Spring Boot 2.x整合模版引擎(1)-Thymeleaf的XML模式,自定义方言属性
背景
前段时间有一需求,需要动态修改xml模版的内容,但是网上能收集的资料多是关于thymeleaf的HTML使用方式;于是,在【科学上网】与自己的研究下,终于成功解决了这个需求。
通过下文,将可以学到Spring Boot2.x+Thymeleaf的XML模式的使用,以及自定义Thymeleaf方言属性两个知识点;水平有限,若有误,欢迎各路英雄指正。
一、Thymeleaf的XML模式
1、创建spring boot工程
使用IDEA创建spring boot工程,具体步骤参考其他资料。
2、引入thymeleaf的依赖
在pom.xml中,添加thymeleaf相关的依赖,如下所示
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.1.7.RELEASE
com.he
springboot-template
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
springboot-template
Spring Boot2.x整合模板引擎技术
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.projectlombok
lombok
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
io.springfox
springfox-swagger2
2.8.0
io.springfox
springfox-swagger-ui
2.8.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
3、在[application.properties]中,修改配置
在此简单起见,我全部使用spring boot默认的配置,可以看到该文件内容是为空的
4、新建Thymeleaf配置类,提供Bean
Thymeleaf的XML模式,不像默认的HTML,需要额外提供两个Bean才可以成功运行;
第一个,是[SpringResourceTemplateResolver],模版解析器;
第二个,是[SpringTemplateEngine],Spring的模版引擎。
- 新建类[ThymeleafConfig.java]如下
package com.he.config;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine;
import org.thymeleaf.spring5.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver;
import org.thymeleaf.templatemode.TemplateMode;
/**
* @date 2019/10/4
* @des Thymeleaf配置
*/
@Configuration
public class ThymeleafConfig {
@Bean
SpringResourceTemplateResolver xmlTemplateResolver(ApplicationContext appCtx) {
SpringResourceTemplateResolver templateResolver = new SpringResourceTemplateResolver();
templateResolver.setApplicationContext(appCtx);
templateResolver.setPrefix("classpath:/templates/");//指定模版前缀,即存放位置,默认是该地址
templateResolver.setSuffix(".xml");//指定模版后缀
templateResolver.setTemplateMode(TemplateMode.XML);//指定使用‘XML’模式
templateResolver.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");//指定使用‘UTF-8’编码
templateResolver.setCacheable(true);//开启缓存
return templateResolver;
}
@Bean
SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine(ApplicationContext appCtx) {
SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine = new SpringTemplateEngine();
templateEngine.setEnableSpringELCompiler(true);
templateEngine.setTemplateResolver(xmlTemplateResolver(appCtx));
return templateEngine;
}
}5、添加Thymeleaf模版
在[resources-templates]中,新建我们的模版[person-test.xml],注意Thymeleaf语法的正确使用
xml模版内容如下,十分简单,我们模拟动态的修改一个人的姓名国籍信息
6、在controller中编写测试示例
在此,我引入swagger2,方便调试,具体引入参考代码,这里不再描述
新建[TestController.java],编写我们的测试示例,如下所示
package com.he.controller;
import com.he.entity.*;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.thymeleaf.context.Context;
import org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @date 2019/10/4
* @des thymeleaf模版
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@Autowired
SpringTemplateEngine springTemplateEngine;
@ApiOperation(value = "Thymeleaf模版的XML模式", notes = "XML模版")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "lastname", value = "姓氏"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "firstname", value = "名字"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "country", value = "国籍")
})
@GetMapping(value = "/test1", produces = {MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE})//produces改为XML
public String test1(@RequestParam String lastname, @RequestParam String firstname, @RequestParam String country) {
Map pinfo = new HashMap<>();
Context context = new Context();
context.setVariable("pinfo", pinfo);
pinfo.put("lastname", lastname);
pinfo.put("firstname", firstname);
pinfo.put("country", country);
log.info("---pinfo:{}", pinfo);
String content = springTemplateEngine.process("person-test", context);
log.info("---xml:\n{}", content);
return content;
}
}
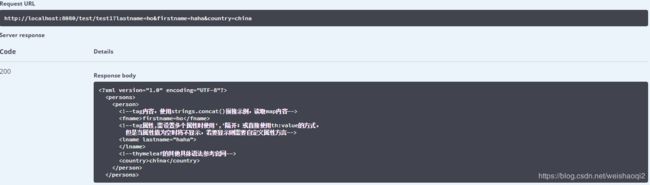
在swagger-ui.html输入测试参数后,日志打印如下
2019-10-12 16:38:23.898 INFO 12504 --- [nio-8080-exec-7] com.he.controller.TestController : ---pinfo:{country=china, firstname=haha, lastname=ho}
2019-10-12 16:38:24.063 INFO 12504 --- [nio-8080-exec-7] com.he.controller.TestController : ---xml:
firstname=ho
china
页面返回如下
可见XML的内容被修改了,到此Thymeleaf的XML模式正式实现。
二、Thymeleaf自定义方言属性
接下来看下Thymeleaf更加高级一点的用法,即自定义标签,自定义方言属性,在此我只介绍[自定义方言属性],并且是基于XML模式下,在HTML文件中引用是一样的,只需把模式切换回HTML即可
1、背景描述
假设我们需要通过SQL查询某一个数据库系统,但是这个SQL是通过xml协议实现的。我们需要动态的修改这个SQL,也就是根据具体的查询语句,动态改变XML的内容。但是,我在改变tag的标签属性时,遇到“属性值为空时,该属性将不被显示”的问题,就是当使用[th:attr]或[th:xxx]这种方式设置属性时,若attr-value为空,将不可见,这对于协议是不允许的。所以只能自定义方言实现这一需求。
在这里,我们将定义我们自己的属性[zdy:attr]
2、使用thymeleaf改造XML模版
原xml协议如下:
改造后,如下:
3、定义对应的实体类
实体类与xml的tag分别对应起来,有5个,分别如下
package com.he.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @date 2019/10/4
* @des XML模版标签
*
*/
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Condition implements Serializable {
/**
* 查询字段,非空
*/
private Select select = new Select();
/**
* 查询条件,可为空
*/
private Where where;
} package com.he.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @date 2019/10/4
* @des XML模版里的 package com.he.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @date 2019/10/4
* @des XML模版里的 package com.he.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @date 2019/10/4
* @des XML模版里的
*/
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Where implements Serializable{
/**
* cd标签:单条件,动态添加
*/
private List cds;
} package com.he.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @date 2019/10/4
* @des XML模版里的里的cd标签
*/
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Cd implements Serializable {
private String func = "";
private String column = "";
private String compare = "";
private String value = "";
private String relation = "";
}
4、定义Thymeleaf属性处理器
自定义属性处理器,需要继承[AbstractAttributeTagProcessor]类,代码如下
package com.he.config;
import org.thymeleaf.IEngineConfiguration;
import org.thymeleaf.context.ITemplateContext;
import org.thymeleaf.engine.AttributeName;
import org.thymeleaf.model.IProcessableElementTag;
import org.thymeleaf.processor.element.AbstractAttributeTagProcessor;
import org.thymeleaf.processor.element.IElementTagStructureHandler;
import org.thymeleaf.standard.expression.IStandardExpression;
import org.thymeleaf.standard.expression.IStandardExpressionParser;
import org.thymeleaf.standard.expression.StandardExpressions;
import org.thymeleaf.templatemode.TemplateMode;
/**
* @date 2019/10/4
* @des 自定义thymeleaf属性处理器
*/
public class CustomAttrProcessor extends AbstractAttributeTagProcessor {
private static final String ATTR_NAME = "attr";//自定义属性名,即(:)后面的名称,与前缀组合后是(zdy:attr)
private static final int PRECEDENCE = 10000;//优先级
public CustomAttrProcessor(final String dialectPrefix) {
super(
TemplateMode.XML, // This processor will apply only to XML mode
dialectPrefix, // Prefix to be applied to name for matching
null, // No tag name: match any tag name
false, // No prefix to be applied to tag name
ATTR_NAME, // Name of the attribute that will be matched
true, // Apply dialect prefix to attribute name
PRECEDENCE, // Precedence (inside dialect's precedence)
true); // Remove the matched attribute afterwards
}
@Override
protected void doProcess(
final ITemplateContext context, final IProcessableElementTag tag,
final AttributeName attributeName, final String attributeValue,
final IElementTagStructureHandler structureHandler) {
/*
* In order to evaluate the attribute value as a Thymeleaf Standard Expression,
* we first obtain the parser, then use it for parsing the attribute value into
* an expression object, and finally execute this expression object.
*/
final IEngineConfiguration configuration = context.getConfiguration();
/*
* Obtain the Thymeleaf Standard Expression parser
*/
final IStandardExpressionParser parser =
StandardExpressions.getExpressionParser(configuration);
/**
* 根据“;”拆分属性组合(同一属性不允许多次出现在同一element中,所以使用‘;’进行属性组合)
*/
System.out.println("--自定义thymeleaf属性值: " + attributeValue);
String[] attrArray = attributeValue.split(";");
if (attrArray != null && attrArray.length > 0) {
//遍历每个属性,设置单个属性值
for (int i = 0; i < attrArray.length; i++) {
//解析单个属性
String attr = attrArray[i];
/**
* Parse the attribute value as a Thymeleaf Standard Expression
*/
final IStandardExpression expression =
parser.parseExpression(context, attr);
/**
* Execute the expression just parsed
*/
final String tagAttr = (String) expression.execute(context);
//根据“=”拆分属性name和value
String[] tagAttrArray = tagAttr.split("=");
String attrName = tagAttrArray[0];
String attrValue = "";
if (tagAttrArray.length > 1) {
attrValue = tagAttrArray[1];
}
//设置属性
structureHandler.setAttribute(attrName, attrValue);
}
}
}
}在doProcess()方法里,根据自定义的属性,读取属性值,然后进行拆分出一个个单独的属性,使用structureHandler.setAttribute()重新给tag设置属性,从而达到修改属性的目的。
5、定义Thymeleaf属性方言
完成了第4步后,还需要自定义属性方言,并添加到模版引擎中。新建CustomAttrDialect.java继承AbstractProcessorDialect
package com.he.config;
import org.thymeleaf.dialect.AbstractProcessorDialect;
import org.thymeleaf.processor.IProcessor;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @date 2019/10/4
* @des 自定义thymeleaf属性方言
*/
public class CustomAttrDialect extends AbstractProcessorDialect {
private static final String DIALECT_NAME = "custom"; // 方言名称
private static final String PREFIX = "zdy"; // 方言前缀,zdy(自定义) ,使用格式(zdy:*)
public static final int PROCESSOR_PRECEDENCE = 1000; // 方言优先级
public CustomAttrDialect() {
super(DIALECT_NAME, PREFIX, PROCESSOR_PRECEDENCE);
}
/*
* 初始化方言处理器
*
*/
public Set getProcessors(final String dialectPrefix) {
final Set processors = new HashSet<>();
processors.add(new CustomAttrProcessor(dialectPrefix));//添加自定义的属性处理器
return processors;
}
} 然后,把它添加到模版引擎中,如下
@Bean
SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine(ApplicationContext appCtx) {
SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine = new SpringTemplateEngine();
templateEngine.setEnableSpringELCompiler(true);
templateEngine.setTemplateResolver(xmlTemplateResolver(appCtx));
templateEngine.addDialect(new CustomAttrDialect());//自定义方言
return templateEngine;
}
6、在controller中添加测试方法
简单测试起见,我们把SQL的参数写死,整个类如下
package com.he.controller;
import com.he.entity.*;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.thymeleaf.context.Context;
import org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @date 2019/10/4
* @des thymeleaf模版
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@Autowired
SpringTemplateEngine springTemplateEngine;
@ApiOperation(value = "Thymeleaf模版的XML模式", notes = "XML模版")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "lastname", value = "姓氏"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "firstname", value = "名字"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "country", value = "国籍")
})
@GetMapping(value = "/test1", produces = {MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE})//produces改为XML
public String test1(@RequestParam String lastname, @RequestParam String firstname, @RequestParam String country) {
Map pinfo = new HashMap<>();
Context context = new Context();
context.setVariable("pinfo", pinfo);
pinfo.put("lastname", lastname);
pinfo.put("firstname", firstname);
pinfo.put("country", country);
log.info("---pinfo:{}", pinfo);
String content = springTemplateEngine.process("person-test", context);
log.info("---xml:\n{}", content);
return content;
}
@ApiOperation(value = "Thymeleaf动态修改XML", notes = "可指定参数动态修改XML")
@GetMapping(value = "/test2", produces = {MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE})//produces改为XML
public String test2() {
Context context = new Context();
//标签
Condition condition = new Condition();
condition = testSql();
context.setVariable("condition", condition);
String content = springTemplateEngine.process("xml-protocol", context);
log.info("Thymeleaf dynamic---xml:\n{}", content);
return content;
}
/**
* ‘select count(c1) as xxx,c2 from tb where ...’
*
* @return Condition
*/
private Condition testSql() {
Condition condition = new Condition();
//select字段
List columns = new ArrayList<>();
Column c1 = new Column();
c1.setFunc("count(id)");
c1.setNickname("id_count");
Column c2 = new Column();
c2.setName("id");
columns.add(c1);
columns.add(c2);
condition.getSelect().setColumns(columns);
//where条件
List cds = new ArrayList<>();
Cd cd1 = new Cd();
cd1.setColumn("name");
cd1.setCompare("=");
cd1.setValue("hehe");
Cd cd2 = new Cd();
cd2.setColumn("age");
cd2.setCompare("=");
cd2.setValue("18");
cd2.setRelation("and");
cds.add(cd1);
cds.add(cd2);
Where where = new Where(cds);
condition.setWhere(where);
return condition;
}
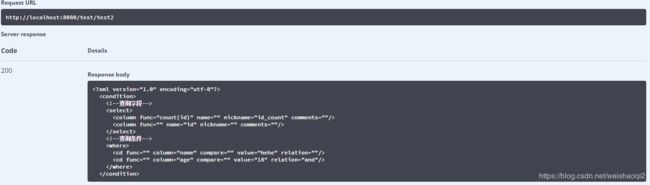
} 在swagger-ui.html调用测试方法后,页面返回内容如下
日志打印如下
--自定义thymeleaf属性值: ${#strings.concat('func=',column.func)};
${#strings.concat('name=',column.name)};
${#strings.concat('nickname=',column.nickname)};
${#strings.concat('comments=',column.comments)}
--自定义thymeleaf属性值: ${#strings.concat('func=',column.func)};
${#strings.concat('name=',column.name)};
${#strings.concat('nickname=',column.nickname)};
${#strings.concat('comments=',column.comments)}
--自定义thymeleaf属性值: ${#strings.concat('func=',cd.func)};
${#strings.concat('column=',cd.column)};
${#strings.concat('compare=',cd.compare)};
${#strings.concat('value=',cd.value)};
${#strings.concat('relation=',cd.relation)}
--自定义thymeleaf属性值: ${#strings.concat('func=',cd.func)};
${#strings.concat('column=',cd.column)};
${#strings.concat('compare=',cd.compare)};
${#strings.concat('value=',cd.value)};
${#strings.concat('relation=',cd.relation)}
2019-10-12 17:41:39.288 INFO 18976 --- [nio-8080-exec-8] com.he.controller.TestController : Thymeleaf dynamic---xml:
可见,测试成功!
至此,Thymeleaf的XML模式,自定义方言属性已介绍完毕,后面将介绍另一模版引擎Freemarker的XML模式使用方式。
全文代码链接:
https://gitee.com/he-running/springboot-template.git