obj文件是一种常用的3D模型文件,本文分析cocos2d解析文件的过程。obj文件也是普通的文本文件,以cocos2d的demo中的boss1.obj文件为例,看看它长啥样:
# "#"后面是注释
# 3ds Max Wavefront OBJ Exporter v0.97b - (c)2007 guruware
# File Created: 15.05.2014 08:13:14
#材质库
mtllib boo1.mtl
#
# object Object
#
#顶点坐标,一行表示一个顶点(x, y, z)
v 0.5491 -0.2313 7.4010
v 0.5491 -0.3996 7.0495
v 0.5491 -0.3669 7.0495
#省略...
# 445 vertices
#顶点法线,一行表示一个顶点法线(x, y, z)
vn 0.6502 0.2638 0.7125
vn 1.0000 0.0000 -0.0000
vn 0.7327 0.6756 -0.0817
#省略...
# 331 vertex normals
#纹理坐标,一行表示一个纹理坐标(s,t),第三个数恒为0
vt 0.3471 0.0763 0.0000
vt 0.4009 0.0969 0.0000
vt 0.4005 0.0921 0.0000
#..
# 409 texture coords
#g是组名称
g Object
#usemtl是材质名称
usemtl _bossdefault
#s是光滑组
s 1
#f是面的索引,每一行代表一个面,如a/b/c,a是顶点索引,b是法线索引,c是纹理坐标索引
f 1/1/1 2/2/2 3/3/2 4/4/3
f 1/1/1 4/4/3 5/5/4
f 6/3/5 7/2/5 8/1/6 9/4/7
#...
# 307 polygons - 102 triangles
如在Sprite3D中要加载一个obj文件,代码如下:
bool Sprite3D::loadFromFile(const std::string& path, NodeDatas* nodedatas, MeshDatas* meshdatas, MaterialDatas* materialdatas)
{
std::string fullPath = FileUtils::getInstance()->fullPathForFilename(path);
std::string ext = FileUtils::getInstance()->getFileExtension(path);
if (ext == ".obj")
{
return Bundle3D::loadObj(*meshdatas, *materialdatas, *nodedatas, fullPath);
}
else if (ext == ".c3b" || ext == ".c3t")
{
//load from .c3b or .c3t
auto bundle = Bundle3D::createBundle();
if (!bundle->load(fullPath))
{
Bundle3D::destroyBundle(bundle);
return false;
}
auto ret = bundle->loadMeshDatas(*meshdatas)
&& bundle->loadMaterials(*materialdatas) && bundle->loadNodes(*nodedatas);
Bundle3D::destroyBundle(bundle);
return ret;
}
return false;
}
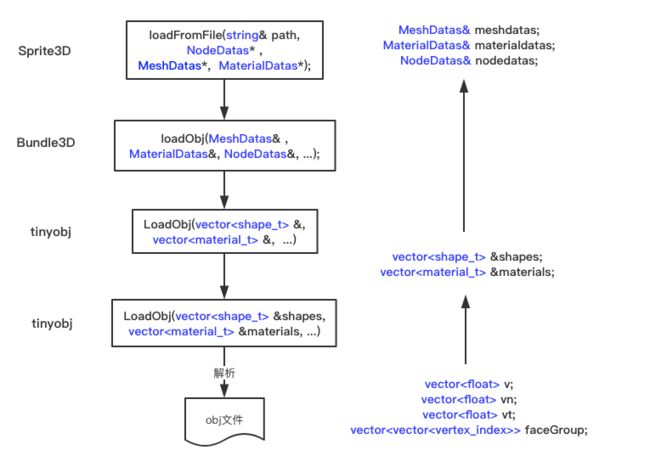
由代码可见,最终的obj文件的信息会被加载到NodeDatas,MeshDatas和MaterialDatas三个结构体中,通过调用Bundle3D的静态函数loadObj加载,具体调用堆栈及数据流如下:
解释下这个图,数据流从下往上,首先解析obj文件,把顶点数据(v开头),法线坐标(vn开头),纹理坐标(vt开头),面索引(f开头),还有其他信息(本次分析忽略了materials材质加载)存储到数组v,数组vn,数组vt和数组faceGroup中,然后再把这些数据整理后存到数组shapes和materials,最后再整理数据到meshdatas,materialdatas和nodedatas。
先看tinyobj::LoadObj的代码:
std::string LoadObj(std::vector &shapes,
std::vector &materials, // [output]
const char *filename, const char *mtl_basepath) {
shapes.clear();
std::stringstream err;
std::istringstream ifs(cocos2d::FileUtils::getInstance()->getStringFromFile(filename));
if (!ifs) {
err << "Cannot open file [" << filename << "]" << std::endl;
return err.str();
}
std::string basePath;
if (mtl_basepath) {
basePath = mtl_basepath;
}
MaterialFileReader matFileReader(basePath);
return LoadObj(shapes, materials, ifs, matFileReader);
}
std::string LoadObj(std::vector &shapes,
std::vector &materials, // [output]
std::istream &inStream, MaterialReader &readMatFn) {
std::stringstream err;
std::vector v; //存储顶点
std::vector vn; //存储顶点法线
std::vector vt; //存储纹理坐标
std::vector > faceGroup; //存储每个面的索引
std::string name;
// material
std::map material_map;
std::map vertexCache;
int material = -1;
shape_t shape;
int maxchars = 8192; // Alloc enough size.
std::vector buf(maxchars); // Alloc enough size.
while (inStream.peek() != -1) {
inStream.getline(&buf[0], maxchars);
std::string linebuf(&buf[0]);
// Trim newline '\r\n' or '\n'
if (linebuf.size() > 0) {
if (linebuf[linebuf.size() - 1] == '\n')
linebuf.erase(linebuf.size() - 1);
}
if (linebuf.size() > 0) {
if (linebuf[linebuf.size() - 1] == '\r')
linebuf.erase(linebuf.size() - 1);
}
// Skip if empty line.
if (linebuf.empty()) {
continue;
}
// Skip leading space.
const char *token = linebuf.c_str();
token += strspn(token, " \t");
assert(token);
if (token[0] == '\0')
continue; // empty line
if (token[0] == '#')
continue; // comment line
// vertex 顶点坐标,v开头
if (token[0] == 'v' && isSpace((token[1]))) {
token += 2;
float x, y, z;
parseFloat3(x, y, z, token);
v.push_back(x);
v.push_back(y);
v.push_back(z);
continue;
}
// normal 法线,vn开头
if (token[0] == 'v' && token[1] == 'n' && isSpace((token[2]))) {
token += 3;
float x, y, z;
parseFloat3(x, y, z, token);
vn.push_back(x);
vn.push_back(y);
vn.push_back(z);
continue;
}
// texcoord 纹理坐标,vt开头
if (token[0] == 'v' && token[1] == 't' && isSpace((token[2]))) {
token += 3;
float x, y;
parseFloat2(x, y, token);
vt.push_back(x);
vt.push_back(y);
continue;
}
// face 面索引,f开头
if (token[0] == 'f' && isSpace((token[1]))) {
token += 2;
token += strspn(token, " \t");
std::vector face;
auto first = static_cast(v.size() / 3);
auto second = static_cast(vn.size() / 3);
auto third = static_cast(vt.size() / 2);
while (!isNewLine(token[0])) {
vertex_index vi =
parseTriple(token, first, second, third);
face.push_back(vi);
size_t n = strspn(token, " \t\r");
token += n;
}
faceGroup.push_back(face);
continue;
}
// use mtl
if ((0 == strncmp(token, "usemtl", 6)) && isSpace((token[6]))) {
char namebuf[TINYOBJ_SSCANF_BUFFER_SIZE];
token += 7;
#ifdef _MSC_VER
sscanf_s(token, "%s", namebuf, _countof(namebuf));
#else
sscanf(token, "%s", namebuf);
#endif
// Create face group per material.
bool ret = exportFaceGroupToShape(shape, vertexCache, v, vn, vt,
faceGroup, material, name, true);
if (ret) {
shapes.push_back(shape);
}
shape = shape_t();
faceGroup.clear();
if (material_map.find(namebuf) != material_map.end()) {
material = material_map[namebuf];
} else {
// { error!! material not found }
material = -1;
}
continue;
}
// load mtl
if ((0 == strncmp(token, "mtllib", 6)) && isSpace((token[6]))) {
char namebuf[TINYOBJ_SSCANF_BUFFER_SIZE];
token += 7;
#ifdef _MSC_VER
sscanf_s(token, "%s", namebuf, _countof(namebuf));
#else
sscanf(token, "%s", namebuf);
#endif
std::string err_mtl = readMatFn(namebuf, materials, material_map);
if (!err_mtl.empty()) {
faceGroup.clear(); // for safety
return err_mtl;
}
continue;
}
// group name
if (token[0] == 'g' && isSpace((token[1]))) {
// flush previous face group.
bool ret = exportFaceGroupToShape(shape, vertexCache, v, vn, vt,
faceGroup, material, name, true);
if (ret) {
shapes.push_back(shape);
}
shape = shape_t();
// material = -1;
faceGroup.clear();
std::vector names;
while (!isNewLine(token[0])) {
std::string str = parseString(token);
names.push_back(str);
token += strspn(token, " \t\r"); // skip tag
}
assert(names.size() > 0);
// names[0] must be 'g', so skip the 0th element.
if (names.size() > 1) {
name = names[1];
} else {
name = "";
}
continue;
}
// object name
if (token[0] == 'o' && isSpace((token[1]))) {
// flush previous face group.
bool ret = exportFaceGroupToShape(shape, vertexCache, v, vn, vt,
faceGroup, material, name, true);
if (ret) {
shapes.push_back(shape);
}
// material = -1;
faceGroup.clear();
shape = shape_t();
// @todo { multiple object name? }
char namebuf[TINYOBJ_SSCANF_BUFFER_SIZE];
token += 2;
#ifdef _MSC_VER
sscanf_s(token, "%s", namebuf, _countof(namebuf));
#else
sscanf(token, "%s", namebuf);
#endif
name = std::string(namebuf);
continue;
}
// Ignore unknown command.
}
//将v, vn, vt, faceGroup的数据转存到shape中
bool ret = exportFaceGroupToShape(shape, vertexCache, v, vn, vt, faceGroup,
material, name, true);
if (ret) {
shapes.push_back(shape);
}
faceGroup.clear(); // for safety
return err.str();
}
LoadObj主要是解析obj文件,把数据存到v, vn, vt, faceGroup中。然后,调用exportFaceGroupToShape把v, vn, vt, faceGroup的数据转存到shape中,代码如下
static bool exportFaceGroupToShape(
shape_t &shape, std::map vertexCache,
const std::vector &in_positions,
const std::vector &in_normals,
const std::vector &in_texcoords,
const std::vector > &faceGroup,
const int material_id, const std::string &name, bool clearCache) {
if (faceGroup.empty()) {
return false;
}
// Flatten vertices and indices
for (size_t i = 0, size = faceGroup.size(); i < size; ++i) {
const std::vector &face = faceGroup[i];
vertex_index i0 = face[0];
vertex_index i1(-1);
vertex_index i2 = face[1];
size_t npolys = face.size();
// Polygon -> triangle fan conversion
for (size_t k = 2; k < npolys; k++) { //一次循环一个三角形
i1 = i2;
i2 = face[k];
unsigned int v0 = updateVertex(
vertexCache, shape.mesh.positions, shape.mesh.normals,
shape.mesh.texcoords, in_positions, in_normals, in_texcoords, i0); //第一个循环:face[0];第二个循环:face[0]
unsigned int v1 = updateVertex(
vertexCache, shape.mesh.positions, shape.mesh.normals,
shape.mesh.texcoords, in_positions, in_normals, in_texcoords, i1); //第一个循环:face[1];第二个循环:face[2]
unsigned int v2 = updateVertex(
vertexCache, shape.mesh.positions, shape.mesh.normals,
shape.mesh.texcoords, in_positions, in_normals, in_texcoords, i2); //第一个循环:face[2];第二个循环:face[3]
shape.mesh.indices.push_back(v0);
shape.mesh.indices.push_back(v1);
shape.mesh.indices.push_back(v2);
shape.mesh.material_ids.push_back(material_id);
}
}
shape.name = name;
if (clearCache)
vertexCache.clear();
return true;
}
整个过程的内存图大致如下:
得到shapes和materials后,就对meshdatas,materialdatas和nodedatas赋值。这三个结构体的类图大概如下:
具体处理在Bundle3D::loadObj函数中,代码如下:
bool Bundle3D::loadObj(MeshDatas& meshdatas, MaterialDatas& materialdatas, NodeDatas& nodedatas, const std::string& fullPath, const char* mtl_basepath)
{
meshdatas.resetData();
materialdatas.resetData();
nodedatas.resetData();
std::string mtlPath = "";
if (mtl_basepath)
mtlPath = mtl_basepath;
else
mtlPath = fullPath.substr(0, fullPath.find_last_of("\\/") + 1);
std::vector shapes;
std::vector materials;
auto ret = tinyobj::LoadObj(shapes, materials, fullPath.c_str(), mtlPath.c_str());
if (ret.empty())
{
//fill data
//convert material
int i = 0;
char str[20];
std::string dir = "";
auto last = fullPath.rfind("/");
if (last != std::string::npos)
dir = fullPath.substr(0, last + 1);
for (auto& material : materials) {
NMaterialData materialdata;
NTextureData tex;
tex.filename = material.diffuse_texname.empty() ? material.diffuse_texname : dir + material.diffuse_texname;
tex.type = NTextureData::Usage::Diffuse;
tex.wrapS = GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE;
tex.wrapT = GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE;
sprintf(str, "%d", ++i);
materialdata.textures.push_back(tex);
materialdata.id = str;
material.name = str;
materialdatas.materials.push_back(materialdata);
}
//convert mesh
i = 0;
for (auto& shape : shapes) {
auto mesh = shape.mesh;
MeshData* meshdata = new (std::nothrow) MeshData();
MeshVertexAttrib attrib;
attrib.size = 3;
attrib.type = GL_FLOAT;
if (mesh.positions.size())
{
attrib.vertexAttrib = GLProgram::VERTEX_ATTRIB_POSITION;
attrib.attribSizeBytes = attrib.size * sizeof(float);
meshdata->attribs.push_back(attrib);
}
bool hasnormal = false, hastex = false;
if (mesh.normals.size())
{
hasnormal = true;
attrib.vertexAttrib = GLProgram::VERTEX_ATTRIB_NORMAL;
attrib.attribSizeBytes = attrib.size * sizeof(float);
meshdata->attribs.push_back(attrib);
}
if (mesh.texcoords.size())
{
hastex = true;
attrib.size = 2;
attrib.vertexAttrib = GLProgram::VERTEX_ATTRIB_TEX_COORD;
attrib.attribSizeBytes = attrib.size * sizeof(float);
meshdata->attribs.push_back(attrib);
}
auto vertexNum = mesh.positions.size() / 3;
for(unsigned int k = 0; k < vertexNum; ++k)
{
meshdata->vertex.push_back(mesh.positions[k * 3]);
meshdata->vertex.push_back(mesh.positions[k * 3 + 1]);
meshdata->vertex.push_back(mesh.positions[k * 3 + 2]);
if (hasnormal)
{
meshdata->vertex.push_back(mesh.normals[k * 3]);
meshdata->vertex.push_back(mesh.normals[k * 3 + 1]);
meshdata->vertex.push_back(mesh.normals[k * 3 + 2]);
}
if (hastex)
{
meshdata->vertex.push_back(mesh.texcoords[k * 2]);
meshdata->vertex.push_back(mesh.texcoords[k * 2 + 1]);
}
}
//split into submesh according to material
std::map > subMeshMap;
for (size_t k = 0, size = mesh.material_ids.size(); k < size; ++k) {
int id = mesh.material_ids[k];
size_t idx = k * 3;
subMeshMap[id].push_back(mesh.indices[idx]);
subMeshMap[id].push_back(mesh.indices[idx + 1]);
subMeshMap[id].push_back(mesh.indices[idx + 2]);
}
auto node = new (std::nothrow) NodeData();
node->id = shape.name;
for (auto& submesh : subMeshMap) {
meshdata->subMeshIndices.push_back(submesh.second);
meshdata->subMeshAABB.push_back(calculateAABB(meshdata->vertex, meshdata->getPerVertexSize(), submesh.second));
sprintf(str, "%d", ++i);
meshdata->subMeshIds.push_back(str);
auto modelnode = new (std::nothrow) ModelData();
modelnode->materialId = submesh.first == -1 ? "" : materials[submesh.first].name;
modelnode->subMeshId = str;
node->modelNodeDatas.push_back(modelnode);
}
nodedatas.nodes.push_back(node);
meshdatas.meshDatas.push_back(meshdata);
}
return true;
}
CCLOG("warning: load %s file error: %s", fullPath.c_str(), ret.c_str());
return false;
}
代码比较简单就不多说了,再简单画一下MeshDatas的内存图