Spring Cloud:Ribbon(客户端负载均衡器)
前言
负载均衡在系统架构中是一个非常重要,是对系统的高可用、 网络压力的缓解和处理能力扩容的重要手段之一。
我们通常所说的负载均衡都指的是服务端负载均衡, 其中分为硬件负载均衡和软件负载均衡,但无论硬件负载均衡的设备或是软件负载均衡的软件模块都会维护一个下挂可用的服务端清单,通过心跳检测来剔除故障的服务端节点以保证清单中都是可以正常访问的服务端节点。
硬件比如:F5、Array等,软件比如:LVS、Nginx等。
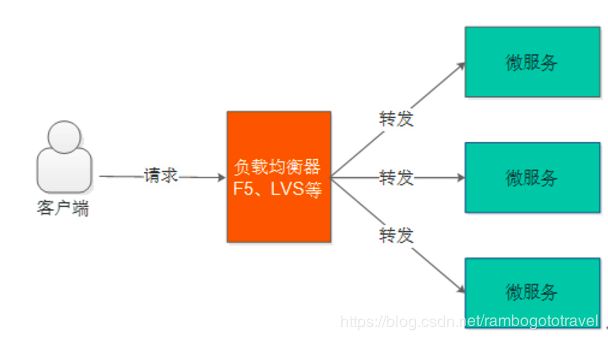
用户请求先到达负载均衡器(也相当于一个服务),负载均衡器根据负载均衡算法将请求转发到微服务。负载均衡算法有:轮训、随机、加权轮训、加权随机、地址哈希等方法,负载均衡器维护一份服务列表,根据负载均衡算法将请求转发到相应的微服务上,所以负载均衡可以为微服务集群分担请求,降低系统的压力
而客户端负载均衡和服务端负载均衡最大的不同点在千上面所提到的服务清单所存储的位置。 在客户端负载均衡中, 所有客户端节点都维护着自己要访问的服务端清单, 而这些服务端的清单来自于服务注册中心,同服务端负载均衡的架构类似,在客户端负载均衡中也需要心跳去维护服务端清单的健康性。
软件比如:Ribbon

一、简介
Ribbon 是 Netflix 公司开源的一个负载均衡的项目,它是一个基于 HTTP 和 TCP 的客户端负载均衡工具。通过 Spring Cloud 的封装,可以让我们轻松地将面向服务的 REST 模板请求自动转换成客户端负载均衡的服务调用。
它有一个核心的概念是命名客户端,每个负载均衡器都是一组组件的一部分,这些组件一起工作以便按需求连接远程服务器,Spring Cloud 通过使用 RibbonClientConfiguration 为每个命名客户端创建一个新的集合作为 ApplicationContext 。
Ribbon主要包含如下组件:
-
IRule,
-
IPing,接口定义了我们如何“ping”服务器检查是否活着
-
ServerList,定义了获取服务器的列表接口,存储服务列表
-
ServerListFilter,接口允许过滤配置或动态获得的候选列表服务器
-
ServerListUpdater,接口使用不同的方法来做动态更新服务器列表
-
IClientConfig,定义了各种api所使用的客户端配置,用来初始化ribbon客户端和负载均衡器,默认实现是DefaultClientConfigImpl
-
ILoadBalancer,接口定义了各种软负载,动态更新一组服务列表及根据指定算法从现有服务器列表中选择一个服务
-
RibbonLoadBalancerContext
-
RetryHandler
-
ServerIntrospector
具体可查看该默认配置类 org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.RibbonClientConfiguration
二、如何使用 Ribbon
- 在 Maven POM 文件中添加依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-ribbon</artifactId> <version>最新版本</version> </dependency> - 在引用启动类添加 @EnableDiscoveryClient 注解启动服务注册发现,声明一个RestTemplate 的bean,用@LoadBalanced注解修饰(无须开发者显示声明,在 RibbonAutoConfiguration 中已自动定义)
三、源码解析
首先要从 Ribbon 加载实例化过程上入手,要知道你做了哪些(加了什么配置或自定义类),Spring Boot 又自动帮你干(向ioc容器注入)了什么,这很重要!接入Spring Cloud Ribbon 也是需要两步:
-
隐式模式(用户不需要做什么,但你要知道),Spring Boot 会自动加载 Ribbon 的配置类 RibbonAutoConfiguration(spring-cloud-netflix-ribbon-2.2.0.RELEASE.jar/META-INF/spring.factories),为 Ribbon 提供运行所需要的环境(各种相关对象)。
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.RibbonAutoConfiguration -
在配置类中添加 @RibbonClient 或者 @RibbonClients(多个),注册类型为RibbonClientSpecification 的 bean,然后由 SpringClientFactory 完成对每一个RibbonClientSpecification 创建子 spring 上下文。
注:@RibbonClient可以为每个serviceId(微服务)使用属于自己的负载均衡配置类(IClientConfig、IRule、IPing、ServerList、ILoadBalancer… )
1. RibbonAutoConfiguration(Ribbon自动配置类)
RibbonAutoConfiguration 定义了 Ribbon 需要的 spring ioc 中一些公共的东西,它里面有非常多重要的东西,有子容器管理类,有非懒加载机制等!
@Configuration
@Conditional(RibbonAutoConfiguration.RibbonClassesConditions.class)
@RibbonClients
@AutoConfigureAfter(name="org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaClientAutoConfiguration")
@AutoConfigureBefore({ LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.class,AsyncLoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.class })
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ RibbonEagerLoadProperties.class, ServerIntrospectorProperties.class })
public class RibbonAutoConfiguration {
//获取ioc中RibbonClientSpecification(每个RibbonClient都会有一个)
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<RibbonClientSpecification> configurations = new ArrayList<>();
//子容器管理器(后面会讲)
@Bean
public SpringClientFactory springClientFactory() {
SpringClientFactory factory = new SpringClientFactory();
factory.setConfigurations(this.configurations);
return factory;
}
//负载均衡客户端(LoadBalancerInterceptor需要)
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(LoadBalancerClient.class)
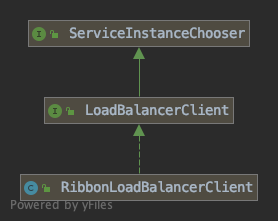
public LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient() {
return new RibbonLoadBalancerClient(springClientFactory());
}
//饥饿加载模式,每个客户端都在首次调用时进行初始化(默认,因此首次调用容易碰上超时现象)
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty("ribbon.eager-load.enabled")
public RibbonApplicationContextInitializer ribbonApplicationContextInitializer() {
return new RibbonApplicationContextInitializer(springClientFactory(),
ribbonEagerLoadProperties.getClients());
}
}
1.1 RibbonApplicationContextInitializer(Ribbon客户端上下文初始化器)
ribbon.eager-load.enabled=true //开启Ribbon的饥饿加载模式
ribbon.eager-load.clients=hello-service, user-service //指定需要饥饿加载的客户端名称、服务名
RibbonApplicationContextInitializer 本质是一个 ioc 的事件监听器,主要的作用是根据定义的每个Ribbon Client初始化响应的子容器。知道了它的作用后,你可能会问:饥饿加载模式是个什么鬼?
饥饿加载模式其实就是提前加载(ioc容器初始化后加载),那你又会问:为何需要提前加载呢?
Ribbon 进行客户端负载均衡的Client并不是在服务启动的时候就初始化好的,而是在调用的时候才会去创建相应的Client,所以第一次调用的耗时不仅仅包含发送HTTP请求的时间,还包含了创建RibbonClient的时间,这样一来如果创建时间速度较慢(需要创建子容器),同时设置的超时时间又比较短的话,很容易就会出现:第一次请求经常会超时,而之后的调用就没有问题了!
//事件驱动的Ribbon client初始化组件
public class RibbonApplicationContextInitializer implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationReadyEvent> {
private final SpringClientFactory springClientFactory;
// Ribbon客户端名称列表
private final List<String> clientNames;
public RibbonApplicationContextInitializer(SpringClientFactory springClientFactory,
List<String> clientNames) {
this.springClientFactory = springClientFactory;
this.clientNames = clientNames;
}
protected void initialize() {
if (clientNames != null) {
for (String clientName : clientNames) {
//创建对应的AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
this.springClientFactory.getContext(clientName);
}
}
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationReadyEvent event) {
initialize();
}
}
这时候,你可能就对SpringClientFactory比较好奇了吧!
1.2 SpringClientFactory(为每一个 Ribbon客户端创建一个 ApplicationContext,是创建客户端、负载均衡、客户端配置实例的工厂类)
SpringClientFactory 非常重要,它为每个@RibbonClient创建一个子容器,并通过serviceId获取子容器中的IClient、ILoadBalancer、IClientConfig、RibbonLoadBalancerContext、AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。
因此可以看出Ribbon实现了子容器的隔离,非常棒的做法!
public class SpringClientFactory extends NamedContextFactory<RibbonClientSpecification> {
static final String NAMESPACE = "ribbon";
public SpringClientFactory() {
//RibbonClientConfiguration 默认配置类型
super(RibbonClientConfiguration.class, NAMESPACE, "ribbon.client.name");
}
//根据serviceId获取rest client
public <C extends IClient<?, ?>> C getClient(String name, Class<C> clientClass) {
return getInstance(name, clientClass);
}
@Override
public <C> C getInstance(String name, Class<C> type) {
C instance = super.getInstance(name, type);
if (instance != null) {
return instance;
}
IClientConfig config = getInstance(name, IClientConfig.class);
return instantiateWithConfig(getContext(name), type, config);
}
//根据serviceId获取Ioc容器(AnnotationConfigApplicationContext)
@Override
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext getContext(String name) {
return super.getContext(name);
}
}
//与上面的是继承关系
public abstract class NamedContextFactory<C extends NamedContextFactory.Specification> implements DisposableBean, ApplicationContextAware {
//所有的子容器映射关系
private Map<String, AnnotationConfigApplicationContext> contexts = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//获取一个子容器
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext getContext(String name) {
if (!this.contexts.containsKey(name)) {
synchronized (this.contexts) {
if (!this.contexts.containsKey(name)) {
//创建子容器
this.contexts.put(name, createContext(name));
}
}
}
return this.contexts.get(name);
}
//创建一个子容器
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext createContext(String name) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
if (this.configurations.containsKey(name)) {
//注入@RibbonClient的configuration
for (Class<?> configuration : this.configurations.get(name).getConfiguration()) {
context.register(configuration);
}
}
for (Map.Entry<String, C> entry : this.configurations.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getKey().startsWith("default.")) {
for (Class<?> configuration : entry.getValue().getConfiguration()) {
context.register(configuration);
}
}
}
//注入RibbonClientConfiguration与配置
context.register(PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration.class,
this.defaultConfigType);
context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources().addFirst(new MapPropertySource(
this.propertySourceName, Collections.<String, Object>singletonMap(this.propertyName, name)));
if (this.parent != null) {
// Uses Environment from parent as well as beans
context.setParent(this.parent);
// jdk11 issue
// https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-netflix/issues/3101
context.setClassLoader(this.parent.getClassLoader());
}
context.setDisplayName(generateDisplayName(name));
context.refresh(); //刷新子容器
return context;
}
}
1.3 RibbonClientConfiguration(Ribbon客户端默认配置类)
RibbonClientConfiguration 定义了客户端访问远程服务器工作的一组组件,这些组件有{@link ILoadBalancer}, {@link ServerListFilter}, {@link IRule} 等。
在首次访问服务时,通过 SpringClientFactory 创建客户端对应的 ApplicationContext 子容器。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Import(RibbonClientConfigurationRegistrar.class) //Ribbon客户端配置注册类
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RibbonClient {
// Ribbon客户端名称
String value() default "";
// Ribbon客户端名称
String name() default "";
//Ribbon客户端自定义的配置类,其定义的组件实例,例如{@link ILoadBalancer}, {@link ServerListFilter}, {@link IRule}.
//可以参照 RibbonClientConfiguration
Class<?>[] configuration() default {};
}
2. LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration(负载均衡自动配置类)
LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration 定义了客户端请求实现负载均衡的一些东西,有负载均衡拦截器、负载均衡请求工厂等!
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass(RestTemplate.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(LoadBalancerClient.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(LoadBalancerRetryProperties.class)
public class LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration {
@LoadBalanced //
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<RestTemplate> restTemplates = Collections.emptyList();
@Bean
public SmartInitializingSingleton loadBalancedRestTemplateInitializerDeprecated(final ObjectProvider<List<RestTemplateCustomizer>> restTemplateCustomizers) {
return () -> restTemplateCustomizers.ifAvailable(customizers -> {
for (RestTemplate restTemplate : LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.this.restTemplates) {
for (RestTemplateCustomizer customizer : customizers) {
//为 RestTemplate 自定义初始化配置
customizer.customize(restTemplate);
}
}
});
}
//负载均衡请求创建工厂
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public LoadBalancerRequestFactory loadBalancerRequestFactory(
LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient) {
return new LoadBalancerRequestFactory(loadBalancerClient, this.transformers);
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnMissingClass("org.springframework.retry.support.RetryTemplate")
static class LoadBalancerInterceptorConfig {
// 负载均衡拦截器
@Bean
public LoadBalancerInterceptor ribbonInterceptor(LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient,LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory) {
return new LoadBalancerInterceptor(loadBalancerClient, requestFactory);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public RestTemplateCustomizer restTemplateCustomizer(final LoadBalancerInterceptor loadBalancerInterceptor) {
return restTemplate -> {
List<ClientHttpRequestInterceptor> list = new ArrayList<>(restTemplate.getInterceptors());
list.add(loadBalancerInterceptor);
//为 RestTemplate 设置负载均衡拦截器
restTemplate.setInterceptors(list);
};
}
}
}
这里涉及的 LoadBalancerRequestFactory、LoadBalancerInterceptor 类的解析,我们在下文进行介绍。
3. RestTemplate
RestTemplate 执行 HTTP 请求的同步客户端,我们通过一次请求调用,来深入了解下 Ribbon 各个组件在这个过程中的使用。
protected <T> T doExecute(URI url, @Nullable HttpMethod method, @Nullable RequestCallback requestCallback,@Nullable ResponseExtractor<T> responseExtractor) throws RestClientException {
...
ClientHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// 创建请求
ClientHttpRequest request = createRequest(url, method);
if (requestCallback != null) {
requestCallback.doWithRequest(request);
}
// 执行请求
response = request.execute();
// 处理请求响应
handleResponse(url, method, response);
return (responseExtractor != null ? responseExtractor.extractData(response) : null);
}
}
// 创建请求
protected ClientHttpRequest createRequest(URI url, HttpMethod method) throws IOException {
//获取请求创建工厂,创建请求实例
ClientHttpRequest request = getRequestFactory().createRequest(url, method);
}
@Override
public ClientHttpRequestFactory getRequestFactory() {
//获取拦截器(LoadBalancerInterceptor)
List<ClientHttpRequestInterceptor> interceptors = getInterceptors();
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {
ClientHttpRequestFactory factory = this.interceptingRequestFactory; //初始化,该工厂实例为null
if (factory == null) {
//创建拦截客户端请求工厂
factory = new InterceptingClientHttpRequestFactory(super.getRequestFactory(), interceptors);
this.interceptingRequestFactory = factory;
}
return factory;
}
从上文中,我们看到 RestTemplate 在外围执行远程调用分为三个步骤:创建请求、执行请求、处理请求的响应。
这里主要研究前两个步骤,了解客户端负载均衡流程,它是如何获取具体的服务实例,并发送请求?
请求实例 InterceptingClientHttpRequest,它是 InterceptingClientHttpRequestFactory 拦截工厂创建。
public final ClientHttpResponse execute() throws IOException {
assertNotExecuted();
ClientHttpResponse result = executeInternal(this.headers);
this.executed = true;
return result;
}
protected final ClientHttpResponse executeInternal(HttpHeaders headers, byte[] bufferedOutput) throws IOException {
InterceptingRequestExecution requestExecution = new InterceptingRequestExecution();
return requestExecution.execute(this, bufferedOutput);
}
//InterceptingClientHttpRequest的内部类
private class InterceptingRequestExecution implements ClientHttpRequestExecution {
private final Iterator<ClientHttpRequestInterceptor> iterator;
public InterceptingRequestExecution() {
this.iterator = interceptors.iterator();
}
@Override
public ClientHttpResponse execute(HttpRequest request, byte[] body) throws IOException {
if (this.iterator.hasNext()) {
ClientHttpRequestInterceptor nextInterceptor = this.iterator.next();
//遍历拦截器,通过负载均衡器查找具体的服务实例
return nextInterceptor.intercept(request, body, this);
}
else {
HttpMethod method = request.getMethod();
Assert.state(method != null, "No standard HTTP method");
//
ClientHttpRequest delegate = requestFactory.createRequest(request.getURI(), method);
request.getHeaders().forEach((key, value) -> delegate.getHeaders().addAll(key, value));
if (body.length > 0) {
if (delegate instanceof StreamingHttpOutputMessage) {
StreamingHttpOutputMessage streamingOutputMessage = (StreamingHttpOutputMessage) delegate;
streamingOutputMessage.setBody(outputStream -> StreamUtils.copy(body, outputStream));
}
else {
StreamUtils.copy(body, delegate.getBody());
}
}
return delegate.execute();
}
}
}
public ClientHttpResponse intercept(final HttpRequest request, final byte[] body, final ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) throws IOException {
//requestFactory(LoadBalancerRequestFactory) 工厂创建请求实例,该实例接收一个服务实例,由负载均衡器调用执行;
//loadBalancer(RibbonLoadBalancerClient)
return this.loadBalancer.execute(serviceName, requestFactory.createRequest(request, body, execution));
}
public <T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException {
//获取负载均衡器
ILoadBalancer loadBalancer = getLoadBalancer(serviceId);
//获取服务实例
Server server = getServer(loadBalancer);
RibbonServer ribbonServer = new RibbonServer(serviceId, server, isSecure(server,
serviceId), serverIntrospector(serviceId).getMetadata(server));
//执行请求
return execute(serviceId, ribbonServer, request);
}
protected ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer(String serviceId) {
//SpringClientFactory 从每个客户端对应的 IOC 子容器中,获取负载均衡实例
return this.clientFactory.getLoadBalancer(serviceId);
}
protected Server getServer(ILoadBalancer loadBalancer, Object hint) {
if (loadBalancer == null) {
return null;
}
// Use 'default' on a null hint, or just pass it on?
return loadBalancer.chooseServer(hint != null ? hint : "default");
}
public <T> T execute(String serviceId, ServiceInstance serviceInstance, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException {
Server server = null;
if(serviceInstance instanceof RibbonServer) {
server = ((RibbonServer)serviceInstance).getServer();
}
RibbonLoadBalancerContext context = this.clientFactory
.getLoadBalancerContext(serviceId);
RibbonStatsRecorder statsRecorder = new RibbonStatsRecorder(context, server);
try {
T returnVal = request.apply(serviceInstance);
statsRecorder.recordStats(returnVal);
return returnVal;
}
}
public Server chooseServer(Object key) {
if (!ENABLED.get() || getLoadBalancerStats().getAvailableZones().size() <= 1) {
return super.chooseServer(key);
}
Server server = null;
try {
LoadBalancerStats lbStats = getLoadBalancerStats();
Map<String, ZoneSnapshot> zoneSnapshot = ZoneAvoidanceRule.createSnapshot(lbStats);
Set<String> availableZones = ZoneAvoidanceRule.getAvailableZones(zoneSnapshot, triggeringLoad.get(), triggeringBlackoutPercentage.get());
if (availableZones != null && availableZones.size() < zoneSnapshot.keySet().size()) {
String zone = ZoneAvoidanceRule.randomChooseZone(zoneSnapshot, availableZones);
if (zone != null) {
BaseLoadBalancer zoneLoadBalancer = getLoadBalancer(zone);
server = zoneLoadBalancer.chooseServer(key);
}
}
}
if (server != null) {
return server;
} else {
logger.debug("Zone avoidance logic is not invoked.");
return super.chooseServer(key);
}
}
引用
官方文档
Spring Cloud Ribbon源码解析
Spring Cloud Ribbon源码分析
Spring Cloud 参考文档(客户端负载均衡器:Ribbon)