Spring AOP源码解析:一:Advisor获取流程
Spring AOP源码解析:一:Advisor获取流程
- 一、流程介绍
- 名词介绍
- 二、主流程源码介绍
- 三、获取增强Advisor
- findCandidateAdvisors获取所有的Advisor
- 获取适用的Advisor
目录:SpringAOP原理解析:
- 获取增强器Advisor
- 代理对象的创建
- 代理对象的执行
一、流程介绍
Spring AOP 是通过BeanPostProcessor来进行处理的。每当实例化一个Bean时,会通过这个处理器来进行增强。
分为三步。
- 获取所有的增强器。
1.1 获取所有的beanName,在beanFactory中所有注册的都提取出来。
1.2 遍历找出所有声明了@AspectJ的类。
1.3 对AspectJ注解的类进行增强器提取,解析其中的一些注解方法。获取Advisor对象。
1.4 将增强器加入缓存。 - 寻找与当前要创建的bean匹配的增强器。
- 通过增强器创建代理对象。
名词介绍
名词介绍:
-
Advice: action to take at a joinpoint。记录了要执行的内容。不同的注解对应着不同的Advice,比如@Before对应AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice,而AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice中包含了这个@Before注解对应的方法和Pointcut信息以及生成这个包含这个注解的对象的工厂,从而在调用Advice增强方法时,可以调用到指定的对象的方法。最终调用示例:AbstractAspectJAdvice类中的this.aspectJAdviceMethod.invoke(this.aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectInstance(), actualArgs);
-
Pointcut: A pointcut is composed of a {@link ClassFilter} and a {@link MethodMatcher}. 用于判断某一个Advice是否可以在某个位置执行,包含两个属性:
2.1 ClassFilter: Should the pointcut apply to the given interface or target class?
2.2 MethodMatcher: Checks whether the target method is eligible for advice. -
Advisor: Base interface holding AOP advice (action to take at a joinpoint)
and a filter determining the applicability of the advice (such as
a pointcut). 也就是记录了Advice和Pointcut
二、主流程源码介绍
通过AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类来进行处理,如下图,可以看出它实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,说明在Bean的创建过程中它做了一些操作。

首先看这个AbstractAutoProxyCreator类,AOP代理处理的主要流程都这个类里了。
我们需要关注的方法有getEarlyBeanReference,postProcessBeforeInstantiation,wrapIfNecessary,还有getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean方法
wrapIfNecessary 是给对象进行AOP代理的入口。
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// 获取增强,如果有的就创建代理,getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean交由子类去实现。
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 根据增强创建代理对象
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
从这里可以看出,AOP的主要流程是通过找到这个bean可以用的增强,然后使用增强来创建代理对象。
三、获取增强Advisor
到了子类AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator中,这个类主要实现了getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean功能,来获取Advisor。
获取Advisor主要流程为:
- 找到容器中所有的候选Advisor。
- 获取切面@Aspect对应的类
- 根据该类中所有方法,每个方法对应一个Advisor,最终返回一个InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl。
- 在InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl这个类的构造函数中调用了getAdvice,将根据不同注解生成不同的Advice,设置到当前Advisor中。
- 从候选Advisor中找到适合当前Bean的Advisor,通过Advisor中的Pointcut来判断是否适合。
@Override
@Nullable
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) {
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
return advisors.toArray();
}
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// 找到所有的增强
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
// 找到可用的增强
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
// 这里埋下一个方法,可以给子类进行扩展
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
这里判断增强能不能使用最终是到了AopUtils类中的静态方法中,判断的依据还是来自于Advisor与targetClass是否匹配,具体的规则是在Pointcut中。详见AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply,这里不展开了。
关于找到所有的增强是通过BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper来实现的,是AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的一个属性,
protected void initBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.advisorRetrievalHelper = new BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelperAdapter(beanFactory);
}
最终是调用了BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Advisor.class, true, false);来从容器中找到所有Advisor类型的Bean。
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Advisor.class, true, false);
这是AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator这个类的获取Advisor的方法,它的子类在其基础上进行了扩充,可以看到AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator这个类也实现了
findCandidateAdvisors方法,具体实现时是:
findCandidateAdvisors获取所有的Advisor
@Override
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
// Add all the Spring advisors found according to superclass rules.
//首先调用父类的方法获取Advisor
List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();
// Build Advisors for all AspectJ aspects in the bean factory.
// 然后在将自己的实现加到父类获取的列表中
if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) {
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
}
return advisors;
}
所以接下来就要看一下BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilder这个类的buildAspectJAdvisors()方法了。
public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {
List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
synchronized (this) {
aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
aspectNames = new ArrayList<>();
String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);
//遍历容器中所有的beanName
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) {
continue;
}
// We must be careful not to instantiate beans eagerly as in this case they
// would be cached by the Spring container but would not have been weaved.
Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName);
if (beanType == null) {
continue;
}
// 是否Aspect,(hasAspectAnnotation(clazz) && !compiledByAjc(clazz));
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {
aspectNames.add(beanName);
//AspectMetadata是切面的元数据,存储了切面的属性
AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);
//如果Aspect是单例的
if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
//委托给了ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvisors实现,这里不展开了,其实就是根据反射的方式获取增强,并且做了一些延迟初始化的处理
List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
// 单例模式缓存adVisors,否则缓存一个工厂。一个Aspect里面可以有很多个Advisor,这里相当于以Aspect为key,Advisors列表为value
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);
}
else {
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
}
advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);
}
else {
// Per target or per this.
// 切面是单例模式的,那承载它的Bean也必须是单例的
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName +
"' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");
}
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
}
this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;
return advisors;
}
}
}
if (aspectNames.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String aspectName : aspectNames) {
List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName);
if (cachedAdvisors != null) {
advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors);
}
else {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
return advisors;
}
这里再看一下ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory这个类,它
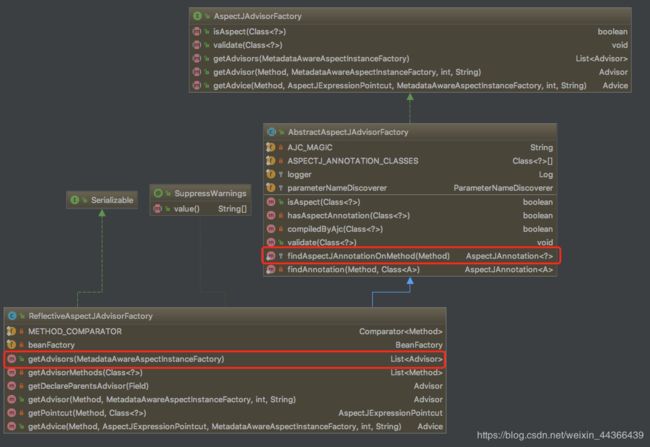
首先在ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory类中,getAdvisor方法中
// 根据遍历Aspect类中的方法,来获取到切点
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory,
int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {
validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
//这里获取所有的切点,切点中记录了切点的参数,表达式什么的
AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut(
candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
if (expressionPointcut == null) {
return null;
}
// 核心,这就是AOP中的Advisor的实现类,初始化时传入了切点,增强的方法,还有一个AspectJAdvisorFactory,这里是当前ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory
return new
InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,
this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);
}
然后InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl这个类会调用instantiateAdvice方法来生成Advice,而它又调用回了ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory的getAdvice方法,这里根据不同的注解,生成了不同的Advice对象。
@Override
@Nullable
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
***********省略部分代码*******
switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) {
case AtPointcut:
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'");
}
return null;
case AtAround:
springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtBefore:
springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfter:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfterReturning:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) {
springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning());
}
break;
case AtAfterThrowing:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) {
springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing());
}
break;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
// Now to configure the advice...
springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName);
springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder);
String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (argNames != null) {
springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames);
}
springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings();
return springAdvice;
}
获取适用的Advisor
利用了Pointcut来进行判断,最终定位的方法为AopUtils.canApply:
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");
// 直接使用抽象的ClasFilter和MethodMatcher来判断
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) {
// No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway...
return true;
}
IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;
if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;
}
Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
classes.add(ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass));
}
classes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
for (Method method : methods) {
if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ?
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) :
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
小结:
目前为止,已经梳理出Spring获取Advisor的流程。回顾一下类的依赖和继承关系。
class AbstractAutoProxyCreator 定义了代理创建的主要流程,如何获取增强交由子类实现。有点像模板方法一样,它并没有指定必须用Advisor的方式来创建代理,它获取的拦截对象都是Object的。
class AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
它重写了获取增强的方法
class AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
class AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
它重写了根据注释获取增强的方法。同时引入了AspectJAdvisorFactory,使得生成增强的实现交给了ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory类,它实例化了Advisor,InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl类。AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator自己仅仅做了一些组合的功能。
下一篇来介绍通过增强创建代理对象的实现。