1. Iterated Local Search(局部搜索算法)介绍
迭代局部搜索属于探索性局部搜索方法(EXPLORATIVE LOCAL SEARCH METHODS)的一种。它在局部搜索得到的局部最优解上,加入了扰动,然后再重新进行局部搜索。
2. Iterated Local Search过程:
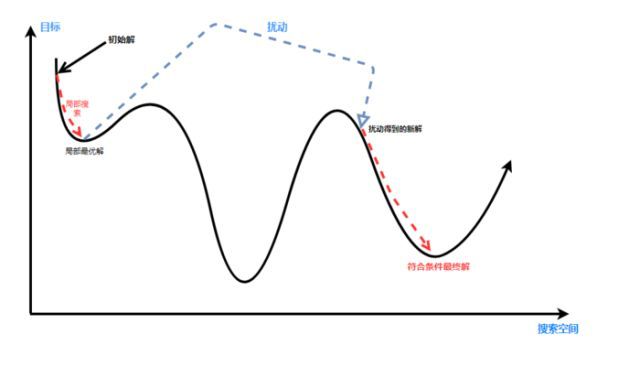
1.初始状态:best_solution(最优解)、current_solution(当前解)。
2.从初始解(best_solution)中进行局部搜索,找到一个局部最优解s1(best_solution)。
3.扰动s1(best_solution),获得新的解s2(current_solution)。
4.从新解s2(current_solution)中进行局部搜索,再次找到一个局部最优解s3(best_solution)。
5.基于判断策略,对s3(current_solution)好坏进行判断。选择是否接受s3(current_solution)作为新的best_solution。
6.直到达到边界条件,不然跳回第二步一直循环搜索。
其图解如下:
伪代码如下:
3. Iterated Local Search代码实现:
////////////////////////
//TSP问题 迭代局部搜索求解代码
//基于Berlin52例子求解
//作者:infinitor
//时间:2018-04-12
////////////////////////
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define DEBUG
using namespace std;
#define CITY_SIZE 52 //城市数量
//城市坐标
typedef struct candidate
{
int x;
int y;
}city, CITIES;
//优化值
int **Delta;
//解决方案
typedef struct Solution
{
int permutation[CITY_SIZE]; //城市排列
int cost; //该排列对应的总路线长度
}SOLUTION;
// 计算邻域操作优化值
int calc_delta(int i, int k, int *tmp, CITIES * cities);
//计算两个城市间距离
int distance_2city(city c1, city c2);
//根据产生的城市序列,计算旅游总距离
int cost_total(int * cities_permutation, CITIES * cities);
//获取随机城市排列, 用于产生初始解
void random_permutation(int * cities_permutation);
//颠倒数组中下标begin到end的元素位置, 用于two_opt邻域动作
void swap_element(int *p, int begin, int end);
//邻域动作 反转index_i <-> index_j 间的元素
void two_opt_swap(int *cities_permutation, int *new_cities_permutation, int index_i, int index_j);
//本地局部搜索,边界条件 max_no_improve
void local_search(SOLUTION & best, CITIES * cities, int max_no_improve);
//判断接受准则
bool AcceptanceCriterion(int *cities_permutation, int *old_cities_permutation, CITIES * p_cities);
//将城市序列分成4块,然后按块重新打乱顺序。
//用于扰动函数
void double_bridge_move(int *cities_permutation, int * new_cities_permutation);
//扰动
void perturbation(CITIES * cities, SOLUTION &best_solution, SOLUTION ¤t_solution);
//迭代搜索
void iterated_local_search(SOLUTION & best, CITIES * cities, int max_iterations, int max_no_improve);
// 更新Delta
void Update(int i, int k, int *tmp, CITIES * cities);
//城市排列
int permutation[CITY_SIZE];
//城市坐标数组
CITIES cities[CITY_SIZE];
//berlin52城市坐标,最优解7542好像
CITIES berlin52[CITY_SIZE] = { { 565,575 },{ 25,185 },{ 345,750 },{ 945,685 },{ 845,655 },
{ 880,660 },{ 25,230 },{ 525,1000 },{ 580,1175 },{ 650,1130 },{ 1605,620 },
{ 1220,580 },{ 1465,200 },{ 1530,5 },{ 845,680 },{ 725,370 },{ 145,665 },
{ 415,635 },{ 510,875 },{ 560,365 },{ 300,465 },{ 520,585 },{ 480,415 },
{ 835,625 },{ 975,580 },{ 1215,245 },{ 1320,315 },{ 1250,400 },{ 660,180 },
{ 410,250 },{ 420,555 },{ 575,665 },{ 1150,1160 },{ 700,580 },{ 685,595 },
{ 685,610 },{ 770,610 },{ 795,645 },{ 720,635 },{ 760,650 },{ 475,960 },
{ 95,260 },{ 875,920 },{ 700,500 },{ 555,815 },{ 830,485 },{ 1170,65 },
{ 830,610 },{ 605,625 },{ 595,360 },{ 1340,725 },{ 1740,245 } };
int main()
{
srand(1);
int max_iterations = 600;
int max_no_improve = 50;
//初始化指针数组
Delta = new int*[CITY_SIZE];
for (int i = 0; i < CITY_SIZE; i ++)
Delta[i] = new int[CITY_SIZE];
SOLUTION best_solution;
iterated_local_search(best_solution, berlin52, max_iterations, max_no_improve);
cout << endl< index_j 间的元素
void two_opt_swap(int *cities_permutation, int *new_cities_permutation, int index_i, int index_j)
{
for (int i = 0; i < CITY_SIZE; i++)
{
new_cities_permutation[i] = cities_permutation[i];
}
swap_element(new_cities_permutation, index_i, index_j);
}
int calc_delta(int i, int k, int *tmp, CITIES * cities){
int delta = 0;
/*
以下计算说明:
对于每个方案,翻转以后没必要再次重新计算总距离
只需要在翻转的头尾做个小小处理
比如:
有城市序列 1-2-3-4-5 总距离 = d12 + d23 + d34 + d45 + d51 = A
翻转后的序列 1-4-3-2-5 总距离 = d14 + d43 + d32 + d25 + d51 = B
由于 dij 与 dji是一样的,所以B也可以表示成 B = A - d12 - d45 + d14 + d25
下面的优化就是基于这种原理
*/
if (i == 0)
{
if (k == CITY_SIZE - 1)
{
delta = 0;
}
else
{
delta = 0
- distance_2city(cities[tmp[k]], cities[tmp[k + 1]])
+ distance_2city(cities[tmp[i]], cities[tmp[k + 1]])
- distance_2city(cities[tmp[CITY_SIZE - 1]], cities[tmp[i]])
+ distance_2city(cities[tmp[CITY_SIZE - 1]], cities[tmp[k]]);
}
}
else
{
if (k == CITY_SIZE - 1)
{
delta = 0
- distance_2city(cities[tmp[i - 1]], cities[tmp[i]])
+ distance_2city(cities[tmp[i - 1]], cities[tmp[k]])
- distance_2city(cities[tmp[0]], cities[tmp[k]])
+ distance_2city(cities[tmp[i]], cities[tmp[0]]);
}
else
{
delta = 0
- distance_2city(cities[tmp[i - 1]], cities[tmp[i]])
+ distance_2city(cities[tmp[i - 1]], cities[tmp[k]])
- distance_2city(cities[tmp[k]], cities[tmp[k + 1]])
+ distance_2city(cities[tmp[i]], cities[tmp[k + 1]]);
}
}
return delta;
}
/*
去重处理,对于Delta数组来说,对于城市序列1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10,如果对3-5应用了邻域操作2-opt , 事实上对于
7-10之间的翻转是不需要重复计算的。 所以用Delta提前预处理一下。
当然由于这里的计算本身是O(1) 的,事实上并没有带来时间复杂度的减少(更新操作反而增加了复杂度)
如果delta计算 是O(n)的,这种去重操作效果是明显的。
*/
void Update(int i, int k, int *tmp, CITIES * cities){
if (i && k != CITY_SIZE - 1){
i --; k ++;
for (int j = i; j <= k; j ++){
for (int l = j + 1; l < CITY_SIZE; l ++){
Delta[j][l] = calc_delta(j, l, tmp, cities);
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < k; j ++){
for (int l = i; l <= k; l ++){
if (j >= l) continue;
Delta[j][l] = calc_delta(j, l, tmp, cities);
}
}
}// 如果不是边界,更新(i-1, k + 1)之间的
else{
for (i = 0; i < CITY_SIZE - 1; i++)
{
for (k = i + 1; k < CITY_SIZE; k++)
{
Delta[i][k] = calc_delta(i, k, tmp, cities);
}
}
}// 边界要特殊更新
}
//本地局部搜索,边界条件 max_no_improve
//best_solution最优解
//current_solution当前解
void local_search(SOLUTION & best_solution, CITIES * cities, int max_no_improve)
{
int count = 0;
int i, k;
int inital_cost = best_solution.cost; //初始花费
int now_cost = 0;
SOLUTION *current_solution = new SOLUTION; //为了防止爆栈……直接new了,你懂的
for (i = 0; i < CITY_SIZE - 1; i++)
{
for (k = i + 1; k < CITY_SIZE; k++)
{
Delta[i][k] = calc_delta(i, k, best_solution.permutation, cities);
}
}
do
{
//枚举排列
for (i = 0; i < CITY_SIZE - 1; i++)
{
for (k = i + 1; k < CITY_SIZE; k++)
{
//邻域动作
two_opt_swap(best_solution.permutation, current_solution->permutation, i, k);
now_cost = inital_cost + Delta[i][k];
current_solution->cost = now_cost;
if (current_solution->cost < best_solution.cost)
{
count = 0; //better cost found, so reset
for (int j = 0; j < CITY_SIZE; j++)
{
best_solution.permutation[j] = current_solution->permutation[j];
}
best_solution.cost = current_solution->cost;
inital_cost = best_solution.cost;
Update(i, k, best_solution.permutation, cities);
}
}
}
count++;
} while (count <= max_no_improve);
}
//判断接受准则
bool AcceptanceCriterion(int *cities_permutation, int *old_cities_permutation, CITIES * p_cities)
{
int acceptance = 500; //接受条件,与当前最解相差不超过acceptance
int old_cost = cost_total(old_cities_permutation, p_cities);
int new_cost = cost_total(cities_permutation, p_cities);
if ((new_cost <= (old_cost + acceptance)) || (new_cost >= (old_cost - acceptance)))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
//将城市序列分成4块,然后按块重新打乱顺序。
//用于扰动函数
void double_bridge_move(int *cities_permutation, int * new_cities_permutation)
{
int temp_perm[CITY_SIZE];
int pos1 = 1 + rand() % (CITY_SIZE / 4);
int pos2 = pos1 + 1 + rand() % (CITY_SIZE / 4);
int pos3 = pos2 + 1 + rand() % (CITY_SIZE / 4);
int i;
vector v;
//第一块
for (i = 0; i < pos1; i++)
{
v.push_back(cities_permutation[i]);
}
//第二块
for (i = pos3; i < CITY_SIZE; i++)
{
v.push_back(cities_permutation[i]);
}
//第三块
for (i = pos2; i < pos3; i++)
{
v.push_back(cities_permutation[i]);
}
//第四块
for (i = pos1; i < pos2; i++)
{
v.push_back(cities_permutation[i]);
}
for (i = 0; i < (int)v.size(); i++)
{
temp_perm[i] = v[i];
}
//if accept判断是否接受当前解
if (AcceptanceCriterion(cities_permutation, temp_perm, cities))
{
memcpy(new_cities_permutation, temp_perm, sizeof(temp_perm));//accept
}
}
//扰动
void perturbation(CITIES * cities, SOLUTION &best_solution, SOLUTION ¤t_solution)
{
double_bridge_move(best_solution.permutation, current_solution.permutation);
current_solution.cost = cost_total(current_solution.permutation, cities);
}
//迭代搜索
//max_iterations用于迭代搜索次数
//max_no_improve用于局部搜索边界条件
void iterated_local_search(SOLUTION & best_solution, CITIES * cities, int max_iterations, int max_no_improve)
{
SOLUTION *current_solution = new SOLUTION;
//获得初始随机解
random_permutation(best_solution.permutation);
best_solution.cost = cost_total(best_solution.permutation, cities);
local_search(best_solution, cities, max_no_improve); //初始搜索
for (int i = 0; i < max_iterations; i++)
{
perturbation(cities, best_solution, *current_solution); //扰动+判断是否接受新解
local_search(*current_solution, cities, max_no_improve);//继续局部搜索
//找到更优解
if (current_solution->cost < best_solution.cost)
{
for (int j = 0; j < CITY_SIZE; j++)
{
best_solution.permutation[j] = current_solution->permutation[j];
}
best_solution.cost = current_solution->cost;
}
cout << setw(13) << setiosflags(ios::left) <<"迭代搜索 " << i << " 次\t" << "最优解 = " << best_solution.cost << " 当前解 = " << current_solution->cost << endl;
}
}
Referecnce:
- 干货|迭代局部搜索算法(Iterated local search)探幽(附C++代码及注释)