手机主流适配
手机主流适配
在android中设配一直是程序员最头疼的一个问题,那么问题来了,web前端不需要么—–的确不需要,web前端一般是百分比适配;
ok~接下来详细介绍一下:
首先在android的layout中不可以使用px,因为不同的机型,用相同的px,dp值会不同,进而会造成布局的不同;影响极大.
1.图片适配
在res下drawable创建不同的drawable文件夹,在这里不建议使用mipmap,因为在as中mipmap中.9图无法识别
drawable;drawable-hpi;drawable-mdpi;drawable-xhdpi;drawable-xxhdpi;drawable-xxxhpi;
2.百分比适配
百分比适配可以很好解决机型的不适配,但是在android中weight<权重>只可以在linearlayout中实现,所以具有一定的局限性
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/bottom_btn"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:background="@color/colorWhite">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="20dp"
android:layout_height="20dp"
android:src="@drawable/tab_find_selector"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="1dp"
android:text="找驾校"
android:textSize="10sp"/>
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="20dp"
android:layout_height="20dp"
android:src="@drawable/tab_license_selector"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="1dp"
android:text="考驾照"
android:textSize="10sp"/>
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="20dp"
android:layout_height="20dp"
android:src="@drawable/tab_mine_selector"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="我的"
android:textSize="10sp"/>
LinearLayout>
LinearLayout>3.dimen尺寸适配
ok~其实以上两种适配比较简单,虽然dp为像素无关量,在不同的机型影响较小,但是也会有一定影响;所以需要匹配不同机型出不同value
在之前需要手动来配置,各种生成jar也参差不穷,综合来看,利用代码生成不同value下的x,y还是比较靠谱的<看不同没有关系,继续往下看>;下面看关键代码—->run—–>会在project下生成res,移到你的香炉里就ok;
package com.example.test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
/**
* Created by zhy on 15/5/3.
*/
public class GenerateValueFiles {
private int baseW;
private int baseH;
private String dirStr = "./res";
private final static String WTemplate = "{1}px \n";
private final static String HTemplate = "{1}px \n";
/**
* {0}-HEIGHT
*/
private final static String VALUE_TEMPLATE = "values-{0}x{1}";
private static final String SUPPORT_DIMESION = "320,480;480,800;480,854;540,960;600,1024;720,1184;720,1196;720,1280;768,1024;800,1280;1080,1812;1080,1920;1440,2560;";
private String supportStr = SUPPORT_DIMESION;
public GenerateValueFiles(int baseX, int baseY, String supportStr) {
this.baseW = baseX;
this.baseH = baseY;
if (!this.supportStr.contains(baseX + "," + baseY)) {
this.supportStr += baseX + "," + baseY + ";";
}
this.supportStr += validateInput(supportStr);
System.out.println(supportStr);
File dir = new File(dirStr);
if (!dir.exists()) {
dir.mkdir();
}
System.out.println(dir.getAbsoluteFile());
}
/**
* @param supportStr
* w,h_...w,h;
* @return
*/
private String validateInput(String supportStr) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
String[] vals = supportStr.split("_");
int w = -1;
int h = -1;
String[] wh;
for (String val : vals) {
try {
if (val == null || val.trim().length() == 0)
continue;
wh = val.split(",");
w = Integer.parseInt(wh[0]);
h = Integer.parseInt(wh[1]);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("skip invalidate params : w,h = " + val);
continue;
}
sb.append(w + "," + h + ";");
}
return sb.toString();
}
public void generate() {
String[] vals = supportStr.split(";");
for (String val : vals) {
String[] wh = val.split(",");
generateXmlFile(Integer.parseInt(wh[0]), Integer.parseInt(wh[1]));
}
}
private void generateXmlFile(int w, int h) {
StringBuffer sbForWidth = new StringBuffer();
sbForWidth.append("\n");
sbForWidth.append("" );
float cellw = w * 1.0f / baseW;
System.out.println("width : " + w + "," + baseW + "," + cellw);
for (int i = 1; i < baseW; i++) {
sbForWidth.append(WTemplate.replace("{0}", i + "").replace("{1}",
change(cellw * i) + ""));
}
sbForWidth.append(WTemplate.replace("{0}", baseW + "").replace("{1}",
w + ""));
sbForWidth.append("");
StringBuffer sbForHeight = new StringBuffer();
sbForHeight.append("\n");
sbForHeight.append("" );
float cellh = h *1.0f/ baseH;
System.out.println("height : "+ h + "," + baseH + "," + cellh);
for (int i = 1; i < baseH; i++) {
sbForHeight.append(HTemplate.replace("{0}", i + "").replace("{1}",
change(cellh * i) + ""));
}
sbForHeight.append(HTemplate.replace("{0}", baseH + "").replace("{1}",
h + ""));
sbForHeight.append("");
File fileDir = new File(dirStr + File.separator
+ VALUE_TEMPLATE.replace("{0}", h + "")//
.replace("{1}", w + ""));
fileDir.mkdir();
File layxFile = new File(fileDir.getAbsolutePath(), "lay_x.xml");
File layyFile = new File(fileDir.getAbsolutePath(), "lay_y.xml");
try {
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream(layxFile));
pw.print(sbForWidth.toString());
pw.close();
pw = new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream(layyFile));
pw.print(sbForHeight.toString());
pw.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static float change(float a) {
int temp = (int) (a * 100);
return temp / 100f;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int baseW = 320;
int baseH = 480;
String addition = "";
try {
if (args.length >= 3) {
baseW = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
baseH = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
addition = args[2];
} else if (args.length >= 2) {
baseW = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
baseH = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
} else if (args.length >= 1) {
addition = args[0];
}
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.err
.println("right input params : java -jar xxx.jar width height w,h_w,h_..._w,h;");
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(-1);
}
new GenerateValueFiles(baseW, baseH, addition).generate();
}
}
姑且看作一个生成不同dimen的一个tool类 ,可以配置相关参数来生成 所需要的value进行尺寸适配
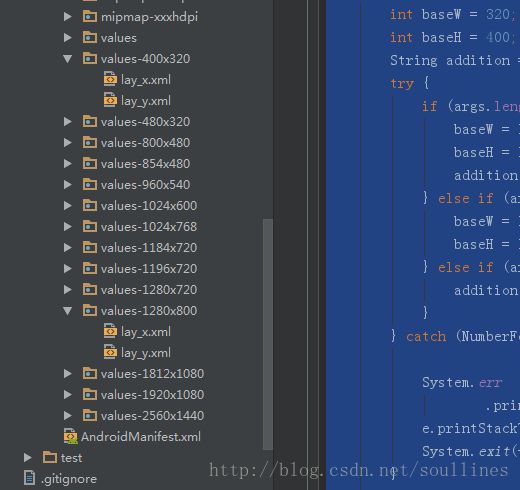
可以看到在每一个value下面有lay_x.xml和lay_y.xml,前者代表width,后者代表height;ok~看里面部分代码:
<dimen name="x47">117.5pxdimen>
<dimen name="x48">120.0pxdimen>
<dimen name="x49">122.5pxdimen>
<dimen name="x50">125.0pxdimen>
<dimen name="x51">127.5pxdimen>
<dimen name="x52">130.0pxdimen>
<dimen name="x53">132.5pxdimen>
<dimen name="x54">135.0pxdimen>
<dimen name="x55">137.5pxdimen>
<dimen name="x56">140.0pxdimen>
<dimen name="x57">142.5pxdimen>
<dimen name="x58">145.0pxdimen>
<dimen name="x59">147.5pxdimen>
<dimen name="x60">150.0pxdimen>
<dimen name="x61">152.5pxdimen>
<dimen name="x62">155.0pxdimen>
<dimen name="x63">157.5pxdimen>
<dimen name="x64">160.0pxdimen>
<dimen name="x65">162.5pxdimen>
<dimen name="x66">165.0pxdimen>前面的xx是代表dp,后面代表px,在代码中引入合适的dp<可以看作百分比,即x1,x2…>,就胡转换为正确px,这样就不会担心机型尺寸的不适配了~有没有感觉这样看来适配很简单