Spring的事务操作
一.事务操作的概念
概念
1、什么事务
(1)事务是数据库操作最基本单元,逻辑上一组操作,要么都成功,如果有一个失败所有操 作都失败 。事务是恢复和并发控制的基本单位。
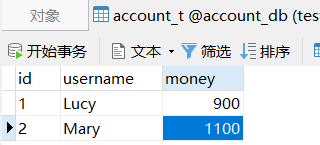
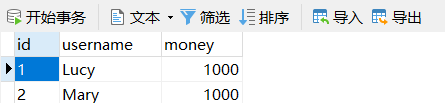
(2)典型场景:银行转账
- lucy 转账 100元 给mary
- lucy 少 100,mary 多 100
2、事务四个特性(ACID)
事务应该具有4个属性:原子性、一致性、隔离性、持久性。这四个属性通常称为ACID特性。
-
原子性(atomicity)
一个事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中包括的诸操作要么都做,要么都不做。 -
一致性(consistency)
事务必须是使数据库从一个一致性状态变到另一个一致性状态。一致性的定义和完整性约束有关系。这些月数可能包括主键约束、外键约束以及用户自定义的约束。事务执行的前后都是合法的数据状态,不能违背任何的数据完整性。这种完整性体现在业务上就是业务规则的约束,比如业务上要求银行转账前后必须总额一致,从业务的角度来看更容易理解,这也是我们最关心的。 -
隔离性(isolation)
一个事务的执行不能被其他事务干扰。即一个事务内部的操作及使用的数据对并发的其他事务是隔离的,并发执行的各个事务之间不能互相干扰。 -
持久性(durability)
持久性也称永久性(permanence),指一个事务一旦提交,它对数据库中数据的改变就应该是永久性的。接下来的其他操作或故障不应该造成其丢失。
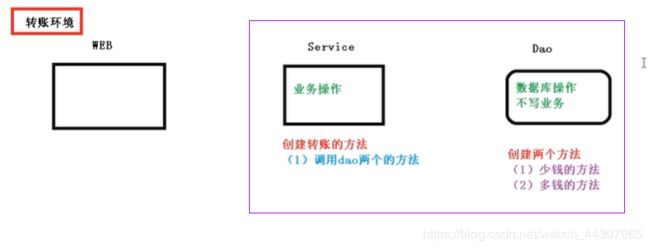
环境搭建
- 如图实现的是一个转账的方法
- 配置数据连接池
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.LinXiaoDe.spring5">context:component-scan>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///account_db?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=UTC" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="12345678" />
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
beans>
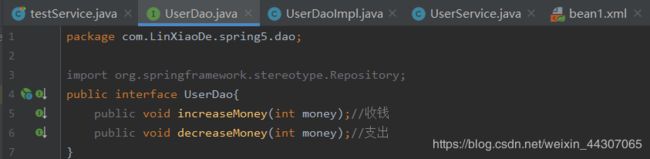
- 在 dao 创建两个方法:多钱和少钱的方法,在 service 创建方法(转账的方法)
//UserDaoService类
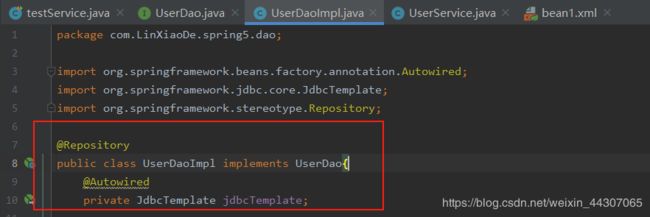
@Repository
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public void increaseMoney(int money) {
String sql="update account_t set money=money-? where username=?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,money,"Lucy");
}
@Override
public void decreaseMoney(int money) {
String sql="update account_t set money=money+? where username=?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,money,"Mary");
}
}
//UserService类
@Service//创建对象
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
//转账方法
public void accountMoney(){
//Lucy少100
userDao.decreaseMoney(100);
//Mary多100
userDao.increaseMoney(100);
}
}
出现的问题,用事务处理解决思路
以上的代码UserService类中,如果某一个环节发生了异常,则会导致账户出现错误。采
- 用事务进行解决:
- 事务操作过程如下:(以下介绍的是编程式管理,一般实际不使用)
public void accountMoney(){
try{
//第一步,开启事务
//第二步,进行事务操作
userDao.decreaseMoney(100);//Lucy少100
//可能发生异常
userDao.increaseMoney(100);//Mary多100
//第三步,没有异常发生,则提交事务
}catch (Exception e){
//第四步,出现异常,事物回滚
}
事务操作(Spring 事务管理介绍)
1、事务添加到 JavaEE 三层结构里面 Service 层(业务逻辑层)
2、在 Spring 进行事务管理操作
(1)有两种方式:编程式事务管理(一般不使用)
(2)声明式事务管理(使用)
3、声明式事务管理
(1)基于注解方式(使用)
(2)基于 xml 配置文件方式
4、在 Spring 进行声明式事务管理,底层使用 AOP原理
5、Spring 事务管理 API
(1)提供一个接口,代表事务管理器,这个接口针对不同的框架提供不同的实现类
PlatformTransactionManager
二. 注解式声明式事务管理
(1)在Spring配置文件中配置事务管理器
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
(2)在 spring 配置文件,开启事务注解
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager">tx:annotation-driven>
(3)在 service 类上面(或者 service 类里面方法上面)添加事务注解@Transactional
- @Transactional,这个注解添加到类上面,也可以添加方法上面
- 如果把这个注解添加类上面,这个类里面所有的方法都添加事务
- 如果把这个注解添加方法上面,为这个方法添加事务
@Service//创建对象
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
//转账方法
@Transactional //事务注解
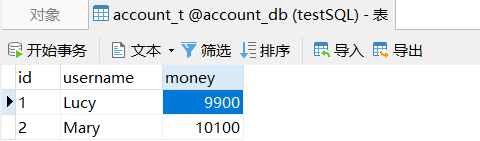
public void accountMoney(){
userDao.decreaseMoney(100);//Lucy少100
int x=1/0; //引发异常
userDao.increaseMoney(100);//Mary多100
}
测试结果
三. 注解式声明式事务管理参数配置
在 service 类上面添加注解@Transactional ,在这个注解里面可以配置事务相关参数
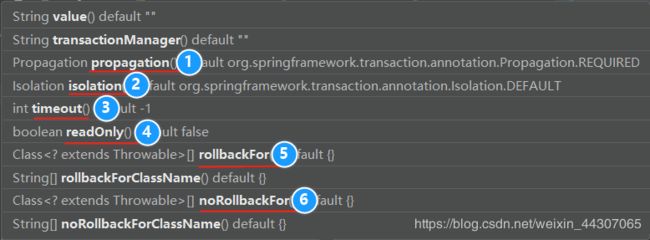
propagation:事务传播行为isolation:事务隔离级别timeout:超时时间readOnly:是否只读rollbackFor:回滚noRollbackFor:不回滚
参数1:propagation事务传播行为
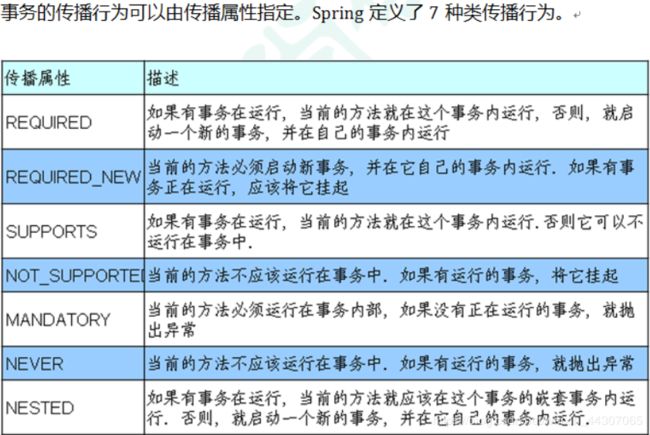
重点介绍的是前两个传播属性,事务方法是指对数据库中的数据进行变化的过程,增删改,操作;传播属性发生在多事务的过程,必须是两个或者两个以上的事务。
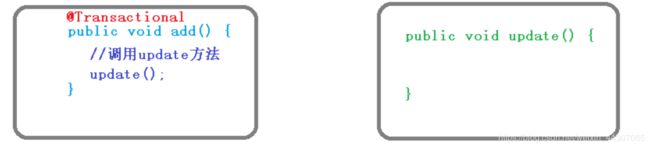
REQUIRED:如果add方法本身有事务,调用 update方法之后, update使用当前add方法里面事务如果add方法本身没有事务,调用 update方法之后,创建新事务REQUIRED_NEW:使用add方法调用 update方法,如果add无论是否有事务,都创建新的事务
举例
@Service//创建对象
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) //REQUIRED是默认的传播属性
public class UserService {
}
@Service//创建对象
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED_NEW) //事务注解
public class UserService {
}
参数2:isolation事务隔离级别
(1)事务有特性成为隔离性,多事务操作之间不会产生影响。不考虑隔离性产生很多问题
(2)有三个读问题:脏读、不可重复读、虚(幻)读
脏读 (致命问题):
脏读就是指当一个事务正在访问数据,并且对数据进行了修改,而这种修改还没有提交到数据库中,这时,另外一个事务也访问这个数据,然后使用了这个数据。
不可重复读(现象) :
是指在一个事务内,多次读同一数据。在这个事务还没有结束时,另外一个事务也访问该同一数据。那么,在第一个事务中的两次读数据之间,由于第二个事务的修改,那么第一个事务两次读到的的数据可能是不一样的。这样就发生了在一个事务内两次读到的数据是不一样的,因此称为是不可重复读。
例如,一个编辑人员两次读取同一文档,但在两次读取之间,作者重写了该文档。当编辑人员第二次读取文档时,文档已更改。原始读取不可重复。如果只有在作者全部完成编写后编辑人员才可以读取文档,则可以避免该问题。
幻(或虚)读(现象) :
是指当事务不是独立执行时发生的一种现象,例如第一个事务对一个表中的数据进行了修改,这种修改涉及到表中的全部数据行。同时,第二个事务也修改这个表中的数据,这种修改是向表中插入一行新数据。那么,以后就会发生操作第一个事务的用户发现表中还有没有修改的数据行,就好象发生了幻觉一样。
例如,一个编辑人员更改作者提交的文档,但当生产部门将其更改内容合并到该文档的主复本时,发现作者已将未编辑的新材料添加到该文档中。如果在编辑人员和生产部门完成对原始文档的处理之前,任何人都不能将新材料添加到文档中,则可以避免该问题。
不可重复读的重点是修改 :
同样的条件 , 你读取过的数据 , 再次读取出来发现值不一样了
幻读的重点在于新增或者删除同样的条件 , 第 1 次和第 2 次读出来的记录数不一样
isolation 属性一共支持五种事务设置,具体介绍如下:
隔离级别:
| 属性 | 含义 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| READ_UNCOMMITTED | 读未提交(隔离级别最低,并发性能高) | 有 | 有 | 有 |
| READ_COMMITTED | 读已提交(锁定正在读取的行) | 无 | 有 | 有 |
| REPEATABLE_READ | 可重复读(锁定所读取的所有行) | 无 | 无 | 有 |
| SERIALIZABLE | 串行化(锁表) | 无 | 无 | 无 |
举例
@Service//创建对象
@Transactional(
propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW, //传播行为
isolation = Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ) //隔离级别,MySQL默认的就是REPEATABLE_READ
public class UserService {
}
参数3:timeout超时时间
(1)事务需要在一定时间内进行提交,如果不提交进行回滚
(2)默认值是 -1 ,设置时间以秒单位进行计算
参数4:readOnly是否只读
(1)读:查询操作,写:添加修改删除操作
(2)readOnly 默认值 false,表示可以查询,可以添加修改删除操作
(3)设置 readOnly 值是 true,设置成 true 之后,只能查询
参数5:rollbackFor回滚
(1)设置出现哪些异常进行事务回滚
参数6:noRollbackFor不回滚
(1)设置出现哪些异常不进行事务回滚
四.XML式声明式事务管理
- 第一步 配置事务管理器
- 第二步 配置通知
- 第三步 配置切入点和切面
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.LinXiaoDe.spring5">context:component-scan>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///account_db?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=UTC" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="12345678" />
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="accountMoney" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pt" expression="execution(* com.LinXiaoDe.spring5.service.UserService.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pt" />
aop:config>
beans>
五.完全按注解开发
(1)配置类
package com.LinXiaoDe.spring5.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
@Configuration // 表示这是配置类
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.LinXiaoDe.spring5") //开始注解扫描
@EnableTransactionManagement //开启事务
public class txConfig {
//创建数据库连接池
@Bean
public DruidDataSource getDruidDataSource(){
DruidDataSource dataSource=new DruidDataSource();
//设置属性
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql:///account_db?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=UTC");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("MySQLqdl0661");
return dataSource;
}
//创建JdbcTemplate对象
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(DruidDataSource dataSource){
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate=new JdbcTemplate();
///注入数据源(连接池)
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
return jdbcTemplate;
}
//创建事务管理器
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager gettransactionManager(DruidDataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager=new DataSourceTransactionManager();
//注入数据源
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return transactionManager;
}
}
(2)测试方式
@Test
public void testAccount2(){
ApplicationContext context=
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(txConfig.class);
//注意使用子接口AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
UserService userService=context.getBean("userService",UserService.class);
userService.accountMoney();
}