探索Android软键盘的疑难杂症
探索Android软键盘的疑难杂症
深入探讨Android异步精髓Handler
详解Android主流框架不可或缺的基石
站在源码的肩膀上全解Scroller工作机制
Android多分辨率适配框架(1)— 核心基础
Android多分辨率适配框架(2)— 原理剖析
Android多分辨率适配框架(3)— 使用指南
自定义View系列教程00–推翻自己和过往,重学自定义View
自定义View系列教程01–常用工具介绍
自定义View系列教程02–onMeasure源码详尽分析
自定义View系列教程03–onLayout源码详尽分析
自定义View系列教程04–Draw源码分析及其实践
自定义View系列教程05–示例分析
自定义View系列教程06–详解View的Touch事件处理
自定义View系列教程07–详解ViewGroup分发Touch事件
自定义View系列教程08–滑动冲突的产生及其处理
在Activity中含有EditText时,我们常常在AndroidManifest.xml中为该Activity设置android:windowSoftInputMode属性,其中最常用的值就是adjustResize和adjustPan。在此请思考几个问题:
- adjustResize和adjustPan有什么区别?
- adjustResize和adjustPan的应用场景有何差异?
- 当设置android:windowSoftInputMode后如何监听软键盘的弹起与隐藏?
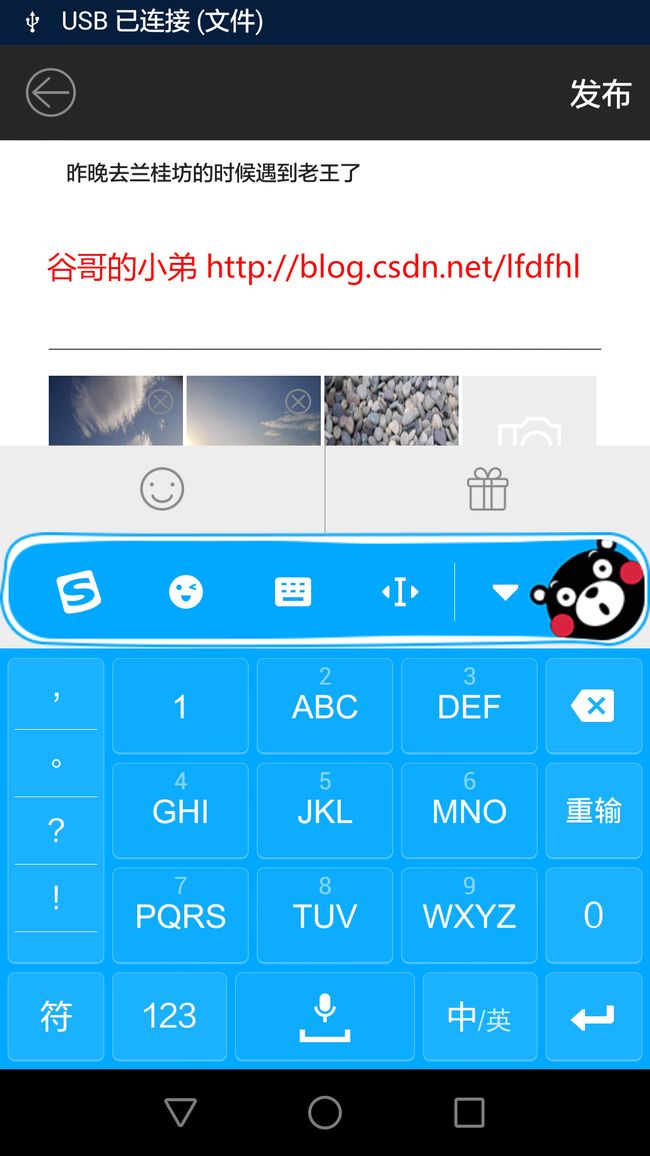
在看到第三个问题的时候,有人会想:
干嘛要去监听软键盘的弹起呢?有什么用呢?
嗯哼,看到了吧:当键盘弹起来的时候在紧靠键盘上方的地方出现了一个自定义布局,点击笑脸就可以发送专属emoji表情,点击礼盒就可以发送福利。
当然,在键盘收起的时候这个布局也就不可见了。
除此以外,在其他不少场景也会有类似的UI设计。在这些情况下,我们都要监听键盘软键盘的弹起与隐藏。善良的童鞋会想:这个没难度呀,调用一下官方的API就行。很久以前,我也是这么想的。可是,事与愿违,官方文档中根本就没有提供检测软键盘状态的接口。
既然官方没有把这个API洗干净整整齐齐的摆在眼前,那我们就自己实现它。
adjustResize
在AndroidManifest.xml中为该Activity设置
android:windowSoftInputMode=”adjustResize”
该模式下系统会调整屏幕的大小以保证软键盘的显示空间。
举个例子:
屏幕的高为1920px,那么整个Activity的布局高度也为1920px。当设置该属性后点击界面中的EditText,此时弹出软键盘其高度为800px。为了完整地显示此软键盘,系统会调整Activity布局的高度为1920px-800px=1120px。
所以,此时的布局与原本的布局就发生了一些变化,比如:整体布局显示不完整,控件外观的变形,控件显示位置的错乱等等。这些现象都是因为原布局的高度变小所导致。
以下,再结合代码详细分析该情况。
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.widget.RelativeLayout;
/**
* 原创作者:
* 谷哥的小弟
*
* 博客地址:
* http://blog.csdn.net/lfdfhl
*
*/
public class RelativeLayoutSubClass extends RelativeLayout{
private OnSoftKeyboardListener mSoftKeyboardListener;
public RelativeLayoutSubClass(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
System.out.println("----> onMeasure");
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
super.onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
mSoftKeyboardListener.onSoftKeyboardChange();
System.out.println("----> onLayout");
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
System.out.println("----> onSizeChanged");
}
public void setSoftKeyboardListener(OnSoftKeyboardListener listener){
mSoftKeyboardListener=listener;
}
public interface OnSoftKeyboardListener{
public void onSoftKeyboardChange();
}
}
我们将该自定义RelativeLayout作为Activity布局的根
<cc.testsoftinputmode.RelativeLayoutSubClass
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/rootLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="cc.testsoftinputmode.MainActivity">
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:background="#7fb80e">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="浅绿色部分在屏幕顶部"
android:textSize="25sp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:textColor="#843900"/>
RelativeLayout>
<EditText
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="这里是一个输入框"
android:textSize="25sp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:textColor="#843900"/>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:background="#ffc20e">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="浅黄色部分在屏幕底部"
android:textSize="25sp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:textColor="#f05b72"/>
RelativeLayout>
cc.testsoftinputmode.RelativeLayoutSubClass>
现象呢,我们已经看到了。我们再来瞅瞅当软键盘状态变化的时候RelativeLayoutSubClass中有哪些行为发生:
- 软键盘状态变化时会调用其onMeasure(),onLayout(),onSizeChanged()
- 在onSizeChanged()中可以确知软键盘状态变化前后布局宽高的数值
至此,发现一个关键点:onSizeChanged()
我们可以以此为切入点检测软键盘的状态变化,所以定义一个接口OnSoftKeyboardListener提供给Activity使用,具体代码如下:
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
/**
* 原创作者:
* 谷哥的小弟
*
* 博客地址:
* http://blog.csdn.net/lfdfhl
*
*/
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private RelativeLayoutSubClass mRootLayout;
private int screenHeight;
private int screenWidth;
private int threshold;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
init();
}
private void init(){
screenHeight=getResources().getDisplayMetrics().heightPixels;
screenWidth=getResources().getDisplayMetrics().widthPixels;
threshold=screenHeight/3;
mRootLayout= (RelativeLayoutSubClass) findViewById(R.id.rootLayout);
mRootLayout.setSoftKeyboardListener(new RelativeLayoutSubClass.OnSoftKeyboardListener() {
@Override
public void onSoftKeyboardChange(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
if (oldh-h>threshold){
System.out.println("----> 软键盘弹起");
}else if(h-oldh>threshold){
System.out.println("----> 软键盘收起");
}
}
});
}
}请注意onSoftKeyboardChange()的回调:
- 假若oldh-h大于屏幕高度的三分之一,则软键盘弹起
- 假若h-oldh大于屏幕高度的三分之一,则软键盘收起
小结:
当软键盘状态发生改变时,通过对Activity布局文件根Layout的onSizeChanged()判断软键盘的弹起或隐藏
adjustPan
在AndroidManifest.xml中为该Activity设置
android:windowSoftInputMode=”adjustPan”
该模式下系统会将界面中的内容自动移动从而使得焦点不被键盘覆盖,即用户能总是看到输入内容的部分
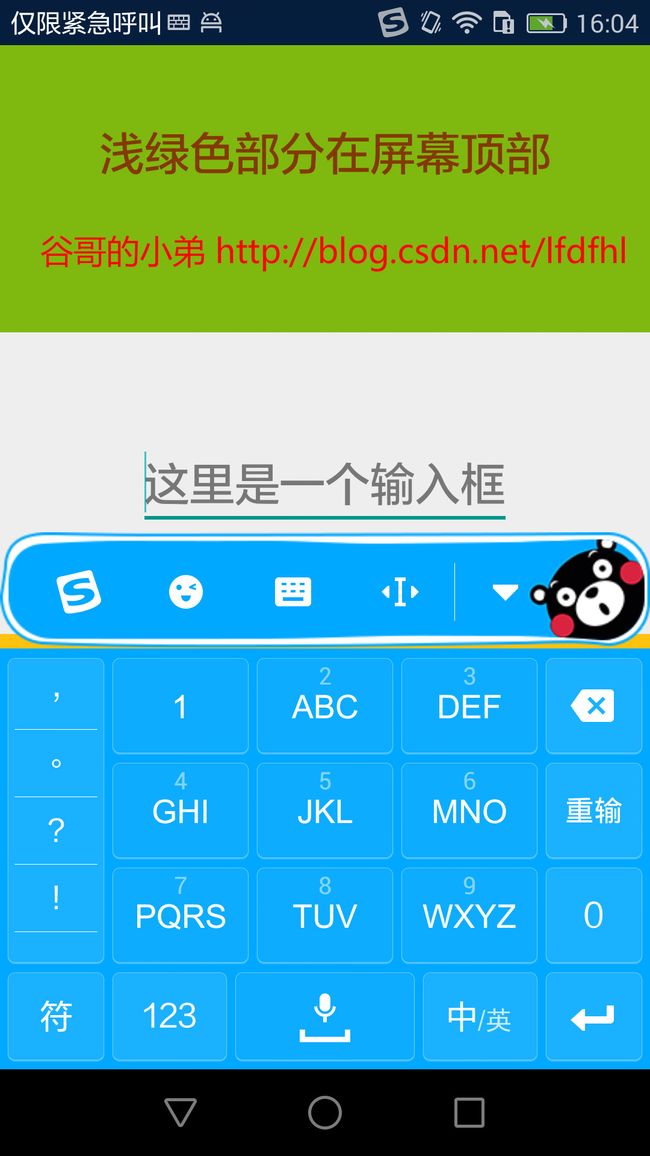
比如,还是刚才的那个布局,现在将其windowSoftInputMode设置为adjustPan再点击EditText,效果如下:
嗯哼,看到了吧:
为了避免软键盘弹起后遮挡EditText,系统将整个布局上移了,也就是我们常说的将布局顶上去了。
此时再来看看当软键盘状态变化的时候RelativeLayoutSubClass中有哪些行为发生:
- 软键盘状态变化时会调用其onMeasure(),onLayout()
- onSizeChanged()并没有被调用
- 整个布局的高度也没有变化
哦噢,这时并没有执行onSizeChanged()方法,这也就说原本检测软键盘状态的方法在这就行不通了,得另辟蹊径了。
当软键盘弹起时,原布局中是不是有一部分被键盘完全遮挡了呢?
对吧,也就是说原布局的可视范围(更精确地说是可视高度)发生了变化:变得比以前小了。所以,我们可以以此为突破口,具体代码如下:
public boolean isSoftKeyboardShow(View rootView) {
screenHeight=getResources().getDisplayMetrics().heightPixels;
screenWidth=getResources().getDisplayMetrics().widthPixels;
threshold=screenHeight/3;
int rootViewBottom=rootView.getBottom();
Rect rect = new Rect();
rootView.getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(rect);
int visibleBottom=rect.bottom;
int heightDiff = rootViewBottom - visibleBottom;
System.out.println("----> rootViewBottom="+rootViewBottom+",visibleBottom="+visibleBottom);
System.out.println("----> heightDiff="+heightDiff+",threshold="+threshold);
return heightDiff > threshold;
}- 获取根布局(RelativeLayoutSubClass)原本的高度
int rootViewBottom=rootView.getBottom();
获取当前根布局的可视高度
Rect rect = new Rect();
rootView.getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(rect);
int visibleBottom=rect.bottom;- 计算两者的差值
int heightDiff = rootViewBottom - visibleBottom;
判断软键盘是否弹起
return heightDiff > threshold;
具体的方法是有了,那么该在哪里调用该方法呢?
其实,和之前的类似,只需在RelativeLayoutSubClass的onLayout()中执行即可。具体代码如下:
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.widget.RelativeLayout;
/**
* 原创作者:
* 谷哥的小弟
*
* 博客地址:
* http://blog.csdn.net/lfdfhl
*
*/
public class RelativeLayoutSubClass extends RelativeLayout{
private OnSoftKeyboardListener mSoftKeyboardListener;
public RelativeLayoutSubClass(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
System.out.println("----> onMeasure");
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
super.onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
mSoftKeyboardListener.onSoftKeyboardChange();
System.out.println("----> onLayout");
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
System.out.println("----> onSizeChanged");
}
public void setSoftKeyboardListener(OnSoftKeyboardListener listener){
mSoftKeyboardListener=listener;
}
public interface OnSoftKeyboardListener{
public void onSoftKeyboardChange();
}
}在对应的Activity中实现该Listener,具体代码如下:
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
/**
* 原创作者:
* 谷哥的小弟
*
* 博客地址:
* http://blog.csdn.net/lfdfhl
*
*/
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity{
private RelativeLayoutSubClass mRootLayout;
private int screenHeight;
private int screenWidth;
private int threshold;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
init();
}
private void init(){
mRootLayout= (RelativeLayoutSubClass) findViewById(R.id.rootLayout);
mRootLayout.setSoftKeyboardListener(new RelativeLayoutSubClass.OnSoftKeyboardListener() {
@Override
public void onSoftKeyboardChange() {
boolean isShow=isSoftKeyboardShow(mRootLayout);
System.out.println("----> isShow="+isShow);
}
});
}
public boolean isSoftKeyboardShow(View rootView) {
screenHeight=getResources().getDisplayMetrics().heightPixels;
screenWidth=getResources().getDisplayMetrics().widthPixels;
threshold=screenHeight/3;
int rootViewBottom=rootView.getBottom();
Rect rect = new Rect();
rootView.getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(rect);
int visibleBottom=rect.bottom;
int heightDiff = rootViewBottom - visibleBottom;
System.out.println("----> rootViewBottom="+rootViewBottom+",visibleBottom="+visibleBottom);
System.out.println("----> heightDiff="+heightDiff+",threshold="+threshold);
return heightDiff > threshold;
}
}嗯哼,至此当windowSoftInputMode设置为adjustPan时软键盘的状态监听也得到了实现