springMVC学习总结(三)数据绑定
一、springMVC的数据绑定,常用绑定类型有:
1、servlet三大域对象:
- HttpServletRequest
- HttpServletResponse
HttpSession
2、Model的方式
- 类型:
Model
@Controller public class Demo01Controller { @RequestMapping(value = "test.action") public String test(Model md){ md.addAttribute("name","xujie"); return "test"; } }ModelMap
@Controller public class Demo01Controller { @RequestMapping(value = "test.action") public String test(ModelMap mp){ mp.addAttribute("name","xujie"); return "test"; //字符串是返回页面的页面名 } }ModelAndView
@Controller public class Demo01Controller { @RequestMapping(value = "test.action") public ModelAndView test(ModelAndView mv){ mv.addObject("name","xujie"); mv.setViewName("test"); return mv; } }
前台页面jsp编码
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@page isELIgnored="false" %>Hello World 1、姓名:${requestScope.name }
- 总结:
- Model和ModelMap类型的model,都要在参数列表中声明。
- ModelAndView可以不用在参数列表中声明,但是最后的跳转页面一定要通过
ModelAndView.setViewName()的方式跳转,否则页面可以成功跳转,但是取不到后台设置的值。
3、绑定简单数据类型
-
示例一:
//在处理器形参位置声明简单数据类型,处理器直接获取 @Controller public class Demo01Controller { @RequestMapping(value = "test.action") public String test(String name){ System.out.println("获取到前台的值是:"+name); return "test"; } }- 支持的简单绑定类型:
- 整型(int、Integer)
- 字符串(String)
- 单精度(Float、float)
- 双精度(Double、double)
- 布尔型(true、false)
- @RequestParam用法:
- @RequestParam 有三个常用属性值:
- value:绑定参数的变量名
- defaultValue:如果没有传这个值,默认取值
required:该变量是否必须要有
示例:@Controller public class Demo01Controller { @RequestMapping(value = "test.action") public String test(@RequestParam(value = "name",defaultValue = "xujie",required = false) String name){ System.out.println("name="+name); return "test"; } }
- @RequestParam 有三个常用属性值:
4、绑定pojo(简单的java对象)类型
Student类:(pojo)
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
get/set...
}Controller类:
@Controller
public class Demo01Controller {
@RequestMapping(value = "test.action",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String test(Student stu){
System.out.println("学生姓名:"+stu.getName());
System.out.println("学生年龄:"+stu.getAge());
return "test";
}
}
+ *这里我是用的postman做的请求测试,所以此处不列举前台是如何发送请求的了,只要是post请求,并且参数名分别为name和age就可以获取到;*5、绑定包装对象(对象里面有对象)
Courses类(pojo):
package com.springMVC.pojo;
public class Courses {
private String coursesName;
private String teacher;
get/set...
}Courses类(pojo):
package com.springMVC.pojo;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private Courses courses;
get/set...
}Controller类:
@Controller
public class Demo01Controller {
@RequestMapping(value = "test.action",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String test(Student stu){
System.out.println("学生姓名:"+stu.getName());
System.out.println("学生年龄:"+stu.getAge());
System.out.println("课程名称"+stu.getCourses().getCoursesName());
System.out.println("课程老师"+stu.getCourses().getTeacher());
return "test";
}
}6、绑定数组(以字符串数组为例)
直接绑定数组类型参数
Controller类:
@Controller
public class Demo01Controller {
@RequestMapping(value = "test.action",method = RequestMethod.POST)
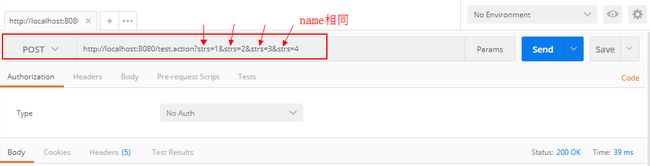
public String test(String[] strs){
for (String str:strs ) {
System.out.println(str);
}
return "test";
}
}接口测试:
通过pojo属性的方式绑定数组
pojo类:
package com.springMVC.pojo;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private Courses courses;
private String[] friends;
get/set...
}Controller类:
@Controller
public class Demo01Controller {
@RequestMapping(value = "test.action",method = RequestMethod.POST)
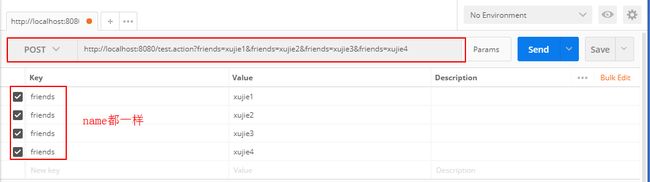
public String test(Student stu){
String[] friends = stu.getFriends();
for (String str:friends ) {
System.out.println(str);
}
return "test";
}
}接口测试
7、绑定List
接收页面数据
接收页面数据的时候,list必须声明为某一个pojo的属性才可以接收到
pojo类:
package com.springMVC.pojo;
import java.util.List;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private Courses courses;
private List friends; //pojo的list
get/set...
} Controller类:
@Controller
public class Demo01Controller {
@RequestMapping(value = "test.action",method = RequestMethod.POST)
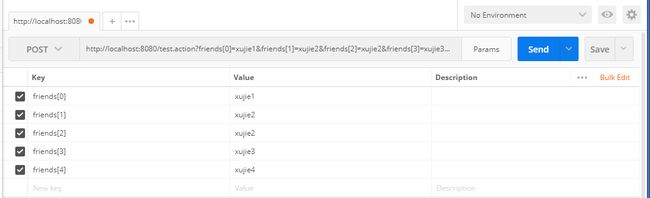
public String test(Student student){
List friends = student.getFriends();
for (String str : friends) {
System.out.println(str);
}
return "test";
}
} 接口测试:
向页面传递数据
Controller类:
此处以ModelMap的方式向页面传递数据
@Controller
public class Demo01Controller {
@RequestMapping(value = "test.action",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String test(ModelMap modelMap){
//ModelMap modelMap = new ModelMap();
Student student = new Student();
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.add("xujie1");
list.add("xujie2");
list.add("xujie3");
list.add("xujie4");
student.setFriends(list);
student.setName("yuanxiliu");
modelMap.addAttribute("student",student);
return "test";
}
} jsp页面:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@page isELIgnored="false" %>
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
Hello World
${friend}<%--循环输出List--%>
8、绑定Map
跟list类似,同样必须定义成某个pojo的属性才可以绑定数据:
pojo类:
package com.springMVC.pojo;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private Courses courses;
private HashMap parents;
get/set...
} Controller类:
@Controller
public class Demo01Controller {
@RequestMapping(value = "test.action",method = RequestMethod.POST)
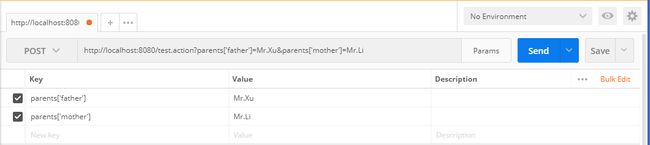
public String test(Student student){
String father = student.getParents().get("father");
String mother = student.getParents().get("mother");
System.out.println("父亲是:"+father);
System.out.println("母亲是:"+mother);
return "test";
}
}