【多线程】JDK提供的线程池及应用场景
线程池
线程池的产生是为了避免重复的创建线程和回收线程。
创建线程池的优点:
1、降低资源消耗。通过重复利用已创建的线程降低线程创建,销毁线程造成的消耗。
2、提高响应速度。当任务到达时,任务可以不需要等待线程创建就能立即执行。
3、提高线程的可管理性。线程是稀缺资源,如果无限制的创建,不仅会消耗系统资源,还会降低系统的稳定性,使用线程池可以进行统一的分配,调优和监控。
ThreadPoolExecutor
在java线程池中的newFixedThreadPool,newSingleThreadExecutor,newCachedThreadPool,newSingleThreadScheduleExecutor,newScheduledThreadPool这五个线程池在底层都是调用了ThreadPoolExecutor()这个构造方法。若Executors这个类无法满足需求的时候,可以自己创建自定义的线程池。
ThreadPoolExecutor类的定义如下:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,//核心线程数--线程池初始化创建的线程数量
int maximumPoolSize,//最大线程数,线程池中能创建的最大线程数
long keepAliveTime,//线程存活时间
TimeUnit unit,//线程存活的时间单位
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,//一个阻塞队列
ThreadFactory threadFactory//拒绝策略
) {……}
- corePoolSize:核心线程数,线程池维护线程的最少数量
- maximumPoolSize:最大线程数,线程池维护线程的最大数量
- keepAliveTime:线程池维护线程所允许的空闲时间
- unit:线程池维护线程所允许的空闲时间的单位
- workQueue:线程池所使用的缓冲队列
- threadFactory:线程池对拒绝任务的处理策略
1.newFixedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
- nThreads:核心线程数和最大线程数都是nThreads指定值,没有非核心线程。即当线程池中的线程数超过核心线程数后,任务都会被放到阻塞队列中。
- 0L:keepAliveTime为0,非工作线程的存活时间为0。当核心线程执行完队列中的任务时,如果队列中没有任务,则核心线程死亡。优点在于极大程度的节约了系统资源。
- 使用LinkedBlockingQueue队列默认最大值是Integer.Max_Value:该队列长度是int最大值,相当于无上限。无论有多少任务都能存储在队列里等待核心线程去执行。
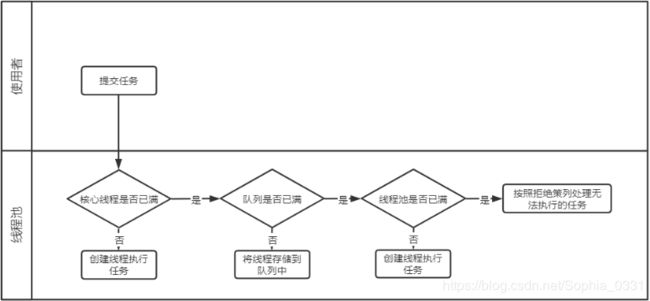
(1)执行流程:
- 线程数少于核心线程数,新建线程执行任务
- 线程数等于核心线程数,将任务加入阻塞队列(由于队列容量大所以可以一直加)
- 执行完任务的线程反复去队列中取任务执行
(2)适用场景:newFixedThreadPool适用于为了满足资源管理的需求,而需要限制当前线程数量的应用场景,它适用于负载比较重的服务器。
2.newSingleThreadExecutor
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
只有一个线程的线程池,多出来的任务会被放到任务队列内,待线程空闲,按先入先出的顺序执行队列中的任务。使用LinkedBlockingQueue队列(无界队列)。
(1)执行流程:
- 线程池中没有线程时,新建一个线程执行任务
- 有一个线程以后,将任务加入阻塞队列
- 唯一的这一个线程不停的去队列里取任务执行
(2)适用场景:用于串行执行任务的场景,每个任务必须按顺序执行,不需要并发执行。
3.newCachedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
- corePoolSize:核心线程数为0
- maximumPoolSize:最大线程数为Integer.MAX_VALUE(相当于无上限)
- keepAliveTime:非工作线程存活时间为60秒,超过后就会被回收
- unit:线程存活的时间单位为秒
- workQueue:队列使用的SynchronousQueue(SynchronousQueue是一个没有容量的队列)
newCachedThreadPool使用的队列是SynchronousQueue,这个队列的作用是传递任务,并不会保存任务。因此当提交任务的速度大于处理任务的速度时,每次提交一个任务,就会创建一个线程。极端情况下会创建过多的线程,耗尽CPU和内存资源。
(1)执行流程:
- 没有核心线程,直接向SynchronousQueue队列中提交任务
- 如果有空闲线程,就去取出任务执行;如果没有空闲线程,就新建一个
- 执行完任务的线程有60秒生存时间,如果在这个时间内可以接到新任务,就可以继续存活下去,否则就被回收
----------由于空闲60秒的线程会被终止,长时间保持空闲的newCachedThreadPool不会占用任何资源。
(2)适用场景:用于并发执行大量短期的小任务,或者是负载较轻的服务器。
4.newScheduledThreadPool
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
DEFAULT_KEEPALIVE_MILLIS, MILLISECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
private static final long DEFAULT_KEEPALIVE_MILLIS = 10L;
- corePoolSize:核心线程数(传入)
- 默认最大线程数是Integer.MAX_VALUE
- 存活时间默认10毫秒:DEFAULT_KEEPALIVE_MILLIS默认10L,单位毫秒
- 队列:DelayedWorkQueue是一个无界限的队列,当添加的任务大于队列时,会重新增加队列的长度。同时DelayedWorkQueue还有着一套按超时时间升序排序的算法,遵循“左节点比右节点小的原则(下次执行的时间更短)”。
DelayedWorkQueue队列的长度具有增长型和按超时时间升序排序算法,使得ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor具有延时执行任务的特性。
(1)执行流程:
(2)适用场景:用于需要多个后台线程执行周期任务,同时需要限制线程数量的场景。
拒绝策略
JDK给我们提供了一些拒绝策略:
- AbortPolicy:直接抛出异常,系统正常工作。(默认策略)
- CallerRunsPolicy:只要线程池未关闭,该策略直接在调用者线程中执行,运行当前被丢弃的任务
- DiscardOrderstPolicy:丢弃最老的请求,尝试再次提交当前任务
- 丢弃无法处理的任务,不给予任何处理
如果需要自定义策略,需要实现RejectedExecutionHandler接口。