CaLayer是CoreAnimation执行所有操作的核心,layer管理可视内容,并提供修改该内容的样式和外观等选项。ios应用程序自动启动了layer支持。
这里我们也需要了解如何配置和操作应用程序的layer以获取所需要的效果。
改变View关联的Layer
默认情况下,view会自动创建Calayer类的实例,在大多数情况下,我们不要要改变layer。但是,coreAnimation提供了不同的layer,每个layer都有自己的专有功能。选择不同的layer可能会使我们可以用更简单的方式提高性能或者支持特定类型的内容。例如CATiledLayer类已经经过优化,可以更高效 的显示大图像。
改变UIView的layer
+ (Class) layerClass {
return [CAMetalLayer class];
}
我们可以通过覆盖UIView的layerClass方式改变UIView的layer。大多数情况下,UIview 是创建CALayer对象用于对储存器内容。在大多数情况,我们不需要改变他,但是当我们发现一个不同的CALayer能更好的提高性能,我们就可以替换他。
例如:
- 当我们的绘制内容用metal或者openGL ES。我们最好选用CAMetalLayer或者CAEAGLLayer对象。
- 专有的layer 有更好的执行效率
- 我们希望利用一些专门的core Aimation layer类,例如粒子反射器
core Animation中 Layer的功能
CAEmitterLayer 用于实现基于CoreAnimation的粒子发射系统。改layer控制粒子对象的生成以及来源。
CAGradientLayer 用于绘制填充图层形状的颜色渐变。
CAMetalLayer 用metal渲染图层内容。CAEAGLLayer/CAOpenGLLayer 使用openGL ES(ios) 或者OPenGL (OS x)绘制图层内容
CAReplicatorLayer 当想要自动复制一个或者多个sublayers使用该layer。复制器为我们制作副本,并使用我们指定的属性来更改副本的外观或者属性。
CAScrollLayer 可滚动layer
CAShapeLayer 用于绘制三阶贝塞尔曲线。该layer有利于绘制基于路径的形状。
CATextLayer 渲染富文本
CATiledLayer 管理大图,可以将其划分为较小的图库并单独渲染,并支持放大或者缩小内容
CATransformLayer 渲染3D layer而不是2d
QCCompositionLayer 用于Quartz Composer 合成。(os x)平台
提供layer Contents
layer 管理应用提供的内容数据对象。一个layer包含需要显示的可视bitmap图组成。
我们可以通过三种方式给layer 提供bitmap图
- 将图像直接分配给图层对象的contents属性。(改技术适用于从不改变或者改变很少的layer contents)
+将delegate分配给layer,让delegate绘制图层的内容(此技术用于可能定期更改并且有外部对象挺高的layer contents) - 定义layer 的子类,让子类覆盖器绘制方法之一让自己提供layer 的contents(如果必须创建自定义layer或者需要改变图层的基本绘制行为,该技术更合适)
方式一 -用image设置layer的contents
因为layer只是一个容器,用来管理bitmap图。你可以直接设置给layer的contents 赋值。将image分配到layer上很简单,你可以指定要在屏幕上需要显示的确切图像。layer直接使用我们提供的image,不会尝试创建image副本。如果您的应用再多个位置使用相同的图像,此行为可以节省内存。
给layer 指定的image必须是CGImageRef类型的。当我们指定image,需要提供分辨率与本机设备分辨率匹配的图像,这里可能需要你调整image的contentsScale.属性。
UIImage * image =[UIImage imageNamed:@"guaguale.jpg"];
self.layer.contents =(__bridge id _Nullable)(image.CGImage);
方式二-用delegate 提供layer内容
如果layer的内容经常动态变换,我们可以给layer提供一个delegate对象来提供需要的内容。每次展示,layer都会calldelegate 让其提供内容。
- 如果delegate实现方法displayLayer:,那么我们可以在该实现中创建bitmap图并且赋值给layer的contents。
- 如果delegate实现方法drawLayer:inContext: 方法,coreAnimation将创建bitmap,创建一个图文上下文(graphics context)用来绘制bitmap。然后调用delegate方法来填充bitmap。delegate用图形上下文绘制的内容都将填充到bitmap图中
delegate对象必须实现 displayLayer: or drawLayer:inContext: 两者中的一个。如果delegate实现了这两个方法,layer只调用displayLayer:方法
当app需要加载或者创建需要展示的bitmaps的时候,覆盖displayLayer:是最好的方式。
- (instancetype)initWithFrame:(CGRect)frame{
if (self = [super initWithFrame:frame]) {
self.layer.delegate = self;
[self.layer display];
}
return self;
}
- (void)displayLayer:(CALayer *)layer{
UIImage * image =[UIImage imageNamed:@"guaguale.jpg"];
layer.contents =(__bridge id _Nullable)(image.CGImage);
}
- (instancetype)initWithFrame:(CGRect)frame{
if (self = [super initWithFrame:frame]) {
self.layer.delegate = self;
[self.layer display];
}
return self;
}
//- (void)displayLayer:(CALayer *)layer{
//
//
//}
如果我们不选择提供bitmap图而是选择图形绘制 的方式我们可以用下列方式。
- (void)drawLayer:(CALayer *)layer inContext:(CGContextRef)ctx{
CGMutablePathRef path = CGPathCreateMutable();
CGPathAddArc(path, NULL, 100, 100, 100, 0, M_PI*2, 0);
CGContextSetRGBFillColor(ctx, 1, 0, 0, 1);
CGContextAddPath(ctx, path);
CGContextDrawPath(ctx, 0);
}
对于自定义内容的view,我们应该覆盖view的方法drawRect:方法,而不要设置代理,带有layer的view会自动帮助layer设置代理为view。像上面的例子,我们更改了流程,那么view的drawRect:方法就不会执行了。
方式三-通过自定义子类展示layer content
如果我们采用子类来展示layerContent,则可以覆盖子类的绘制方法来展示layercontent.layer 自身生成自定义的内容是不常见的,但是layer还是可以管理自定义的内容的显示的。例如:CATileLayer 类通过将大图像分成单独管理和呈现小图快来管理大图像。因为只有layer 具有关于tiled在何时渲染那些图块 的信息,所以,layer可以直接管理绘制行为。
覆盖子类有下面两种方式
- 覆盖 display 方法,通过设置contents属性来直接设置layer contetns
- 覆盖 drawInContext:方法 ,用context绘制文本
这里需要强调下,用contents 是直接用我们提供的bitmaps
而drawInContext: 需要系统为我们听过bitmaps图,我们在bitmaps上进行绘图操作。
覆盖那种方法取决于我们在绘制过程中需要多少控制。display 方法是更新layer的contents 内容的主要入口,覆盖改方法可以我们完全控制该过程。覆盖display 方法也意味着我们需要负责创建bitmap 图给contents。如果我们仅仅是想进行绘制操作,覆盖drawInContext:方法,让layer 在backing Strore 为我们创建好bitmap图。
layer- 调整内容
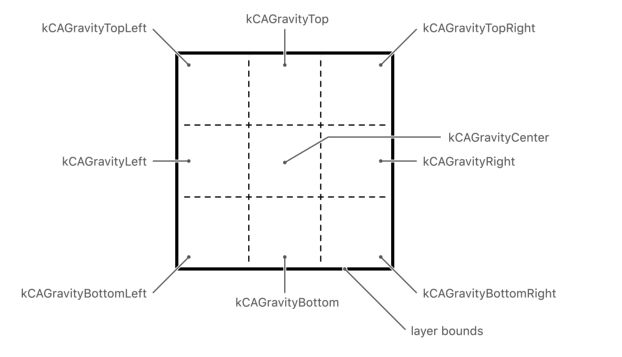
当我们给layer的contents 赋值一个image的时候,layer 的contentsGrayity 属性确定如何处理该image的边界。默认情况下,如果image大于或者小于当前边界,layer对象会对image进行缩放处理。如果layer边界的纵横比与image的不同,则可能导致图像失真。我们可以通过contentsGravity属性来确保图像的显示内容。
我们可以将contnetsGravity 属性的值分为两类:
- 基于位置权重(position-based gravity),固定image到特定的变或者角,不缩放图像
- 基于缩放权重(scaling-based gravity),对image进行拉伸或者缩放操作
基于位置权重(position-based gravity)
基于缩放权重(scaling-based gravity)
layer 的contentsGravity 默认值是KCAGravityResize 。
因为contentsGravity 是NSString*类型,因此,我们只能进行变更位置权重或者变更缩放权重,而不能同时选择这两种权重
layer-高分辨率图片
layer对屏幕的分辨率不是很了解。layer只是存储指向bitmap的指针,并以给定的像素以最佳的方式显示。如果将image制定给layer的contents,我们必须通关layer的contents属性设置适当的值告知CoreAnimation image的分辨率。改属性默认是1.0,适用于在标准的分辨率屏幕上显示。如果图像用与Retina 显示,我们应该将值设置为2.0;(意思是我们在ios中使用view是不需要关心改属性,单独使用layer可能需要关心下)
这里需要说明下,只有在直接给layer指定bitmaps的时候,我们才需要更改contensScale属性的值,UIKit 中的lview 会根据屏幕分辨率和view管理的内容自动将图层的比例因此设置成适当的值。
layer- 可视样式和显示
layer 对象内置了视觉样式,例如边框和背景颜色,这些可以补充layer的contents。由于这些样式不要进行任何渲染,因此在某些情况下降layer用作独立对象。我们需要做的就是在layer上设置属性,layer会处理必要的绘制,包括动画在内。
layer 有自己的background 和border
layer可能在image中展示一完全充满的背景和边框。其实背景是在image的后面渲染,而border是在image的前面渲染。下图展示具体层次结构。
背景我们可以用任何颜色,包括半透明或者 pattern image。 当我们使用core Graphics处理图案图像的渲染时候使用的是标准坐标系来处理(左下角),与ios上的坐标系不同,会导致图像翻转。
如果layer的背景是不透明的,那么我们最好将layer的opaque设置为YES,这样可以提高执行效率,而已也不需要layer的backing Store来管理alpha通道。如果layer 具有圆角,则不能将layer 标记为不透明,这样圆角出就是黑色的了。
layer 支持圆角
我们可以给layer增加一个圆角。圆角是一种视觉效果,可以遮盖layer边界矩形的角落的一部分,让底层内容显示。因为我们用的透明mask,所有半径不会影响layer的contents属性中的image,除非我们将maskToBounds=yes属性。
layer - 内置的阴影
layer 有几个属性是关于阴影的。阴影使图像看起来好像是漂浮在底层内容之上,从而增加了图层的深度,有立体感了。这也是一种视觉装饰,这其实在特定的情况下是有用的。我们可以控制引用的的颜色,相对于图层的位置,透明度和形状。
layer的shadows 的opacty默认是0,是隐藏阴影的。改成非零值就让core Animation 绘制阴影。默认的情况下,shadows是在layer的正下方的,我们可以设置shadow的offset来更改他的位置。这里需要注意,shadow的offset使用的是坐标系是和layer的坐标系一致。
如果我们增加一个shadows,这个阴影出于layer的bounds ,我们可以设置maskTobounds将其剪切掉。如果layer 有透明contents,这可能会引起奇怪的效果,layer下方的shadows仍然可见的。如果我们想用shadows,又想用边界 mask,最好使用两个layer,而不是用一个,将mask 应用于包含contents的layer,然后将该图层整体嵌入到启用了shadows效果的完全相同大小的第二层中。
构建layer 图层
大多数情况下,在app使用view的最佳方式是将他们与view对象结合使用。但是,有时候我们需要通过向其添加其他layer来增强视图层次效果。当一个view不能不能满足我们的要去的时候,我们可以增加layer满足我们的要求,因此,我们需要知道如何管理layer的图层结构。
排列layer到图层结构
layer的层次结构和view的层次结构差不多。我们将一个layer嵌入别的layer,嵌入的layer就是 sublayer,被嵌入的视图是super layer,这种关系对sublayer有影响。例如:sublayer的contents位于superlayer的上面,位置是相对于superlayer指定,如果父视图有变化,子视图也会变化。
sublayer的增删改查
- Adding layers
addSublayer:
- Inserting layers
insertSublayer:above:
insertSublayer:atIndex:
insertSublayer:below:
- Removing layers
removeFromSuperlayer
- Exchanging layers
replaceSublayer:with:
layer 的位置和大小
myLayer.bounds = CGRectMake(0, 0, 100, 100);
myLayer.position = CGPointMake(200, 200);
position 和锚点共同作用才能确定sublayer在superlayer的具体位置
sublayers 和裁剪
layer和view不一样,没有自动裁剪功能。因此,superlayer是默认允许sublayer超出其边界显示的。不过我们可以设置masksToBounds属性来裁剪超过superlayer边界的部分。
举例如下:
layer 之间的坐标转换
- convertPoint:fromLayer:
- convertPoint:toLayer:
- convertRect:fromLayer:
- convertRect:toLayer:
layer的属性动画
在渲染工程中,CoreAnimation采用layer的不同属性,并以特定的顺序呈现他们。该顺序决定layer的最终外观。
几何属性
layer的几何属性指定他相对于superlayer显示的方式。几何图形还指定了用于圆化角的半径以及layer级sublayer的transform。
layer的几何属性下列
bounds
position
frame (computed from the
boundsandpositionand is not animatable)anchorPoint
cornerRadius
transform
zPosition
背景属性
我们通过前面章节指定,背景是layer图层中的最后面一层了。CoreAnimation渲染的第一件事就是背景了。我们可以为背景指定颜色。
在ios支持的属性
- backgroundColor
这里需要说下,backgroundColor 因为支持pattern;因此背景不单单的就是纯色。
layer content属性
如果layer 有contents 属性,那么contents属性一定渲染在background的上面。我们可以给contents属性直接赋值给bitmap,或者通过delegate指定content或者依靠子类直接绘制content。我们可以用很多技术提供contents。例如:quzrtz,metal,openGL等。
相关属性
- contents
- contentsGravity
- masksToBounds
Sublayers Content属性
一个layer可以包含很多subLayer,。sublayer根据父类的相对坐标被渲染在父类上。这些很基础,这里只列举下相关属性。
相关属性
- sublayers
- masksToBounds
- sublayerTransform
Border 属性
layer的边框
- borderColor
- borderWidth
Shadow 属性
layer可以展示shadow效果,我们可以配置他们的形状,透明度,颜色,偏移和模糊半径。如果不指定自定义阴影形状,则阴影基于不完全透明的layer的部分
上图显示了相同的样本层的几个不同版本,其中应用了红色阴影。左侧和中间版本包括背景颜色,因此阴影仅出现在该层的边界周围。但是,右边的版本不包括背景颜色。在这种情况下,阴影被应用到层的内容、边界和子层。
- shadowColor
- shadowOffset
- shadowOpacity
- shadowRadius
- shadowPath
这里性能优化里面说了,阴影最好给指定个shadowPath,可以极大的提高绘制性能。具体怎么使用看shadowPath的官方文档。
Opacity 属性
Opacity 属性决定了有多少背景显示出来。
相关属性
- opacity
Mask 属性
我们可以使用mask来遮蔽layer层的内容的全部或者部分。mask本身就是layer对象,其alpha的值来告知什么时候遮挡,什么时候传输。mask的不透明部分允许底层layer显示,而透明部分部分或者完全模糊底层layer 的内容。
上图示出了与mask层和两个不同背景复合的样品层。在左边的版本中,图层的不透明度设置为1。在右边的版本中,layer的不透明度被设置为0.5,我们发现我们稍微能看见背景的元素了。
-
- mask
这里图层的优先级变化测试结果是
mask>border>contents>background
动画属性
| Property | Default animation |
|---|---|
| anchorPoint | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| backgroundColor | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| backgroundFilters | Uses the default implied CATransition object, described in Table B-3. Sub-properties of the filters are animated using the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| borderColor | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| borderWidth | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimationobject, described in Table B-2. |
| bounds | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| compositingFilter | Uses the default implied CATransition object, described in Table B-3. Sub-properties of the filters are animated using the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| contents | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimationobject, described in Table B-2. |
| contentsRect | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimationobject, described in Table B-2. |
| cornerRadius | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| doubleSided | There is no default implied animation. |
| filters | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. Sub-properties of the filters are animated using the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| frame | This property is not animatable. You can achieve the same results by animating the bounds and position properties. |
| hidden | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| mask | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| masksToBounds | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| opacity | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| position | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| shadowColor | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in [Table B-2](https://developer.apple.com/library/archive/documentation/Cocoa/Conceptual/CoreAnimation_guide/AnimatableProperties/AnimatableProperties.html#//apple_ref/doc/uid/TP40004514-CH11-SW2 |
| shadowOffset | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| shadowOpacity | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| shadowPath | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| shadowRadius | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| sublayers | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| sublayerTransform | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
| transform | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation` object, described in Table B-2. |
| zPosition | Uses the default implied CABasicAnimation object, described in Table B-2. |
Table B-2 Default Implied Basic Animation
| Description | Value |
|---|---|
| Class | CABasicAnimation |
| Duration | 0.25 seconds, or the duration of the current transaction |
| Key path | Set to the property name of the layer. |
Table B-3 Default Implied Transition
| Description | Value |
|---|---|
| Class | CATransition |
| Duration | 0.25 seconds, or the duration of the current transaction |
| Type | Fade (kCATransitionFade) |
| Start progress | 0.0 |
| End progress | 1.0 |
键值编码
CoreAnimation 拓展了NSKeyValueCoding协议。CAAnimation和CALayer中实现了该协议。该extension添加了一些默认值,并且为CGPoint,CGRect,CGSize和CATTransform3D 类型添加路径支持。
键值编码编译容器
CAAnimation 和CALayer是键值编码的容器,这意味着可以为任意键设置值。即使key键不是Calayer定义的属性,我们仍然可以设置值。
[theLayer setValue:[NSNumber numberWithInteger:50] forKey:@"someKey"];
我们也可以检索值。例如
someKeyValue=[theLayer valueForKey:@"someKey"];
默认值
CoreAnimation将一个约定添加到键值编码中,从而一个类可以为没有设置的值提供默认值。CAAnimation 和 CALayer 受用defaultValueForKey:方法来支持这个约定。
+ (id)defaultValueForKey:(NSString *)key
{
if ([key isEqualToString:@"masksToBounds"])
return [NSNumber numberWithBool:YES];
return [super defaultValueForKey:key];
}
包装类型
在键值编码中,没有办法对结构体进行编码因此需要转换,
下列表是将结构体类型转换成的对象。
| C type | Wrapping class | |
|---|---|---|
| CGPoint | NSValue | |
| CGSize | NSValue | |
| CGRect | NSValue | |
| CATransform3D | NSValue | |
| CGAffineTransform | NSAffineTransform (OS X only) |
对结构体的键值编码
CAAnimation和CALayer 允许我们用keyPath访问结构体类型的数据。此特性是指定需要动画的数据结构字段的简便方法。我们还可以结合setValue:forKeyPath:和valueForKeyPath:方法使用这些约定来设置和获取那些字段
CATransform3D Key Paths
对于CATransform3D ,我们可以直接通过键值编码直接设置值。这样方便写。下列就是简直编码对应的字符串。
| Field Key Path | Description |
|---|---|
| rotation.x | Set to an NSNumber object whose value is the rotation, in radians, in the x axis. |
| rotation.y | Set to an NSNumber object whose value is the rotation, in radians, in the y axis. |
| rotation.z | Set to an NSNumber object whose value is the rotation, in radians, in the z axis. |
| rotation | Set to an NSNumber object whose value is the rotation, in radians, in the z axis. This field is identical to setting the rotation.z field. |
| scale.x | Set to an NSNumber object whose value is the scale factor for the x axis. |
| scale.y | Set to an NSNumber object whose value is the scale factor for the y axis. |
| scale.z | Set to an NSNumber object whose value is the scale factor for the z axis. |
| scale | Set to an NSNumber object whose value is the average of all three scale factors. |
| translation.x | Set to an NSNumber object whose value is the translation factor along the x axis. |
| translation.y | Set to an NSNumber object whose value is the translation factor along the y axis. |
| translation.z | Set to an NSNumber object whose value is the translation factor along the z axis. |
| translation | Set to an NSValue object containing an NSSize or CGSize data type. That data type indicates the amount to translate in the x and y axis. |
用法举例
[myLayer setValue:[NSNumber numberWithFloat:10.0] forKeyPath:@"transform.translation.x"];
CGPoint Key Paths
| Structure Field | Description |
|---|---|
x |
The x component of the point. |
y |
The y component of the point. |
CGSize Key Paths
| Structure Field | Description |
|---|---|
width |
The width component of the size. |
height |
The height component of the size. |
CGRect Key Paths
| Structure Field | Description |
|---|---|
| origin | The origin of the rectangle as a CGPoint. |
| origin.x | The x component of the rectangle origin. |
| origin.y | The y component of the rectangle origin. |
| size | The size of the rectangle as a CGSize. |
| size.width | The width component of the rectangle size. |
| size.height | The height component of the rectangle size. |