开题
一、 Python 、Tensorflow 安装及环境配置
二、 Object Detection API配置
三、 LabelImage对训练样本标注处理
四、 标注后训练样本验证样本格式转换tfrecord
五、 训练模型选取及参数配置
六、 定位在Object Detection文件下train.py开始训练
七、 上一步训练结果固化成pb模型
八、 视频流中调用模型预测
跟着上一篇的节奏,接下来是
3、模型类别选择参数配置
现在已经有了可供tensorflow直接使用的tfrecord数据了,接下来是对模型类别的选择,
官方模型分类 https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/object_detection/g3doc/detection_model_zoo.md 提供了众多可使用完整模型样例
红色标记栏是官方给出的对应模型预测耗时(实际应用中远高出标准),也可以看出ssd_mobilenet_****系列的的确是轻量化快速化的(速度快但识别率相对rcnn类偏低)
了解了各个模型性能后在该文件下选择适合的模型配置文件
实时类的ssd系列的好点,追求精度的话就是faster_rcnn_resnet50系列的,其实打开不同config文件里面需要我们配置的东西都是一样的(ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco 、faster_rcnn_inception_v2_pets这两个我特意都配置完训练一遍),还是以ssd_mobilenet_v1_pets.config为例,从config目录下复制一份到设定位置后打开,需要我们配置的自上往下依次为:
num_class 对应模型识别的对象分类数量
batch_size对应每次喂的图片数据数目,根据电脑性能自己调整
1. 156 157这两行是选择原有模型(ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco)的节点作为我们自定义模型训练,可以直接删除掉
- num_steps训练步数设置
分别对应训练数据tfrecord 和验证数据tfrecord路径如:
train_input_reader: {
tf_record_input_reader {
input_path: "D:\PyCharm\\raccoon_dataset_sample\\data\\train.record"
}
label_map_path: "D:\PyCharm\\raccoon_dataset_sample\\object_label_map.pbtxt"
}
eval_config: {
num_examples: 4
max_evals: 10
}
eval_input_reader: {
tf_record_input_reader {
input_path: "D:\PyCharm\\raccoon_dataset_sample\\data\\test.record"
}
label_map_path: "D:\PyCharm\\raccoon_dataset_sample\\object_label_map.pbtxt"
shuffle: false
num_readers: 1
}
同样建议绝对路径 + 双斜杠 避免歧义 报错
完整如下:
model {
ssd {
num_classes: 2
box_coder {
faster_rcnn_box_coder {
y_scale: 10.0
x_scale: 10.0
height_scale: 5.0
width_scale: 5.0
}
}
matcher {
argmax_matcher {
matched_threshold: 0.5
unmatched_threshold: 0.5
ignore_thresholds: false
negatives_lower_than_unmatched: true
force_match_for_each_row: true
}
}
similarity_calculator {
iou_similarity {
}
}
anchor_generator {
ssd_anchor_generator {
num_layers: 6
min_scale: 0.2
max_scale: 0.95
aspect_ratios: 1.0
aspect_ratios: 2.0
aspect_ratios: 0.5
aspect_ratios: 3.0
aspect_ratios: 0.3333
}
}
image_resizer {
fixed_shape_resizer {
height: 300
width: 300
}
}
box_predictor {
convolutional_box_predictor {
min_depth: 0
max_depth: 0
num_layers_before_predictor: 0
use_dropout: false
dropout_keep_probability: 0.8
kernel_size: 1
box_code_size: 4
apply_sigmoid_to_scores: false
conv_hyperparams {
activation: RELU_6,
regularizer {
l2_regularizer {
weight: 0.00004
}
}
initializer {
truncated_normal_initializer {
stddev: 0.03
mean: 0.0
}
}
batch_norm {
train: true,
scale: true,
center: true,
decay: 0.9997,
epsilon: 0.001,
}
}
}
}
feature_extractor {
type: 'ssd_mobilenet_v1'
min_depth: 16
depth_multiplier: 1.0
conv_hyperparams {
activation: RELU_6,
regularizer {
l2_regularizer {
weight: 0.00004
}
}
initializer {
truncated_normal_initializer {
stddev: 0.03
mean: 0.0
}
}
batch_norm {
train: true,
scale: true,
center: true,
decay: 0.9997,
epsilon: 0.001,
}
}
}
loss {
classification_loss {
weighted_sigmoid {
anchorwise_output: true
}
}
localization_loss {
weighted_smooth_l1 {
anchorwise_output: true
}
}
hard_example_miner {
num_hard_examples: 3000
iou_threshold: 0.99
loss_type: CLASSIFICATION
max_negatives_per_positive: 3
min_negatives_per_image: 0
}
classification_weight: 1.0
localization_weight: 1.0
}
normalize_loss_by_num_matches: true
post_processing {
batch_non_max_suppression {
score_threshold: 1e-8
iou_threshold: 0.6
max_detections_per_class: 100
max_total_detections: 100
}
score_converter: SIGMOID
}
}
}
train_config: {
batch_size: 1
optimizer {
rms_prop_optimizer: {
learning_rate: {
exponential_decay_learning_rate {
initial_learning_rate: 0.004
decay_steps: 800720
decay_factor: 0.95
}
}
momentum_optimizer_value: 0.9
decay: 0.9
epsilon: 1.0
}
}
num_steps: 200000
data_augmentation_options {
random_horizontal_flip {
}
}
data_augmentation_options {
ssd_random_crop {
}
}
}
train_input_reader: {
tf_record_input_reader {
input_path: "D:\PyCharm\\raccoon_dataset_sample\\data\\train.record"
}
label_map_path: "D:\PyCharm\\raccoon_dataset_sample\\object_label_map.pbtxt"
}
eval_config: {
num_examples: 4
max_evals: 10
}
eval_input_reader: {
tf_record_input_reader {
input_path: "D:\PyCharm\\raccoon_dataset_sample\\data\\test.record"
}
label_map_path: "D:\PyCharm\\raccoon_dataset_sample\\object_label_map.pbtxt"
shuffle: false
num_readers: 1
}
object_label_map.pbtxt文件则是训练的标签文件如:有几个写几个 id 递增
item{
id:1
name:'cigarette'
}
item{
id:2
name:'raccoon'
}
4.开始训练
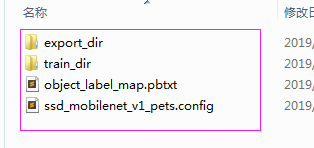
新建一个train_dir保存训练过程数据
新建一个export_dir保存导出模型数据如下
在****\models\research\object_detection 下 按shift + 右键打开命令窗口,输入指令执行
python legacy\\train.py --train_dir ***\\train_dir\ --pipeline_config_path *****\\ssd_mobilenet_v1_pets.config
若报错类型为
tensorflow.python.framework.errors_impl.NotFoundError: NewRandomAccessFile failed to Create/Open: : ϵͳ\udcd5Ҳ\udcbb\udcb5\udcbdָ\udcb6\udca8\udcb5\udcc4·\udcbe\u
dcb6\udca1\udca3
检查路径问题,再来! 不出意外进入如下训练过程,开启漫长等待! 每隔10分钟会保存一次训练节点数据信息。
5.导出模型
训练完成后在train_dir目录下文件信息,events文件供tensorboard可视化训练过程 ,model.ckpt-****.meta是我们需要操作的文件,****代表的数字也是你训练过程根据训练步数生成的。
在****\models\research\object_detection 下 按shift + 右键打开命令窗口,输入指令执行
模型导出 pb文件
python export_inference_graph.py --input_type image_tensor --pipeline_config_path YOUR_PATH/ssd_mobilenet_v1_pets.config --trained_checkpoint_prefix YOUR_PATH/train_dir/model.ckpt-***** --output_directory YOUR_PATH/export_dir/
6.模型调用(在官方基础上的优化)
先上代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Thu Jan 11 16:55:43 2018
@author: Xiang Guo
"""
# Imports
import time
start = time.time()
import numpy as np
import os
import sys
import tensorflow as tf
import cv2
from PIL import Image
from object_detection.utils import label_map_util
from object_detection.utils import visualization_utils as vis_util
if tf.__version__ < '1.0.0':
raise ImportError('Please upgrade your tensorflow installation to v1.4.* or later!')
os.chdir('D:\\ObjectDetection\\models\\research\\object_detection')
# Object detection imports
sys.path.append("..")
# Path to frozen detection graph. This is the actual model that is used for the object detection.
PATH_TO_CKPT = 'F:\\mymodel\\frozen_inference_graph.pb' # 修改成自己的
# List of the strings that is used to add correct label for each box.
PATH_TO_LABELS = os.path.join('F:\mymodel', 'object_label_map.pbtxt') # 修改成自己的
NUM_CLASSES = 1 # 修改成自己的
# Load a (frozen) Tensorflow model into memory.
detection_graph = tf.Graph()
# Loading label map
label_map = label_map_util.load_labelmap(PATH_TO_LABELS)
categories = label_map_util.convert_label_map_to_categories(label_map, max_num_classes=NUM_CLASSES,
use_display_name=True)
category_index = label_map_util.create_category_index(categories)
# Helper code
def load_image_into_numpy_array(image):
(im_width, im_height) = image.size
return np.array(image.getdata()).reshape(
(im_height, im_width, 3)).astype(np.uint8)
# 相机实时视频
def video_capture(image_tensor, detection_boxes, detection_scores, detection_classes, num_detections, sess):
# 0是代表摄像头编号,只有一个的话默认为0
capture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
i = 0
while (True):
ref, frame = capture.read()
if ref:
i = i + 1
if i % 3 == 0:
i = 0
frame_show(image_tensor, detection_boxes, detection_scores, detection_classes, num_detections, frame,
sess)
else:
cv2.imshow("frame", frame)
# 等待30ms显示图像,若过程中按“Esc”退出
c = cv2.waitKey(30) & 0xff
if c == 27: # ESC 按键 对应键盘值 27
capture.release()
break
else:
break
# 视频帧实时预测
def init_ogject_detection():
with detection_graph.as_default():
with tf.Session(graph=detection_graph) as sess:
od_graph_def = tf.GraphDef()
with tf.gfile.GFile(PATH_TO_CKPT, 'rb') as fid:
serialized_graph = fid.read()
od_graph_def.ParseFromString(serialized_graph)
tf.import_graph_def(od_graph_def, name='')
# Definite input and output Tensors for detection_graph
image_tensor = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('image_tensor:0')
# Each box represents a part of the image where a particular object was detected.
detection_boxes = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('detection_boxes:0')
# Each score represent how level of confidence for each of the objects.
# Score is shown on the result image, together with the class label.
detection_scores = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('detection_scores:0')
detection_classes = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('detection_classes:0')
num_detections = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('num_detections:0')
video_capture(image_tensor, detection_boxes, detection_scores, detection_classes, num_detections, sess)
# 视频实时类预测
def frame_show(image_tensor, detection_boxes, detection_scores, detection_classes, num_detections, image_np, sess):
starttime = time.time()
image_np = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(image_np, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
image_np = load_image_into_numpy_array(image_np)
# Expand dimensions since the model expects images to have shape: [1, None, None, 3]
image_np_expanded = np.expand_dims(image_np, axis=0)
# Actual detection.
(boxes, scores, classes, num) = sess.run(
[detection_boxes, detection_scores, detection_classes, num_detections],
feed_dict={image_tensor: image_np_expanded})
# Visualization of the results of a detection.
vis_util.visualize_boxes_and_labels_on_image_array(
image_np,
np.squeeze(boxes),
np.squeeze(classes).astype(np.int32),
np.squeeze(scores),
category_index,
use_normalized_coordinates=True,
line_thickness=8,
min_score_thresh=.6)
# write images
# 保存识别结果图片
print("------------use time ====> ", time.time() - starttime)
image_np = cv2.cvtColor(image_np, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
cv2.imshow("frame", image_np)
# 预测单张图片
def load_pic():
i = 0
starttime = time.time()
i = i + 1
with detection_graph.as_default():
with tf.Session(graph=detection_graph) as sess:
# Definite input and output Tensors for detection_graph
image_tensor = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('image_tensor:0')
# Each box represents a part of the image where a particular object was detected.
detection_boxes = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('detection_boxes:0')
# Each score represent how level of confidence for each of the objects.
# Score is shown on the result image, together with the class label.
detection_scores = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('detection_scores:0')
detection_classes = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('detection_classes:0')
num_detections = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('num_detections:0')
image = Image.open("D:\PyCharm\Test213\\raccoon_dataset_sample\\smoken_528.jpg")
# the array based representation of the image will be used later in order to prepare the
# result image with boxes and labels on it.
image_np = load_image_into_numpy_array(image)
# Expand dimensions since the model expects images to have shape: [1, None, None, 3]
image_np_expanded = np.expand_dims(image_np, axis=0)
# Actual detection.
(boxes, scores, classes, num) = sess.run(
[detection_boxes, detection_scores, detection_classes, num_detections],
feed_dict={image_tensor: image_np_expanded})
# Visualization of the results of a detection.
vis_util.visualize_boxes_and_labels_on_image_array(
image_np,
np.squeeze(boxes),
np.squeeze(classes).astype(np.int32),
np.squeeze(scores),
category_index,
use_normalized_coordinates=True,
line_thickness=8)
# write images
# 保存识别结果图片
print(str(i), "------------use time ====> ", time.time() - starttime)
image_np = cv2.cvtColor(image_np, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
cv2.imshow("image", image_np)
cv2.waitKey(0)
# init_ogject_detection() # 视频实时预测
# load_pic() # 单张图片预测
init_ogject_detection() # 视频实时预测
load_pic() # 单张图片预测
def visualize_boxes_and_labels_on_image_array(
image,
boxes,
classes,
scores,
category_index,
instance_masks=None,
instance_boundaries=None,
keypoints=None,
use_normalized_coordinates=False,
max_boxes_to_draw=20,
min_score_thresh=.5,
agnostic_mode=False,
line_thickness=4,
groundtruth_box_visualization_color='black',
skip_scores=False,
skip_labels=False):
"""Overlay labeled boxes on an image with formatted scores and label names.
This function groups boxes that correspond to the same location
and creates a display string for each detection and overlays these
on the image. Note that this function modifies the image in place, and returns
that same image.
Args:
image: uint8 numpy array with shape (img_height, img_width, 3)
boxes: a numpy array of shape [N, 4]
classes: a numpy array of shape [N]. Note that class indices are 1-based,
and match the keys in the label map.
scores: a numpy array of shape [N] or None. If scores=None, then
this function assumes that the boxes to be plotted are groundtruth
boxes and plot all boxes as black with no classes or scores.
category_index: a dict containing category dictionaries (each holding
category index `id` and category name `name`) keyed by category indices.
instance_masks: a numpy array of shape [N, image_height, image_width] with
values ranging between 0 and 1, can be None.
instance_boundaries: a numpy array of shape [N, image_height, image_width]
with values ranging between 0 and 1, can be None.
keypoints: a numpy array of shape [N, num_keypoints, 2], can
be None
use_normalized_coordinates: whether boxes is to be interpreted as
normalized coordinates or not.
max_boxes_to_draw: maximum number of boxes to visualize. If None, draw
all boxes.
min_score_thresh: minimum score threshold for a box to be visualized
agnostic_mode: boolean (default: False) controlling whether to evaluate in
class-agnostic mode or not. This mode will display scores but ignore
classes.
line_thickness: integer (default: 4) controlling line width of the boxes.
groundtruth_box_visualization_color: box color for visualizing groundtruth
boxes
skip_scores: whether to skip score when drawing a single detection
skip_labels: whether to skip label when drawing a single detection
Returns:
uint8 numpy array with shape (img_height, img_width, 3) with overlaid boxes.
"""
这个函数原型见上,默认预测值50%的会再图片才显示出来,所以可以根据要求自定义:如
修改,
vis_util.visualize_boxes_and_labels_on_image_array(
image_np,
np.squeeze(boxes),
np.squeeze(classes).astype(np.int32),
np.squeeze(scores),
category_index,
use_normalized_coordinates=True,
line_thickness=8,
min_score_thresh=.6)
后60%以上的才会显示框出来
优化处理主要针对视频实时类,将原来先读取视频,每帧都调用的with...with 逻辑
(思路来源于Stack Overflow上的一个问答)
with detection_graph.as_default():
with tf.Session(graph=detection_graph) as sess:
更改为先加载模型后维持一个session,在开启视频帧预测,时间上由原来的一帧(640*480)耗时2秒左右缩减为现在的0.3秒--0.5秒,效率提升很明显!
欢迎测试优化!