在Linux上调试C++项目
在Linux调试C++项目的学习笔记。参考:
1 linux系统下如何在vscode中调试C++代码
2 Linux VSCode调试C++
3 在Linux中使用VS Code编译调试C++项目
| Date | Version | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 2019/10/12 | V0.1 | Init |
文章目录
- 单个CPP文件
- 编译过程
- 调试过程
- 多个文件调试
- VS code
- Makefile
- 使用到的文件
单个CPP文件
编译过程
首先对单个文件的编译过程有个简单了解,写一个cpp文件:
/*test.cpp*/
#include 然后确定电脑上安装好了g++。如果没有的话通过指令安装。
sudo apt-get install build-essential
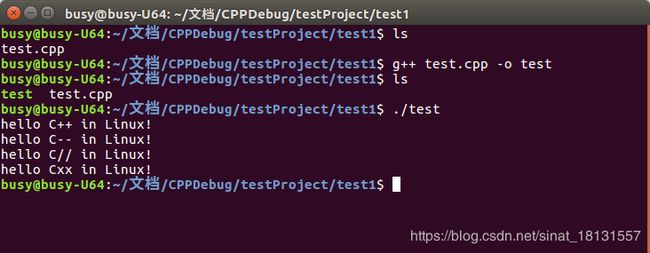
通过指令g++ --version查看是否安装成功了。正常会出现类似如下界面:

正常以后通过指令g++ test.cpp -o test编译一个可执行程序test,然后./test执行这个可执行程序就可以看到结果。g++是专门用来编译c++文件的指令,如果编译的是C语言程序,就是指令gcc,test.cpp是待编译的文件,后面的-o表示需要输出,输出的文件就是后面的一个test。
调试过程
调试过程需要使用到gdb工具,需要使用gdb调试的话,在生成test可执行程序时候需要使用到-g指令,也就是指令变为
g++ test.cpp -g -o test
这样就生成了可以被调试的test文件。

使用gdb test进入调试模式,如果电脑上安装其他软件时候,修改了LD_LIBRARY_PATH的话,有可能会有问题,在调试之前可以使用ldd test查看一下,是不是有自己安装的部分软件的依赖库。如果是可以暂时将/etc/profile或者~/.bashrc里面的修改的LD_LIBRARY_PATH暂时注释掉。像这样的话,没有自己安装软件的东西就没有问题:

那么输入gdb test进入调试模式如下图就是正常的:

常用的gdb指令有[1]:
| 指令 | 含义 | 样例 |
|---|---|---|
| b num | 在num行插入断点 | b 3 |
| b func | 在函数func的入口插入断点 | b main |
| r | 运行程序(run) | |
| n | 下一步(next) | |
| c | 继续到下一个断点(continue) | |
| p a | 打印a的值(print(a)) | p a |
| q | 退出调试 |
多个文件调试
VS code
多个文件的调试也可以通过gdb来完成,但是效率比较低,还是VS code方便一些,在VS code官网上可以直接下载安装包。我在Ubuntu上下载了.deb的包,通过管理员权限安装
sudo dpkg -i code_1.39.1-1570750687_amd64.deb

就可以打开VS code了。把之前的test文件删除了,然后文件夹直接拖到VS code里面来打开这个项目,先把环境搭建好。

可以看到下方有推荐安装一个东西读C/C++文件,点击安装即可。安装完成以后,按F5第一次尝试调试:
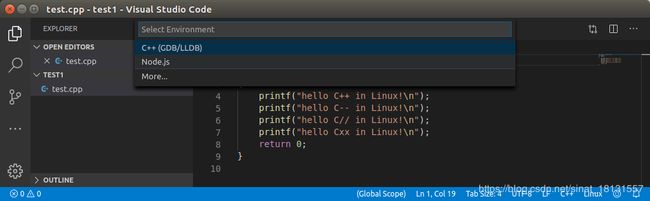
上方正中间提示选择环境,使用C++(GDB/LLDB),然后选择默认方式(Default),得到一个launch.json文件
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "(gdb) Launch",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "enter program name, for example ${workspaceFolder}/a.out",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": false,
"MIMode": "gdb",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
]
}
]
}
这里需要改变"program": "enter program name, for example ${workspaceFolder}/a.out"这一行,由于我们希望生成的是test,所以改为"program": "${workspaceFolder}/test"需要生成什么,这里的test就替换为什么。第二次按F5尝试,说是没有找到test文件,意思是需要自己生成一个?

所以还需要添加一行"preLaunchTask": "g++ test.cpp -g -o test",注意不要漏了逗号,就是创建test的指令,不知道对不对,继续F5。
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "(gdb) Launch",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/test",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"preLaunchTask": "g++ test.cpp -g -o test",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": false,
"MIMode": "gdb",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
]
}
]
}
继续黄金F5,什么task?点configuration Task看看再说。

让我创建一个task。

好吧那就Create一个,并且选择其他Other创建。

就得到了一个tasks.json文件。
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "echo",
"type": "shell",
"command": "echo Hello"
}
]
}
原来这里的command才是写g++指令的,label就是preLaunchTask后面跟的参数。所以tasks.json改为:
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "gppMyTest",
"type": "shell",
"command": "g++ test.cpp -g -o test"
}
]
}
这里的label内容写啥都行,但是要和launch.json的preLaunchTask的一样。launch.json的文件需要改为:
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "(gdb) Launch",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/test",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"preLaunchTask": "gppMyTest",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": false,
"MIMode": "gdb",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
]
}
]
}
黄金F5,看到这样的窗口就表示可以了:


并且打断点的话,也可以进行调试:

通过这个过程了解了,原来VS code调试程序要满足两个条件:
1 有launch.json文件,指定需要调试的程序是什么,这里是test这个可执行程序
2 通过tasks.json,指定生成test文件的方式,就是在launch之前通过preLaunchTask生成的。这个task就是g++指令。
有问题,不知道是不是配置正确了,直接按F5,看下弹出的提示是什么。
Makefile
实际项目中,往往不是只有一个文件,而是多个文件的项目。比如这里有三个文件夹s1,s2,mainProject都有文件(test1是上面的单个文件的文件夹)。
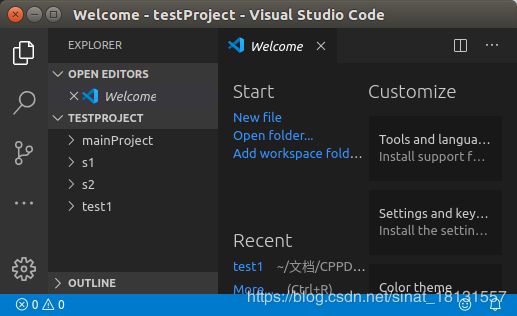
并且创建如下的文件:

/*support1.cpp*/
#include /*support2.cpp*/
#include /*support1.h*/
class Support1 {
public:
void s1();
};
/*support2.h*/
class Support2 {
public:
void s2();
};
/*mainProject.cpp*/
#include 按照前面的想法,按F5先后创建launch.json文件和tasks.json文件。
// launch.json
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "(gdb) Launch",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/myProject.out",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"preLaunchTask": "makeMyProject",
"externalConsole": false,
"MIMode": "gdb",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
]
}
]
}
// tasks.json
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "makeMyProject",
"type": "shell",
"command": "echo Hello"
}
]
}
嗯?这里的command怎么写?让我想想,这里其实就是先把support1.cpp和support2.cpp编译出来,然后和mainProject.cpp一起编译。

那么可以打开VS code的terminal或者系统的terminal写编译命令。g++ -g -c support1.cpp和g++ -g -c support2.cpp(在各自的目录中),这里只能使用-c,而不能使用-o,因为没有定义main函数。使用-c默认就会生成和cpp文件名字一样的.o文件。

然后使用生成的.o文件与mainProject.cpp一起编译一个可执行文件,g++ myProject.cpp ../s1/support1.o ../s2/support2.o -g -o mainProject.out:

这样就成功了,这只有3个文件,要是有很多文件,有比较多的逻辑问题,那每次都去写这个g++指令就麻烦了,所以就需要makefile[2]。在mainProject目录下创建一个makefile文件,没有后缀。
makefile的语法为:
target … : prerequisites …
command // 前面有一个table键
project : ../s1/support1.o ../s2/support2.o
g++ myProject.cpp ../s1/support1.o ../s2/support2.o -g -o mainProject.out
makes1 : ../s1/support1.cpp ../s1/support1.h
g++ -g -c ../s1/support1.cpp
makes2 : ../s2/support2.cpp ..s2/support2.h
g++ -g -c ../s2/support2.cpp
在进行make时候,会对第一个target进行创建,也就是project,创建project时候,发现缺少两个.o文件,所以会执行后面的makes1和makes2。如果已经不缺任何依赖了,那么后面的就不执行。写好了makefile就需要完善tasks.json和launch.json。
// tasks.json
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "makeMyProject",
"type": "shell",
"command": "cd mainProject && make"
}
]
}
把label改成makeMyProject或者任何其他字符串,与launch.json中的preLaunchTask保持一致就可以了,command写为cd mainProject && make。需要cd mainProject是因为项目在TestProject这个文件目录下,而makefile文件在mainProject这个子文件夹下,生成的可执行文件mainProject.out也在mainProject文件夹下,所以launch.json中还有一个program也需要更新下:"program": "${workspaceFolder}/mainProject/myProject.out",也就在指定最后输出.out文件的路径。
// launch.json
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "(gdb) Launch",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/mainProject/mainProject.out",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"preLaunchTask": "makeMyProject",
"externalConsole": false,
"MIMode": "gdb",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
]
}
]
}
都完成以后,F5。

COOL。同样的,加上断点也可以调试。现在有个问题,由于只有3个文件夹,3个cpp文件,所以在生成.out文件时候,使用了三个文件(一个.cpp,两个.o)来完成g++ myProject.cpp ../s1/support1.o ../s2/support2.o -g -o mainProject.out。如果有很多文件?需要一个一个先把调用的文件编译了,然后一起编译.out?并且添加一个文件就需要改变makefile文件?所以需要对makefile进行优化,不管.cpp文件在哪里,都拉过来链接成为.o文件,不管.o文件在哪里,都统统拉过来编译为.out文件。
CC := g++
CFLAGS := -g
TARGET := mainProject.out
SOURCE := $(wildcard *.cpp ../s1/*.cpp ../s2/*.cpp)
OBJS := $(patsubst %.cpp,%.o,$(SOURCE))
Tar : $(OBJS)
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(OBJS) -o $(TARGET)
%.o : %.cpp
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -c $< -o $@
.PHONY : clean
clean :
rm -rf $(TARGET) *.o ../s1/*.o ../s2/*.o
使用了CC作为变量名,变量内容为g++。CFLAGS同理,可以使用$(CC)和$(CFLAGS)的方式使用两个变量。使用SOURCE表示源码的所有位置,由于makefile在mainProject文件夹下,所以文件路径就是当前文件夹下的所有.cpp文件,使用*通配所有后缀为.cpp的文件,以及同级的s1文件夹和s2文件夹的所有.cpp文件,如果只有文件发生变化,那么使用通配的方式还是能找到新增的文件,如果文件夹的位置发生变化或者新增,就需要更改这个SOURCE变量。OBJS是将通配出来的所有SOURCE的后缀.cpp换成.o(通过函数patsubst实现)。所以Tar这个命令就是利用所有的.o文件生成mainProject.out,而.o文件需要%.o这步生成。这里有$<和$@等符号介绍一下[3,4]:
| 符号 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| $^ | 代表所有的依赖文件 |
| $@ | 代表所有的目标文件 |
| $< | 代表第一个依赖文件 |
| $? | 所有比目标新的依赖文件名称的集合,以空格分隔 |
| $+ | 很像$^,也是所有依赖文件的集合,但是它不去除重复的依赖 |
| $* | 匹配目标模式中“%”之前的部分 |
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -c $< -o $@就是将所有的依赖cpp文件,生成所有的目标.o。
说一下.PHONY的作用,.PHONY后面写的是伪目标,也就是说这种目标只是占用一个符号一个名字而已,无论当前目录下是否有clean文件,不会对比是否最新,只要执行make clean,clean目标下面定义的命令永远都会执行!在包含makefile的文件夹下执行make clean就可以清除所有的.o以及.out文件。

可以看到,执行make之后生成的.o以及.out文件在执行make clean以后都被删除了。
生成库文件的Makefile万能模板:
CC := g++
LD := ld
CFLAGS = -shared -fPIC -Wall -O -g
LDFLAGS := -shared -fPIC
SOURCE := $(wildcard *.cpp ./subpath1/*.cpp ./subpath2/*.cpp)
OBJS := $(patsubst %.cpp,%.o,$(SOURCE))
TARGET_LIB := main
makeso:
g++ $(SOURCE) -fPIC -shared -o $(TARGET_LIB)
all:$(OBJS)
echo $(OBJS)
$(CC) $(LDFLAGS) -o $(TARGET_LIB) $(OBJS)
%.o:%.cpp
@echo Compiling $< ...
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -c $< -o $@
.PHONY: clean
clean:
rm *.so *.o ./subpath1/*.o ./subpath2/*.o $(TARGET_LIB) -rf
使用到的文件
github:https://github.com/BusyDataForFS/CPPStudyRemarks
本来想上传到CSDN文件下载的,结果文件下载都是5积分,现在的积分还要充钱,吃相太难看了…
用GDB调试程序(一), https://blog.csdn.net/haoel/article/details/2879 ↩︎
Linux makefile 教程 非常详细,且易懂, https://blog.csdn.net/liang13664759/article/details/1771246 ↩︎
Linux——makefile编写, https://www.cnblogs.com/tp-16b/p/8955462.html ↩︎
Linux之Makefile, https://www.cnblogs.com/yuyifeiyang/p/9455809.html ↩︎
