11.Java面向对象-包装类-static-单例模式
Java面向对象-包装类-static
一、JUnit单元测试
/*
* 一、Junit单元测试
* 1. 选中工程-右键-build path - add libraries - Junit - Junit 4
* 2. 新建一个测试类,此类称为:单元测试类
* 要求:1. 此单元测试类必须声明为public的。2. 必须提供public权限的空参构造器
* 3. 类中导包:import org.junit.Test;
* 4. 新建一个方法,在方法前声明@Test
* 要求:此方法是public的,void的,且没有形参
* 此方法即为单元测试方法
* 5. 在单元测试方法中可以定义变量,可以调用类中的方法等操作,进行测试即可
*
* 二、说明
* 1. 如果单元测试方法正常执行结束,则显示:绿条
* 2. 如果单元测试方法执行过程中出现异常,则显示:红条
*
*/
public class JunitTest {
// public static void main(String[] args) {//程序的入口
//
// }
@Test
public void test1(){
System.out.println("hello");
int num = 10;
num += 2;
System.out.println(num);
}
@Test
public void test2(){
System.out.println("今天天气不错!但是不能出去溜达。。。");
String info = info();
System.out.println(info);
int[] arr = new int[10];
System.out.println(arr[10]);
}
public String info(){
return "北京-上海-深圳";
}
}
二、包装类的使用
1. 为什么要有包装类
-
针对八种基本数据类型定义相应的引用类型—包装类(封装类)
-
有了类的特点,就可以调用类中的方法,Java才是真正的面向对象
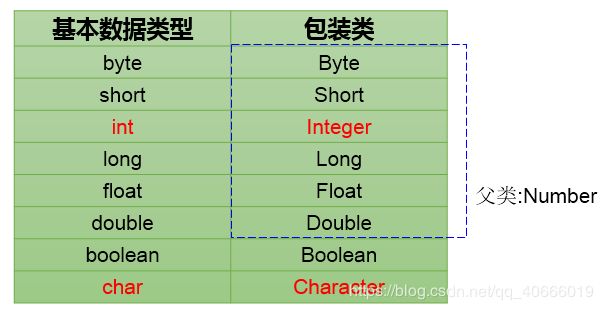
2. 基本数据类型与对应的包装类
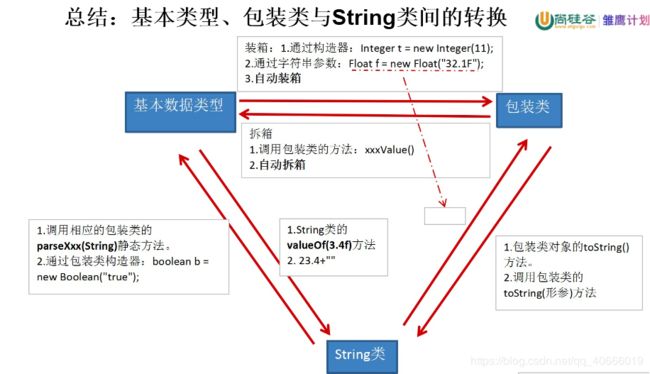
3. 基本数据类型、包装类与String之间的转换
3.1 基本数据类型变量 与 包装类之间的转换
方式一:
//装箱:基本数据类型的变量 --> 包装类:调用包装类的构造器
@Test
public void test1(){
int i1 = 10;
// System.out.println(i1.toString());//编译错误
Integer i2 = new Integer(i1);
System.out.println(i2.toString());//10
float f1 = 12.3F;
Float f2 = new Float(f1);
System.out.println(f2);
// Float f3 = new Float("abc");//报NumberFormatException
Float f4 = new Float("12.3");
System.out.println(f4);
Boolean b1 = new Boolean(true);
b1 = new Boolean("TRue");
System.out.println(b1);
Boolean b2 = new Boolean("true123");
System.out.println(b2);//不报异常,false.
}
//拆箱:包装类--->基本数据类型:调用包装类Xxx的xxxValue()方法
@Test
public void test2(){
Integer i1 = new Integer(11);
//
int i2 = i1.intValue();
int i3 = i2 + 10;
Boolean b1 = new Boolean(true);
boolean b2 = b1.booleanValue();
}
- 方式二:jdk5.0引入了自动的装箱和拆箱
//jdk5.0引入了自动的装箱和拆箱
@Test
public void test3(){
int i1 = 10;
Integer i2 = i1; //自动装箱
System.out.println(i2.toString());
int i3 = i2;//自动拆箱
double d1 = 12.3;
Double d2 = d1;//自动装箱
double d3 = d2;//自动拆箱
//应用:
boolean b = d2.equals(d1);//自动装箱
double d4 = i2 - d2;//自动拆箱
}
3.2 基本数据类型、包装类 与 字符串之间的转换
//基本数据类型、包装类 --->字符串:① 连接运算 ② 调用String类的valueOf(xxx )
@Test
public void test4(){
int i1 = 10;
Integer i2 = new Integer(20);
//方式一:+运算
String str1 = i1 + "";
//方式二:
String str2 = String.valueOf(i1);
System.out.println(str2);//"10"
String str3 = String.valueOf(i2);
System.out.println(str3);//"20"
}
//字符串 ---> 基本数据类型、包装类:调用包装类Xxx的parseXxx()
@Test
public void test5(){
String s1 = "123";
// int i1 = (int)s1;//编译报错
int i2 = Integer.parseInt(s1);
System.out.println(i2);//123
String s2 = "false";
Boolean b1 = Boolean.parseBoolean(s2);//自动装箱
System.out.println(b1);
}
练习:
信息给予题:
利用Vector代替数组处理:从键盘读入学生成绩(以负数代表输入结束),找出最高分,并输出学生成绩等级。
提示:数组一旦创建,长度就固定不变,所以在创建数组前就需要知道它的长度。而向量类java.util.Vector可以根据需要动态伸缩。
创建Vector对象:Vector v=new Vector();
给向量添加元素:v.addElement(Object obj); //obj必须是对象
取出向量中的元素:Object obj=v.elementAt(0);
注意第一个元素的下标是0,返回值是Object类型的。
计算向量的长度:v.size();
若与最高分相差10分内:A等;20分内:B等;
30分内:C等;其它:D等
public class ScoreTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.实例化Vector
Vector v = new Vector();
//2.实例化Scanner
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//3.通过for循环向vector中添加学生成绩
int maxScore = 0;
for(;;){
//方式1:jdk5.0之前
// int number = scanner.nextInt();
// Integer score = new Integer(number);
// v.addElement(score);
//方式2:jdk5.0之后可以自动装箱
int number = scanner.nextInt();
//如果输入的负数,则跳出循环结构
if(number < 0){
break;
}
v.addElement(number);
//4.获取最高分
if(maxScore < number){
maxScore = number;
}
}
//5.遍历每个学生成绩,并获取各自的等级
for(int i = 0;i < v.size();i++){
Object element = v.elementAt(i);
if(element instanceof Integer){
//方式1:jdk5.0之前
// Integer score = (Integer) element;
// int myScore = score.intValue();
//方式2:jdk5.0之后可以自动装箱
int myScore = (Integer) element;
char grade;
if(myScore >= maxScore - 10){
grade = 'A';
}else if(myScore >= maxScore - 20){
grade = 'B';
}else if(myScore >= maxScore - 30){
grade = 'C';
}else{
grade = 'D';
}
System.out.println("student " + i + " score is "
+ myScore + ", grade is " + grade);
}
}
}
}
三、static关键字的使用
1. static的理解
-
- static:静态的。
-
- static 用来修饰的结构:属性、方法;代码块、内部类
2. static修饰属性
3.1 变量的分类: 成员变量(或属性):静态变量(或类变量)、非静态变量(或实例变量)
* 局部变量:方法内、方法的形参、构造器内部、构造器形参、代码块内部
3.2 静态变量:如果属性使用static修饰以后,就是静态变量。
* 特点:创建一个类的多个对象,每个对象拥有一套实例变量。(如果修改一个对象的实例变量,不影响其他对象的实例变量)。但是,此类的多个对象,会共享此类的静态变量(或类变量)。(如果通过一个对象修改其静态变量的话,会影响其他所有对象对此静态变量的调用)
* 3.3 说明:
① 静态变量,在内存中就只有一份。存储在内存的静态域中。
* ② 静态变量,随着类的加载而加载。而且,只会加载一次。 比如:Math里的PI,System里的out
* (相比来讲,实例变量,随着对象的创建而加载)
* ③ 从生命周期角度,理解静态变量
* 静态变量 实例变量
* 类 yes no
* 对象 yes yes
3.static修饰方法
static 修饰方法:静态方法(或类方法)
* ① 随着类的加载而加载
* ② 可以直接通过"类.静态方法"的方式进行调用
* ③ 从生命周期角度,理解静态方法
* 静态方法 实例方法
* 类 yes no
* 对象 yes yes
* ④ 静态方法中,可以调用当前类中的静态结构,但是不能调用当前类的非静态的结构:属性、方法
* 非静态方法中,既可以调用当前类中的类中的静态结构,也可以调用当前类的非静态的结构:属性、方法
* 比如:Arrays工具类、Math工具类中的方法基本都是静态的方法:Arrays.sort(),Math.random();
* ⑤ 静态方法内,不能使用this、super
测试代码:
class Chinese{//中国人
String name;
int age;
static String nation;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Chinese [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", nation=" + nation + "]";
}
public static void show(){
System.out.println("我是一个中国人");
System.out.println("nation : " + nation);
//不可以在静态方法中,调用类中的非静态结构
// System.out.println("name : " + name + ", age : " + age);
// eat();
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("中国人喜欢吃中国菜");
}
public void info(){
System.out.println("name : " + name + ", age : " + age);
eat();
//可以在非静态方法中,调用类中的静态结构
System.out.println("nation : " + nation);
show();
}
}
public class StaticTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Chinese.nation = "中国";
System.out.println(Chinese.nation);
// Chinese.name = "Tom";//编译不通过
Chinese c1 = new Chinese();
c1.name = "成龙";
c1.age = 60;
c1.nation = "CHN";
Chinese c2 = new Chinese();
c2.name = "周杰伦";
c2.age = 34;
// c2.nation = "China";
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
System.out.println(Chinese.nation);
Chinese.show();
c1.show();
//*******************************
// StaticTest test = new StaticTest();
// test.display();
StaticTest.display();
}
public static void display(){
System.out.println("测试");
}
}
4. 何时属性、方法适合设置为static的
开发中,什么时候需要将属性声明为静态的?
* > 属性是否可以多个对象所共享,不会随着对象的不同而不同。
* > 类的中常量通常会设置为静态的。
*
* 什么时候需要将方法声明为静态的?
* > 修改、调用静态属性的方法,通常都是静态方法。
* > 工具类中的方法,通常都是静态方法。
5. 应用举例:
//static的应用
public class CircleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Circle c1 = new Circle();
Circle c2 = new Circle(3.2);
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
System.out.println("共创建了" + Circle.count + "个对象");
}
}
class Circle{
private double radius;//半径
private int id;//编号,自动生成
public static int count;//记录创建的Circle对象的个数
private static int init = 1001;//用来生成自增长的数据
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
//
public Circle(double radius) {
this();
this.radius = radius;
// id = init++;
// count++;
}
public Circle() {
super();
id = init++;
count++;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Circle [radius=" + radius + ", id=" + id + "]";
}
}
6. 练习
编写一个类实现银行账户的概念,包含的属性有“帐号”、“密码”、“存款余额”、“利率”、“最小余额”,定义封装这些属性的方法。账号要自动生成。
编写主类,使用银行账户类,输入、输出3个储户的上述信息。
考虑:哪些属性可以设计成static属性。
四、单例模式
- 一、设计模式:是在大量的实践中总结和理论化之后优选的代码结构、编程风格、以及解决问题的思考方式。
- 经典的设计模式一共有23种。
- 二、单例模式:采取一定的方法保证在整个的软件系统中,对某个类只能存在一个对象实例
- 三、如何实现单例模式
- 饿汉式
public class SingletonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Bank bank1 = new Bank();
// Bank bank2 = new Bank();
Bank bank1 = Bank.getInstance();
Bank bank2 = Bank.getInstance();
System.out.println(bank1 == bank2);
}
}
class Bank{
//1.私有化类的构造器
private Bank(){
}
//2.内部创建当前类的实例
private static Bank bank = new Bank();
//3.提供公共的,静态的方法,返回当前类的唯一对象
public static Bank getInstance(){
return bank;
}
}
- 懒汉式
//单例模式的懒汉式
public class SingletonTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
School s1 = School.getInstance();
School s2 = School.getInstance();
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
}
}
class School {
// 1.私有化类的构造器
private School() {
}
//2. 声明当前类对象的属性
private static School school = null;
//3. 在静态方法中为当前对象赋值
public static School getInstance(){
if(school == null){
school = new School();
}
return school;
}
}
- 对比两种模式
- 从节省内存空间角度:懒汉式好
- 线程安全性的角度:饿汉式好。 在多线程中讲解如何解决线程安全问题。
//单例模式的懒汉式
public class SingletonTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
School s1 = School.getInstance();
School s2 = School.getInstance();
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
}
}
class School {
// 1.私有化类的构造器
private School() {
}
//2. 声明当前类对象的属性
private static School school = null;
//3. 在静态方法中为当前对象赋值
public static School getInstance(){
if(school == null){
school = new School();
}
return school;
}
}
- 对比两种模式
- 从节省内存空间角度:懒汉式好
- 线程安全性的角度:饿汉式好。 在多线程中讲解如何解决线程安全问题。
五、练习题
编写一个类实现银行账户的概念,包含的属性有“帐号”、“密码”、“存款余额”、“利率”、“最小余额”,定义封装这些属性的方法。账号要自动生成。
编写主类,使用银行账户类,输入、输出3个储户的上述信息。
考虑:哪些属性可以设计成static属性。
public class Account{
private int id;//账号
private String passWord = "123456";//初始密码
private double balance;//余额
private static int init = 1001;//账号号码自动生成
private static double annualInterestRate = 0.015;//利率
private static double minBalance = 100;//最小余额
public Account() {
id = init++;
}
public Account(String passWord,double balance) {
this();
this.passWord = passWord;
this.balance = balance;
}
public String getPassWord() {
return passWord;
}
public void setPassWord(String passWord) {
this.passWord = passWord;
}
public static double getAnnualInterestRate() {
return annualInterestRate;
}
public static void setAnnualInterestRate(double annualInterestRate) {
Account.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate;
}
public static double getMinBalance() {
return minBalance;
}
public static void setMinBalance(double minBalance) {
Account.minBalance = minBalance;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BankAccount [id=" + id + ", passWord=" + passWord + ", balance=" + balance + "]";
}
}
//使用银行账户类,输入、输出3个储户的上述信息。
public class AccountTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account account1 = new Account("666666", 1000);
Account account2 = new Account("system", 3000);
Account account3 = new Account("qwerdf", 500);
Account.setAnnualInterestRate(0.0123);
Account.setMinBalance(250);
System.out.println("利率:" + Account.getAnnualInterestRate());
System.out.println("最小余额:" + Account.getMinBalance());
System.out.println(account1);
System.out.println(account2);
System.out.println(account3);
}
}
思考题
public class StaticDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new SDText().x+","+new SDText().y+","+new SDText().x);
}
}
class SDText{
static SDText sd=new SDText();
static int x=3;
static int y;
public SDText(){
x++;
y++;
}
}
答案:
4,3,6
六、小结
-
单元测试方法的使用
-
包装类的使用
- 基本数据类型 与 包装类的转换:自动装箱、自动拆箱
- 基本数据类型、包装类 与 String之间的转换:① String中的重载方法:valueOf() ②调用包装类Xxx的parseXxx();
- 调用包装类Xxx的parseXxx();可能会出现:NumberFormatException。
-
static关键字
- static修饰的结构:属性、方法; 代码块、内部类。
- 随着类的加载而加载。
- “类.属性” 或 "类.方法"的方式进行调用
- 属性、方法在类中只有一份
- 哪些属性或方法适合声明为静态的!!
-
设计模式与单例模式
- 饿汉式
- 懒汉式(暂时存在线程安全问题,后面在多线程中解决)