Realm是专门为移动端开发的数据库引擎。它具有跨平台,简单易用,速度快,占用空间小,支持java,objec-c,swift语言等特点,迅速的得到了开发者的青睐。项目中使用了Realm,将中间的过程记录下来以备查阅。
环境
- 系统:OS X 10.11.5,
- Xcode:Version 7.2 (7C68)
- 开发语言:Objective-C
准备
1.下载Realm对应的Objective-C版本。下载地址在这里,选择realm-cocoa下载源代码。
2.将Realm集成到项目。
Realm框架支持常用的静态库,动态库,CocoaPads和Carthage 几种集成方式。
本文使用动态库的方式。-
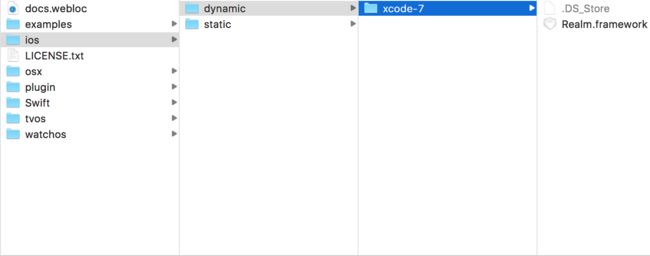
首先将下载 Realm 的最新版本并解压;解压后文件如下
前往Xcode 工程的”General”设置项中,从ios/dynamic/中将’Realm.framework’拖曳到”Embedded Binaries”选项中。确认Copy items if needed被选中后,点击Finish按钮;
-
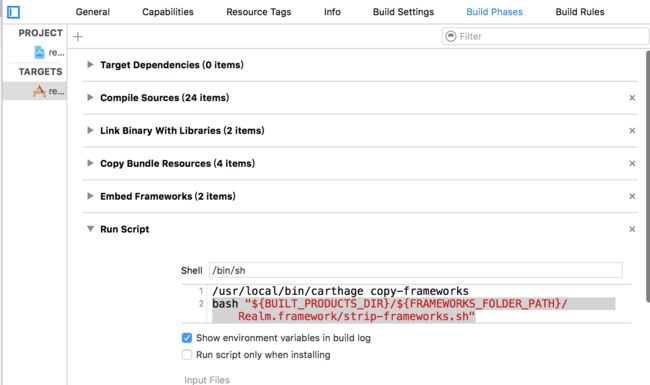
在项目的”Build Phases”中,创建一个新的”Run Script Phase”,并将
bash "${BUILT_PRODUCTS_DIR}/${FRAMEWORKS_FOLDER_PATH}/Realm.framework/strip-frameworks.sh"
这条脚本复制到文本框中。
-
下载Realm Browser的Mac应用以便 对.realm数据库进行读取和编辑。
同时Xcode也有个Realm Browser的插件。使用Alcatraz安装即可。由于我使用的Xcode7.2版本。会不支持该插件出现想这样的错误。
PluginLoading: Required plug-in compatibility UUID F41BD31E-2683-44B8-AE7F-5F09E919790E for plug-in at path '~/Library/Application Support/Developer/Shared/Xcode/Plug-ins/RealmBrowser.xcplugin' not present in DVTPlugInCompatibilityUUIDs```
解决办法:找到该插件的配置文件,将7.2的UUID添加到配置文件即可。
+ 安装Xcode 插件
RealmPlugin插件可以快速的创建基于RLMObject的模型对象。

安装完成后,直接command + N新建对应的模型文件。

####Realm数据模型
Realm数据模型是基于标准 Objective-C 类来进行定义的,使用属性来完成模型的具体定义。
通过简单的继承 RLMObject 或者一个已经存在的模型类,您就可以创建一个新的 Realm 数据模型对象。
构建一个银行卡模型BankInfo
import
import
@interface BankInfo : RLMObject
//银行卡信息
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *bank_accnoalias;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *bank_accname;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *bankname;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *bankid;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *status;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *acc_nature;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *bank_accno;
+(instancetype)bankInfoWithDict:(NSDictionary * )dict;
-(instancetype)initWithBankDict:(NSDictionary *)dict;
@end
RLM_ARRAY_TYPE(BankInfo)
构建持卡人模型Person
import
import "BankInfo.h"
@interface Person : RLMObject
@property NSString *name;
@property RLMArray
@end
+ 其中在BankInfo模型类的声明的结尾使用RLM_ARRAY_TYPE(BankInfo)宏来创建一个协议,从而允许 RLMArray 语法的使用。
然后在Person模型类中声明属性```@property RLMArray *banks;```这样两个类构建成了一对多的关系。
> 如果是互相包含的关系呢?
在Realm中通过反向关系来实现即:
```@property (readonly) RLMLinkingObjects *owners;```
先在BankInfo模型类声明声明owners属性,然后重写 +[RLMObject linkingObjectsProperties] 来指明关系,说明 ownders 中包含了 Person 模型对象。
具体代码
@interface BankInfo : RLMObject
@property (readonly) RLMLinkingObjects *owners;
@end
RLM_ARRAY_TYPE(BankInfo)
@implementation BankInfo
- (NSDictionary *)linkingObjectsProperties
{
return @{ @"owners": [RLMPropertyDescriptor descriptorWithClass:Person.class propertyName:@"banks"] };
}
@end
@interface Person : RLMObject
@property NSString *name;
@property RLMArray< BankInfo > *banks;
@end
@implementation Person
@end
+ Realm支持以下的属性类型:BOOL、bool、int、NSInteger、long、long long、float、double、NSString、NSDate、NSData 以及 被特殊类型标记的 NSNumber 。CGFloat 属性的支持被取消了,因为它的类型不依赖于平台。
+ 模型类属性是否可以为nil
@interface Person : RLMObject
@property NSString *name;
@property NSDate *birthday;
@end
@implementation Person
- (NSArray *)requiredProperties {
return @[@"name"];
}
@end
重写了requiredProperties方法代表name不能为nil
+ 添加索引
重写 +indexedProperties 方法可以为数据模型中需要添加索引的属性建立索引
@interface Book : RLMObject
@property float price;
@property NSString *title;
@end
@implementation Book
- (NSArray *)indexedProperties {
return @[@"title"];
}
@end
Realm 支持字符串、整数、布尔值以及 NSDate 属性作为索引。
+ 添加属性默认值
重写+defaultPropertyValues可以在每次对象创建之后为其提供默认值。
@interface Book : RLMObject
@property float price;
@property NSString *title;
@end
@implementation Book
- (NSDictionary *)defaultPropertyValues {
return @{@"price" : @0, @"title": @""};
}
@end
+ 设置主键
重写 +primaryKey 可以设置模型的主键。声明主键之后,对象将被允许查询,更新速度更加高效,并且要求每个对象保持唯一性。 一旦带有主键的对象被添加到 Realm 之后,该对象的主键将不可修改。
@interface Person : RLMObject
@property NSInteger id;
@property NSString *name;
@end
@implementation Person
- (NSString *)primaryKey {
return @"id";
}
@end
+ 忽略属性
重写 +ignoredProperties 可以防止 Realm 存储数据模型的某个属性
@interface Person : RLMObject
@property NSInteger tmpID;
@property (readonly) NSString *name; // 只读属性将被自动忽略
@property NSString *firstName;
@property NSString *lastName;
@end
@implementation Person
- (NSArray *)ignoredProperties {
return @[@"tmpID"];
}
- (NSString *)name {
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ %@", self.firstName, self.lastName];
}
@end
####Realm集合
Realm 拥有一系列能够帮助表示一组对象的类型,我们称之为『Realm 集合』:
RLMResults类,表示从检索 中所返回的对象集合。
RLMArray类,表示模型中的对多关系。
RLMLinkingObjects类,表示模型中的反向关系。
RLMCollection协议,定义了所有 Realm 集合所需要遵守的常用接口。
####Realm增删改查
将常用的增删改查进行封装,代码如下。
// 构建Realm数据库
RLMRealm *realm = [RLMRealm defaultRealm];
RLMRealmConfiguration *config = [RLMRealmConfiguration defaultConfiguration];
[RLMRealmConfiguration setDefaultConfiguration:config];
// Realm内存数据库
//RLMRealmConfiguration *config = [RLMRealmConfiguration defaultConfiguration];
//config.inMemoryIdentifier = @"MyInMemoryRealm";
//RLMRealm *realm = [RLMRealm realmWithConfiguration:config error:nil];
//self.rlmRealm = realm;// 在使用Realm内存数据库的时候,必须使用强指针引用,如果某个内存 Realm 数据库实例没有被引用,那么所有的数据就会被释放。
// 增加数据
-
(BOOL)realmsInsertData:(NSArray *)data{
NSError *error;
// Add an object
[self.rlmRealm beginWriteTransaction];
for (int i = 0; i < data.count; i++) {BankInfo *obj = [[BankInfo alloc] initWithBankDict:data[i]]; [self.rlmRealm addOrUpdateObject:obj];}
return [self.rlmRealm commitWriteTransaction:&error];
}
// 查询数据
-
(id)realmSelectData:(NSString *)object theCondition:(NSString *)condition{
Class cls = NSClassFromString(object);
RLMResults *result = [cls objectsInRealm:self.rlmRealm where:condition];
return result;
}
// 删除数据
-
(BOOL)realmsDeleteData:(NSString *)object theCondition:(NSString *)condition type:(realmDelType)type{
Class cls = NSClassFromString(object);
if (cls == nil) {
return NO;
}
RLMResults *results = [self realmsselectData:[BankInfo className] theCondition:condition];
if (!results.count) {
return YES;
}
NSError *error = nil;
// 开始事务
[self.rlmRealm beginWriteTransaction];
switch (type) {
case realmDelTypeAll:
[self.rlmRealm deleteObjects:[cls allObjectsInRealm:self.rlmRealm]];
break;
case realmDelTypeFirst:
[self.rlmRealm deleteObject:[cls allObjectsInRealm:self.rlmRealm].firstObject];
break;
case realmDelTypeLast:
[self.rlmRealm deleteObject:[cls allObjectsInRealm:self.rlmRealm].lastObject];
break;
case realmDelTypeOther:
[self.rlmRealm deleteObjects:results];
break;
default:
break;
}
// 提交事务
return [self.rlmRealm commitWriteTransaction:&error];
}
// 更新数据
-
(BOOL)realmsUpdateData:(NSString *)object theCondition:(NSString *)condition property:(NSDictionary *)dict{
Class cls = NSClassFromString(object);
if (cls == nil) {
return NO;
}RLMResults *results = [self realmsselectData:object theCondition:condition];
if (!results.count) {
return YES;
}if (dict == nil) {
return NO;
}// 检查属性
if (![self CheckPropertys:object propertyDict:dict]) {
return NO;
}NSError *error = nil;
[self.rlmRealm beginWriteTransaction];//将每条数据的每个 属性设置为对应的值
for (NSString *updateKey in dict.allKeys) {
[results setValue:dict[updateKey] forKeyPath:updateKey];
}
// 如果没有值,就新插入一条数据
//[cls createOrUpdateInRealm:self.rlmRealm withValue:dict];return [self.rlmRealm commitWriteTransaction:&error];
}
// 检查该类中是否有该属性
-
(BOOL)CheckPropertys:(NSString *)object propertyDict:(NSDictionary *)dict{
Class cls = NSClassFromString(object);
// 属性字符串数组
NSMutableArray *clspropertys = [NSMutableArray array];unsigned pCount;
objc_property_t *properties = class_copyPropertyList(cls, &pCount);//属性数组for(int i = 0; i < pCount; i++){
objc_property_t property = properties[i];
NSString *str =[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%s", property_getName(property)];
[clspropertys addObject:str];
//NSLog(@"propertyName:%s",property_getName(property));
//NSLog(@"propertyAttributes:%s",property_getAttributes(property));
}NSArray *keys = dict.allKeys;
for (NSString *dictkey in keys) {
if ([clspropertys containsObject:dictkey]) {
NSLog(@"This class does contain attributes.:%@",dictkey);
}else {
NSLog(@"This class does not contain attributes.:%@",dictkey);
return NO;
}
}
return YES;
}
代码调用
RLMResults *results = [BankInfo objectsInRealm:self.rlmRealm where:@"bank_accno = '6228481234567891235' "];
NSLog(@"results = %@", results);
NSLog(@"banklistselect = %@", [BankInfo allObjectsInRealm:self.rlmRealm]);
//[self realmsDeleteData:NSStringFromClass([BankInfo class]) theCondition:@"bank_accno = '6228481234567891235' or bank_accno = '6228481234567891242' " type:realmDelTypeOther];
//NSLog(@"banklistDelete = %@", [BankInfo allObjectsInRealm:self.rlmRealm]);
[self realmsUpdateData:NSStringFromClass([BankInfo class]) theCondition:nil property:@{@"status":@"6", @"bank_accnoalias":@"123"}];
NSLog(@"banklistUpdate = %@", [BankInfo allObjectsInRealm:self.rlmRealm]);
[self.rlmRealm beginWriteTransaction];
// 先删除数据
[self.rlmRealm deleteObjects:[Person allObjects]];
Person *p = [[Person alloc] init];
p.name = @"张三";
[p.banks addObjects:[BankInfo allObjectsInRealm:self.rlmRealm]];
[self.rlmRealm addObject:p];
[self.rlmRealm commitWriteTransaction:nil];
+ Realm中所有有关数据库的操作都是一个事务。
即所有的代码都需要去被包含在beginWriteTransaction和commitWriteTransaction之间。
+ Realm查询结果,Realm将会返回包含 RLMObject 集合的RLMResults实例。RLMResults 的表现和 NSArray 十分相似,并且包含在 RLMResults 中的对象能够通过索引下标进行访问。和 NSArray 不同,RLMResults 需要指定类型,并且其当中只能包含RLMObject 子类类型的属性。
所有的查询(包括查询和属性访问)在 Realm 中都是延迟加载的,只有当属性被访问时,才能够读取相应的数据。
+ Realm 支持许多常见的断言:
比较操作数(comparison operand)可以是属性名称或者某个常量,但至少有一个操作数必须是属性名称;
比较操作符 ==、<=、<、>=、>、!=, 以及 BETWEEN 支持 int, long, long long, float, double, 以及 NSDate 属性类型的比较,比如说 age == 45;
相等比较 ==以及!=,比如说[Employee objectsWhere:@"company == %@", company]
比较操作符 == and != 支持布尔属性;
对于 NSString 和 NSData 属性来说,我们支持 ==、!=、BEGINSWITH、CONTAINS 以及 ENDSWITH 操作符,比如说 name CONTAINS ‘Ja’;
字符串支持忽略大小写的比较方式,比如说 name CONTAINS[c] ‘Ja’ ,注意到其中字符的大小写将被忽略;
Realm 支持以下复合操作符:“AND”、“OR” 以及 “NOT”。比如说 name BEGINSWITH ‘J’ AND age >= 32;
包含操作符 IN,比如说 name IN {‘Lisa’, ‘Spike’, ‘Hachi’};
==、!=支持与 nil 比较,比如说 [Company objectsWhere:@"ceo == nil"]。注意到这只适用于有关系的对象,这里 ceo 是 Company 模型的一个属性。
通过 ==, != 进行空值比较,比如说 [Company objectsWhere:@"ceo == nil"]; 注意,Realm 将 nil 视为一个特殊的值而不是“缺失值”,不像 SQL 那样 nil 等于自身。
ANY 比较,比如说 ANY student.age < 21
RLMArray 以及 RLMResults 属性支持集合表达式:@count、@min、@max、@sum 以及 @avg,例如 [Company objectsWhere:@"employees.@count > 5"] 用以寻找所有超过 5 名雇员的公司。
支持子查询,不过有限制:
@count 是唯一能应用在 SUBQUERY 表达式中的操作符
SUBQUERY(…).@count 表达式必须与常量进行比较
####其他
在测试的过程中,如果模型类的属性进行了添加或者删除操作,重新执行会报错,重新删除app的数据即可。
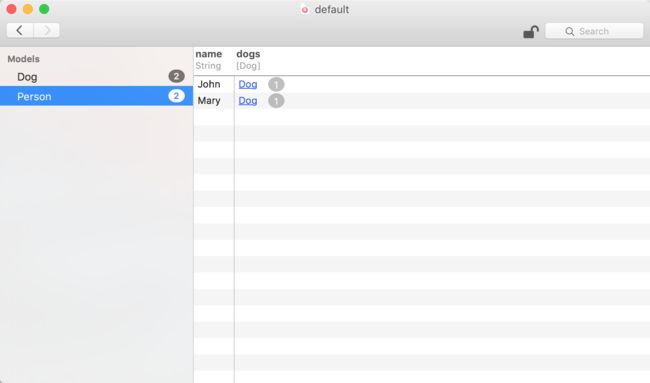
最后执行结果


####参考地址
[官网地址](https://realm.io)
[参考地址1](http://www.cocoachina.com/ios/20150505/11756.html)