Shell编程3_echo/printf/test/输入输出重定向
目录
一、Shell echo/printf 命令
1、Shell显示命令-echo
2、printf 命令操作
常用的一些格式化字符
二、test命令
三、输入输出重定向
1、输入重定向:<
2、输出重定向:> / >>
3、空设备:/dev/null
一、Shell echo/printf 命令
Shell echo/printf 命令
1、Shell显示命令-echo
打印普通字符串
[root@master ~]# echo "hello shell"
hello shell创建和清空文件
1、创建文件
[root@master ~]# ls test.sh
ls: cannot access test.sh: No such file or directory
[root@master ~]# echo "hello shell" >test.sh
[root@master ~]# cat test.sh
hello shell
2、清空文件
[root@master ~]# cat test.sh
hello shell
[root@master ~]# echo >test.sh
[root@master ~]# cat test.sh 2、printf 命令操作
printf 功能为格式化打印数据,语法为:printf format-string [arguments]。
- format-string: 为格式控制字符串;
- arguments: 为参数列表。
常用的一些格式化字符
%c ASCII字符.显示相对应参数的第一个字符
%d,%i 十进制整数(常用)
%e 浮点格式([-d].precisione [+-dd])
%E 浮点格式([-d].precisionE [+-dd])
%g %e或%f转换,看哪一个较短,则删除结尾的零
%G %E或%f转换,看哪一个较短,则删除结尾的零
%s 字符串(常用)
%u 不带正负号的十进制值
%x 不带正负号的十六进制.使用a至f表示10至15
%% 字面意义的%
%X 不带正负号的十六进制.使用A至F表示10至15格式只指定了一个参数,但多出的参数仍然会按照该格式输出,format-string 被重用进行多行输出
[root@master ~]# printf 'hello %s\n' shell python go
hello shell
hello python
hello go
[root@master ~]# printf "%s %s %s %s\n" a b c d e f g h i j
a b c d
e f g h
i j如果没有 arguments,那么则对应使用默认值表示, % s 用 NULL 代替,% d 用 0 代替
[root@master ~]# printf "%s default %d \n"
default 0 二、test命令
test 为 Shell 内置命令,其通常需要与 if 语句一块使用。
语法格式为 test expression, 当 test 判断 expression 为成立时,返回状态为 0,否则为非 0 值。
test 命令还可以简写为 [ ], 需要在两边中括号与 expression 是有一个空格,这个空格是必须的,否则会导致语法错误。[] 的写法更加简洁,比 test 使用频率更高。
[root@master shell_test]# cat test1.sh
#!/bin/bash
// 使用中括号
if test 10 -ne 1;then
echo "true"
else
echo "false"
fi
[root@master shell_test]# bash test1.sh
true
[root@master shell_test]# cat test2.sh
#!/bin/bash
// 使用test
if [ 10 -eq 1 ];then
echo "true"
else
echo "false"
fi
[root@master shell_test]# bash test2.sh
true三、输入输出重定向
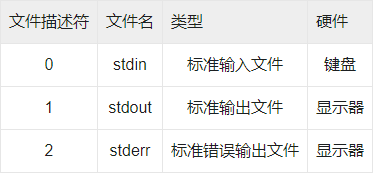
文件描述符
在 Linux 中一切皆文件,包括标准输入设备(键盘)和标准输出设备(显示器)在内的所有计算机硬件都是文件。为了表示和区分已经打开的文件,Linux 会给每个文件分配一个 ID,这个 ID 就是一个整数,被称为文件描述符(File Descriptor)。
如下是文件描述符的类型及其对应的设备。
1、输入重定向:<
command
[root@xuel-terraform-cvm-0 ~]# cat testfile.txt
test content
[root@xuel-terraform-cvm-0 ~]# < testfile.txt cat
test content解析器解析到 “<” 以后会先处理重定向,将标准输入重定向到 file,之后 cat 再从标准输入读取指令的时候,由于标准输入已经重定向到了 file ,于是 cat 就从 file 中读取指令了。
command <
command <
该输入重定向可以很方便用于批量文件的输入,可以用此来创建文件,例如:
[root@xuel-terraform-cvm-0 ~]# cat > file1.txt < hello shell
> hello go
> test file
> EOF
[root@xuel-terraform-cvm-0 ~]# cat file1.txt
hello shell
hello go
test file 2、输出重定向:> / >>
输出方向为数据输出到那个终端,输出重定向即改变默认的显示器输出,改变其从其他设备输出。
- 覆盖方式
语法:command >file
[root@xuel-terraform-cvm-0 ~]# cat file1.txt
hello shell
hello go
test file
[root@xuel-terraform-cvm-0 ~]# echo "test" > file1.txt
[root@xuel-terraform-cvm-0 ~]# cat file1.txt
test- 追加方式
语法:command >>file
[root@xuel-terraform-cvm-0 ~]# cat file1.txt
test
[root@xuel-terraform-cvm-0 ~]# echo "test222" >> file1.txt
[root@xuel-terraform-cvm-0 ~]# cat file1.txt
test
test2223、空设备:/dev/null
在 Linux 系统中存在一个空设备,也称为黑洞设备,其为 /dev/null。当我们将内容重定向到它时会被丢弃,对其也无法进行读取内容操作。