springboot自带定时任务用法
定时任务的实现方式有很多种,本文是基于springboot注解方法的一种实现。
一、单线程定时任务
springboot实现定时任务主要是依靠两个注解@Scheduled和@EnableScheduling,具体用法如下:
1)@Scheduled
在执行定时任务的方法上添加,代码如下:
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* springboot 注解单线程定时任务
*/
@Component
public class ScheduledSyncService {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ScheduledSyncService.class);
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000)
public void executeScheduledTask1 () {
LOGGER.info("this is {}", "executeScheduledTask1");
LOGGER.info("the task execute time is {}", System.currentTimeMillis());
}
@Scheduled(cron = "0/2 * * * * ?")
public void executeScheduledTask2 () {
LOGGER.info("this is {}", "executeScheduledTask2");
LOGGER.info("the task execute time is {}", System.currentTimeMillis());
}
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 3000, initialDelay = 2000)
public void executeScheduledTask3 () {
LOGGER.info("this is {}", "executeScheduledTask3");
LOGGER.info("the task execute time is {}", System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
2)@EnableScheduling
在项目启动类上添加,代码如下:
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableScheduling
public class MrtApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MrtApplication.class, args);
}
}
单线程定时任务比较简单,但多个定时任务由一个线程串行执行,一旦其中某个任务出现堵塞或不可预知问题,就会影响其它任务的执行。
二、多线程定时任务
多线程定时任务是在单线程定时任务的基础开启springboot异步调用功能,使用@EnableAsync、@Async和线程池实现的。
1)@EnableAsync
在项目启动类上添加,代码如下:
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableScheduling
@EnableAsync
public class MrtApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MrtApplication.class, args);
}
}
此时即开启了异步调用功能。
2)@Async
在定时任务类或执行方法上添加,如下:
@Scheduled(cron = "0/2 * * * * ?")
@Async
public void executeScheduledTask2 () {
LOGGER.info("this is {}", "executor executeScheduledTask2");
LOGGER.info("the task execute time is {}", System.currentTimeMillis());
}
3)线程池
可实现AsyncConfigurer接口,也可自定义实现,示例代码是实现AsyncConfigurer接口。
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncConfigurer;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
@Configuration
public class AsyncConfig implements AsyncConfigurer {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AsyncConfig.class);
private int corePoolSize = 10;
private int maxPoolSize = 90;
private int queueCapacity = 15;
@Bean
@Override
public Executor getAsyncExecutor () {
LOGGER.info("this is {}", "getTaskExecutor");
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(corePoolSize);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(maxPoolSize);
executor.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity);
return executor;
}
}
以上即实现多线程定时任务执行。
三、定时任务执行时间设置
在定时任务中使用@Scheduled注解参数来设置任务的执行时间,共有如下三种方式:
1、fixedRate:定义一个按一定频率执行的定时任务
2、fixedDelay:定义一个按一定频率执行的定时任务,与上面不同的是,该属性可以配合initialDelay属性, 定义该任务延迟执行时间。
3、cron:通过表达式来配置任务执行时间
下面重点介绍一下cron表达式设置方式,如下:
cron表达式是一个字符串,以5或6个空格隔开,分开共6或7个域,每一个域代表一个含义。
语法如下:
[秒] [分] [小时] [日] [月] [周] [年]
其中“年”不是必须域,可以省略。每个域的用法如下:
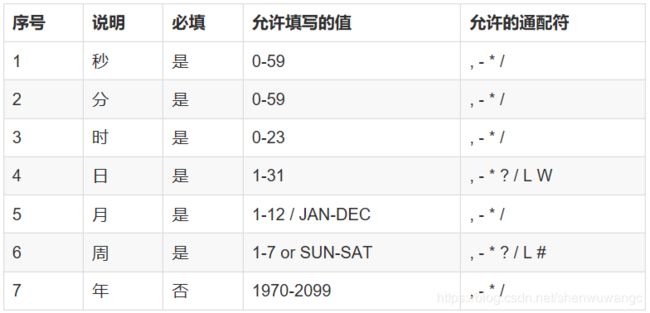
通配符用法说明:
*表示所有值。 例如:在分的字段上设置 *,表示每一分钟都会触发。?表示不指定值。使用的场景为不需要关心当前设置这个字段的值,仅被用于天(月)和天(星期)两个子表达式,当2个子表达式其中之一被指定了值以后,为了避免冲突,需要将另一个子表达式的值设为“?”。例如:要在每月的10号触发一个操作,但不关心是周几,所以需要周位置的那个字段设置为”?” ,即设置为 0 0 0 10 * ?-表示区间。例如 :在小时上设置 “10-12”,表示 10、11、12点都会触发。,表示指定多个值,例如在周字段上设置 “MON,WED,FRI” 表示周一、周三和周五触发。/用于递增触发。例如:在秒上面设置“5/15” 表示从5秒开始,每增15秒触发(5、20、35、50)。 在月字段上设置“1/3”所示每月1号开始,每隔三天触发一次。L表示最后的意思。在日字段设置上,表示当月的最后一天(依据当前月份,如果是二月还会依据是否是润年[leap]),在周字段上表示星期六,相当于”7”或”SAT”。如果在”L”前加上数字,则表示该数据的最后一个。例如在周字段上设置“6L”这样的格式,则表示“本月最后一个星期五”。W表示离指定日期的最近那个工作日(周一至周五)。例如在日字段上置“5W”,表示离每月15号最近的那个工作日触发。如果15号正好是周六,则找最近的周五(14号)触发, 如果15号是周未,则找最近的下周一(16号)触发;如果15号正好在工作日(周一至周五),则就在该天触发。如果指定格式为 “1W”,它则表示每月1号往后最近的工作日触发。如果1号正是周六,则将在3号下周一触发。(注,”W”前只能设置具体的数字,不允许区间”-“)。#序号(表示每月的第几个周几),例如在周字段上设置“6#3”表示在每月的第三个周六。注意如果指定”#5”,正好第五周没有周六,则不会触发该配置(用在母亲节和父亲节再合适不过了) ;- 小提示:
L和W可以一组合使用。如果在日字段上设置“LW”,则表示在本月的最后一个工作日触发;周字段的设置,若使用英文字母是不区分大小写的,即MON与mon相同。
在线生成表达式:http://qqe2.com/cron/index
举例如下:
- /5 * * * ? 每隔5秒执行一次
- 0 /1 * * ? 每隔1分钟执行一次
- 0 0 10,14,16 * * ? 每天上午10点,下午2点,4点
- 0 0/30 9-17 * * ? 朝九晚五工作时间内每半小时
- 0 0 12 ? * WED 表示每个星期三中午12点
- 0 0 12 * * ? 每天中午12点触发
- 0 15 10 ? * * 每天上午10:15触发
- 0 15 10 * * ? 每天上午10:15触发
- 0 15 10 * * ? * 每天上午10:15触发
- 0 15 10 * * ? 2005 2005年的每天上午10:15触发
- 0 * 14 * * ? 在每天下午2点到下午2:59期间的每1分钟触发
- 0 0/5 14 * * ? 在每天下午2点到下午2:55期间的每5分钟触发
- 0 0/5 14,18 * * ? 在每天下午2点到2:55期间和下午6点到6:55期间的每5分钟触发
- 0 0-5 14 * * ? 在每天下午2点到下午2:05期间的每1分钟触发
- 0 10,44 14 ? 3 WED 每年三月的星期三的下午2:10和2:44触发
- 0 15 10 ? * MON-FRI 周一至周五的上午10:15触发
- 0 15 10 15 * ? 每月15日上午10:15触发
- 0 15 10 L * ? 每月最后一日的上午10:15触发
- 0 15 10 ? * 6L 每月的最后一个星期五上午10:15触发
- 0 15 10 ? * 6L 2002-2005 2002年至2005年的每月的最后一个星期五上午10:15触发
- 0 15 10 ? * 6#3 每月的第三个星期五上午10:15触发