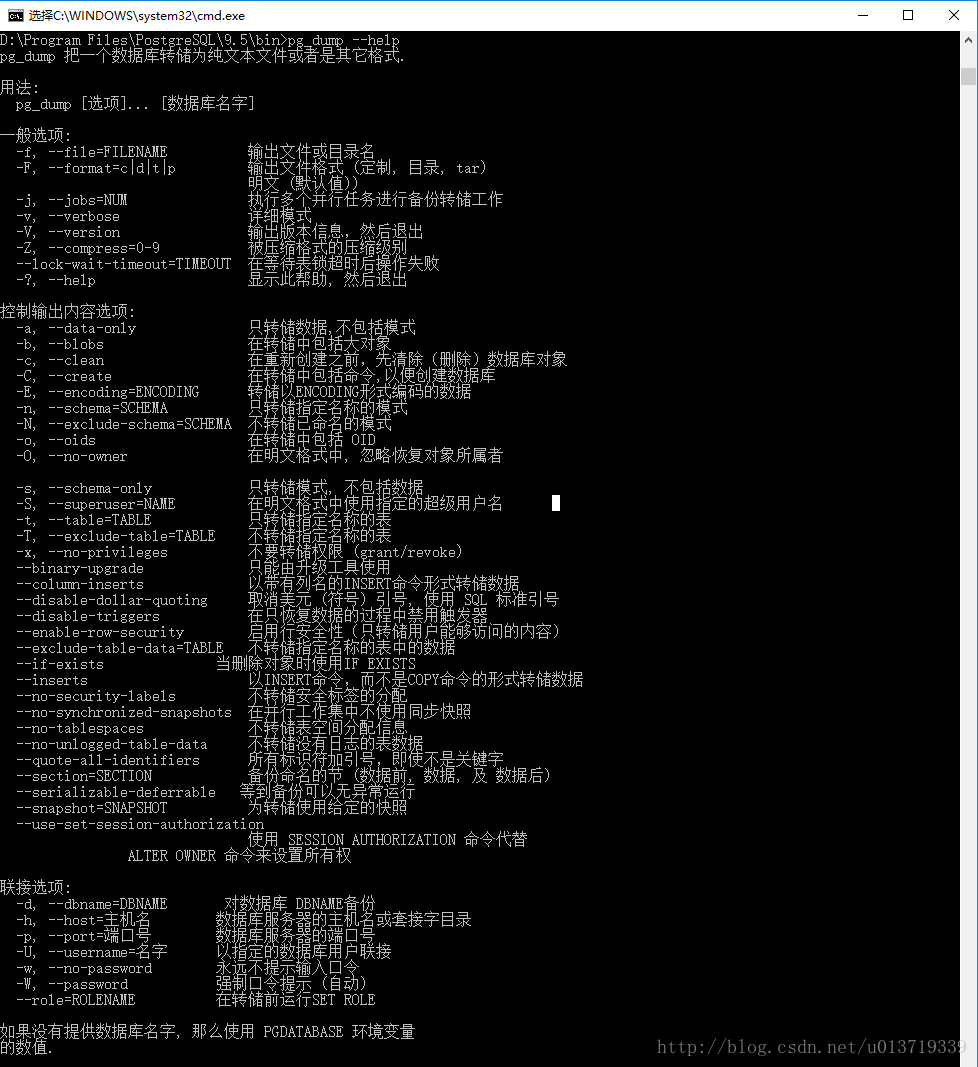
在安装目录下有一个应用程序:pg_dump.exe,这是专门用来备份的,首先看帮助了解它的用法:
pg_dump.exe --help
(1)根据使用方法备份数据库datatb(命令执行后会显示备份的每一个条目):
// 使用postgres连接本地服务器
// --format 输出格式为custom,即默认格式(后缀名为.backup,如果自己的输出名字里未加后缀名则不会出现后缀),明文输出
// --blobs 在转储时包括大对象(PostgreSQL存储二进制数据的一种独有类型)
// --verbose 详细模式
// --file "E:/datatb" 将数据库备份到E盘根目录下,备份文件的名字为datatb(如果要输出后缀名则要写成datadb.backup),如果不指定路径则备份到bin目录下
pg_dump.exe --host localhost --port 5432 --username "postgres" --no-password --format custom --blobs --verbose --file "E:/datatb" "datatb"
2、在C#中进行数据库备份
private Process theProcess = new Process();
string arguments = @"--host localhost --port 5432 --username ""postgres"" --no-password --format custom --blobs --verbose --file ""E:/datatb"" ""datatb""";
theProcess.StartInfo.FileName = @"D:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\9.5\bin\pg_dump.exe";
theProcess.StartInfo.Arguments = arguments;
theProcess.Start();//启动程序
四、数据库恢复
在数据库中进行可视化恢复时,在最上方可以看到执行的恢复语句。将这句话直接复制下来,在cmd中就可以执行。
注意,被恢复的数据库一定要先存在!也就是一定要先在服务器中创建一个数据库(数据库名就是你希望的名字),然后再将文件恢复进这个数据库。恢复成功后数据库名字还是你取的那个名字。
1、在cmd中进行数据库恢复
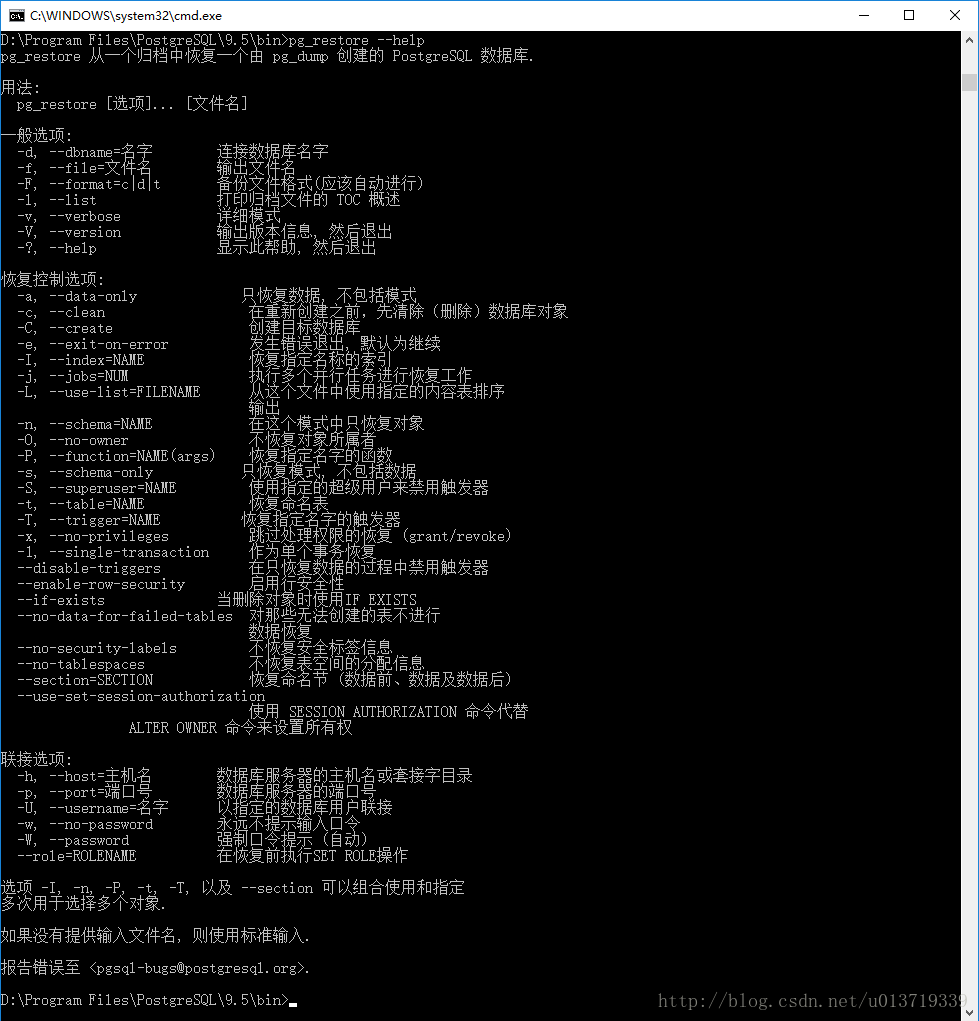
在安装目录下有一个应用程序:pg_restore.exe,这是专门用来恢复的,首先看帮助了解它的用法:
pg_restore.exe --help
(1)根据使用方法将datatb恢复到数据库newtb(命令执行后会显示恢复的每一个条目):
// 使用postgres连接本地服务器
// --dbname "newtb" 被恢复的数据库(在服务器中要存在)
// -- 在转储时包括大对象(PostgreSQL存储二进制数据的一种独有类型)
// --verbose 详细模式
// 要恢复的数据库为E盘下的datatb
pg_restore.exe --host localhost --port 5432 --username "postgres" --dbname "newtb" --no-password --verbose "E:\datatb"
2、在C#中进行数据库恢复
private Process theProcess = new Process();
string arguments = @"--host localhost --port 5432 --username ""postgres"" --dbname ""newtb"" --no-password --verbose ""E:\datatb""";
theProcess.StartInfo.FileName = @"D:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\9.5\bin\pg_restore.exe";
theProcess.StartInfo.Arguments = arguments;
theProcess.Start();//启动程序
五、在C#中进行用户创建、数据库创建和数据库恢复的综合应用
前面指出了,在恢复数据库时,服务器中必须要有一个空数据库的存在,否则恢复失败。因此,使用恢复语句前要先使用创建数据库语句,如果数据库所属的用户不存在,那么还要先创建用户,因此语句执行顺序为:
创建用户——创建数据库——恢复数据库
1、在cmd中执行命令
d: && cd D:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\9.5\bin && createuser.exe --superuser --username "postgres" --no-password superuser && createdb.exe --owner "superuser" --username "postgres" --no-password datatb && pg_restore.exe --host localhost --port 5432 --username "postgres" --dbname "datatb" --no-password --verbose "E:\datatb"
假设要恢复的数据库在E盘下,名为datatb,那么打开cmd后直接复制上面的语句即执行完所有步骤。它的构成为:
//进入D盘(此处大小写无关)
d:
//进入PostgreSQL安装路径下,也即为以下3个应用程序所在目录
cd D:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\9.5\bin
//创建用户superuser
createuser.exe --superuser --username "postgres" --no-password superuser
//创建属于superuser的数据库datatb
createdb.exe --owner "superuser" --username "postgres" --no-password datatb
//将E盘下的datatb恢复到服务器中刚刚创建的datatb中
pg_restore.exe --host localhost --port 5432 --username "postgres" --dbname "datatb" --no-password --verbose "E:\datatb"
代码中的&&是批处理语句符号,表示前一个命令成功后执行下一个命令。类似的还有||(表示前一个命令失败后执行下一个命令)、|(表示不论前一个命令成功失败都执行下一个命令)。
2、在C#中执行命令
根据前面在C#中执行命令的方法,最直观的方法是实例化三个Process类,然后执行。根据上面在cmd中执行命令的综合应用来看,实例化一个Process类,调用cmd.exe并传入这个综合参数(因为这三个命令调用的是三个不同的应用程序),是最方便的方法:
private Process theProcess = new Process();
string arguments = @"d: && cd D:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\9.5\bin && createuser.exe --superuser --username ""postgres"" --no-password superuser && createdb.exe --owner ""superuser"" --username ""postgres"" --no-password datatb && pg_restore.exe --host localhost --port 5432 --username ""postgres"" --dbname ""datatb"" --no-password --verbose ""E:\KPJD""";
theProcess.StartInfo.FileName = "cmd.exe";
theProcess.StartInfo.Arguments = arguments;
theProcess.Start();//启动程序
但是你会发现命令并没有被执行,cmd的命令文件位置也一直是这个C#程序的bin目录下的Debug。这是因为Process.StartInfo.Arguments的作用为获取或设置启动应用程序时要使用的一组命令行参数,也就是说此时theProcess这个进程资源并不是由FileName 这个应用或文件决定,而是由FileName和Arguments共同决定的,显然上面设的这两个参数并不能关联一个进程资源。
那么,如果只创建一个简单的cmd.exe进程,而把其他操作放到进程创建成功后会如何呢?就像我们手动操作cmd一样:先打开cmd(即成功创建cmd.exe进程),然后输入命令。看下面这段代码:
string argpostgre = @"d: && cd D:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\9.5\bin";
string arguser = @"createuser.exe --superuser --username ""postgres"" --no-password superuser";
string argatadbase = @"createdb.exe --owner ""superuser"" --username ""postgres"" --no-password datatb";
string argrecovery = @"pg_restore.exe --host localhost --port 5432 --username ""postgres"" --dbname ""datatb"" --no-password --verbose ""E:\datatb""";
Process theProcess = new Process();
theProcess.StartInfo.FileName = "cmd.exe"; //设置要启动的应用程序
theProcess.StartInfo.UseShellExecute = false; //设置是否使用操作系统shell启动进程,当要使用标准输入输出流时要设置为false
theProcess.StartInfo.RedirectStandardInput = true; //指示应用程序是否从StandardInput流中读取
theProcess.StartInfo.RedirectStandardOutput = true; //将应用程序的输入写入到StandardOutput流中
theProcess.StartInfo.RedirectStandardError = true; //将应用程序的错误输出写入到StandarError流中
theProcess.StartInfo.CreateNoWindow = false; //是否在新窗口中启动进程
string strOutput = null;
try
{
theProcess.Start();
//将cmd命令写入StandardInput流中。在命令最后要执行退出进程命令:exit,如果不执行它,后面调用ReadToEnd()方法会假死
theProcess.StandardInput.WriteLine(argpostgre + " && " + arguser + " && " + argatadbase + " & exit");
//strOutput = theProcess.StandardOutput.ReadToEnd(); //读取所有输出的流的所有字符
theProcess.WaitForExit(); //无限期等待,直至进程退出
//恢复数据库的命令没有在创建数据库后立刻执行,而是退出进程后使用最开始的方法重新关联进程
//这是因为pg_restore这个应用程序不会自动退出,所以如果用流输入命令,则进程会一直停留在pg_restore.exe中而导致程序永远不会结束
theProcess.StartInfo.FileName = @"D:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\9.5\bin\pg_restore.exe";
theProcess.StartInfo.Arguments = @"--host localhost --port 5432 --username ""postgres"" --dbname ""datatb"" --no-password --verbose ""E:\datatb""";
theProcess.Start();
theProcess.Close(); //释放进程,关闭进程
//Console.WriteLine(strOutput); //输出进程的输出内容
}
catch (Exception e)
{
strOutput = e.Message;
}