背景
日常coding中,要解决项目当中遇到的问题,难免会需要写一个Converter,aspect,或者扩展一个MediaType等等。这时候需要写一个侵入性小的扩展,就需要了解源码。我找了很多博客文章,甚至看了《看透Spring MVC:源代码分析与实践》,写的很好,但是视角都是从整体框架出发,大而全,而我仅仅只是想解决当前的问题,所以我以代码跟踪的视角记录下这篇文章,免得下次忘了还要重新跟踪源码,直接过来看就好了。
目的
从源码中提取可能用到的工具,特别是标注好注意事项,下次扩展可以查阅。
准备
- springboot 2.1.1.RELEASE的demo
- pom依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-actuator
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
- 示例类Employee,省略getter/setter
public class Employee {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Date birthday;
private Date createTime;
}
- Controller示例类
@RestController
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
@PostMapping("/employee")
public ResponseEntity insert(Employee employee){
employee.setId(1L);
employee.setCreateTime(new Date());
return ResponseEntity.ok(employee);
}
}
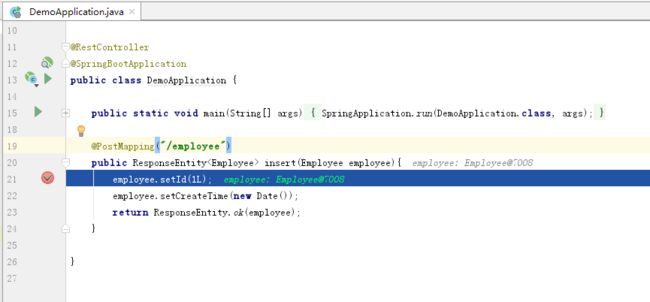
断点
如图上断点
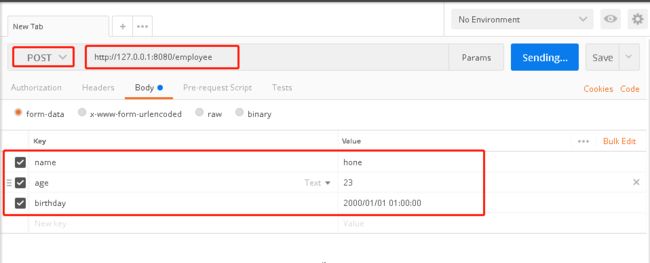
请求参数如图
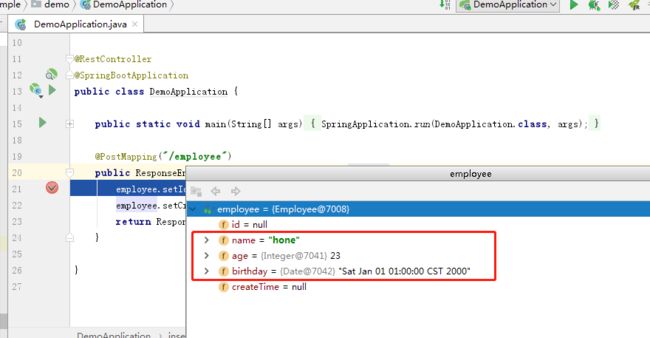
ALT+左键点击employee检查参数
FrameworkServlet
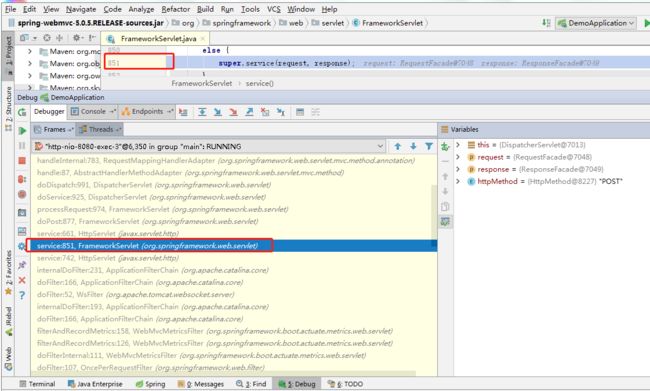
- 我们在Debugger视图的Frames里从底部往上,找到第一个属于spring-webmvc包的类,FrameworkServlet
- 通过查看源码,我们GET到第一个工具类,HttpMethod,这个枚举类包含了所有的http方法。
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());
if (httpMethod == HttpMethod.PATCH || httpMethod == null) {
processRequest(request, response);
}
else {
super.service(request, response);
}
}
- 在Frames视图继续向上推,可以发现从 HttpServlet 转了一遭到了 FrameworkServlet.doPost ,然后来到了 FrameworkServlet.processRequest (删减版)
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// (1)
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
// (2)
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
// (3)
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
看得出来,做了三件事
- ContextHolder的设置和重置
具体见:源码跟踪-springmvc(二):LocaleContextHolder和RequestContextHolder - 执行
doService方法,也是真正执行handler的方法。 - 执行了
publishRequestHandledEvent,代码如下
private void publishRequestHandledEvent(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
long startTime, @Nullable Throwable failureCause) {
if (this.publishEvents && this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// Whether or not we succeeded, publish an event.
long processingTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.webApplicationContext.publishEvent(
new ServletRequestHandledEvent(this,
request.getRequestURI(), request.getRemoteAddr(),
request.getMethod(), getServletConfig().getServletName(),
WebUtils.getSessionId(request), getUsernameForRequest(request),
processingTime, failureCause, response.getStatus()));
}
}
我们知道webApplicationContext继承了ApplicationEventPublisher,拥有了发布事件的能力,我把发布的事件打印出来看一下
@EventListener
public void printServletRequestHandledEvent(ServletRequestHandledEvent event){
System.out.println(event);
}
打印结果如下
ServletRequestHandledEvent: url=[/employee]; client=[127.0.0.1]; method=[POST]; servlet=[dispatcherServlet]; session=[null]; user=[null]; time=[52ms]; status=[OK]
如果发现打印的内容满足需要,我们就不需要再写个aop用来记录日志啦。
DispatcherSevlet
- 现在进入了DispatcherSevlet.doService方法(删减版)
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
Map attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
这里有两件事
- 如果满足一定的条件(
WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)),会把request的attributes做一份快照备份(attributesSnapshot),执行完handler后还原备份(restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot))。但是这里如果没有成立,也就没有执行,就先不管。但是很明显,这个手法和上面的ContextHolder如出一辙。这时候其实能够象出来,这样做的目的是为了安全。 - 在request中设置了一堆的attributes,有一个特别显眼,
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());,这个时候我们又get到一个获取webApplicationContext的办法。
WebApplicationContext wac = (WebApplicationContext) request.getAttribute(DispatcherServlet.WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
- 进入了DispatcherSevlet.doDispatch方法(删减版)
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// ....
try {
//...
try {
// (1)
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// (2)
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// (3)
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// (4)
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// (5)
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
// (6)
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
// (7)
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// (7)
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// (7)
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
}
这里非常重要了,对应代码中的注释,解释如下
- 获取到mappedHandler,其实也就HandlerExecutionChain
具体见源码跟踪-springmvc(三):RequestMappingHandlerMapping - 获取处理器适配器,就是RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
- http协议中的缓存实现,可以看Spring mvc HTTP协议之缓存机制
- 分别调用mappedHandler中的三个拦截器的preHandle方法
- 执行真正的handler
具体见:源码跟踪-springmvc(四):RequestMappingHandlerAdapter - 执行拦截器的postHandle方法
- 执行拦截器的afterCompletion方法