Java ThreadLocalMap 源码解析
目录
- 1. 概述
- 2. 组成
- 3. Entry
- 4. Initor
- 4.1 单Entry初始化构造器
- 4.2 批量初始化构造器
- 5. Expunge
- 5.1 cleanSomeSlots
- 5.2 expungeStaleEntries
- 6. set
- 7. replaceStaleEntry
- 8. getEntry
- 8.1 直接命中
- 8.2 碰撞查找
- 9. remove
- 10. 动态扩容
- 11. 总结
1. 概述
ThreadLocalMap是一种类似java.util.HashMap的数据结构。
ThreadLocalMap是java.lang.ThreadLocal类的静态内部类。
ThreadLocalMap主要是作为成员变量,应用在java.lang.Thread类。
探索ThreadLocalMap,有助于理解多线程并发环境下ThreadLocal的实现原理。
本文涉及的源码为Oracle JDK 1.8版本。
2. 组成
参照下图,下文从ThreadLocalMap类的基础元素Entry、构造器Initor、增删查方法,以及元素擦除机制等方面展开探讨。

3. Entry
源码:
static class Entry extends WeakReference> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}

如上,Entry继承WeakReference,包括两个元素,一个ThreadLocal类型的成员和一个Object类型的成员value。其中ThreadLocal类型的成员是一个弱引用,其特点是,当引用元素无强引用时,JVM GC时会立即回收引用元素。关于Java强引用、软引用、弱引用、幽灵引用,可以参考[理解Java的GC与幽灵引用]。
4. Initor
ThreadLocalMap类有两个构造器。
4.1 单Entry初始化构造器
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal firstKey, Object firstValue) {
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
size = 1;
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
首先初始化Entry数组,然后根据初始化Key计算Hash Index,最后在Entry数组中指定Index设置Entry。
4.2 批量初始化构造器
private ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {
Entry[] parentTable = parentMap.table;
int len = parentTable.length;
setThreshold(len);
table = new Entry[len];
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
Entry e = parentTable[j];
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
ThreadLocal根据传入批量Entries,将所有Key非空Entry设置到该类Entry数组。
5. Expunge
在探讨增删查之前,先分析下擦除机制。
根据前文所述,Entry对象Key为弱引用,当Key所指对象无强引用时,JVM GC时会自动回收该对象,从而造成Entry状态变为STALE,即无效状态。此时,必须对该Entry对象及其Value引用进行擦除,防止内存泄漏。
private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// expunge entry at staleSlot
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = null;
size--;
// Rehash until we encounter null
Entry e;
int i;
for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
e.value = null;
tab[i] = null;
size--;
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
if (h != i) {
tab[i] = null;
// Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until
// null because multiple entries could have been stale.
while (tab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
tab[h] = e;
}
}
}
return i;
}
如上,expungeStaleEntry方法参数为Entry数组索引start_i,返回值为Entry数组中,从start_i开始,遇到的第一个空Entry的索引end_i。
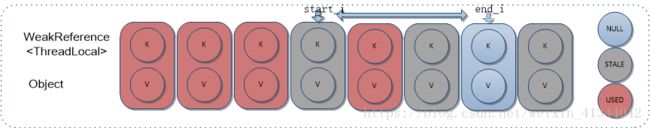
方法体执行步骤如下:
1)直接擦除参数指定索引位置Entry;
2)从下一个位置开始遍历,直到遇到空Entry返回;
2.1)如遍历位置为STALE状态Entry,擦除;
2.2)如遍历位置非STALE状态Entry,重新计算HashIndex,如和当前索引无冲突,则继续下个遍历;否则,重新插入,并把当前位置置空。
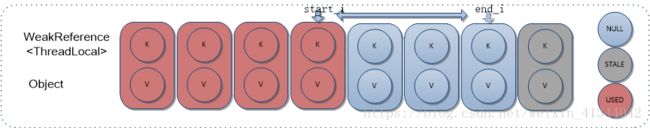
5.1 cleanSomeSlots
启发式扫描擦除,其扫描次数由第二个参数n(最大等于Entry数组长度)控制,实际为log2n,是一种折中式的扫描方式。
private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) {
boolean removed = false;
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
do {
i = nextIndex(i, len);
Entry e = tab[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == null) {
n = len;
removed = true;
i = expungeStaleEntry(i);
}
} while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0);
return removed;
}
方法从第一个参数指示索引的下一个元素开始扫描,返回值为是否找到擦除元素,即STALE状态元素。
5.2 expungeStaleEntries
全量扫描擦除,即扫描整个Entry数组。
private void expungeStaleEntries() {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
Entry e = tab[j];
if (e != null && e.get() == null)
expungeStaleEntry(j);
}
}
6. set
设置Entry到Entry数组。
private void set(ThreadLocal key, Object value) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
方法对应参数为Key,Value组合。
1)首先根据Key值计算HashIndex,对应至Entry数组索引start_i,并从start_i开始遍历;
2)如果查找到对应Key的Entry,则直接替换Value值,返回;
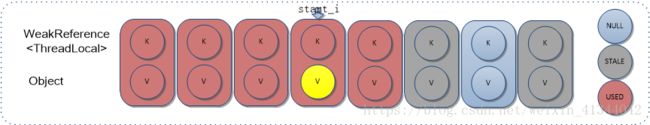
3)如果查找到STALE状态Entry,则执行替换无效状态方法,并返回,详见下节;

4)如果遇到空Entry,则直接设置Key,Value值,并判断Entry数组是否需要扩容;因为此处Entry数组新增了一个Entry,所以首先执行一次启发式擦除过程,如果成功擦除了元素,表明Entry数组并无变大,不需要扩容,否则,新增一个元素后,如果Entry数组大小大于阈值,则进行扩容。
[执行前]
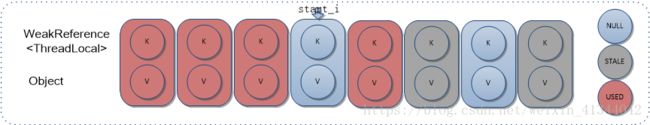
[执行后]
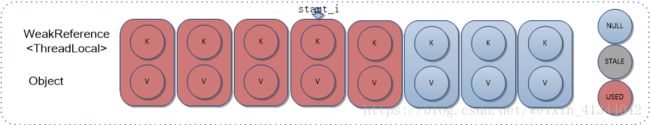
7. replaceStaleEntry
替换STALE状态Entry。需要注意,该方法和set方法结合使用才能产生正确结果。依赖前提是,第三个参数staleSlot必须是第一个参数key对应HashIndex后第一个非空且STATE状态Entry对应索引,且从start_i到stale_i之间,不存在第一个参数key对应有效元素。
private void replaceStaleEntry(ThreadLocal key, Object value,
int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
Entry e;
// Back up to check for prior stale entry in current run.
// We clean out whole runs at a time to avoid continual
// incremental rehashing due to garbage collector freeing
// up refs in bunches (i.e., whenever the collector runs).
int slotToExpunge = staleSlot;
for (int i = prevIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = prevIndex(i, len))
if (e.get() == null)
slotToExpunge = i;
// Find either the key or trailing null slot of run, whichever
// occurs first
for (int i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
// If we find key, then we need to swap it
// with the stale entry to maintain hash table order.
// The newly stale slot, or any other stale slot
// encountered above it, can then be sent to expungeStaleEntry
// to remove or rehash all of the other entries in run.
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
tab[i] = tab[staleSlot];
tab[staleSlot] = e;
// Start expunge at preceding stale entry if it exists
if (slotToExpunge == staleSlot)
slotToExpunge = i;
cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);
return;
}
// If we didn't find stale entry on backward scan, the
// first stale entry seen while scanning for key is the
// first still present in the run.
if (k == null && slotToExpunge == staleSlot)
slotToExpunge = i;
}
// If key not found, put new entry in stale slot
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = new Entry(key, value);
// If there are any other stale entries in run, expunge them
if (slotToExpunge != staleSlot)
cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);
}
方法执行过程如下:
1)从当前STALE元素向前探寻其它STALE元素,遇到空元素结束;
2)从当前STALE元素stale_i下一个元素,开始遍历,如果查找到包含传参key的Entry,即key_i,则交换stale_i和key_i两个Entry,并从确定的STALE元素开始擦除操作,再从结束位置开始启发式擦除;
[执行前]
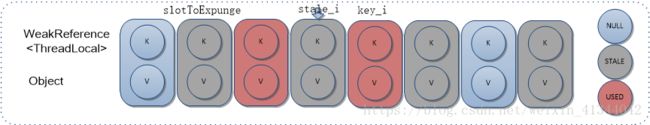
[执行后]
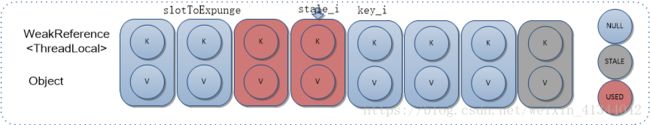
3)如果未查到到包含传参key的Entry,则直接在stale_i位置设置传参key对应Entry,并从确定的STALE元素开始擦除操作,再从结束位置开始启发式擦除。
[执行前]

[执行后]

8. getEntry
根据传参Key值获取对应Entry,包括直接命中获取和碰撞查找获取。
8.1 直接命中
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal key) {
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
计算传参Key对应HashIndex,hit_t,如果Entry[hit_t]对应Entry与传参一致,则直接返回Entry。否则,开始碰撞查找。
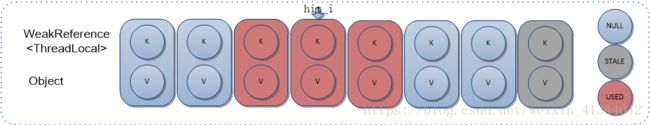
8.2 碰撞查找
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
while (e != null) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
if (k == key)
return e;
if (k == null)
expungeStaleEntry(i);
else
i = nextIndex(i, len);
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}
从Entry数组指定位置i开始遍历查找key对应Entry:
1)查找到,直接返回对应Entry;
2)未找到;
2.1)如果当前位置Entry为 SATLE无效状态,则执行擦除过程(擦除过程会重新计算遇到的有效Entry HashIndex,并重新设置所在Entry数组位置),并从当前位置继续开始查找判断;
2.2)如果当前位置Entry为有效状态,则递进至下一位置;
3)如果遇到空Entry,退出循环,并返回null。
[执行前]
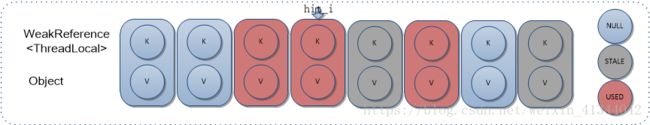
[擦除后]

[执行后]
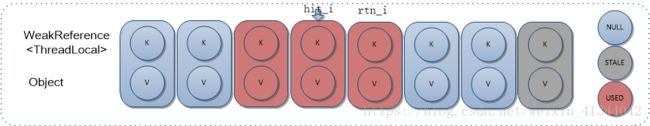
9. remove
/**
* Remove the entry for key.
*/
private void remove(ThreadLocal key) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
if (e.get() == key) {
e.clear();
expungeStaleEntry(i);
return;
}
}
}
在Entry数组中,删除指定Key的元素。如果找到待删除元素,首先将引用key值置空,然后从当前位置开始执行擦除过程。
10. 动态扩容
/**
* Set the resize threshold to maintain at worst a 2/3 load factor.
*/
private void setThreshold(int len) {
threshold = len * 2 / 3;
}
如上,Entry数组扩容阈值为数组长度的2/3。
private void set(ThreadLocal key, Object value) {
...
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
如上,只有在成功向Entry数组添加Entry后,才会触发数组扩容过程,条件为数组大小不小于阈值。
/**
* Re-pack and/or re-size the table. First scan the entire
* table removing stale entries. If this doesn't sufficiently
* shrink the size of the table, double the table size.
*/
private void rehash() {
expungeStaleEntries();
// Use lower threshold for doubling to avoid hysteresis
if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4)
resize();
}
扩容前,再做一次全表扫描擦除,如果擦除后的Entry数组不小于3/4倍阈值,则开始扩容。
/**
* Double the capacity of the table.
*/
private void resize() {
Entry[] oldTab = table;
int oldLen = oldTab.length;
int newLen = oldLen * 2;
Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen];
int count = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) {
Entry e = oldTab[j];
if (e != null) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
e.value = null; // Help the GC
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1);
while (newTab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, newLen);
newTab[h] = e;
count++;
}
}
}
setThreshold(newLen);
size = count;
table = newTab;
}
resize方法首先将数组长度扩容一倍,然后开始遍历重设:
1)如果遇到STALE无效Entry,执行擦除;
2)否则,根据扩容后数组,重新计算Entry在新数组中HashIndex。
11. 总结
java.lang包中的ThreadLocalMap和java.util包的WeakHashMap有相似之处,不同之处在于,后者会在Key被GC后,自动删除对应Entry。那么此处为什么不用WeakHashMap呢?