SystemUI之任务管理器
任务管理器让用户能够更加便捷的管理运行的任务,方便切换应用,根据需要实时关闭应用。
1.RecentsActivity.java
路径:frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/recents/
多任务相应是从RecentsActivity类开始,我们来看下onCreate方法,
/** Called with the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
mFinishedOnStartup = false;
// In the case that the activity starts up before the Recents component has initialized
// (usually when debugging/pushing the SysUI apk), just finish this activity.
SystemServicesProxy ssp = Recents.getSystemServices();
if (ssp == null) {
mFinishedOnStartup = true;
finish();
return;
}
// Register this activity with the event bus
EventBus.getDefault().register(this, EVENT_BUS_PRIORITY);
// Initialize the package monitor
mPackageMonitor = new RecentsPackageMonitor();
mPackageMonitor.register(this);
// Set the Recents layout
setContentView(R.layout.recents);
takeKeyEvents(true);
mRecentsView = (RecentsView) findViewById(R.id.recents_view);
mRecentsView.setSystemUiVisibility(View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_STABLE |
View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_FULLSCREEN |
View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_HIDE_NAVIGATION);
mScrimViews = new SystemBarScrimViews(this);
getWindow().getAttributes().privateFlags |=
WindowManager.LayoutParams.PRIVATE_FLAG_FORCE_DECOR_VIEW_VISIBILITY;
Configuration appConfiguration = Utilities.getAppConfiguration(this);
mLastDeviceOrientation = appConfiguration.orientation;
mLastDisplayDensity = appConfiguration.densityDpi;
mFocusTimerDuration = getResources().getInteger(R.integer.recents_auto_advance_duration);
mIterateTrigger = new DozeTrigger(mFocusTimerDuration, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
dismissRecentsToFocusedTask(MetricsEvent.OVERVIEW_SELECT_TIMEOUT);
}
});
// Set the window background
getWindow().setBackgroundDrawable(mRecentsView.getBackgroundScrim());
// Create the home intent runnable
mHomeIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MAIN, null);
mHomeIntent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME);
mHomeIntent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK |
Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_RESET_TASK_IF_NEEDED);
// Register the broadcast receiver to handle messages when the screen is turned off
IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter();
filter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_SCREEN_OFF);
filter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_TIME_CHANGED);
registerReceiver(mSystemBroadcastReceiver, filter);
getWindow().addPrivateFlags(LayoutParams.PRIVATE_FLAG_NO_MOVE_ANIMATION);
// Reload the stack view
reloadStackView();
}/**
* Reloads the stack views upon launching Recents.
*/
private void reloadStackView() {
// If the Recents component has preloaded a load plan, then use that to prevent
// reconstructing the task stack
RecentsTaskLoader loader = Recents.getTaskLoader();
RecentsTaskLoadPlan loadPlan = RecentsImpl.consumeInstanceLoadPlan();
if (loadPlan == null) {
loadPlan = loader.createLoadPlan(this);
}
// Start loading tasks according to the load plan
RecentsConfiguration config = Recents.getConfiguration();
RecentsActivityLaunchState launchState = config.getLaunchState();
if (!loadPlan.hasTasks()) {
loader.preloadTasks(loadPlan, launchState.launchedToTaskId,
!launchState.launchedFromHome);
}
RecentsTaskLoadPlan.Options loadOpts = new RecentsTaskLoadPlan.Options();
loadOpts.runningTaskId = launchState.launchedToTaskId;
loadOpts.numVisibleTasks = launchState.launchedNumVisibleTasks;
loadOpts.numVisibleTaskThumbnails = launchState.launchedNumVisibleThumbnails;
loader.loadTasks(this, loadPlan, loadOpts);
TaskStack stack = loadPlan.getTaskStack();
mRecentsView.onReload(mIsVisible, stack.getTaskCount() == 0);
mRecentsView.updateStack(stack, true /* setStackViewTasks */);
// Update the nav bar scrim, but defer the animation until the enter-window event
boolean animateNavBarScrim = !launchState.launchedViaDockGesture;
mScrimViews.updateNavBarScrim(animateNavBarScrim, stack.getTaskCount() > 0, null);
// If this is a new instance relaunched by AM, without going through the normal mechanisms,
// then we have to manually trigger the enter animation state
boolean wasLaunchedByAm = !launchState.launchedFromHome &&
!launchState.launchedFromApp;
if (wasLaunchedByAm) {
EventBus.getDefault().send(new EnterRecentsWindowAnimationCompletedEvent());
}
// Keep track of whether we launched from the nav bar button or via alt-tab
if (launchState.launchedWithAltTab) {
MetricsLogger.count(this, "overview_trigger_alttab", 1);
} else {
MetricsLogger.count(this, "overview_trigger_nav_btn", 1);
}
// Keep track of whether we launched from an app or from home
if (launchState.launchedFromApp) {
Task launchTarget = stack.getLaunchTarget();
int launchTaskIndexInStack = launchTarget != null
? stack.indexOfStackTask(launchTarget)
: 0;
MetricsLogger.count(this, "overview_source_app", 1);
// If from an app, track the stack index of the app in the stack (for affiliated tasks)
MetricsLogger.histogram(this, "overview_source_app_index", launchTaskIndexInStack);
} else {
MetricsLogger.count(this, "overview_source_home", 1);
}
// Keep track of the total stack task count
int taskCount = mRecentsView.getStack().getTaskCount();
MetricsLogger.histogram(this, "overview_task_count", taskCount);
// After we have resumed, set the visible state until the next onStop() call
mIsVisible = true;
}
/** Preloads recents tasks using the specified plan to store the output. */
public void preloadTasks(RecentsTaskLoadPlan plan, int runningTaskId,
boolean includeFrontMostExcludedTask) {
plan.preloadPlan(this, runningTaskId, includeFrontMostExcludedTask);
}
/**
* Preloads the list of recent tasks from the system. After this call, the TaskStack will
* have a list of all the recent tasks with their metadata, not including icons or
* thumbnails which were not cached and have to be loaded.
*
* The tasks will be ordered by:
* - least-recent to most-recent stack tasks
* - least-recent to most-recent freeform tasks
*/
public synchronized void preloadPlan(RecentsTaskLoader loader, int runningTaskId,
boolean includeFrontMostExcludedTask) {
Resources res = mContext.getResources();
ArrayList allTasks = new ArrayList<>();
if (mRawTasks == null) {
// if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "preloadPlan mRawTasks == null");
preloadRawTasks(includeFrontMostExcludedTask);
}
SparseArray affiliatedTasks = new SparseArray<>();
SparseIntArray affiliatedTaskCounts = new SparseIntArray();
String dismissDescFormat = mContext.getString(
R.string.accessibility_recents_item_will_be_dismissed);
String appInfoDescFormat = mContext.getString(
R.string.accessibility_recents_item_open_app_info);
long lastStackActiveTime = Prefs.getLong(mContext,
Prefs.Key.OVERVIEW_LAST_STACK_TASK_ACTIVE_TIME, 0);
if (RecentsDebugFlags.Static.EnableMockTasks) {
lastStackActiveTime = 0;
}
long newLastStackActiveTime = -1;
int taskCount = mRawTasks.size();
// if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "preloadPlan taskCount = " + taskCount);
for (int i = 0; i < taskCount; i++) {
ActivityManager.RecentTaskInfo t = mRawTasks.get(i);
// Compose the task key
Task.TaskKey taskKey = new Task.TaskKey(t.persistentId, t.stackId, t.baseIntent,
t.userId, t.firstActiveTime, t.lastActiveTime);
// This task is only shown in the stack if it statisfies the historical time or min
// number of tasks constraints. Freeform tasks are also always shown.
boolean isFreeformTask = SystemServicesProxy.isFreeformStack(t.stackId);
boolean isStackTask = isFreeformTask || !isHistoricalTask(t) ||
(t.lastActiveTime >= lastStackActiveTime && i >= (taskCount - MIN_NUM_TASKS));
boolean isLaunchTarget = taskKey.id == runningTaskId;
// The last stack active time is the baseline for which we show visible tasks. Since
// the system will store all the tasks, we don't want to show the tasks prior to the
// last visible ones, otherwise, as you dismiss them, the previous tasks may satisfy
// the other stack-task constraints.
if (isStackTask && newLastStackActiveTime < 0) {
newLastStackActiveTime = t.lastActiveTime;
}
// Load the title, icon, and color
ActivityInfo info = loader.getAndUpdateActivityInfo(taskKey);
String title = loader.getAndUpdateActivityTitle(taskKey, t.taskDescription);
String titleDescription = loader.getAndUpdateContentDescription(taskKey, res);
String dismissDescription = String.format(dismissDescFormat, titleDescription);
String appInfoDescription = String.format(appInfoDescFormat, titleDescription);
Drawable icon = isStackTask
? loader.getAndUpdateActivityIcon(taskKey, t.taskDescription, res, false)
: null;
Bitmap thumbnail = loader.getAndUpdateThumbnail(taskKey, false /* loadIfNotCached */);
int activityColor = loader.getActivityPrimaryColor(t.taskDescription);
int backgroundColor = loader.getActivityBackgroundColor(t.taskDescription);
boolean isSystemApp = (info != null) &&
((info.applicationInfo.flags & ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM) != 0);
// Add the task to the stack
Task task = new Task(taskKey, t.affiliatedTaskId, t.affiliatedTaskColor, icon,
thumbnail, title, titleDescription, dismissDescription, appInfoDescription,
activityColor, backgroundColor, isLaunchTarget, isStackTask, isSystemApp,
t.isDockable, t.bounds, t.taskDescription, t.resizeMode, t.topActivity);
allTasks.add(task);
affiliatedTaskCounts.put(taskKey.id, affiliatedTaskCounts.get(taskKey.id, 0) + 1);
affiliatedTasks.put(taskKey.id, taskKey);
}
if (newLastStackActiveTime != -1) {
Prefs.putLong(mContext, Prefs.Key.OVERVIEW_LAST_STACK_TASK_ACTIVE_TIME,
newLastStackActiveTime);
}
// Initialize the stacks
mStack = new TaskStack();
mStack.setTasks(mContext, allTasks, false /* notifyStackChanges */);
} /**
* An optimization to preload the raw list of tasks. The raw tasks are saved in least-recent
* to most-recent order.
*/
public synchronized void preloadRawTasks(boolean includeFrontMostExcludedTask) {
int currentUserId = UserHandle.USER_CURRENT;
updateCurrentQuietProfilesCache(currentUserId);
SystemServicesProxy ssp = Recents.getSystemServices();
mRawTasks = ssp.getRecentTasks(ActivityManager.getMaxRecentTasksStatic(),
currentUserId, includeFrontMostExcludedTask, mCurrentQuietProfiles);
// Since the raw tasks are given in most-recent to least-recent order, we need to reverse it
Collections.reverse(mRawTasks);
}这里使用SystemServicesProxy来获取task。
路径:frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/recents/misc/SystemServicesProxy.java
/**
* Returns a list of the recents tasks.
*
* @param includeFrontMostExcludedTask if set, will ensure that the front most excluded task
* will be visible, otherwise no excluded tasks will be
* visible.
*/
public List getRecentTasks(int numLatestTasks, int userId,
boolean includeFrontMostExcludedTask, ArraySet quietProfileIds) {
if (mAm == null) return null;
// If we are mocking, then create some recent tasks
if (RecentsDebugFlags.Static.EnableMockTasks) {
ArrayList tasks =
new ArrayList();
int count = Math.min(numLatestTasks, RecentsDebugFlags.Static.MockTaskCount);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
// Create a dummy component name
int packageIndex = i % RecentsDebugFlags.Static.MockTasksPackageCount;
ComponentName cn = new ComponentName("com.android.test" + packageIndex,
"com.android.test" + i + ".Activity");
String description = "" + i + " - " +
Long.toString(Math.abs(new Random().nextLong()), 36);
// Create the recent task info
ActivityManager.RecentTaskInfo rti = new ActivityManager.RecentTaskInfo();
rti.id = rti.persistentId = rti.affiliatedTaskId = i;
rti.baseIntent = new Intent();
rti.baseIntent.setComponent(cn);
rti.description = description;
rti.firstActiveTime = rti.lastActiveTime = i;
if (i % 2 == 0) {
rti.taskDescription = new ActivityManager.TaskDescription(description,
Bitmap.createBitmap(mDummyIcon), null,
0xFF000000 | (0xFFFFFF & new Random().nextInt()),
0xFF000000 | (0xFFFFFF & new Random().nextInt()));
} else {
rti.taskDescription = new ActivityManager.TaskDescription();
}
tasks.add(rti);
}
return tasks;
}
// Remove home/recents/excluded tasks
int minNumTasksToQuery = 10;
int numTasksToQuery = Math.max(minNumTasksToQuery, numLatestTasks);
int flags = ActivityManager.RECENT_IGNORE_HOME_STACK_TASKS |
ActivityManager.RECENT_INGORE_DOCKED_STACK_TOP_TASK |
ActivityManager.RECENT_INGORE_PINNED_STACK_TASKS |
ActivityManager.RECENT_IGNORE_UNAVAILABLE |
ActivityManager.RECENT_INCLUDE_PROFILES;
if (includeFrontMostExcludedTask) {
flags |= ActivityManager.RECENT_WITH_EXCLUDED;
}
List tasks = null;
try {
tasks = mAm.getRecentTasksForUser(numTasksToQuery, flags, userId);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to get recent tasks", e);
}
// Break early if we can't get a valid set of tasks
if (tasks == null) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
boolean isFirstValidTask = true;
Iterator iter = tasks.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
ActivityManager.RecentTaskInfo t = iter.next();
// NOTE: The order of these checks happens in the expected order of the traversal of the
// tasks
// Remove the task if it or it's package are blacklsited
if (sRecentsBlacklist.contains(t.realActivity.getClassName()) ||
sRecentsBlacklist.contains(t.realActivity.getPackageName())) {
iter.remove();
continue;
}
// Remove the task if it is marked as excluded, unless it is the first most task and we
// are requested to include it
boolean isExcluded = (t.baseIntent.getFlags() & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_EXCLUDE_FROM_RECENTS)
== Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_EXCLUDE_FROM_RECENTS;
isExcluded |= quietProfileIds.contains(t.userId);
// M: Add Debug Log
Task.TaskKey taskKey = new Task.TaskKey(t.persistentId, t.stackId, t.baseIntent,
t.userId, t.firstActiveTime, t.lastActiveTime);
Log.d(TAG, "getRecentTasks:TASK = " + taskKey.toString()
+ "/isExcluded = " + isExcluded
+ "/includeFrontMostExcludedTask = " + includeFrontMostExcludedTask
+ "/isFirstValidTask = " + isFirstValidTask
+ "/t.id = " + t.id);
if (isExcluded && (!isFirstValidTask || !includeFrontMostExcludedTask)) {
iter.remove();
}
isFirstValidTask = false;
}
return tasks.subList(0, Math.min(tasks.size(), numLatestTasks));
} 2.布局显示
recent列表画面:
recents.xml
recents_task_view_header.xml 是 app icon和title部分,对应TaskViewHeader.java
recents_task_view_header_overlay.xml
recents_empty.xml 没有recent app
RecentsView是recent的重要部分,显示最近app列表的,其中成员变量
private TaskStackView mTaskStackView;记录了全部的TaskViews,TaskView就是每个RecentApp
TaskView Override了onLongClick方法,作为拖动的入口
TaskView <---->Task
Task记录了对应的app intent等重要信息
onLongClick中有如下两句是处理事件的开始
EventBus.getDefault().register(this, RecentsActivity.EVENT_BUS_PRIORITY + 1);
EventBus.getDefault().send(new DragStartEvent(mTask, this, mDownTouchPos));
*****************
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
EventBus.Event
所有继承Event的类 extends EventBus.Event
src/com/android/systemui/recents/events/activity/* ------>画面迁移相关事件
src/com/android/systemui/recents/events/ui/dragndrop/* ------>拖拽相关事件
src/com/android/systemui/recents/events/ui/focus/* ------>focus变更相关事件
src/com/android/systemui/recents/events/ui/* ------>其他UI相关事件
onBusEvent
所有事件回调都是这个,只是事件类型不同
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
启动后Recent的隐藏
PhoneStatusBar中调用了disable
12-19 20:17:06.041 1624-1624/com.android.systemui D/PhoneStatusBar: disable: < EXPAND* icons alerts system_info BACK* HOME* RECENT* clock SEARCH* quick_settings >
RECENT*表示需要隐藏recent app画面
if ((state1 & StatusBarManager.DISABLE_RECENT) != 0) {
// close recents if it's visible
mHandler.removeMessages(MSG_HIDE_RECENT_APPS);
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MSG_HIDE_RECENT_APPS);
}
接着调用BaseStatusBar中的
MSG_HIDE_RECENT_APPS
处理隐藏recents app的机能
case MSG_HIDE_RECENT_APPS:
hideRecents(m.arg1 > 0, m.arg2 > 0);
break;
调用Recents中的hideRecents
调用RecentsImpl中的hideRecents
EventBus.getDefault().post(new HideRecentsEvent(triggeredFromAltTab,
triggeredFromHomeKey));
通过EventBus发送了一个HideRecentsEvent
RecentsActivity的public final void onBusEvent(HideRecentsEvent event)
接收到EventBus的事件并进行处理
public final void onBusEvent(HideRecentsEvent event) {
if (event.triggeredFromAltTab) {
// If we are hiding from releasing Alt-Tab, dismiss Recents to the focused app
if (!mIgnoreAltTabRelease) {
dismissRecentsToFocusedTaskOrHome();
}
} else if (event.triggeredFromHomeKey) {
dismissRecentsToHome(true /* animateTaskViews */);
// Cancel any pending dozes
EventBus.getDefault().send(mUserInteractionEvent);
} else {
// Do nothing
}
}
我们还是从recentActivity.java的onCreate()方法出发,
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
...
// Set the Recents layout
setContentView(R.layout.recents);
takeKeyEvents(true);
mRecentsView = (RecentsView) findViewById(R.id.recents_view);
mRecentsView.setSystemUiVisibility(View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_STABLE |
View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_FULLSCREEN |
View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_HIDE_NAVIGATION);
mScrimViews = new SystemBarScrimViews(this);
getWindow().getAttributes().privateFlags |=
WindowManager.LayoutParams.PRIVATE_FLAG_FORCE_DECOR_VIEW_VISIBILITY;
...
// Reload the stack view
reloadStackView();
}在之里加载了布局文件R.id.recents_view,我们来看下具体内容
可以看到由三个部分组成,recent view、Incompatible task overlayy以及Nav Bar Scrim View,
我们进到reloadStackView()方法看下,
private void reloadStackView() {
...
loader.loadTasks(this, loadPlan, loadOpts);
TaskStack stack = loadPlan.getTaskStack();
mRecentsView.onReload(mIsVisible, stack.getTaskCount() == 0);
mRecentsView.updateStack(stack, true /* setStackViewTasks */);
...
}
路径:frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/recents/views/RecentsView.java
/**
* Called from RecentsActivity when it is relaunched.
*/
public void onReload(boolean isResumingFromVisible, boolean isTaskStackEmpty) {
RecentsConfiguration config = Recents.getConfiguration();
RecentsActivityLaunchState launchState = config.getLaunchState();
if (mTaskStackView == null) {
isResumingFromVisible = false;
mTaskStackView = new TaskStackView(getContext());
mTaskStackView.setSystemInsets(mSystemInsets);
addView(mTaskStackView);
}
// Reset the state
mAwaitingFirstLayout = !isResumingFromVisible;
mLastTaskLaunchedWasFreeform = false;
// Update the stack
mTaskStackView.onReload(isResumingFromVisible);
if (isResumingFromVisible) {
// If we are already visible, then restore the background scrim
animateBackgroundScrim(1f, DEFAULT_UPDATE_SCRIM_DURATION);
} else {
// If we are already occluded by the app, then set the final background scrim alpha now.
// Otherwise, defer until the enter animation completes to animate the scrim alpha with
// the tasks for the home animation.
if (launchState.launchedViaDockGesture || launchState.launchedFromApp
|| isTaskStackEmpty) {
mBackgroundScrim.setAlpha(255);
} else {
mBackgroundScrim.setAlpha(0);
}
}
}路径:rameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/recents/views/TaskStackView.java
/**
* Called from RecentsActivity when it is relaunched.
*/
void onReload(boolean isResumingFromVisible) {
if (!isResumingFromVisible) {
// Reset the focused task
resetFocusedTask(getFocusedTask());
}
// Reset the state of each of the task views
List taskViews = new ArrayList<>();
taskViews.addAll(getTaskViews());
taskViews.addAll(mViewPool.getViews());
for (int i = taskViews.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
taskViews.get(i).onReload(isResumingFromVisible);
}
// Reset the stack state
readSystemFlags();
mTaskViewsClipDirty = true;
mEnterAnimationComplete = false;
mUIDozeTrigger.stopDozing();
if (isResumingFromVisible) {
// Animate in the freeform workspace
int ffBgAlpha = mLayoutAlgorithm.getStackState().freeformBackgroundAlpha;
animateFreeformWorkspaceBackgroundAlpha(ffBgAlpha, new AnimationProps(150,
Interpolators.FAST_OUT_SLOW_IN));
} else {
mStackScroller.reset();
mStableLayoutAlgorithm.reset();
mLayoutAlgorithm.reset();
}
// Since we always animate to the same place in (the initial state), always reset the stack
// to the initial state when resuming
mAwaitingFirstLayout = true;
mInitialState = INITIAL_STATE_UPDATE_ALL;
requestLayout();
}
遍历数组taskViews,重置每个task view的状态,我们进到taskViews的onReload()方法看下:
路径:frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/recents/views/TaskView.java
/**
* Called from RecentsActivity when it is relaunched.
*/
void onReload(boolean isResumingFromVisible) {
resetNoUserInteractionState();
if (!isResumingFromVisible) {
resetViewProperties();
}
} /** Resets the state tracking that the user has not interacted with the stack after a certain time. */
void resetNoUserInteractionState() {
mHeaderView.resetNoUserInteractionState();
}/**
* Resets the state tracking that the user has not interacted with the stack after a certain
* time.
*/
void resetNoUserInteractionState() {
mDismissButton.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
mDismissButton.setAlpha(0f);
mDismissButton.setClickable(false);
if (mMoveTaskButton != null) {
mMoveTaskButton.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
mMoveTaskButton.setAlpha(0f);
mMoveTaskButton.setClickable(false);
}
}当用户没有对任务栈进行操作的时候,系统会重置栈的状态。
3.EventBus的使用
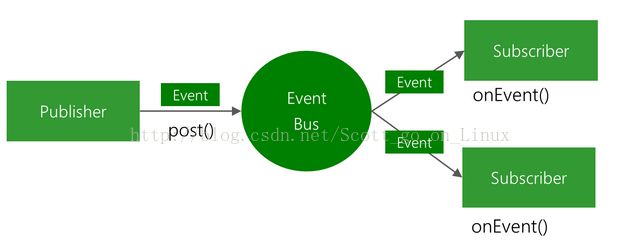
EventBus是一款针对Android优化的发布/订阅事件总线。主要功能是替代Intent,Handler,BroadCast在Fragment,Activity,Service,线程之间传递消息.优点是开销小,代码更优雅,以及将发送者和接收者解耦。
EventBus框架中涉及四个成分
订阅者,发布者,订阅事件,事件总线
它们的关系可以用官方的图表示:
使用方法,官方给出的介绍如下:
(1)Define events://定义事件
public class MessageEvent { /* Additional fields if needed */ }
(2)Prepare subscribers//注册订阅者
Register your subscriber (in your onCreate or in a constructor):
eventBus.register(this);
(3)Declare your subscribing method://订阅事件的动作
@Subscribe
public void onEvent(AnyEventType event) {/* Do something */};
(4)Post events://发布者发送事件
eventBus.post(event);注册保存方法
调用的时候post一个event
遍历方法,调用相应方法
路径:
frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/recents/events/EventBus.java
frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/recents/RecentsActivity.java
在使用EventBus之前,首先需要注册它。查看RecentsActivity.java的onCreate()方法,
/** Called with the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
...
// Register this activity with the event bus
EventBus.getDefault().register(this, EVENT_BUS_PRIORITY);
// Initialize the package monitor
mPackageMonitor = new RecentsPackageMonitor();
mPackageMonitor.register(this);
....
}EventBus.getDefault().register(this, EVENT_BUS_PRIORITY);此处对EventBus进行了注册。
并且在RecentsActivity.java中定义了处理方法,
/**** EventBus events ****/
public final void onBusEvent(ToggleRecentsEvent event) {
RecentsActivityLaunchState launchState = Recents.getConfiguration().getLaunchState();
if (launchState.launchedFromHome) {
dismissRecentsToHome(true /* animateTaskViews */);
} else {
dismissRecentsToLaunchTargetTaskOrHome();
}
}
public final void onBusEvent(IterateRecentsEvent event) {
final RecentsDebugFlags debugFlags = Recents.getDebugFlags();
// Start dozing after the recents button is clicked
int timerIndicatorDuration = 0;
if (debugFlags.isFastToggleRecentsEnabled()) {
timerIndicatorDuration = getResources().getInteger(
R.integer.recents_subsequent_auto_advance_duration);
mIterateTrigger.setDozeDuration(timerIndicatorDuration);
if (!mIterateTrigger.isDozing()) {
mIterateTrigger.startDozing();
} else {
mIterateTrigger.poke();
}
}
// Focus the next task
EventBus.getDefault().send(new FocusNextTaskViewEvent(timerIndicatorDuration));
MetricsLogger.action(this, MetricsEvent.ACTION_OVERVIEW_PAGE);
}
这些event Method必须是public final,必须return void,必须命名为onBusEvent,必须只有一个参数。
Event Bus已经注册好了,并且event method也已经申明了。现在需要找到调用的地方,这里通过反射来实现,我们先找到负责发出event的publisher,
路径:
frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/recents/views/TaskView.java
frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/recents/views/TaskStackView.java
在TaskView.java里面,调用了dismissTask方法,回调EventBus发出TaskViewDismissedEvent,
/** Dismisses this task. */
void dismissTask() {
// Animate out the view and call the callback
final TaskView tv = this;
DismissTaskViewEvent dismissEvent = new DismissTaskViewEvent(tv);
dismissEvent.addPostAnimationCallback(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
EventBus.getDefault().send(new TaskViewDismissedEvent(mTask, tv,
new AnimationProps(TaskStackView.DEFAULT_SYNC_STACK_DURATION,
Interpolators.FAST_OUT_SLOW_IN)));
}
});
EventBus.getDefault().send(dismissEvent);
}public final void onBusEvent(TaskViewDismissedEvent event) {
// Announce for accessibility
announceForAccessibility(getContext().getString(
R.string.accessibility_recents_item_dismissed, event.task.title));
// Remove the task from the stack
mStack.removeTask(event.task, event.animation, false /* fromDockGesture */);
EventBus.getDefault().send(new DeleteTaskDataEvent(event.task));
MetricsLogger.action(getContext(), MetricsEvent.OVERVIEW_DISMISS,
event.task.key.getComponent().toString());
}
发送DeleteTaskDataEvent事件,在RecentsActivity.java响应该event事件
路径:frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/recents/RecentsActivity.java
public final void onBusEvent(DeleteTaskDataEvent event) {
// Remove any stored data from the loader
RecentsTaskLoader loader = Recents.getTaskLoader();
loader.deleteTaskData(event.task, false);
// Remove the task from activity manager
SystemServicesProxy ssp = Recents.getSystemServices();
ssp.removeTask(event.task.key.id);
}
这里我们来看下eventBus是怎么找到对应的方法的。
http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/40920453
当subscriber在注册的时候,EventBus.getDefault().register(this, EVENT_BUS_PRIORITY);,这里的register方法会把onBusEvent存储起来。
/**
* Registers a subscriber to receive events with the given priority.
*
* @param subscriber the subscriber to handle events. If this is the first instance of the
* subscriber's class type that has been registered, the class's methods will
* be scanned for appropriate event handler methods.
* @param priority the priority that this subscriber will receive events relative to other
* subscribers
*/
public void register(Object subscriber, int priority) {
registerSubscriber(subscriber, priority, null);
}/**
* Registers a new subscriber.
*/
private void registerSubscriber(Object subscriber, int priority,
MutableBoolean hasInterprocessEventsChangedOut) {
// Fail immediately if we are being called from the non-main thread
long callingThreadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
if (callingThreadId != mHandler.getLooper().getThread().getId()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can not register() a subscriber from a non-main thread.");
}
// Return immediately if this exact subscriber is already registered
if (findRegisteredSubscriber(subscriber, false /* removeFoundSubscriber */)) {
return;
}
long t1 = 0;
if (DEBUG_TRACE_ALL) {
t1 = SystemClock.currentTimeMicro();
logWithPid("registerSubscriber(" + subscriber.getClass().getSimpleName() + ")");
}
Subscriber sub = new Subscriber(subscriber, SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
Class subscriberType = subscriber.getClass();
ArrayList subscriberMethods = mSubscriberTypeMap.get(subscriberType);
if (subscriberMethods != null) {
if (DEBUG_TRACE_ALL) {
logWithPid("Subscriber class type already registered");
}
// If we've parsed this subscriber type before, just add to the set for all the known
// events
for (EventHandlerMethod method : subscriberMethods) {
ArrayList eventTypeHandlers = mEventTypeMap.get(method.eventType);
eventTypeHandlers.add(new EventHandler(sub, method, priority));
sortEventHandlersByPriority(eventTypeHandlers);
}
mSubscribers.add(sub);
return;
} else {
if (DEBUG_TRACE_ALL) {
logWithPid("Subscriber class type requires registration");
}
// If we are parsing this type from scratch, ensure we add it to the subscriber type
// map, and pull out he handler methods below
subscriberMethods = new ArrayList<>();
mSubscriberTypeMap.put(subscriberType, subscriberMethods);
mSubscribers.add(sub);
}
// Find all the valid event bus handler methods of the subscriber
MutableBoolean isInterprocessEvent = new MutableBoolean(false);
Method[] methods = subscriberType.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method m : methods) {
Class[] parameterTypes = m.getParameterTypes();
isInterprocessEvent.value = false;
if (isValidEventBusHandlerMethod(m, parameterTypes, isInterprocessEvent)) {
Class eventType = (Class) parameterTypes[0];
ArrayList eventTypeHandlers = mEventTypeMap.get(eventType);
if (eventTypeHandlers == null) {
eventTypeHandlers = new ArrayList<>();
mEventTypeMap.put(eventType, eventTypeHandlers);
}
if (isInterprocessEvent.value) {
try {
// Enforce that the event must have a Bundle constructor
eventType.getConstructor(Bundle.class);
mInterprocessEventNameMap.put(eventType.getName(),
(Class) eventType);
if (hasInterprocessEventsChangedOut != null) {
hasInterprocessEventsChangedOut.value = true;
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Expected InterprocessEvent to have a Bundle constructor");
}
}
EventHandlerMethod method = new EventHandlerMethod(m, eventType);
EventHandler handler = new EventHandler(sub, method, priority);
eventTypeHandlers.add(handler);
subscriberMethods.add(method);
sortEventHandlersByPriority(eventTypeHandlers);
if (DEBUG_TRACE_ALL) {
logWithPid(" * Method: " + m.getName() +
" event: " + parameterTypes[0].getSimpleName() +
" interprocess? " + isInterprocessEvent.value);
}
}
}
if (DEBUG_TRACE_ALL) {
logWithPid("Registered " + subscriber.getClass().getSimpleName() + " in " +
(SystemClock.currentTimeMicro() - t1) + " microseconds");
}
} 我们看到,先获得subscriberType 的类型和它的所有方法subscriberMethods ,然后加到mSubscribers.add(sub);里。
接着就是遍历获取处理event事件的方法。获取方法的参数类型m.getParameterTypes();,然后通过isValidEventBusHandlerMethod()方法判断该方法是否有效。
/**
* @return whether {@param method} is a valid (normal or interprocess) event bus handler method
*/
private boolean isValidEventBusHandlerMethod(Method method, Class[] parameterTypes,
MutableBoolean isInterprocessEventOut) {
int modifiers = method.getModifiers();
if (Modifier.isPublic(modifiers) &&
Modifier.isFinal(modifiers) &&
method.getReturnType().equals(Void.TYPE) &&
parameterTypes.length == 1) {
if (EventBus.InterprocessEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(parameterTypes[0]) &&
method.getName().startsWith(INTERPROCESS_METHOD_PREFIX)) {
isInterprocessEventOut.value = true;
return true;
} else if (EventBus.Event.class.isAssignableFrom(parameterTypes[0]) &&
method.getName().startsWith(METHOD_PREFIX)) {
isInterprocessEventOut.value = false;
return true;
} else {
if (DEBUG_TRACE_ALL) {
if (!EventBus.Event.class.isAssignableFrom(parameterTypes[0])) {
logWithPid(" Expected method take an Event-based parameter: " + method.getName());
} else if (!method.getName().startsWith(INTERPROCESS_METHOD_PREFIX) &&
!method.getName().startsWith(METHOD_PREFIX)) {
logWithPid(" Expected method start with method prefix: " + method.getName());
}
}
}
} else {
if (DEBUG_TRACE_ALL) {
if (!Modifier.isPublic(modifiers)) {
logWithPid(" Expected method to be public: " + method.getName());
} else if (!Modifier.isFinal(modifiers)) {
logWithPid(" Expected method to be final: " + method.getName());
} else if (!method.getReturnType().equals(Void.TYPE)) {
logWithPid(" Expected method to return null: " + method.getName());
}
}
}
return false;
}
判断该方法是否为isPublic,isFinal,Void.TYPE,parameterTypes.length == 1。并且判断EventBus.InterprocessEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(parameterTypes[0]) &&
method.getName().startsWith(INTERPROCESS_METHOD_PREFIX 。
获取处理event事件的方法后,把方法放入mEventTypeMap中。创建对应的EventHandler,添加到eventTypeHandlers,并把方法添加到subscriberMethods中,把方法根据priority的值来排序,对应方法sortEventHandlersByPriority()。然后我们来看看发送端。以TaskStackView.java里的EventBus.getDefault().send(new DeleteTaskDataEvent(tasks.get(i)));为例,发出事件DeleteTaskDataEvent,我们去EventBus里面看下send()方法。
/**
* Sends an event to the subscribers of the given event type immediately. This can only be
* called from the same thread as the EventBus's looper thread (for the default EventBus, this
* is the main application thread).
*/
public void send(Event event) {
// Fail immediately if we are being called from the non-main thread
long callingThreadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
if (callingThreadId != mHandler.getLooper().getThread().getId()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can not send() a message from a non-main thread.");
}
if (DEBUG_TRACE_ALL) {
logWithPid("send(" + event.getClass().getSimpleName() + ")");
}
// Reset the event's cancelled state
event.requiresPost = false;
event.cancelled = false;
queueEvent(event);
}这里进到queueEvent()方法看下,
/**
* Adds a new message.
*/
private void queueEvent(final Event event) {
ArrayList eventHandlers = mEventTypeMap.get(event.getClass());
if (eventHandlers == null) {
return;
}
// Prepare this event
boolean hasPostedEvent = false;
event.onPreDispatch();
// We need to clone the list in case a subscriber unregisters itself during traversal
// TODO: Investigate whether we can skip the object creation here
eventHandlers = (ArrayList) eventHandlers.clone();
int eventHandlerCount = eventHandlers.size();
for (int i = 0; i < eventHandlerCount; i++) {
final EventHandler eventHandler = eventHandlers.get(i);
if (eventHandler.subscriber.getReference() != null) {
if (event.requiresPost) {
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
processEvent(eventHandler, event);
}
});
hasPostedEvent = true;
} else {
processEvent(eventHandler, event);
}
}
}
// Clean up after this event, deferring until all subscribers have been called
if (hasPostedEvent) {
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
event.onPostDispatch();
}
});
} else {
event.onPostDispatch();
}
}