SpringBoot 之设计API接口实现统一格式返回
文章目录
- 前言
- 接口交互
- 返回格式
- CODE状态码
- Message信息提示
- Data数据体
- 控制层Controller
- 返回体统一处理
- @ExceptionHandler
- @ModelAttribute
- @RestControllerAdvice
- 标记注解类
- 请求拦截器
- 重写返回体
- 重写Controller
前言
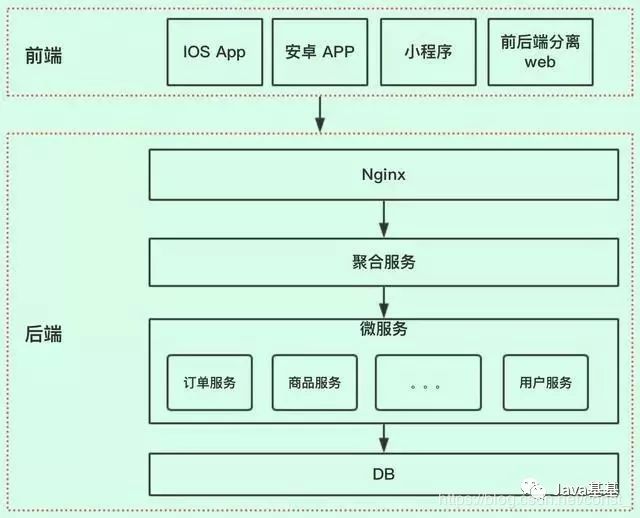
在移动互联网,分布式、微服务盛行的今天,现在项目绝大部分都采用的微服务框架,前后端分离方式。
前后端的工作职责越来越明确。
接口交互
前端和后端进行交互,前端按照约定请求URL路径,并传入相关参数,后端服务器接收请求,进行业务处理,返回数据给前端。
返回格式
后端返回给前端我们一般用JSON体方式,定义如下:
{
#返回状态码
code:integer,
#返回信息描述
message:string,
#返回值
data:object
}
CODE状态码
code返回状态码可以参考HTTP请求返回的状态码来设计,这样的好处就把错误类型归类到某个区间内。
#1000~1999 区间表示参数错误
#2000~2999 区间表示用户错误
#3000~3999 区间表示接口异常
这样前端开发人员在得到返回值后,根据状态码就可以知道,大概什么错误,再根据message相关的信息描述,可以快速定位。
Message信息提示
错误信息提示。一般和code状态码一起设计,如:
public enum ResultCode {
/*成功状态码*/
SUCCESS(1, "成功"),
SYSTEM_ERROR(400, "系统繁忙,请稍后重试"),
/*参数错误: 1001-1999 */
PARAM_IS_INVALID(1001, "参数无效"),
PARAM_IS_BLANK(1002, "参数为空"),
PARAM_TYPE_BIND_ERROR(1003, "参数类型错误"),
PARAM_NOT_COMPLETE(1004, "参数缺失"),
/*用户错误: 2001-2999*/
USER_NOT_LOGGED_IN(2001, "用户未登录,访问的路径需要验证,请登录"),
USER_LOGIN_ERROR(2002, "账号不存在或密码错误"),
USER_ACCOUNT_FORBIDDEN(2003, "账号已被禁用"),
USER_NOT_EXIST(2004, "用户不存在"),
USER_HAS_EXISTED(2005, "用户已存在");
private Integer code;
private String message;
ResultCode(Integer code, String message) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
public Integer code() {
return this.code;
}
public String message(){
return this.message;
}
}
Data数据体
返回数据体,JSON格式,返回体类Result。
// 成功结果实体
@Data
public class Result implements Serializable {
private Integer code;
private String message;
private Object data;
public void setResultCode(ResultCode resultCode) {
this.code = resultCode.code();
}
public static Result success() {
Result result = new Result();
result.setResultCode(ResultCode.SUCCESS);
return result;
}
public static Result success(Object data) {
Result result = new Result();
result.setResultCode(ResultCode.SUCCESS);
result.setData(data);
return result;
}
public static Result failure(Integer code, String message) {
Result result = new Result();
result.setCode(code);
result.setMessage(message);
return result;
}
}
// 错误结果实体
@Data
public class ErrorResult {
private Integer code;
private String message;
public ErrorResult(Integer code, String message){
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
}
控制层Controller
后端会在controller层处理业务请求,并返回给前端。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoController {
@GetMapping("/ok")
public Result ok() {
return Result.success("ok...");
}
}
返回体统一处理
@ExceptionHandler
接受请求处理方法抛出的异常。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoController {
@GetMapping("/ok")
public String ok2() {
int i = 10 / 0;
return "ok..";
}
@ExceptionHandler(RuntimeException.class)
public String runtimeExceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest request, final Exception e, HttpServletResponse response) {
return e.getMessage();
}
}
@ModelAttribute
往请求的Model里加数据。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoController {
@GetMapping("/ok")
public String ok(ModelMap modelMap) {
return modelMap.get("name").toString();
}
@GetMapping("/ok2")
public String ok2(@ModelAttribute("name") String name) {
return name;
}
@ModelAttribute
public void model(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("name", "James");
}
}
@RestControllerAdvice
将@ExceptionHandler和@ModelAttribute注解应用到所有的控制器上。是@ControllerAdvice和@ResponseBody注解的结合体。
因为@RestControllerAdvice被元注解@Component标记,所以它也是可以被组件扫描扫到并放入Spring容器的。
如果只想对一部分控制器添加通知,比如某个包下的控制器,可以这样写:

如果只想对某几个控制器添加通知,可以这样写:
![]()
标记注解类
用来标记方法的返回值,是否需要包装。
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Documented
public @interface ResponseResult {
}
请求拦截器
拦截请求,是否此请求返回的值需要包装,其实就是运行的时候,解析@ResponseResult注解。
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
/**
* 响应处理拦截器
*/
@Component
public class ResponseResultInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
public static final String RESPONSE_RESULT_ANN = "RESPONSE_RESULT_ANN";
/**
* 解析控制器类或方法上是否有@ResponseResult注解,如果有表示返回值需要包装
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
if (handler instanceof HandlerMethod) {
final HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler;
final Class<?> clazz = handlerMethod.getBeanType();
final Method method = handlerMethod.getMethod();
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(ResponseResult.class)) {
// 判断是否在类对象上加了注解
request.setAttribute(RESPONSE_RESULT_ANN, clazz.getAnnotation(ResponseResult.class));
} else if (method.isAnnotationPresent(ResponseResult.class)) {
// 判断是否在方法上加了注解
request.setAttribute(RESPONSE_RESULT_ANN, method.getAnnotation(ResponseResult.class));
}
}
return true;
}
}
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class WebAppConfigurer implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Autowired
private ResponseResultInterceptor responseResultInterceptor;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
InterceptorRegistration registration = registry.addInterceptor(responseResultInterceptor);
// 拦截所有请求
registration.addPathPatterns("/**");
// 添加不拦截路径
registration.excludePathPatterns("/login", "/error", "/logout", "/login.html");
}
}
此代码核心思想,就是获取此请求,是否需要返回值包装,设置一个属性标记。
重写返回体
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.core.MethodParameter;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.http.server.ServerHttpRequest;
import org.springframework.http.server.ServerHttpResponse;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseBodyAdvice;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
public class ResponseResultHandler implements ResponseBodyAdvice<Object> {
public static final String RESPONSE_RESULT_ANN = "RESPONSE_RESULT_ANN";
/**
* 捕获 CustomException异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(CustomException.class)
public ErrorResult runtimeExceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest request, final Exception e,
HttpServletResponse response) {
CustomException customException = (CustomException) e;
return new ErrorResult(customException.getCode(), customException.getMessage());
}
/**
* 捕获 Exception异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ErrorResult exceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest request, final Exception e, HttpServletResponse response) {
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value());
return new ErrorResult(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value(), e.getMessage());
}
/**
* 获取请求中是否有包装注解标记,没有直接返回,如果有则需要重写返回体
*/
@Override
public boolean supports(MethodParameter methodParameter, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType) {
ServletRequestAttributes sra = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = sra.getRequest();
// 获取请求是否有包装标记
ResponseResult responseResultAnn = (ResponseResult) request.getAttribute(RESPONSE_RESULT_ANN);
return responseResultAnn == null ? false : true;
}
/**
* 重写返回体
*/
@Override
public Object beforeBodyWrite(Object body, MethodParameter returnType, MediaType selectedContentType,
Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> selectedConverterType, ServerHttpRequest request,
ServerHttpResponse response) {
log.info("进入返回体处理");
if (body instanceof ErrorResult) {
ErrorResult errorResult = (ErrorResult) body;
return Result.failure(errorResult.getCode(), errorResult.getMessage());
}
return Result.success(body);
}
}
上面代码首先做了全局的异常处理,然后判断是否需要返回值包装,如果需要就直接包装。
重写Controller
最后在控制器类上或者方法体上加上@ResponseResult注解,就可以进行返回值统一处理了。
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoController {
@ResponseResult
@GetMapping("/ok2")
public String ok2() {
try {
int i = 10 / 0;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CustomException(ResultCode.SYSTEM_ERROR.code(), ResultCode.SYSTEM_ERROR.message());
}
return "ok..";
}
}
参考:
Java项目构建基础:统一结果,统一异常,统一日志