Linux电源管理(五)thermal
thermal子系统概述
thermal子系统是内核提供的温控管理框架,一套软件温度解决方案,配合ic内部温度传感器,对ic温度进行管控,保证系统稳定性。
thermal系统多用于对ic内部的重点发热模块的功能管控,如cpu、gpu。
thermal sensor驱动负责读取硬件温度sensor的温度,并传给thermal 子系统,thermal子系统将根据调控对象的温度,决定是否触发对应的冷却措施,如限制CPU最大工作频率,以及CPU打开的核数等,从而实现对系统的冷却。
thermal zone
Thermal zone代表一个温控管理区间,可以将其看做一个虚拟意义上的温度Sensor, 需要有对应的物理Sensor与其关联再能发挥作用。
一个Thermal Zone最多可以关联一个Sensor,但该Sensor可以是多个硬件Sensor的混合。Trip Point
即触发点,由Thermal Zone维护。每个thermal zone可以维护多个trip point。Trip Point包含以下信息:
temp:触发温度,当温度到达触发温度则该trip point被触发。
type:trip point类型,沿袭PC散热方式,分为四种类型—passive、active、hot、critical。
cooling device绑定信息:
记录在thermal_instance结构体中,描述trip point与cooling device的绑定关系,即当trip point触发后由那个cooling device去实施冷却措施。每个trip point必须与一个cooling device绑定,才有实际意义。cooling device
实际对系统实施冷却措施的驱动,温控的执行者。cooling device 维护一个cooling等级,即state,一般state越高即系统的冷却需求越高。cooling device根据不同等级的冷却需求进行冷却行为。
cooling device只根据state进行冷却操作,是实施者,而state的计算由thermal governor完成。
thermal软件框架
要实现一个温度控制的需求,试想一下我们是不是最少要有获取温度的设备和控制温度的设备这两个最基本的东西?当然附带的也会产生一些使用温度控制设备的策略。
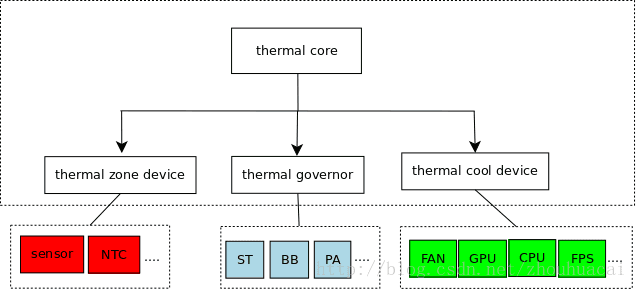
那上面这些东西在 Linux Thermal 框架中怎么体现呢?通过阅读源码我们发现代码中对上面的东西进行了一些抽象。
获取温度的设备:在 Thermal 框架中被抽象为 Thermal Zone Device;
控制温度的设备:在 Thermal 框架中被抽象为 Thermal Cooling Device;
控制温度策略:在 Thermal 框架中被抽象为 Thermal Governor;
thermal zone
dts里的配置如下:
thermal-zones{
cpu_thermal_zone{
polling-delay-passive = <1000>; //超过阀值轮询时间
polling-delay = <2000>; //未超阀值轮询时间
thermal-sensors = <&ths_combine0 0>;
trips{
cpu_trip0:t0{
temperature = <70>;
type = "passive";
hysteresis = <0>;
};
cpu_trip1:t1{
temperature = <90>;
type = "passive";
hysteresis = <0>;
};
cpu_trip2:t2{
temperature = <100>;
type = "passive";
hysteresis = <0>;
};
cpu_trip3:t3{
temperature = <105>;
type = "passive";
hysteresis = <0>;
};
cpu_trip4:t4{
temperature = <110>;
type = "passive";
hysteresis = <0>;
};
crt_trip0:t5{
temperature = <115>;
type = "critical";
hysteresis = <0>;
};
};
cooling-maps{
bind0{
contribution = <0>;
trip = <&cpu_trip0>;
cooling-device = <&cpu_budget_cooling 1 1>;
};
bind1{
contribution = <0>;
trip = <&cpu_trip1>;
cooling-device = <&cpu_budget_cooling 2 2>;
};
bind2{
contribution = <0>;
trip = <&cpu_trip2>;
cooling-device = <&cpu_budget_cooling 3 3>;
};
bind3{
contribution = <0>;
trip = <&cpu_trip3>;
cooling-device = <&cpu_budget_cooling 4 5>;
};
bind4{
contribution = <0>;
trip = <&cpu_trip4>;
cooling-device = <&cpu_budget_cooling 6 6>;
};
};
};内核使用thermal_zone_device 抽象获取温度的device.
struct thermal_zone_device {
int id;
char type[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
struct device device;
struct thermal_attr *trip_temp_attrs;
struct thermal_attr *trip_type_attrs;
struct thermal_attr *trip_hyst_attrs;
void *devdata;
int trips;
int passive_delay;
int polling_delay;
int temperature;
int last_temperature;
int emul_temperature;
int passive;
unsigned int forced_passive;
struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops;
const struct thermal_zone_params *tzp;
struct thermal_governor *governor;
struct list_head thermal_instances;
struct idr idr;
struct mutex lock; /* protect thermal_instances list */
struct list_head node;
struct delayed_work poll_queue;
}
struct thermal_zone_device_ops {
int (*bind) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
struct thermal_cooling_device *);
int (*unbind) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
struct thermal_cooling_device *);
int (*get_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int *);
int (*get_mode) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
enum thermal_device_mode *);
int (*set_mode) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
enum thermal_device_mode);
int (*get_trip_type) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
enum thermal_trip_type *);
int (*get_trip_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
int *);
int (*set_trip_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
int);
int (*get_trip_hyst) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
int *);
int (*set_trip_hyst) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
int);
int (*get_crit_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int *);
int (*set_emul_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int);
int (*get_trend) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
enum thermal_trend *);
int (*notify) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
enum thermal_trip_type);
}thermal governal
降温策略一个抽象,与cpufreq的governal概念类似。
内核已经实现了一些策略,step_wise, user_space, power_allocator, bang_bang 。我们常用step_wise。
/**
* struct thermal_governor - structure that holds thermal governor information
* @name: name of the governor
* @throttle: callback called for every trip point even if temperature is
* below the trip point temperature
* @governor_list: node in thermal_governor_list (in thermal_core.c)
*/
struct thermal_governor {
char name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
/* 策略函数 */
int (*throttle)(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int trip);
struct list_head governor_list;
};thermal cooling device
Thermal Cooling Device 是可以降温设备的抽象,能降温的设备比如风扇,这些好理解,但是想 CPU,GPU 这些 Cooling devices 怎么理解呢?
其实降温可以从两方面来理解,一个是加快散热,另外一个就是降低产热量。风扇,散热片这些是用来加快散热,CPU,GPU 这些 Cooling devices 是通过降低产热来降温。
struct thermal_cooling_device {
int id;
char type[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
struct device device;
struct device_node *np;
void *devdata;
/* cooling device 操作函数 */
const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops;
bool updated; /* true if the cooling device does not need update */
struct mutex lock; /* protect thermal_instances list */
struct list_head thermal_instances;
struct list_head node;
};
struct thermal_cooling_device_ops {
int (*get_max_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long *);
int (*get_cur_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long *);
/* 设定等级 */
int (*set_cur_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long);
};thermal core
Thermal Core作为中枢注册Governor,注册Thermal类,并且基于Device Tree注册Thermal Zone;提供Thermal Zone注册函数、Cooling Device注册函数、提供将Cooling设备绑定到Zone的函数,一个Thermal Zone可以有多个Cooling设备;同时还提供一个核心函数thermal_zone_device_update作为Thermal中断处理函数和轮询函数,轮询时间会根据不同Trip Delay调节。
模块流程图如下:
![]()
