MyBatis的resultMap简单使用
MyBatis的resultMap简单使用
在工作中,我们经常遇到一对多,一对一,多对一等查询情况。例如一个主订单记录应该包含多个明细单,一个老师对应多个学生等。mybatis为我们提供了强大的map映射。这边我做个记录,方便日后复习。如若有错,欢迎指出。
-
-
- MyBatis的resultMap简单使用
- 1.实体类
- 2.Sql语句
- 3.一对多查询
- 3.1第一种方式:多表关联查询
- 3.2第二种方式:多表单独查询
- 4.多对一查询
- 5.总结
- MyBatis的resultMap简单使用
-
1.实体类
首先贴两个类。一个老师类,一个学生类。假设情况是,一个老师对应多个学生,一个学生只能师从一个老师。
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Teacher {
/** 主键 */
private Integer id;
/** 老师姓名 */
private String name;
/** 老师年龄 */
private Integer age;
/*
* 该老师所管理的学生集合
*/
private List studentList;
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Student {
/** 主键 */
private Integer id;
/** 老师id */
private Integer tId;
/** 学生姓名 */
private String name;
/** 学生年龄 */
private Integer age;
/*
* 学生对应的老师对象
*/
private Teacher teacher;
} 2.Sql语句
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
`t_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '老师id',
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '学生姓名',
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '学生年龄',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=31 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
CREATE TABLE `teacher` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '老师姓名',
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '老师年龄',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;3.一对多查询
要求:根据老师主键id,查询出老师记录,并组装该老师管理的学生集合。
3.1第一种方式:多表关联查询
关联查询就是select * from table1,table2 where xxx=xxx….这种
<select id="selectByPrimaryKey" resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">
select
t.id as tId,
t.name as tName,
t.age as tAge,
s.id as sId,
s.t_id as sTId,
s.name as sName,
s.age as sAge
from teacher t,student s
where t.id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER} and t.id=s.t_id
select>
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.yckj.springboot.api.teacher.entity.Teacher">
<id column="tId" property="id" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result column="tName" property="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result column="tAge" property="age" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<collection property="studentList" ofType="com.yckj.springboot.api.student.entity.Student">
<id column="sId" property="id"/>
<result column="sTId" property="tId"/>
<result column="sName" property="name"/>
<result column="sAge" property="age"/>
collection>
resultMap>@Test
public void queryTest(){
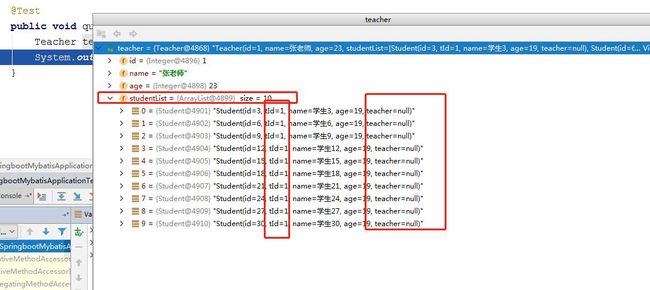
Teacher teacher = teacherMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1);
System.out.println(teacher);
}以下是查询结果:
可以看到,查询出来的Teacher对象里面的学生集合也正确的进行了封装。而studentList里面的每个Student里面的teacher为null是因为我在collection标签中没有配置teacher对象的映射规则。
该方式需要多表关联查询,且无法实现延迟加载。
3.2第二种方式:多表单独查询
多表单独查询,就是先查一个表,获取某条记录的某个列的值,然后把这个值传给另外一个查询sql。
例如,先查老师记录,获取了某一条老师记录的id主键的值,然后把该值传给查询学生的sql,领其t_id=传入的id
<select id="selectByPrimaryKey" resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">
select id,name,age from teacher where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}
select>
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.yckj.springboot.api.teacher.entity.Teacher">
<id column="id" property="id" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result column="name" property="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result column="age" property="age" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<collection property="studentList" --属性名-->
ofType="com.yckj.springboot.api.student.entity.Student"
column="id"
select="selectStudentByTId"/>
resultMap>
<select id="selectStudentByTId" resultType="com.yckj.springboot.api.student.entity.Student">
select id,t_id as tId,name,age from student where t_id=#{id}
select>@Test
public void queryTest(){
Teacher teacher = teacherMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1);
System.out.println(teacher);
}以下是查询结果:
可以看到,查询结果和第一种多表关联查询效果是一样的。
第二种方式的多表单独查询支持延迟加载
若要实现延迟加载的效果,处理使用单独查询,我们还需要在mybatis-config.xml中配置缓存机制
<settings> <setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J"/> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/> settings>另外,侵入式缓存,延迟加载等相关的介绍和配置在我另一片文章Mybatis的使用与Spring的整合的第28,29点
4.多对一查询
要求:根据学生主键查询学生记录,并组装该学生对应的老师对象
多对一查询也可以分为多表关联查询和多表单独查询,这边我就只写多表单独查询了,写发和上面的是一样的。
<select id="selectByPrimaryKey" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select id, t_id, name, age from student where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}
select>
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.yckj.springboot.api.student.entity.Student">
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="t_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="tId"/>
<result column="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name"/>
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age"/>
<association property="teacher"
javaType="com.yckj.springboot.api.teacher.entity.Teacher"
select="selectTeacherById"
column="t_id"/>
resultMap>
<select id="selectTeacherById" resultType="com.yckj.springboot.api.teacher.entity.Teacher">
select id, name, age from teacher where id = #{t_id,jdbcType=INTEGER}
select>@Test
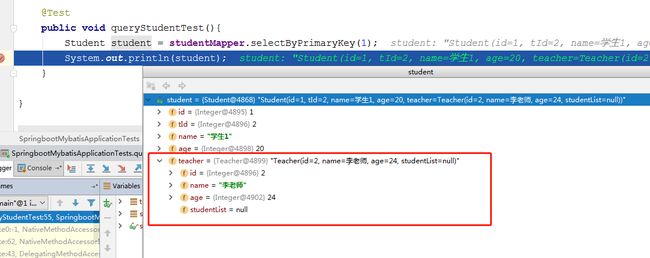
public void queryStudentTest(){
Student student = studentMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1);
System.out.println(student);
}查询结果:
可以看到,已经正确的进行了封装。student里面的teacher对象的studentList为null是因为我并未配置映射规则。
接下来我们修改一下,改成查询所有的学生,看看返回的是否正常。
<select id="selectAll" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select id, t_id, name, age from student
select>@Repository
public interface StudentMapper {
//省略。。。。
//新增方法
List selectAll();
} @Test
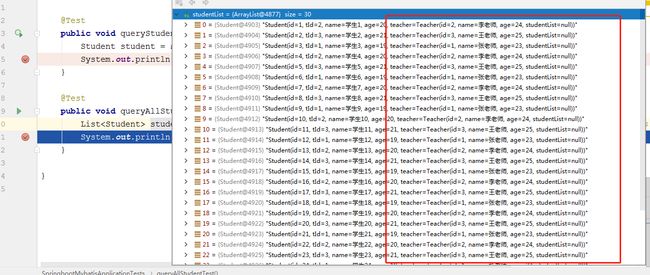
public void queryAllStudentTest(){
List studentList = studentMapper.selectAll();
System.out.println(studentList);
} 查询结果:
可以看到,结果正常封装返回。
5.总结
我们发现不管是是多对于,一对多,多对多,主要还是resultMap映射规则的编写。
- 如果是id主键类的摄影用id标签
- 如果是普通列就用result标签
- 如果是集合类型的就用collection标签,然后指定ofType
- 如果是单个对象类型的就用association标签,然后指定javaType
- 其他标签的使用……
所以,多多练习。其实也挺简单的。
还有自关联查询,例如分类表,插入某一个分类id,查询该分类下即子孙分类等(主要是map的自调用)。
参考我的另一篇Mybatis的使用与Spring的整合第27点。