Request processing workflow in Spring Web MVC :
Image courtesy: springsource.org-
Front Controller (DispatcherServlet) receives requests based on the url-pattern mentioned inside servlet-mapping in web.xml.
-
Based on HandlerMapping (map of URL and Controller), Front Controller delegates the request to the matching controller.
-
Handler method of the matching controller is responsible for processing the delegated request and returns ModeAndView to the Front Controller (DispatcherServlet).
-
DispatcherServlet resolves the logical view name to actual view using ViewResolver and passes the Model object to the view.
-
Response is prepared using the Model and actual view. Then the control goes back to the DispatcherServlet.
-
DispatcherServlet returns the response which gets rendered in the browser.
Tools and Technologies used in this article :
-
Spring 3.1
-
JDK 1.6
-
Eclipse 3.7
-
Maven Integration for Eclipse WTP (a.k.a m2e-wtp)
-
Tomcat 7
1. Create a Java Web Project using m2e
Select from the menu File --> New --> Other --> Maven --> Maven Project. Browse to the workspace location and click 'Next' button.
Type 'webapp' in the 'Filter' field and select archetype 'maven-archetype-webapp' to generate a simple java web application using Maven. Click 'Next' button.
Specify archetype parameters (Group Id, Artifact, Version and Package) and click 'Finish' button.
2. Add Project Dependencies in pom.xml
Add dependency of Spring MVC 3 in Maven pom.xml.
File : pom.xml|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
<
project
xmlns
=
"http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi
=
"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation
=
"http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd"
>
<
modelVersion
>4.0.0
<
groupId
>com.srccodes.spring
<
artifactId
>SpringMVCHelloWorld
<
packaging
>war
<
version
>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
<
name
>SpringMVCHelloWorld Maven Webapp
<
url
>http://maven.apache.org
<
properties
>
<
org.springframework.version
>3.1.2.RELEASE
<
dependencies
>
<
dependency
>
<
groupId
>org.springframework
<
artifactId
>spring-webmvc
<
version
>${org.springframework.version}
<
build
>
<
finalName
>SpringMVCHelloWorld
<
plugins
>
<
plugin
>
<
groupId
>org.apache.maven.plugins
<
artifactId
>maven-compiler-plugin
<
version
>2.5.1
<
configuration
>
<
source
>1.6
<
target
>1.6
|
3. Controller Class and Request Mapping
Create a spring controller class called SpringMVCHelloController in package 'com.srccodes.spring.controller' and copy following code into it.
File : SpringMVCHelloController.java|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
package com.srccodes.spring.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
/**
* @author Abhijit Ghosh
* @version 1.0
*/
@Controller
public class SpringMVCHelloController {
@RequestMapping("/")
public String printHelloWorld(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "Hello World!");
return "helloWorld";
}
}
|
@Controller annotation indicates that this class serves the role of a controller. The Servlet dispatcher scans @Controller annotated Controller classes for mapped handler methods and detects @RequestMapping annotations.
@RequestMapping annotation specifies that this handler method will process all requests beginning with '/' in the URL and return the logical view name.
'org.springframework.ui.Model' object is a map which is passed by the Spring container while invoking the handler method 'printHelloWorld'. The message string 'Hello World!' has been added to 'Model' object against the key 'message'. This model object is available in the view. We can use the key 'message' to get the value and display the same in the UI.
4. Create a JSP page as View
Now we need to create a JSP page called helloWorld.jsp under 'WEB-INF/pages' directory and copy the following jsp file content. We have used the key 'message' in expression '${message}' to get the value and display the same in 'helloWorld.jsp'.
File : helloWorld.jsp|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<
html
>
<
body
>
<
h2
>${message}
|
5. Add Spring Configuration File
Create an xml file called dispatcher-servlet.xml under 'WEB-INF' directory and copy the following content.
File : dispatcher-servlet.xml|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<
beans
xmlns
=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi
=
"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p
=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context
=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc
=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.1.xsd">
<
context:component-scan
base-package
=
"com.srccodes.spring.controller"
/>
<
mvc:annotation-driven
/>
<
bean
id
=
"viewResolver"
class
=
"org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"
>
<
property
name
=
"prefix"
value
=
"/WEB-INF/pages/"
/>
<
property
name
=
"suffix"
value
=
".jsp"
/>
|
The above configuration file provides context information to the Spring container. '
'
ViewResolver provides a mapping between logical view name and actual view. It enables us to render models in UI without tying us to a specific view technology like JSPs, JSF, Velocity templates etc. Handler method defined in Controller class must resolve to a logical view name. In our case, 'printHelloWorld' handler method returns 'helloWorld' view name. It gets resolved to the path 'WEB-INF/pages/helloWorld.jsp' by the 'InternalResourceViewResolver' by adding prefix '/WEB-INF/pages/' and suffix '.jsp' to the view name 'helloWorld'.
6. Integrate Spring with Web Application
Copy the following content in your web.xml file.
File: web.xml|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
<
web-app
xmlns
=
"http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi
=
"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation
=
"http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"
version
=
"2.5"
>
<
servlet
>
<
servlet-name
>dispatcher
<
servlet-class
>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
<
load-on-startup
>1
<
servlet-mapping
>
<
servlet-name
>dispatcher
<
url-pattern
>/
|
DispatcherServlet (Front Controller) is mapped with the
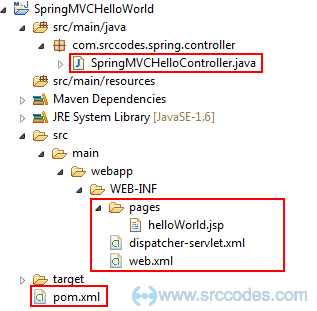
7. Overall Project Structure
8. Deploy and Run the Application
Right click on the project 'SpringMVCHelloWorld' and select from context menu 'Run As' --> 'Run on Server'. Select the existing tomcat server. If not available then manually define a new web server.Click "Finish" button. The web application will be deployed in the tomcat web server and a browser will be opened with 'Hello World!' message as shown below
http://localhost:8080/SpringMVCHelloWorld
Download Source Code
References
- Introduction to Spring Web MVC framework
- Spring Framework 3.2 API
- Video: Quick m2e-wtp introduction