STM32 之四 标准外设版 USB 驱动 + MSC(Host) + Fatfs 移植
写在前面
- 现在,网上关于STM32的USB的文章数不胜数。写这篇文章仅仅是对于自我学习的一个记录。主要是对实际学习中遇到的一些棘手问题做个备忘录。使用的芯片为STM32F407VG 。
- 目前,ST的USB驱动有两套,一套是早期的独立版USB驱动,官方培训文档中称为Legacy library,最新版为2.2.0;一套为针对其Cube系列的驱动,根据芯片不同可能有区别,具体见对应芯片的Cube驱动包,官方培训文档中称为Cube library。 本文使用的为Legacy libraryUSB驱动。更详细的请参考博文STM32 之 USB IP(USB模块) 详解。
- HAL库 + Legacy library USB库两个混用
- 目前,Fatfs 驱动最新版为R0.13a 。
- 本文多出自于ST的官方文档,读者也可以直接去ST官网查阅相关文档。
- 本文主要涉及USB Host(全速)+ MSC + Fatfs的移植。其他移植后续用到再说。
- 关于独立版USB驱动库的详解见 http://blog.csdn.net/zcshoucsdn/article/details/78936456
USB驱动部分
源码移植
源码的移植相对来说比较简单,使用时,根据需要复制相关的文件即可。需要注意的是,整理一下源码的结构。这个在上一篇博文中已经由说明了。具体见下图:
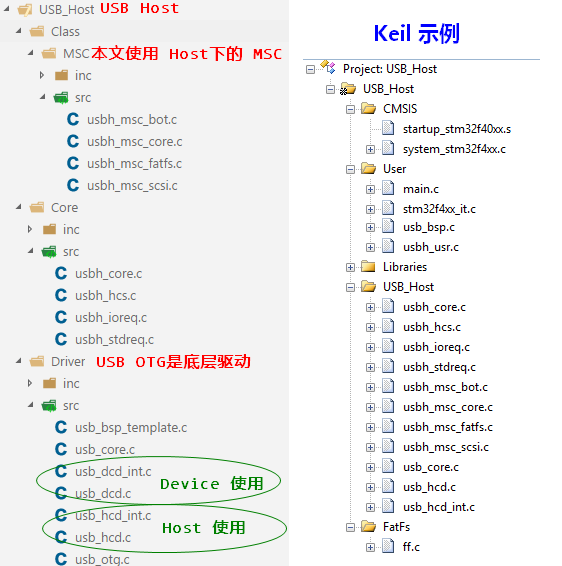
在移植其他部分的时候与之类似,只需要替换成对应部分的源码文件即可。
- 源码中的 USB OTG部分是所有其他模块的驱动程序。
usbh_msc_fatfs.c为ST提供的FatFs的diskio.c的具体实现文件。在使用了该文件后,用户不必再自行实现FafFs的diskio.c了。
###源码配置
整个USB驱动用于灵活的配置选项,且通过一个配置文件的形式给出。这样,使用者可以尽量少的修改的驱动源代码。这些配置文件均为用户级别的文件,通常来说置于用户代码目录下。如下如所示:

作为用户级文件,通常所有的用户代码均在以上文件做修改即可,只有少数特殊处理会设计到驱动程序源码的修改。在配置好后,一般来说,所有修改均在usbh_usr.h/.c中。
usb_config.h
usb_config.h是USB OTG 底层驱动的配置文件。在USB OTG的源代码中,ST提供了usb_conf_template.h。使用者只需要复制该文件到自己的代码目录下,修改即可。具体配置见下文的注释部分:
/** ******************************************************************************
* @file usb_conf.h
* @author
* @version V2.2.0
* @date 2017.12.27
* @brief USB的底层驱动配置
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* © COPYRIGHT 2017 ST
*
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* Define to prevent recursive inclusion -------------------------------------*/
#ifndef __USB_CONF__H__
#define __USB_CONF__H__
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "stm32f4xx.h" /* 这里需要包含自己使用的ST的库的头文件 */
/** @addtogroup USB_OTG_DRIVER
* @{
*/
/** @defgroup USB_CONF
* @brief USB 底层驱动配置文件
* @{
*/
/** @defgroup USB_CONF_Exported_Defines
* @{
*/
/* USB Core and PHY interface 配置.
Tip: To avoid modifying these defines each time you need to change the USB configuration, you can declare the needed define in your toolchain compiler preprocessor.
*/
/**** 配置文件包含了Full Speed 和 High Speed 两种速率的配置,使用时,从两者选择其一即可。****/
/****************** USB OTG FS PHY 配置 *******************************
* USB OTG FS Core 支持 one on-chip Full Speed PHY。通常,ST芯片内部已经集成了该PHY。
*
* 当使用了FS core时,宏USE_EMBEDDED_PHY 需要在编译器中定义.
*
*******************************************************************************/
#ifndef USE_USB_OTG_FS
#define USE_USB_OTG_FS /* 使用 FS, 与下面的 HS 只能选一个。目前,终端只支持FS */
#endif /* USE_USB_OTG_FS */
#ifdef USE_USB_OTG_FS
#define USB_OTG_FS_CORE
#endif
/****************** USB OTG HS PHY 配置 *******************************
* USB OTG HS Core 支持 两种 PHY 接口:
* (i) 使用外部高速PHY的ULPI 接口: USB HS Core 工作在高速模式下
* (ii) 片内Full Speed PHY: USB HS Core 工作在全速模式下
* 通过下面两个宏,选择使用哪种PHY:
* (i) USE_ULPI_PHY: if the USB OTG HS Core is to be used in High speed mode
* (ii) USE_EMBEDDED_PHY: if the USB OTG HS Core is to be used in Full speed mode
*
* Notes:
* - The USE_ULPI_PHY symbol is defined in the project compiler preprocessor as default PHY when HS core is used.
* - On STM322xG-EVAL and STM324xG-EVAL boards, only configuration(i) is available.
* Configuration (ii) need a different hardware, for more details refer to your STM32 device datasheet.
*******************************************************************************/
#ifndef USE_USB_OTG_HS
//#define USE_USB_OTG_HS
#endif /* USE_USB_OTG_HS */
#ifndef USE_ULPI_PHY
//#define USE_ULPI_PHY
#endif /* USE_ULPI_PHY */
#ifndef USE_EMBEDDED_PHY
//#define USE_EMBEDDED_PHY
#endif /* USE_EMBEDDED_PHY */
#ifdef USE_USB_OTG_HS
#define USB_OTG_HS_CORE
#endif
/*******************************************************************************
* FIFO Size Configuration in Device mode
*
* (i) Receive data FIFO size = RAM for setup packets +
* OUT endpoint control information +
* data OUT packets + miscellaneous
* Space = ONE 32-bits words
* --> RAM for setup packets = 10 spaces
* (n is the nbr of CTRL EPs the device core supports)
* --> OUT EP CTRL info = 1 space
* (one space for status information written to the FIFO along with each
* received packet)
* --> data OUT packets = (Largest Packet Size / 4) + 1 spaces
* (MINIMUM to receive packets)
* --> OR data OUT packets = at least 2*(Largest Packet Size / 4) + 1 spaces
* (if high-bandwidth EP is enabled or multiple isochronous EPs)
* --> miscellaneous = 1 space per OUT EP
* (one space for transfer complete status information also pushed to the
* FIFO with each endpoint's last packet)
*
* (ii)MINIMUM RAM space required for each IN EP Tx FIFO = MAX packet size for
* that particular IN EP. More space allocated in the IN EP Tx FIFO results
* in a better performance on the USB and can hide latencies on the AHB.
*
* (iii) TXn min size = 16 words. (n : Transmit FIFO index)
* (iv) When a TxFIFO is not used, the Configuration should be as follows:
* case 1 : n > m and Txn is not used (n,m : Transmit FIFO indexes)
* --> Txm can use the space allocated for Txn.
* case2 : n < m and Txn is not used (n,m : Transmit FIFO indexes)
* --> Txn should be configured with the minimum space of 16 words
* (v) The FIFO is used optimally when used TxFIFOs are allocated in the top
* of the FIFO.Ex: use EP1 and EP2 as IN instead of EP1 and EP3 as IN ones.
*******************************************************************************/
/*******************************************************************************
* FIFO Size Configuration in Host mode
*
* (i) Receive data FIFO size = (Largest Packet Size / 4) + 1 or
* 2x (Largest Packet Size / 4) + 1, If a
* high-bandwidth channel or multiple isochronous
* channels are enabled
*
* (ii) For the host nonperiodic Transmit FIFO is the largest maximum packet size
* for all supported nonperiodic OUT channels. Typically, a space
* corresponding to two Largest Packet Size is recommended.
*
* (iii) The minimum amount of RAM required for Host periodic Transmit FIFO is
* the largest maximum packet size for all supported periodic OUT channels.
* If there is at least one High Bandwidth Isochronous OUT endpoint,
* then the space must be at least two times the maximum packet size for
* that channel.
*******************************************************************************/
/****************** USB OTG HS CONFIGURATION **********************************/
/* 以下暂不使用 */
#ifdef USB_OTG_HS_CORE
#define RX_FIFO_HS_SIZE 512 /* 设置高速内核的接收FIFO大小。*/
/* 设置设备端点的发送FIFO大小(高速),其中0~3是要使用的端点的索引。*/
#define TX0_FIFO_HS_SIZE 512
#define TX1_FIFO_HS_SIZE 512
#define TX2_FIFO_HS_SIZE 0
#define TX3_FIFO_HS_SIZE 0
#define TX4_FIFO_HS_SIZE 0
#define TX5_FIFO_HS_SIZE 0
#define TXH_NP_HS_FIFOSIZ 96 /* 设置主机模式(高速)的非周期性发送FIFO大小。 */
#define TXH_P_HS_FIFOSIZ 96 /* 设置主机模式(高速)的周期性发送FIFO大小。*/
// #define USB_OTG_HS_LOW_PWR_MGMT_SUPPORT /* 实现高速核心(USB核心时钟门控等)的低功耗管理。 */
// #define USB_OTG_HS_SOF_OUTPUT_ENABLED
// #define USB_OTG_INTERNAL_VBUS_ENABLED
#define USB_OTG_EXTERNAL_VBUS_ENABLED
#ifdef USE_ULPI_PHY
#define USB_OTG_ULPI_PHY_ENABLED /* 启用高速内核的ULPI PHY。 */
#endif
#ifdef USE_EMBEDDED_PHY
#define USB_OTG_EMBEDDED_PHY_ENABLED /* 为高速内核启用嵌入式FS PHY。 */
#endif
#define USB_OTG_HS_INTERNAL_DMA_ENABLED /* 启用高速内核的内部DMA功能。 */
#define USB_OTG_HS_DEDICATED_EP1_ENABLED /* 在高速内核中为器件模式启用专用的端点1功能。 */
#endif
/****************** USB OTG FS CONFIGURATION **********************************/
#ifdef USB_OTG_FS_CORE
#define RX_FIFO_FS_SIZE 128 /* 设置全速内核的接收FIFO大小。 */
/* 设置设备端点的发送FIFO大小(全速),其中0~3是要使用的端点的索引。*/
#define TX0_FIFO_FS_SIZE 64
#define TX1_FIFO_FS_SIZE 128
#define TX2_FIFO_FS_SIZE 0
#define TX3_FIFO_FS_SIZE 0
#define TXH_NP_FS_FIFOSIZ 96 /* 设置主机模式(全速)的非周期性发送FIFO大小。 */
#define TXH_P_FS_FIFOSIZ 96 /* 设置主机模式(全速)的周期性发送FIFO大小。*/
// #define USB_OTG_FS_LOW_PWR_MGMT_SUPPORT /* 实现全速核心(USB核心时钟门控等)的低功耗管理。 */
// #define USB_OTG_FS_SOF_OUTPUT_ENABLED
#endif
/****************** USB OTG MISC CONFIGURATION ********************************/
//#define VBUS_SENSING_ENABLED
/****************** USB OTG MODE CONFIGURATION ********************************/
#define USE_HOST_MODE /* 采用 Host 模式 与下面的 USE_DEVICE_MODE 和 USE_OTG_MODE 任选其一 */
//#define USE_DEVICE_MODE
//#define USE_OTG_MODE
#ifndef USB_OTG_FS_CORE
#ifndef USB_OTG_HS_CORE
#error "USB_OTG_HS_CORE or USB_OTG_FS_CORE should be defined"
#endif
#endif
#ifndef USE_DEVICE_MODE
#ifndef USE_HOST_MODE
#error "USE_DEVICE_MODE or USE_HOST_MODE should be defined"
#endif
#endif
#ifndef USE_USB_OTG_HS
#ifndef USE_USB_OTG_FS
#error "USE_USB_OTG_HS or USE_USB_OTG_FS should be defined"
#endif
#else //USE_USB_OTG_HS
#ifndef USE_ULPI_PHY
#ifndef USE_EMBEDDED_PHY
#error "USE_ULPI_PHY or USE_EMBEDDED_PHY should be defined"
#endif
#endif
#endif
/****************** C Compilers dependant keywords ****************************/
/* In HS mode and when the DMA is used, all variables and data structures dealing
with the DMA during the transaction process should be 4-bytes aligned */
#ifdef USB_OTG_HS_INTERNAL_DMA_ENABLED
#if defined (__GNUC__) /* GNU Compiler */
#define __ALIGN_END __attribute__ ((aligned (4)))
#define __ALIGN_BEGIN
#else
#define __ALIGN_END
#if defined (__CC_ARM) /* ARM Compiler */
#define __ALIGN_BEGIN __align(4)
#elif defined (__ICCARM__) /* IAR Compiler */
#define __ALIGN_BEGIN
#elif defined (__TASKING__) /* TASKING Compiler */
#define __ALIGN_BEGIN __align(4)
#endif /* __CC_ARM */
#endif /* __GNUC__ */
#else
#define __ALIGN_BEGIN
#define __ALIGN_END
#endif /* USB_OTG_HS_INTERNAL_DMA_ENABLED */
/* __packed keyword used to decrease the data type alignment to 1-byte */
#if defined (__CC_ARM) /* ARM Compiler */
#define __packed __packed
#elif defined (__ICCARM__) /* IAR Compiler */
#define __packed __packed
#elif defined ( __GNUC__ ) /* GNU Compiler */
#define __packed __attribute__ ((__packed__))
#elif defined (__TASKING__) /* TASKING Compiler */
#define __packed __unaligned
#endif /* __CC_ARM */
/**
* @}
*/
/*省略*/
#endif //__USB_CONF__H__
/**
* @}
*/
/**
* @}
*/
/************************ (C) COPYRIGHT *****END OF FILE****/
usbh_config.h
usbh_config.h是USB Host 底层驱动的配置文件。在USB OTG的源代码中,ST提供了usbh_conf_template.h。使用者只需要复制该文件到自己的代码目录下,修改即可。具体配置见下文的注释部分:
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file usbh_conf.h
* @author
* @version V2.2.0
* @date 2017.12.27
* @brief USB Host library 配置
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* © COPYRIGHT 2017
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* Define to prevent recursive inclusion -------------------------------------*/
#ifndef __USBH_CONF__H__
#define __USBH_CONF__H__
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
// #include "xxx.h" /* 包含自己的各种头文件*/
/** @addtogroup USBH_OTG_DRIVER
* @{
*/
/** @defgroup USBH_CONF
* @brief USB Host 底层驱动配置文件
* @{
*/
/** @defgroup USBH_CONF_Exported_Defines
* @{
*/
#define USBH_MAX_NUM_ENDPOINTS 2 /* 支持端点的最大数量 1 bulk IN + 1 bulk Out */
#define USBH_MAX_NUM_INTERFACES 2 /* 支持接口的最大数量 */
#ifdef USE_USB_OTG_FS
#define USBH_MSC_MPS_SIZE 0x40
#else
#define USBH_MSC_MPS_SIZE 0x200
#endif
#define USBH_MAX_DATA_BUFFER 0x400
/* 错误信息打印函数 重定向 这里需要注意:该库使用了LCD_ErrLog,需要进行重定向,否则报错 */
/* 感觉 库直接将 其改名为 USB_Log 或者 USB_ErrLog 最好了 */
#define LCD_ErrLog(str) udwComSendData(COM_CONSOLE, str, strlen(str));
/* 与Fatfs对接使用 */
#define _USE_IOCTL 1
/**
* @}
*/
/** @defgroup USBH_CONF_Exported_Types
* @{
*/
/**
* @}
*/
/** @defgroup USBH_CONF_Exported_Macros
* @{
*/
/**
* @}
*/
/** @defgroup USBH_CONF_Exported_Variables
* @{
*/
/**
* @}
*/
/** @defgroup USBH_CONF_Exported_FunctionsPrototype
* @{
*/
/**
* @}
*/
#endif //__USBH_CONF__H__
/**
* @}
*/
/**
* @}
*/
/************************ (C) COPYRIGHT *****END OF FILE****/
usbh_bsp.c
包含(在USB OTG低级驱动程序的usb_bsp.h文件中声明)来初始化GPIO的核心,延时方法和中断启用/禁用的函数的实现。在USB OTG的源代码中,ST提供了usb_bsp_template.c。使用者只需要复制该文件到自己的代码目录下,修改即可。具体需要实现的函数在usb_bsp.h中已经定义好了,使用者不能更改接口名。见下文的注释部分:
void USB_OTG_BSP_Init (USB_OTG_CORE_HANDLE *pdev); /* 该接口中 实现 USB Host 使用的各种 GPIO等*/
void USB_OTG_BSP_uDelay (const uint32_t usec); /* USB 使用的延时函数 */
void USB_OTG_BSP_mDelay (const uint32_t msec); /* USB 使用的延时函数 */
void USB_OTG_BSP_EnableInterrupt (USB_OTG_CORE_HANDLE *pdev); /* USB 使用的中断 */
void USB_OTG_BSP_TimerIRQ (void);
/* 以下主要是用于 高速模式下的配置,如VBUS的过流检测等 */
#ifdef USE_HOST_MODE
void USB_OTG_BSP_ConfigVBUS(USB_OTG_CORE_HANDLE *pdev);
void USB_OTG_BSP_DriveVBUS(USB_OTG_CORE_HANDLE *pdev,uint8_t state);
void USB_OTG_BSP_Resume(USB_OTG_CORE_HANDLE *pdev);
void USB_OTG_BSP_Suspend(USB_OTG_CORE_HANDLE *pdev);
#endif /* USE_HOST_MODE */
usbh_usr.c/.h
包含(在USB库的usbh_usr.h文件中声明)来处理来自用户层(事件消息)的库事件的函数实现。需要实现的函数接口(注意:以下是针对MSC的,其他如HID的用户接口是不同的)见下文:
void USBH_USR_Init(void);
void USBH_USR_DeInit(void);
void USBH_USR_DeviceAttached(void);
void USBH_USR_ResetDevice(void);
void USBH_USR_DeviceDisconnected (void);
void USBH_USR_OverCurrentDetected (void);
void USBH_USR_DeviceSpeedDetected(uint8_t DeviceSpeed);
void USBH_USR_Device_DescAvailable(void *);
void USBH_USR_DeviceAddressAssigned(void);
void USBH_USR_Configuration_DescAvailable(USBH_CfgDesc_TypeDef * cfgDesc,
USBH_InterfaceDesc_TypeDef *itfDesc,
USBH_EpDesc_TypeDef *epDesc);
void USBH_USR_Manufacturer_String(void *);
void USBH_USR_Product_String(void *);
void USBH_USR_SerialNum_String(void *);
void USBH_USR_EnumerationDone(void);
USBH_USR_Status USBH_USR_UserInput(void);
void USBH_USR_DeviceNotSupported(void);
void USBH_USR_UnrecoveredError(void);
int USBH_USR_MSC_Application(void);
对于MSC,使用以下回调:USBH_USR_MSC_Application()。 在类初始化结束之后,这个函数被MSC状态机调用,以便向用户提供文件系统访问操作。使用者最终需要在该函数中实现自己的用户代码。在此回调中,用户可以使用FAT FS文件系统API实现对FAT文件系统的任何访问(文件打开,文件读取,文件写入…)。 用户还可以访问从库MSC类驱动程序导出的结构变量:USBH_MSC_Param。
其他接口是这个USB Host 状态机一步一步执行过程的函数。使用者可以在不同的步骤添加对应的处理。最终,使用类型USBH_Usr_cb_TypeDef,将所有函数注册进USB Host驱动。
/* USB Host 用户接口 类型定义 */
typedef struct _USBH_USR_PROP
{
void (*Init)(void); /* HostLibInitialized */
void (*DeInit)(void); /* HostLibInitialized */
void (*DeviceAttached)(void); /* DeviceAttached */
void (*ResetDevice)(void);
void (*DeviceDisconnected)(void);
void (*OverCurrentDetected)(void);
void (*DeviceSpeedDetected)(uint8_t DeviceSpeed); /* DeviceSpeed */
void (*DeviceDescAvailable)(void *); /* DeviceDescriptor is available */
void (*DeviceAddressAssigned)(void); /* Address is assigned to USB Device */
void (*ConfigurationDescAvailable)(USBH_CfgDesc_TypeDef *,
USBH_InterfaceDesc_TypeDef *,
USBH_EpDesc_TypeDef *);
/* Configuration Descriptor available */
void (*ManufacturerString)(void *); /* ManufacturerString*/
void (*ProductString)(void *); /* ProductString*/
void (*SerialNumString)(void *); /* SerialNubString*/
void (*EnumerationDone)(void); /* Enumeration finished */
USBH_USR_Status (*UserInput)(void);
int (*UserApplication) (void);
void (*DeviceNotSupported)(void); /* Device is not supported*/
void (*UnrecoveredError)(void);
}
USBH_Usr_cb_TypeDef;
/* USB Host 用户接口 使用示例 */
USBH_Usr_cb_TypeDef USR_cb =
{
USBH_USR_Init,
USBH_USR_DeInit,
USBH_USR_DeviceAttached,
USBH_USR_ResetDevice,
USBH_USR_DeviceDisconnected,
USBH_USR_OverCurrentDetected,
USBH_USR_DeviceSpeedDetected,
USBH_USR_Device_DescAvailable,
USBH_USR_DeviceAddressAssigned,
USBH_USR_Configuration_DescAvailable,
USBH_USR_Manufacturer_String,
USBH_USR_Product_String,
USBH_USR_SerialNum_String,
USBH_USR_EnumerationDone,
USBH_USR_UserInput,
USBH_USR_MSC_Application,
USBH_USR_DeviceNotSupported,
USBH_USR_UnrecoveredError
};
注意事项
- 一旦使用了DMA( 高速模式下),所有结构体必须是四字节对齐的。
- 如下即可使用 USB Host
/* 定义 USB_OTG_Core */
#ifdef USB_OTG_HS_INTERNAL_DMA_ENABLED
#if defined ( __ICCARM__ ) /*!< IAR Compiler */
#pragma data_alignment=4
#endif
#endif /* USB_OTG_HS_INTERNAL_DMA_ENABLED */
__ALIGN_BEGIN USB_OTG_CORE_HANDLE USB_OTG_Core __ALIGN_END;
/* 定义 USB_Host */
#ifdef USB_OTG_HS_INTERNAL_DMA_ENABLED
#if defined ( __ICCARM__ ) /*!< IAR Compiler */
#pragma data_alignment=4
#endif
#endif /* USB_OTG_HS_INTERNAL_DMA_ENABLED */
__ALIGN_BEGIN USBH_HOST USB_Host __ALIGN_END;
/****注意:在非启用到了DMA的高速模式下, 以上两个定义可直接简化(不需要对齐处理)如下:
* USB_OTG_CORE_HANDLE USB_OTG_Core;
* USBH_HOST USB_Host;
****/
/* 初始化 USB Host 库 */
USBH_Init( &USB_OTG_Core,
#ifdef USE_USB_OTG_FS
USB_OTG_FS_CORE_ID,
#else
USB_OTG_HS_CORE_ID,
#endif
&USB_Host,
&USBH_MSC_cb,
&USR_cb );
/* 最后,周期调用以下函数即可 */
USBH_Process(&USB_OTG_Core, &USB_Host);
- 还需要在中断处理文件中,添加以下中断(如果使用了其他功能的终端,自行添加):
/**
* @brief OTG_FS_IRQHandler
* This function handles USB-On-The-Go FS global interrupt request.
* requests.
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
#ifdef USE_USB_OTG_FS
void OTG_FS_IRQHandler(void)
#else
void OTG_HS_IRQHandler(void)
#endif
{
USBH_OTG_ISR_Handler(&USB_OTG_Core);
}
Fatfs部分
源码移植
目前,FatFS的最新版为R0.13a。从R0.13开始,作者将配置宏统一为可FF_开头。目前网上多数文章都是针对之前的,许多配置名与最新新版的源码是对不上。

使用FatFs最简单的只需要关系两个文件即可:ff.c/h和diskio.c/h。其中,diskio.c/h是一个模板,用户需要自行实现与底层磁盘的读写。在ST提供的USB Host驱动中,已经实现了该文件,名为usbh_msc_fatfs.c。
更进一步,在使用了其他编码例如中文及长文件名时,则需要将ffunicode.c包含到自己的项目中。此外,在使用了系统时,还必须将ffsystem.c包含到项目中,并按照自己的系统,修改该文件。
源码配置
FatFS的配置通过一个名为ffconf.h的文件实现。对于每个选项,模板中都有很详细的说明。同时,为减小FatFs占用的空间,一般只开启需要的选项。以下仅对几个特殊的进行注释性说明。
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ FatFs - Configuration file
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FFCONF_DEF 89352 /* Revision ID */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ Function Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_FS_READONLY 0
/* This option switches read-only configuration. (0:Read/Write or 1:Read-only)
/ Read-only configuration removes writing API functions, f_write(), f_sync(),
/ f_unlink(), f_mkdir(), f_chmod(), f_rename(), f_truncate(), f_getfree()
/ and optional writing functions as well. */
#define FF_FS_MINIMIZE 0
/* This option defines minimization level to remove some basic API functions.
/
/ 0: Basic functions are fully enabled.
/ 1: f_stat(), f_getfree(), f_unlink(), f_mkdir(), f_truncate() and f_rename()
/ are removed.
/ 2: f_opendir(), f_readdir() and f_closedir() are removed in addition to 1.
/ 3: f_lseek() function is removed in addition to 2. */
#define FF_USE_STRFUNC 1
/* This option switches string functions, f_gets(), f_putc(), f_puts() and f_printf().
/
/ 0: Disable string functions.
/ 1: Enable without LF-CRLF conversion.
/ 2: Enable with LF-CRLF conversion. */
#define FF_USE_FIND 0
/* This option switches filtered directory read functions, f_findfirst() and
/ f_findnext(). (0:Disable, 1:Enable 2:Enable with matching altname[] too) */
#define FF_USE_MKFS 0
/* This option switches f_mkfs() function. (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_FASTSEEK 0
/* This option switches fast seek function. (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_EXPAND 0
/* This option switches f_expand function. (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_CHMOD 0
/* This option switches attribute manipulation functions, f_chmod() and f_utime().
/ (0:Disable or 1:Enable) Also FF_FS_READONLY needs to be 0 to enable this option. */
#define FF_USE_LABEL 0
/* This option switches volume label functions, f_getlabel() and f_setlabel().
/ (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_FORWARD 0
/* This option switches f_forward() function. (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ Locale and Namespace Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Code Page,是字符编码的另一种说法。Code Page包含了一个表,表中的值,用于表示针对某种语言所用的字符集。更简单点说,就是Code Page中,用一个数字编号,表示了所要采用何种字符编码,去编解码相应的值,用于正确显示出相应的字符。*/
#define FF_CODE_PAGE 932
/* This option specifies the OEM code page to be used on the target system.
/ Incorrect code page setting can cause a file open failure.
/
/ 437 - U.S.
/ 720 - Arabic
/ 737 - Greek
/ 771 - KBL
/ 775 - Baltic
/ 850 - Latin 1
/ 852 - Latin 2
/ 855 - Cyrillic
/ 857 - Turkish
/ 860 - Portuguese
/ 861 - Icelandic
/ 862 - Hebrew
/ 863 - Canadian French
/ 864 - Arabic
/ 865 - Nordic
/ 866 - Russian
/ 869 - Greek 2
/ 932 - Japanese (DBCS)
/ 936 - Simplified Chinese (DBCS)
/ 949 - Korean (DBCS)
/ 950 - Traditional Chinese (DBCS)
/ 0 - Include all code pages above and configured by f_setcp()
*/
/* 长文件名。这个是微软的专利!开启后 必须包含 ffunicode.c */
#define FF_USE_LFN 0
#define FF_MAX_LFN 255
/* The FF_USE_LFN switches the support for LFN (long file name).
/
/ 0: Disable LFN. FF_MAX_LFN has no effect.
/ 1: Enable LFN with static working buffer on the BSS. Always NOT thread-safe.
/ 2: Enable LFN with dynamic working buffer on the STACK.
/ 3: Enable LFN with dynamic working buffer on the HEAP.
/
/ To enable the LFN, ffunicode.c needs to be added to the project. The LFN function
/ requiers certain internal working buffer occupies (FF_MAX_LFN + 1) * 2 bytes and
/ additional (FF_MAX_LFN + 44) / 15 * 32 bytes when exFAT is enabled.
/ The FF_MAX_LFN defines size of the working buffer in UTF-16 code unit and it can
/ be in range of 12 to 255. It is recommended to be set 255 to fully support LFN
/ specification.
/ When use stack for the working buffer, take care on stack overflow. When use heap
/ memory for the working buffer, memory management functions, ff_memalloc() and
/ ff_memfree() in ffsystem.c, need to be added to the project. */
/* 必须开启 Unicode支持 */
#define FF_LFN_UNICODE 0
/* This option switches the character encoding on the API when LFN is enabled.
/
/ 0: ANSI/OEM in current CP (TCHAR = char)
/ 1: Unicode in UTF-16 (TCHAR = WCHAR)
/ 2: Unicode in UTF-8 (TCHAR = char)
/
/ Also behavior of string I/O functions will be affected by this option.
/ When LFN is not enabled, this option has no effect. */
#define FF_LFN_BUF 255
#define FF_SFN_BUF 12
/* This set of options defines size of file name members in the FILINFO structure
/ which is used to read out directory items. These values should be suffcient for
/ the file names to read. The maximum possible length of the read file name depends
/ on character encoding. When LFN is not enabled, these options have no effect. */
#define FF_STRF_ENCODE 3
/* When FF_LFN_UNICODE >= 1 with LFN enabled, string I/O functions, f_gets(),
/ f_putc(), f_puts and f_printf() convert the character encoding in it.
/ This option selects assumption of character encoding ON THE FILE to be
/ read/written via those functions.
/
/ 0: ANSI/OEM in current CP
/ 1: Unicode in UTF-16LE
/ 2: Unicode in UTF-16BE
/ 3: Unicode in UTF-8
*/
#define FF_FS_RPATH 0
/* This option configures support for relative path.
/
/ 0: Disable relative path and remove related functions.
/ 1: Enable relative path. f_chdir() and f_chdrive() are available.
/ 2: f_getcwd() function is available in addition to 1.
*/
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ Drive/Volume Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_VOLUMES 1
/* Number of volumes (logical drives) to be used. (1-10) */
#define FF_STR_VOLUME_ID 0
#define FF_VOLUME_STRS "RAM","NAND","CF","SD","SD2","USB","USB2","USB3"
/* FF_STR_VOLUME_ID switches string support for volume ID.
/ When FF_STR_VOLUME_ID is set to 1, also pre-defined strings can be used as drive
/ number in the path name. FF_VOLUME_STRS defines the drive ID strings for each
/ logical drives. Number of items must be equal to FF_VOLUMES. Valid characters for
/ the drive ID strings are: A-Z and 0-9. */
#define FF_MULTI_PARTITION 0
/* This option switches support for multiple volumes on the physical drive.
/ By default (0), each logical drive number is bound to the same physical drive
/ number and only an FAT volume found on the physical drive will be mounted.
/ When this function is enabled (1), each logical drive number can be bound to
/ arbitrary physical drive and partition listed in the VolToPart[]. Also f_fdisk()
/ funciton will be available. */
#define FF_MIN_SS 512
#define FF_MAX_SS 512
/* This set of options configures the range of sector size to be supported. (512,
/ 1024, 2048 or 4096) Always set both 512 for most systems, generic memory card and
/ harddisk. But a larger value may be required for on-board flash memory and some
/ type of optical media. When FF_MAX_SS is larger than FF_MIN_SS, FatFs is configured
/ for variable sector size mode and disk_ioctl() function needs to implement
/ GET_SECTOR_SIZE command. */
#define FF_USE_TRIM 0
/* This option switches support for ATA-TRIM. (0:Disable or 1:Enable)
/ To enable Trim function, also CTRL_TRIM command should be implemented to the
/ disk_ioctl() function. */
#define FF_FS_NOFSINFO 0
/* If you need to know correct free space on the FAT32 volume, set bit 0 of this
/ option, and f_getfree() function at first time after volume mount will force
/ a full FAT scan. Bit 1 controls the use of last allocated cluster number.
/
/ bit0=0: Use free cluster count in the FSINFO if available.
/ bit0=1: Do not trust free cluster count in the FSINFO.
/ bit1=0: Use last allocated cluster number in the FSINFO if available.
/ bit1=1: Do not trust last allocated cluster number in the FSINFO.
*/
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ System Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_FS_TINY 0
/* This option switches tiny buffer configuration. (0:Normal or 1:Tiny)
/ At the tiny configuration, size of file object (FIL) is shrinked FF_MAX_SS bytes.
/ Instead of private sector buffer eliminated from the file object, common sector
/ buffer in the filesystem object (FATFS) is used for the file data transfer. */
#define FF_FS_EXFAT 0
/* This option switches support for exFAT filesystem. (0:Disable or 1:Enable)
/ When enable exFAT, also LFN needs to be enabled.
/ Note that enabling exFAT discards ANSI C (C89) compatibility. */
#define FF_FS_NORTC 0
#define FF_NORTC_MON 1
#define FF_NORTC_MDAY 1
#define FF_NORTC_YEAR 2017
/* The option FF_FS_NORTC switches timestamp functiton. If the system does not have
/ any RTC function or valid timestamp is not needed, set FF_FS_NORTC = 1 to disable
/ the timestamp function. All objects modified by FatFs will have a fixed timestamp
/ defined by FF_NORTC_MON, FF_NORTC_MDAY and FF_NORTC_YEAR in local time.
/ To enable timestamp function (FF_FS_NORTC = 0), get_fattime() function need to be
/ added to the project to read current time form real-time clock. FF_NORTC_MON,
/ FF_NORTC_MDAY and FF_NORTC_YEAR have no effect.
/ These options have no effect at read-only configuration (FF_FS_READONLY = 1). */
#define FF_FS_LOCK 0
/* The option FF_FS_LOCK switches file lock function to control duplicated file open
/ and illegal operation to open objects. This option must be 0 when FF_FS_READONLY
/ is 1.
/
/ 0: Disable file lock function. To avoid volume corruption, application program
/ should avoid illegal open, remove and rename to the open objects.
/ >0: Enable file lock function. The value defines how many files/sub-directories
/ can be opened simultaneously under file lock control. Note that the file
/ lock control is independent of re-entrancy. */
#define FF_FS_REENTRANT 0
#define FF_FS_TIMEOUT 1000
#define FF_SYNC_t HANDLE
/* The option FF_FS_REENTRANT switches the re-entrancy (thread safe) of the FatFs
/ module itself. Note that regardless of this option, file access to different
/ volume is always re-entrant and volume control functions, f_mount(), f_mkfs()
/ and f_fdisk() function, are always not re-entrant. Only file/directory access
/ to the same volume is under control of this function.
/
/ 0: Disable re-entrancy. FF_FS_TIMEOUT and FF_SYNC_t have no effect.
/ 1: Enable re-entrancy. Also user provided synchronization handlers,
/ ff_req_grant(), ff_rel_grant(), ff_del_syncobj() and ff_cre_syncobj()
/ function, must be added to the project. Samples are available in
/ option/syscall.c.
/
/ The FF_FS_TIMEOUT defines timeout period in unit of time tick.
/ The FF_SYNC_t defines O/S dependent sync object type. e.g. HANDLE, ID, OS_EVENT*,
/ SemaphoreHandle_t and etc. A header file for O/S definitions needs to be
/ included somewhere in the scope of ff.h. */
/* #include // O/S definitions */
/*--- End of configuration options ---*/
注意事项
- FatFs从R0.13开始,源码结构与之间变化不少,变得更简洁。需要使用者修改了diskio.c和ffsystem.也给出了模板,只需要做对应修改即可。
- 关于字符编码(Code Page)参考字符编码详解。字符编码选择错误可能导致读写文件失败!!!
- 长文件名是微软的专利,使用时需要注意!长文件名使用Unicode编码,因此必须包含
ffunicode.c。在该文件中,FatFs的作者给出了对应文件编码的转换表和对应的转换函数ff_convert()和ff_wtoupper()。
参考文档
- STM32F105xx, STM32F107xx, STM32F2xx and STM32F4xx USB On-The-Go host and device library User manual
- Universal Serial Bus Revision 2.0 specification
- USB 2.0 On-The-Go Specification Supplement Adopters Agreement
- Fatfs 官方文档 http://elm-chan.org/fsw/ff/00index_e.html