07.Thymeleaf使用与语法最全详解(精)
Spring Boot模板引擎thymeleaf
- 什么是Thymeleaf?
- 为什么要使用Thymeleaf?
- 使用Thymeleaf步骤
- Thymeleaf语法详细
- 源码分析
- th属性
1、Thymeleaf是什么?
简单说, Thymeleaf 是一个跟 Velocity、FreeMarker 类似的模板引擎,它可以完全替代 JSP 。
从代码层次上讲:Thymeleaf是一个java类库,他是一个xml/xhtml/html5的模板引擎,可以作为mvc的web应用的view层。
2、为什么要使用Thymeleaf?
使用jsp的弊端
- 项目目录结构繁琐
- 页面不简洁
- jsp内置错误页面不能覆盖springboot默认的错误页面
- 只能打成war不能打成jar
- 内置的jetty服务器不支持jsp
Thymeleaf的优点:
- 开箱即用,它提供标准和spring标准两种方言,可以直接套用模板实现JSTL、 OGNL表达式效果,避免每天套模板、改jstl、改标签的困扰。同时开发人员也可以扩展和创建自定义的方言;
- Thymeleaf 提供spring标准方言和一个与 SpringMVC 完美集成的可选模块,可以快速的实现表单绑定、属性编辑器、国际化等功能。
- 有网无网的情况下模版页面都可以执行,美工的页面拿来就可以用,相对jsp减少了额外的标签,页面也更加简洁。
注意:Spring-boot支持FreeMarker、Thymeleaf、jsp、veocity 。但是对freemarker和thymeleaf的支持最好,不推荐使用jsp
3、使用Thymeleaf
① jar包依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>
② 在application.properties中配置thymleaf
spring.thymeleaf.mode = LEGACYHTML5
这个配置不是必须的,但是spring.thymeleaf.mode的默认值是HTML5,其实是一个很严格的检查,改为LEGACYHTML5可以得到一个可能更友好亲切的格式要求。
4、Thymeleaf语法
①源码分析
根据以下路径找到源码
![]()
查看部分源码:
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.thymeleaf"
)
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING;
//规则前缀
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
//规则后缀
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";
...
}
查看以上源码,thymeleaf的自动配置了规则前缀和后缀,所以只要我们把html页面放在calsspath:/templates/下,thymeleaf就能自动渲染。
案例:
新建Controller
@Controller
public class ThController {
@RequestMapping("/success")
public String success(){
//前缀:classpath:/templates/ success 后缀.html
return "success";
}
}
在resources/templates下新建success.html
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<h1>this is success.htmlh1>
body>
html>
也可以在配置文件中指定自己的模板,这里通过yml配置修改:
spring:
thymeleaf:
prefix: classpath:/templates/
check-template-location: true
cache: false
suffix: .html
encoding: UTF-8
content-type: text/html
mode: HTML5
-
prefix:指定模板所在的目录
-
check-tempate-location: 检查模板路径是否存在
-
cache: 是否缓存,开发模式下设置为false,避免改了模板还要重启服务器,线上设置为true,可以提高性能。
-
encoding&content-type:这个大家应该比较熟悉了,与Servlet中设置输出对应属性效果一致。
-
mode:这个还是参考官网的说明吧,并且这个是2.X与3.0不同。
② th属性
html有的属性,Thymeleaf基本都有,而常用的属性大概有七八个。其中th属性执行的优先级从1~8,数字越低优先级越高。
-
th:text :设置当前元素的文本内容,相同功能的还有th:utext,两者的区别在于前者不会转义html标签,后者会。优先级不高:order=7
-
th:value:设置当前元素的value值,类似修改指定属性的还有th:src,th:href。优先级不高:order=6
-
th:each:遍历循环元素,和th:text或th:value一起使用。注意该属性修饰的标签位置,详细往后看。优先级很高:order=2
-
th:if:条件判断,类似的还有th:unless,th:switch,th:case。优先级较高:order=3
-
th:insert:代码块引入,类似的还有th:replace,th:include,三者的区别较大,若使用不恰当会破坏html结构,常用于公共代码块提取的场景。优先级最高:order=1
-
th:fragment:定义代码块,方便被th:insert引用。优先级最低:order=8
-
th:object:声明变量,一般和*{}一起配合使用,达到偷懒的效果。优先级一般:order=4
-
th:attr:修改任意属性,实际开发中用的较少,因为有丰富的其他th属性帮忙,类似的还有th:attrappend,th:attrprepend。优先级一般:order=5
使用Thymeleaf属性需要注意点以下五点:
-
若要使用Thymeleaf语法,首先要声明名称空间:
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" -
设置文本内容 th:text,设置input的值 th:value,循环输出 th:each,条件判断 th:if,插入代码块 th:insert,定义代码块 th:fragment,声明变量 th:object
-
th:each 的用法需要格外注意,打个比方:如果你要循环一个div中的p标签,则th:each属性必须放在p标签上。若你将th:each属性放在div上,则循环的是将整个div。
-
变量表达式中提供了很多的内置方法,该内置方法是用#开头,请不要与#{}消息表达式弄混。
-
th:insert,th:replace,th:include 三种插入代码块的效果相似,但区别很大。
案例:
1. 在controller中绑定数据:
@Controller
public class ThController {
@RequestMapping("/success")
public String success(Model model){
//1.绑定一个字符串
model.addAttribute("msg","this is a String");
model.addAttribute("msgUtext","this is a String");
//2.绑定一个pojo对象--先去创建一个Emp
Emp emp=new Emp("张三",20);
model.addAttribute("emp",emp);
//3.绑定一个list
List list=new ArrayList();
list.add(emp);
list.add(new Emp("李四",20));
list.add(new Emp("王五",20));
model.addAttribute("emps",list);
//4.绑定一个map
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("Boss",new Emp("boss",30));
model.addAttribute("map",map);
//前缀:classpath:/templates/ success 后缀.html
return "success";
}
}
2. 在html中使用thmeleaf语法获取数据
2.1 先声明命名空间
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
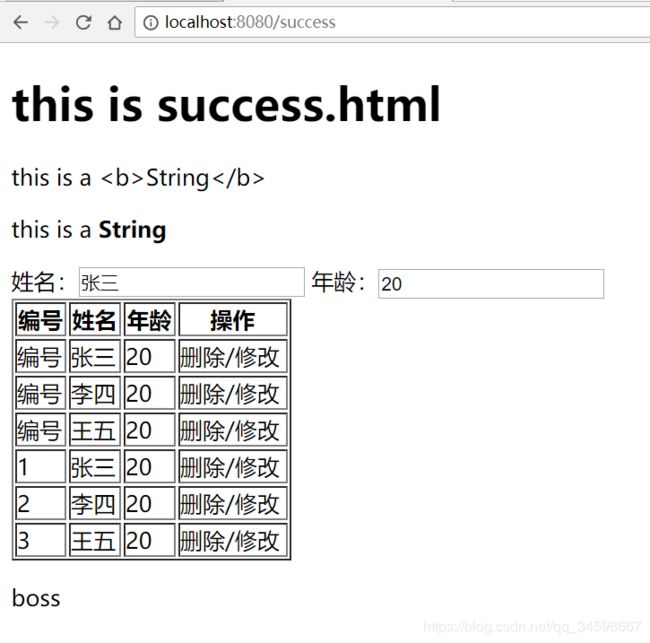
<h1>this is success.htmlh1>
body>
html>
2.2 th:text和th:value
...
<body>
<h1>this is success.htmlh1>
<p th:text="${msg}">p>
<p th:utext="${msgUtext}">p>
姓名:<input type="text" th:value="${emp.name}" />
年龄:<input type="text" th:value="${emp.age}" />
body>
...
2.3 th:each
...
<body>
<h1>this is success.htmlh1>
<table border="1px" th:width="200px">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>编号th>
<th>姓名th>
<th>年龄th>
<th>操作th>
tr>
thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="e:${emps}">
<td>编号td>
<td th:text="${e.name}">td>
<td th:text="${e.age}">td>
<td>删除/修改td>
tr>
tbody>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="e,eState:${emps}">
<td th:text="${eState.index+1}">td>
<td th:text="${e.name}">td>
<td th:text="${e.age}">td>
<td>删除/修改td>
tr>
tbody>
table>
...
说明:
th:each="e,eState : ${emps}"
其中e为循环的每一项,eState是下标属性(可省略),eState属性包括:
index:列表状态的序号,从0开始;
count:列表状态的序号,从1开始;
size:列表状态,列表数据条数;
current:列表状态,当前数据对象
even:列表状态,是否为奇数,boolean类型
odd:列表状态,是否为偶数,boolean类型
first:列表状态,是否为第一条,boolean类型
last:列表状态,是否为最后一条,boolean类型
2.4 th:if
<p th:text="${map.Boss.name}" th:if="${map.Boss.age gt 20}">p>
其中关系运算:
gt:great than(大于)
ge:great equal(大于等于)
eq:equal(等于)
lt:less than(小于)
le:less equal(小于等于)
ne:not equal(不等于)
③标准表达式语法
变量表达式使用频率最高,其功能也是非常的丰富。所以我们先从简单的代码块表达式开始,然后是消息表达式,再是链接表达式,最后是变量表达式,随带介绍选择变量表达式。
3.1 ~{…} 代码块表达式
支持两种语法结构:
-
推荐:
~{templatename::fragmentname} -
支持:
~{templatename::#id}templatename:模版名,Thymeleaf会根据模版名解析完整路径:
/resources/templates/templatename.html,要注意文件的路径。fragmentname:片段名,Thymeleaf通过th:fragment声明定义代码块,即:
th:fragment="fragmentname"id:HTML的id选择器,使用时要在前面加上#号,不支持class选择器。
代码块表达式的使用:
代码块表达式需要配合th属性(th:insert,th:replace,th:include)一起使用。
-
th:insert:将代码块片段整个插入到使用了th:insert的HTML标签中
-
th:replace:将代码块片段整个替换使用了th:replace的HTML标签中
-
th:include:将代码块片段包含的内容插入到使用了th:include的HTML标签中
案例:
<footer th:fragment="copy">
© 2019 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
footer>
<div th:insert="footer :: copy">div>
<div th:replace="footer :: copy">div>
<div th:include="footer :: copy">div>
使用后的结果其实如下:
<div>
<footer>
© 2019 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
footer>
div>
<footer>
© 2019 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
footer>
<div>
© 2019 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
div>
3.2 #{…} 消息表达式
消息表达式一般用于国际化的场景。结构:th:text="#{msg}" 。下面有一块再详细介绍。
3.3 @{…} 链接表达式
链接表达式好处:不管是静态资源的引用,form表单的请求,凡是链接都可以用@{…} 。这样可以动态获取项目路径,即便项目名变了,依然可以正常访问。
#修改项目名,链接表达式会自动修改路径,避免资源文件找不到
server.context-path=/itdragon
链接表达式结构:
-
无参:@{/xxx}
-
有参:@{/xxx(k1=v1,k2=v2)} 对应url结构:xxx?k1=v1&k2=v2
-
引入本地资源:@{/项目本地的资源路径}
-
引入外部资源:@{/webjars/资源在jar包中的路径}
案例:
<link th:href="@{/webjars/bootstrap/4.0.0/css/bootstrap.css}" rel="stylesheet">
<link th:href="@{/main/css/itdragon.css}" rel="stylesheet">
<form class="form-login" th:action="@{/user/login}" th:method="post" >
<a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/login.html(l='zh_CN')}">中文a>
<a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/login.html(l='en_US')}">Englisha>
3.4 ${…}变量表达式
变量表达式有丰富的内置方法,使其更强大,更方便。
变量表达式功能:
- 可以获取对象的属性和方法
- 可以使用ctx,vars,locale,request,response,session,servletContext内置对象
- 可以使用dates,numbers,strings,objects,arrays,lists,sets,maps等内置方法(重点介绍)
常用的内置对象:
4. ctx :上下文对象。
-
vars :上下文变量。
-
locale:上下文的语言环境。
-
request:(仅在web上下文)的 HttpServletRequest 对象。
-
response:(仅在web上下文)的 HttpServletResponse 对象。
-
session:(仅在web上下文)的 HttpSession 对象。
-
servletContext:(仅在web上下文)的 ServletContext 对象
这里以常用的Session举例,用户刊登成功后,会把用户信息放在Session中,Thymeleaf通过内置对象将值从session中获取。
// java 代码将用户名放在session中
session.setAttribute("userinfo",username);
// Thymeleaf通过内置对象直接获取
th:text="${session.userinfo}"
常用的内置方法:
11. strings:字符串格式化方法,常用的Java方法它都有。比如:equals,equalsIgnoreCase,length,trim,toUpperCase,toLowerCase,indexOf,substring,replace,startsWith,endsWith,contains,containsIgnoreCase等
-
numbers:数值格式化方法,常用的方法有:formatDecimal等
-
bools:布尔方法,常用的方法有:isTrue,isFalse等
-
arrays:数组方法,常用的方法有:toArray,length,isEmpty,contains,containsAll等
-
lists,sets:集合方法,常用的方法有:toList,size,isEmpty,contains,containsAll,sort等
-
maps:对象方法,常用的方法有:size,isEmpty,containsKey,containsValue等
-
dates:日期方法,常用的方法有:format,year,month,hour,createNow等
案例:
在controller中绑定字符串
//5.绑定一个字符串
model.addAttribute("itdragonStr","this is a DEMO");
在html中使用内置方法:
...
<h3>#strings h3>
<div th:if="${not #strings.isEmpty(itdragonStr)}" >
<p>Old Str : <span th:text="${itdragonStr}"/>p>
<p>toUpperCase : <span th:text="${#strings.toUpperCase(itdragonStr)}"/>p>
<p>toLowerCase : <span th:text="${#strings.toLowerCase(itdragonStr)}"/>p>
<p>equals : <span th:text="${#strings.equals(itdragonStr, 'itdragonblog')}"/>p>
<p>equalsIgnoreCase : <span th:text="${#strings.equalsIgnoreCase(itdragonStr, 'itdragonblog')}"/>p>
<p>indexOf : <span th:text="${#strings.indexOf(itdragonStr, 'r')}"/>p>
<p>substring : <span th:text="${#strings.substring(itdragonStr, 2, 8)}"/>p>
<p>replace : <span th:text="${#strings.replace(itdragonStr, 'it', 'IT')}"/>p>
<p>startsWith : <span th:text="${#strings.startsWith(itdragonStr, 'it')}"/>p>
<p>contains : <span th:text="${#strings.contains(itdragonStr, 'IT')}"/>p>
div>
...
以上是Thymeleaf的语法和使用,以下还提供了一个Thymeleaf在SpringBoot中的应用,包括“提取公共界面”,“页面显示和国际化”
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34598667/article/details/94614177