RTMP串流服务
准备
nginx-rtmp-module
nginx-rtmp-module为nginx的一个模块,提供了:
- RTMP/HLS/MPEG-DASH直播
- FLV/MP4文件格式的RTMP视频点播,可以从本地文件系统或HTTP播放
- 对分布式流媒体的支持
- H264/AAC支持
- 使用FFmpeg进行在线转码
- HTTP回调(发布/播放/记录/更新等)
- 在某些事件上运行外部程序(exec)
- HTTP控制模块,用于录制音频/视频和丢弃客户端
- 高级缓冲技术可将内存分配保持在最低水平,以实现更快的流式传输和更低的内存占用
- 可以使用Wirecast,FMS,Wowza,JWPlayer,FlowPlayer,StrobeMediaPlayback,ffmpeg,avconv,rtmpdump,flvstreamer等等
- XML/XSL中的统计信息,支持机器和人类可读的形式
- Linux/FreeBSD/MacOS/Windows
安装
./configure --prefix=/usr/soft/nginx-1.12.0 --add-module=/usr/soft/nginx-rtmp-module-1.2.1
make && make install
配置
路径配置
mkdir -p /opt/rtmp/vod
cp /usr/soft/nginx-rtmp-module-1.2.1/stat.xsl /opt/rtmp
nginx配置
rtmp {
server {
listen 9000;
chunk_size 4096;
}
}
http {
...
server {
listen 80;
...
location /stat {
rtmp_stat all;
rtmp_stat_stylesheet stat.xsl;
}
location /stat.xsl {
# XSL文件路径为/opt/rtmp/stat.xsl
root /opt/rtmp/;
}
}
}
启动nginx
访问http://example.com/stat
点播
修改nginx配置
设置vod路径为/opt/rtmp/vod
rtmp {
server {
listen 9000;
chunk_size 4096;
application vod {
play /opt/rtmp/vod;
}
}
}
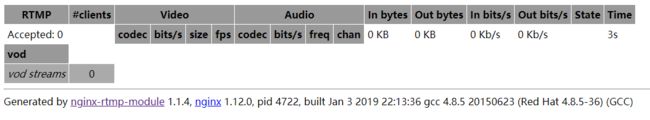
此时访问访问http://example.com/stat可以查看到控制台多出了vod一行。如果此时有人在访问点播视频,则可以在控制台看到每个视频的在线访问人数、网络速度等数据。
操作
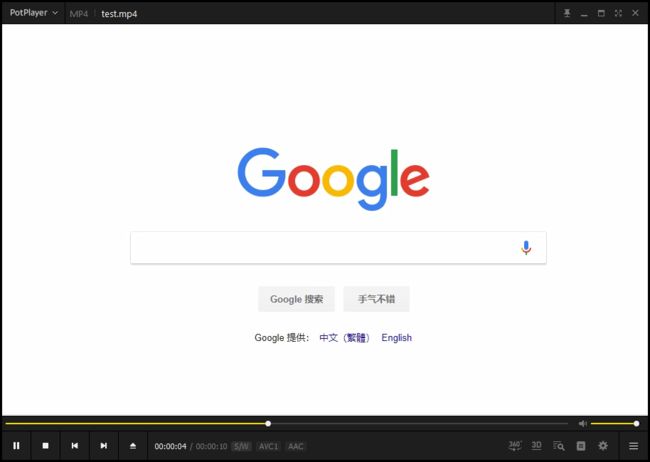
将视频文件放到vod路径下,例如/opt/rtmp/vod/test.mp4,然后就可以通过串流直接观看该视频。访问该视频文件的串流地址为rtmp://example.com:9000/vod/{文件名},例如:rtmp://example.com:9000/vod/test.mp4
直播
修改nginx配置
rtmp {
server {
listen 9000;
chunk_size 4096;
application vod {
play /opt/rtmp/vod;
}
application live{
live on;
}
}
}
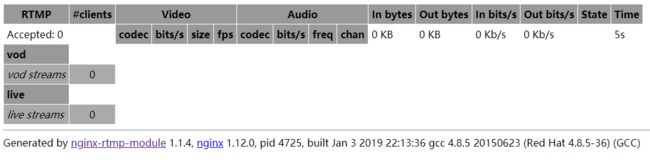
此时访问访问http://example.com/stat可以查看到控制台多出了live一行。如果此时有人在直播,则可以在控制台看到当前在线的直播频道以及每个直播频道的访问人数、网络速度等数据。
操作
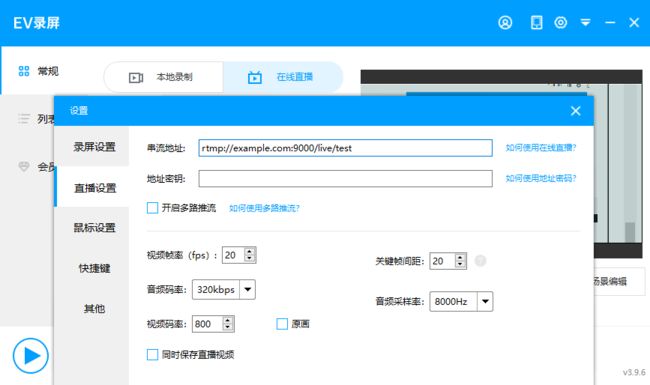
通过直播软件(例如EV录屏)设置串流地址rtmp://example.com:9000/live/{自定义ID}例如rtmp://example.com:9000/live/test,就可以将直播的视频数据发送到nginx。
观看直播则访问与直播软件设置的相同的的串流地址即可,例如:rtmp://example.com:9000/live/test
更多配置
rtmp {
server {
listen 1935;
chunk_size 4000;
# TV mode: one publisher, many subscribers
application mytv {
# enable live streaming
live on;
# record first 1K of stream
record all;
record_path /tmp/av;
record_max_size 1K;
# append current timestamp to each flv
record_unique on;
# publish only from localhost
allow publish 127.0.0.1;
deny publish all;
#allow play all;
}
# Transcoding (ffmpeg needed)
application big {
live on;
# On every pusblished stream run this command (ffmpeg)
# with substitutions: $app/${app}, $name/${name} for application & stream name.
#
# This ffmpeg call receives stream from this application &
# reduces the resolution down to 32x32. The stream is the published to
# 'small' application (see below) under the same name.
#
# ffmpeg can do anything with the stream like video/audio
# transcoding, resizing, altering container/codec params etc
#
# Multiple exec lines can be specified.
exec ffmpeg -re -i rtmp://localhost:1935/$app/$name -vcodec flv -acodec copy -s 32x32
-f flv rtmp://localhost:1935/small/${name};
}
application small {
live on;
# Video with reduced resolution comes here from ffmpeg
}
application webcam {
live on;
# Stream from local webcam
exec_static ffmpeg -f video4linux2 -i /dev/video0 -c:v libx264 -an
-f flv rtmp://localhost:1935/webcam/mystream;
}
application mypush {
live on;
# Every stream published here
# is automatically pushed to
# these two machines
push rtmp1.example.com;
push rtmp2.example.com:1934;
}
application mypull {
live on;
# Pull all streams from remote machine
# and play locally
pull rtmp://rtmp3.example.com pageUrl=www.example.com/index.html;
}
application mystaticpull {
live on;
# Static pull is started at nginx start
pull rtmp://rtmp4.example.com pageUrl=www.example.com/index.html name=mystream static;
}
# video on demand
application vod {
play /var/flvs;
}
application vod2 {
play /var/mp4s;
}
# Many publishers, many subscribers
# no checks, no recording
application videochat {
live on;
# The following notifications receive all
# the session variables as well as
# particular call arguments in HTTP POST
# request
# Make HTTP request & use HTTP retcode
# to decide whether to allow publishing
# from this connection or not
on_publish http://localhost:8080/publish;
# Same with playing
on_play http://localhost:8080/play;
# Publish/play end (repeats on disconnect)
on_done http://localhost:8080/done;
# All above mentioned notifications receive
# standard connect() arguments as well as
# play/publish ones. If any arguments are sent
# with GET-style syntax to play & publish
# these are also included.
# Example URL:
# rtmp://localhost/myapp/mystream?a=b&c=d
# record 10 video keyframes (no audio) every 2 minutes
record keyframes;
record_path /tmp/vc;
record_max_frames 10;
record_interval 2m;
# Async notify about an flv recorded
on_record_done http://localhost:8080/record_done;
}
# HLS
# For HLS to work please create a directory in tmpfs (/tmp/hls here)
# for the fragments. The directory contents is served via HTTP (see
# http{} section in config)
#
# Incoming stream must be in H264/AAC. For iPhones use baseline H264
# profile (see ffmpeg example).
# This example creates RTMP stream from movie ready for HLS:
#
# ffmpeg -loglevel verbose -re -i movie.avi -vcodec libx264
# -vprofile baseline -acodec libmp3lame -ar 44100 -ac 1
# -f flv rtmp://localhost:1935/hls/movie
#
# If you need to transcode live stream use 'exec' feature.
#
application hls {
live on;
hls on;
hls_path /tmp/hls;
}
# MPEG-DASH is similar to HLS
application dash {
live on;
dash on;
dash_path /tmp/dash;
}
}
}
# HTTP can be used for accessing RTMP stats
http {
server {
listen 8080;
# This URL provides RTMP statistics in XML
location /stat {
rtmp_stat all;
# Use this stylesheet to view XML as web page
# in browser
rtmp_stat_stylesheet stat.xsl;
}
location /stat.xsl {
# XML stylesheet to view RTMP stats.
# Copy stat.xsl wherever you want
# and put the full directory path here
root /path/to/stat.xsl/;
}
location /hls {
# Serve HLS fragments
types {
application/vnd.apple.mpegurl m3u8;
video/mp2t ts;
}
root /tmp;
add_header Cache-Control no-cache;
}
location /dash {
# Serve DASH fragments
root /tmp;
add_header Cache-Control no-cache;
}
}
}