(七十四)Android O Service启动流程梳理——startForegroundService
前言:之前梳理了startService和bindService,现在接着梳理下Android O比较有特点的startForegroundService。
- (六十四)Android O Service启动流程梳理——startService
- (六十五)Android O StartService的 anr timeout 流程分析
- (七十)Android O Service启动流程梳理——bindService
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/lylddinghffw/article/details/80366791
1.service启动简述
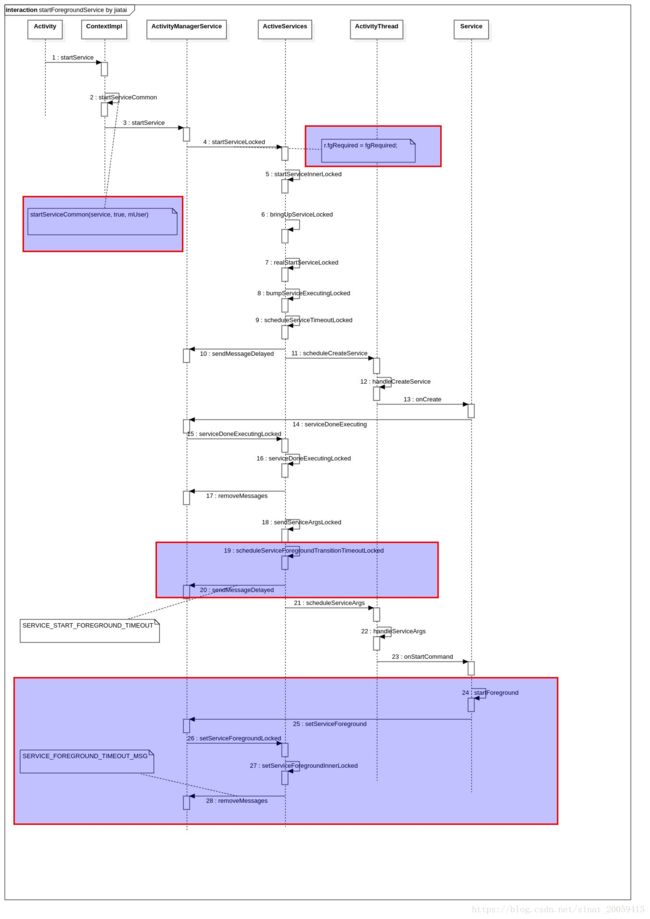
service启动分三种,比较简单的就是startService,Android O用于后台应用启动前台服务的startForegroundService和绑定服务的bindService。本篇继续梳理startForegroundService,startForegroundService使用需要注意的是Service启动后要在5s之内调用startForeground显示一个通知,不然就会anr。
2.startForegroundService流程梳理
2.1 ContextImpl
@Override
public ComponentName startForegroundService(Intent service) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return startServiceCommon(service, true, mUser);
}
private ComponentName startServiceCommon(Intent service, boolean requireForeground,
UserHandle user) {
try {
validateServiceIntent(service);
service.prepareToLeaveProcess(this);
ComponentName cn = ActivityManager.getService().startService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), service, service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(
getContentResolver()), requireForeground,
getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
if (cn != null) {
if (cn.getPackageName().equals("!")) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Not allowed to start service " + service
+ " without permission " + cn.getClassName());
} else if (cn.getPackageName().equals("!!")) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Unable to start service " + service
+ ": " + cn.getClassName());
} else if (cn.getPackageName().equals("?")) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Not allowed to start service " + service + ": " + cn.getClassName());
}
}
return cn;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}对照下之前梳理的startService,发现只是requireForeground参数由false改为true表明需要置为前台Service,其他流程是一样的。注意关注下这个参数带来的变化。
@Override
public ComponentName startService(Intent service) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return startServiceCommon(service, false, mUser);
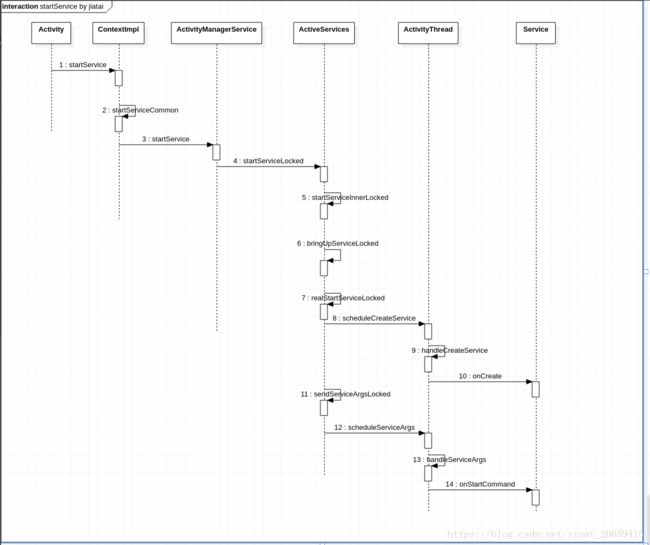
}那这里附一下startService的时序图,一样的流程就略过不赘述了。
2.2 AMS
@Override
public ComponentName startService(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service,
String resolvedType, boolean requireForeground, String callingPackage, int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startService");
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (service != null && service.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
if (callingPackage == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("callingPackage cannot be null");
}
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE,
"*** startService: " + service + " type=" + resolvedType + " fg=" + requireForeground);
synchronized(this) {
final int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
ComponentName res;
try {
res = mServices.startServiceLocked(caller, service,
resolvedType, callingPid, callingUid,
requireForeground, callingPackage, userId);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
return res;
}
}可以看到AMS并没有对requireForeground进行特殊处理,只是接着往下传。
2.3 ActiveServices
ComponentName startServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType,
int callingPid, int callingUid, boolean fgRequired, String callingPackage, final int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
if (DEBUG_DELAYED_STARTS) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "startService: " + service
+ " type=" + resolvedType + " args=" + service.getExtras());
final boolean callerFg;
if (caller != null) {
final ProcessRecord callerApp = mAm.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
if (callerApp == null) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Unable to find app for caller " + caller
+ " (pid=" + callingPid
+ ") when starting service " + service);
}
callerFg = callerApp.setSchedGroup != ProcessList.SCHED_GROUP_BACKGROUND;
} else {
callerFg = true;
}
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType, callingPackage,
callingPid, callingUid, userId, true, callerFg, false);
if (res == null) {
return null;
}
if (res.record == null) {
return new ComponentName("!", res.permission != null
? res.permission : "private to package");
}
ServiceRecord r = res.record;
if (!mAm.mUserController.exists(r.userId)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Trying to start service with non-existent user! " + r.userId);
return null;
}
// If this isn't a direct-to-foreground start, check our ability to kick off an
// arbitrary service
if (!r.startRequested && !fgRequired) {
// Before going further -- if this app is not allowed to start services in the
// background, then at this point we aren't going to let it period.
final int allowed = mAm.getAppStartModeLocked(r.appInfo.uid, r.packageName,
r.appInfo.targetSdkVersion, callingPid, false, false);
if (allowed != ActivityManager.APP_START_MODE_NORMAL) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Background start not allowed: service "
+ service + " to " + r.name.flattenToShortString()
+ " from pid=" + callingPid + " uid=" + callingUid
+ " pkg=" + callingPackage);
if (allowed == ActivityManager.APP_START_MODE_DELAYED) {
// In this case we are silently disabling the app, to disrupt as
// little as possible existing apps.
return null;
}
// This app knows it is in the new model where this operation is not
// allowed, so tell it what has happened.
UidRecord uidRec = mAm.mActiveUids.get(r.appInfo.uid);
return new ComponentName("?", "app is in background uid " + uidRec);
}
}
NeededUriGrants neededGrants = mAm.checkGrantUriPermissionFromIntentLocked(
callingUid, r.packageName, service, service.getFlags(), null, r.userId);
// If permissions need a review before any of the app components can run,
// we do not start the service and launch a review activity if the calling app
// is in the foreground passing it a pending intent to start the service when
// review is completed.
if (mAm.mPermissionReviewRequired) {
if (!requestStartTargetPermissionsReviewIfNeededLocked(r, callingPackage,
callingUid, service, callerFg, userId)) {
return null;
}
}
if (unscheduleServiceRestartLocked(r, callingUid, false)) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "START SERVICE WHILE RESTART PENDING: " + r);
}
r.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
r.startRequested = true;
r.delayedStop = false;
r.fgRequired = fgRequired;
r.pendingStarts.add(new ServiceRecord.StartItem(r, false, r.makeNextStartId(),
service, neededGrants, callingUid));
final ServiceMap smap = getServiceMapLocked(r.userId);
boolean addToStarting = false;
if (!callerFg && !fgRequired && r.app == null
&& mAm.mUserController.hasStartedUserState(r.userId)) {
ProcessRecord proc = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(r.processName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
if (proc == null || proc.curProcState > ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_RECEIVER) {
// If this is not coming from a foreground caller, then we may want
// to delay the start if there are already other background services
// that are starting. This is to avoid process start spam when lots
// of applications are all handling things like connectivity broadcasts.
// We only do this for cached processes, because otherwise an application
// can have assumptions about calling startService() for a service to run
// in its own process, and for that process to not be killed before the
// service is started. This is especially the case for receivers, which
// may start a service in onReceive() to do some additional work and have
// initialized some global state as part of that.
if (DEBUG_DELAYED_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Potential start delay of "
+ r + " in " + proc);
if (r.delayed) {
// This service is already scheduled for a delayed start; just leave
// it still waiting.
if (DEBUG_DELAYED_STARTS) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Continuing to delay: " + r);
return r.name;
}
if (smap.mStartingBackground.size() >= mMaxStartingBackground) {
// Something else is starting, delay!
Slog.i(TAG_SERVICE, "Delaying start of: " + r);
smap.mDelayedStartList.add(r);
r.delayed = true;
return r.name;
}
if (DEBUG_DELAYED_STARTS) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Not delaying: " + r);
addToStarting = true;
} else if (proc.curProcState >= ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE) {
// We slightly loosen when we will enqueue this new service as a background
// starting service we are waiting for, to also include processes that are
// currently running other services or receivers.
addToStarting = true;
if (DEBUG_DELAYED_STARTS) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE,
"Not delaying, but counting as bg: " + r);
} else if (DEBUG_DELAYED_STARTS) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(128);
sb.append("Not potential delay (state=").append(proc.curProcState)
.append(' ').append(proc.adjType);
String reason = proc.makeAdjReason();
if (reason != null) {
sb.append(' ');
sb.append(reason);
}
sb.append("): ");
sb.append(r.toString());
Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, sb.toString());
}
} else if (DEBUG_DELAYED_STARTS) {
if (callerFg || fgRequired) {
Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Not potential delay (callerFg=" + callerFg + " uid="
+ callingUid + " pid=" + callingPid + " fgRequired=" + fgRequired + "): " + r);
} else if (r.app != null) {
Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Not potential delay (cur app=" + r.app + "): " + r);
} else {
Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE,
"Not potential delay (user " + r.userId + " not started): " + r);
}
}
ComponentName cmp = startServiceInnerLocked(smap, service, r, callerFg, addToStarting);
return cmp;
}这里对于fgRequired为true的情况其实也只是赋值了一下
r.fgRequired = fgRequired;后面流程和startService的onCreate一样的,没啥好重复说的,直到流程到了onStartCommand有点不一样了。
onStartCommand的开始是
private final void sendServiceArgsLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean execInFg,
boolean oomAdjusted) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
final int N = r.pendingStarts.size();
if (N == 0) {
return;
}
ArrayList args = new ArrayList<>();
while (r.pendingStarts.size() > 0) {
ServiceRecord.StartItem si = r.pendingStarts.remove(0);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) {
Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Sending arguments to: "
+ r + " " + r.intent + " args=" + si.intent);
}
if (si.intent == null && N > 1) {
// If somehow we got a dummy null intent in the middle,
// then skip it. DO NOT skip a null intent when it is
// the only one in the list -- this is to support the
// onStartCommand(null) case.
continue;
}
si.deliveredTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
r.deliveredStarts.add(si);
si.deliveryCount++;
if (si.neededGrants != null) {
mAm.grantUriPermissionUncheckedFromIntentLocked(si.neededGrants,
si.getUriPermissionsLocked());
}
mAm.grantEphemeralAccessLocked(r.userId, si.intent,
r.appInfo.uid, UserHandle.getAppId(si.callingId));
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "start");
if (!oomAdjusted) {
oomAdjusted = true;
mAm.updateOomAdjLocked(r.app, true);
}
if (r.fgRequired && !r.fgWaiting) {
if (!r.isForeground) {
if (DEBUG_BACKGROUND_CHECK) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Launched service must call startForeground() within timeout: " + r);
}
scheduleServiceForegroundTransitionTimeoutLocked(r);
} else {
if (DEBUG_BACKGROUND_CHECK) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Service already foreground; no new timeout: " + r);
}
r.fgRequired = false;
}
}
int flags = 0;
if (si.deliveryCount > 1) {
flags |= Service.START_FLAG_RETRY;
}
if (si.doneExecutingCount > 0) {
flags |= Service.START_FLAG_REDELIVERY;
}
args.add(new ServiceStartArgs(si.taskRemoved, si.id, flags, si.intent));
}
ParceledListSlice slice = new ParceledListSlice<>(args);
slice.setInlineCountLimit(4);
Exception caughtException = null;
try {
r.app.thread.scheduleServiceArgs(r, slice);
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Transaction too large for " + args.size()
+ " args, first: " + args.get(0).args);
Slog.w(TAG, "Failed delivering service starts", e);
caughtException = e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// Remote process gone... we'll let the normal cleanup take care of this.
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Crashed while sending args: " + r);
Slog.w(TAG, "Failed delivering service starts", e);
caughtException = e;
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Unexpected exception", e);
caughtException = e;
}
if (caughtException != null) {
// Keep nesting count correct
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
for (int i = 0; i < args.size(); i++) {
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
}
if (caughtException instanceof TransactionTooLargeException) {
throw (TransactionTooLargeException)caughtException;
}
}
} 这里面有下面一句比较关键
if (r.fgRequired && !r.fgWaiting) {
if (!r.isForeground) {
if (DEBUG_BACKGROUND_CHECK) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Launched service must call startForeground() within timeout: " + r);
}
scheduleServiceForegroundTransitionTimeoutLocked(r);
} else {
if (DEBUG_BACKGROUND_CHECK) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Service already foreground; no new timeout: " + r);
}
r.fgRequired = false;
}
} void scheduleServiceForegroundTransitionTimeoutLocked(ServiceRecord r) {
if (r.app.executingServices.size() == 0 || r.app.thread == null) {
return;
}
Message msg = mAm.mHandler.obtainMessage(
ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_FOREGROUND_TIMEOUT_MSG);
msg.obj = r;
r.fgWaiting = true;
mAm.mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg, SERVICE_START_FOREGROUND_TIMEOUT);
}这里表示在onStartCommand的流程开始时会设置一个5s的anr timeout,超过5s就会anr并且停止Service。
// How long the startForegroundService() grace period is to get around to
// calling startForeground() before we ANR + stop it.
static final int SERVICE_START_FOREGROUND_TIMEOUT = 5*1000;也附带看下AMS是怎么处理这个消息的:
final class MainHandler extends Handler {
public MainHandler(Looper looper) {
super(looper, null, true);
}
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case UPDATE_CONFIGURATION_MSG: {
final ContentResolver resolver = mContext.getContentResolver();
Settings.System.putConfigurationForUser(resolver, (Configuration) msg.obj,
msg.arg1);
} break;
case GC_BACKGROUND_PROCESSES_MSG: {
synchronized (ActivityManagerService.this) {
performAppGcsIfAppropriateLocked();
}
} break;
case SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG: {
mServices.serviceTimeout((ProcessRecord)msg.obj);
} break;
case SERVICE_FOREGROUND_TIMEOUT_MSG: {
mServices.serviceForegroundTimeout((ServiceRecord)msg.obj);
} break;还是扔回来调用ActiveServices来处理。
void serviceForegroundTimeout(ServiceRecord r) {
ProcessRecord app;
synchronized (mAm) {
if (!r.fgRequired || r.destroying) {
return;
}
if (DEBUG_BACKGROUND_CHECK) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Service foreground-required timeout for " + r);
}
app = r.app;
r.fgWaiting = false;
stopServiceLocked(r);
}
if (app != null) {
mAm.mAppErrors.appNotResponding(app, null, null, false,
"Context.startForegroundService() did not then call Service.startForeground()");
}
}直接停止Service并且通过AMS使应用 anr,提示“Context.startForegroundService() did not then call Service.startForeground()”。
3. startForeground流程梳理
3.1 Service
/**
* If your service is started (running through {@link Context#startService(Intent)}), then
* also make this service run in the foreground, supplying the ongoing
* notification to be shown to the user while in this state.
* By default started services are background, meaning that their process won't be given
* foreground CPU scheduling (unless something else in that process is foreground) and,
* if the system needs to kill them to reclaim more memory (such as to display a large page in a
* web browser), they can be killed without too much harm. You use
* {@link #startForeground} if killing your service would be disruptive to the user, such as
* if your service is performing background music playback, so the user
* would notice if their music stopped playing.
*
* Note that calling this method does not put the service in the started state
* itself, even though the name sounds like it. You must always call
* {@link #startService(Intent)} first to tell the system it should keep the service running,
* and then use this method to tell it to keep it running harder.
*
* @param id The identifier for this notification as per
* {@link NotificationManager#notify(int, Notification)
* NotificationManager.notify(int, Notification)}; must not be 0.
* @param notification The Notification to be displayed.
*
* @see #stopForeground(boolean)
*/
public final void startForeground(int id, Notification notification) {
try {
mActivityManager.setServiceForeground(
new ComponentName(this, mClassName), mToken, id,
notification, 0);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
}
3.2 AMS
@Override
public void setServiceForeground(ComponentName className, IBinder token,
int id, Notification notification, int flags) {
synchronized(this) {
mServices.setServiceForegroundLocked(className, token, id, notification, flags);
}
}
3.3 ActiveServices
public void setServiceForegroundLocked(ComponentName className, IBinder token,
int id, Notification notification, int flags) {
final int userId = UserHandle.getCallingUserId();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
ServiceRecord r = findServiceLocked(className, token, userId);
if (r != null) {
setServiceForegroundInnerLocked(r, id, notification, flags);
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
private void setServiceForegroundInnerLocked(ServiceRecord r, int id,
Notification notification, int flags) {
if (id != 0) {
if (notification == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("null notification");
}
// Instant apps need permission to create foreground services.
if (r.appInfo.isInstantApp()) {
final int mode = mAm.mAppOpsService.checkOperation(
AppOpsManager.OP_INSTANT_APP_START_FOREGROUND,
r.appInfo.uid,
r.appInfo.packageName);
switch (mode) {
case AppOpsManager.MODE_ALLOWED:
break;
case AppOpsManager.MODE_IGNORED:
Slog.w(TAG, "Instant app " + r.appInfo.packageName
+ " does not have permission to create foreground services"
+ ", ignoring.");
return;
case AppOpsManager.MODE_ERRORED:
throw new SecurityException("Instant app " + r.appInfo.packageName
+ " does not have permission to create foreground services");
default:
try {
if (AppGlobals.getPackageManager().checkPermission(
android.Manifest.permission.INSTANT_APP_FOREGROUND_SERVICE,
r.appInfo.packageName, UserHandle.getUserId(r.appInfo.uid))
!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
throw new SecurityException("Instant app " + r.appInfo.packageName
+ " does not have permission to create foreground"
+ "services");
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new SecurityException("Failed to check instant app permission." ,
e);
}
}
}
if (r.fgRequired) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE || DEBUG_BACKGROUND_CHECK) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Service called startForeground() as required: " + r);
}
r.fgRequired = false;
r.fgWaiting = false;
mAm.mHandler.removeMessages(
ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_FOREGROUND_TIMEOUT_MSG, r);
}
if (r.foregroundId != id) {
cancelForegroundNotificationLocked(r);
r.foregroundId = id;
}
notification.flags |= Notification.FLAG_FOREGROUND_SERVICE;
r.foregroundNoti = notification;
if (!r.isForeground) {
final ServiceMap smap = getServiceMapLocked(r.userId);
if (smap != null) {
ActiveForegroundApp active = smap.mActiveForegroundApps.get(r.packageName);
if (active == null) {
active = new ActiveForegroundApp();
active.mPackageName = r.packageName;
active.mUid = r.appInfo.uid;
active.mShownWhileScreenOn = mScreenOn;
if (r.app != null) {
active.mAppOnTop = active.mShownWhileTop =
r.app.uidRecord.curProcState
<= ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_TOP;
}
active.mStartTime = active.mStartVisibleTime
= SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
smap.mActiveForegroundApps.put(r.packageName, active);
requestUpdateActiveForegroundAppsLocked(smap, 0);
}
active.mNumActive++;
}
r.isForeground = true;
}
r.postNotification();
if (r.app != null) {
updateServiceForegroundLocked(r.app, true);
}
getServiceMapLocked(r.userId).ensureNotStartingBackgroundLocked(r);
mAm.notifyPackageUse(r.serviceInfo.packageName,
PackageManager.NOTIFY_PACKAGE_USE_FOREGROUND_SERVICE);
} else {
if (r.isForeground) {
final ServiceMap smap = getServiceMapLocked(r.userId);
if (smap != null) {
decActiveForegroundAppLocked(smap, r);
}
r.isForeground = false;
if (r.app != null) {
mAm.updateLruProcessLocked(r.app, false, null);
updateServiceForegroundLocked(r.app, true);
}
}
if ((flags & Service.STOP_FOREGROUND_REMOVE) != 0) {
cancelForegroundNotificationLocked(r);
r.foregroundId = 0;
r.foregroundNoti = null;
} else if (r.appInfo.targetSdkVersion >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
r.stripForegroundServiceFlagFromNotification();
if ((flags & Service.STOP_FOREGROUND_DETACH) != 0) {
r.foregroundId = 0;
r.foregroundNoti = null;
}
}
}
}setServiceForegroundInnerLocked这个方法很关键,关键代码分如下几部分梳理:
1)首先Service创建的notification id不能是0并且notification不能是null,并且Android O 如果创建通知的话还要设置channel的。
if (id != 0) {
if (notification == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("null notification");
}
2)设置r.fgRequired为false,表明已经设置Service为foreground了,不需要了。并且移除了之前发给AMS的SERVICE_FOREGROUND_TIMEOUT_MSG,这样就不会anr了。但是这句话要在发出消息的5s之内调用到,否则还是会anr。
由于消息是在onStartCommand流程开始时发出的,如果我们的Service在onCreate就开始调用startForeground,时限也许会长于5s。但由于一个是AMS的流程,一个是APP的流程,是异步的,长也长不了多少,不是等onCreate执行完再发的。
if (r.fgRequired) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE || DEBUG_BACKGROUND_CHECK) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Service called startForeground() as required: " + r);
}
r.fgRequired = false;
r.fgWaiting = false;
mAm.mHandler.removeMessages(
ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_FOREGROUND_TIMEOUT_MSG, r);
}3)取消通知,但会检查应用的其他前台Service是否有相同的notification id,如果一样,则不取消。
if (r.foregroundId != id) {
cancelForegroundNotificationLocked(r);
r.foregroundId = id;
} private void cancelForegroundNotificationLocked(ServiceRecord r) {
if (r.foregroundId != 0) {
// First check to see if this app has any other active foreground services
// with the same notification ID. If so, we shouldn't actually cancel it,
// because that would wipe away the notification that still needs to be shown
// due the other service.
ServiceMap sm = getServiceMapLocked(r.userId);
if (sm != null) {
for (int i = sm.mServicesByName.size()-1; i >= 0; i--) {
ServiceRecord other = sm.mServicesByName.valueAt(i);
if (other != r && other.foregroundId == r.foregroundId
&& other.packageName.equals(r.packageName)) {
// Found one! Abort the cancel.
return;
}
}
}
r.cancelNotification();
}
}4)将Service设为前台Service
notification.flags |= Notification.FLAG_FOREGROUND_SERVICE;
r.foregroundNoti = notification;
if (!r.isForeground) {
final ServiceMap smap = getServiceMapLocked(r.userId);
if (smap != null) {
ActiveForegroundApp active = smap.mActiveForegroundApps.get(r.packageName);
if (active == null) {
active = new ActiveForegroundApp();
active.mPackageName = r.packageName;
active.mUid = r.appInfo.uid;
active.mShownWhileScreenOn = mScreenOn;
if (r.app != null) {
active.mAppOnTop = active.mShownWhileTop =
r.app.uidRecord.curProcState
<= ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_TOP;
}
active.mStartTime = active.mStartVisibleTime
= SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
smap.mActiveForegroundApps.put(r.packageName, active);
requestUpdateActiveForegroundAppsLocked(smap, 0);
}
active.mNumActive++;
}
r.isForeground = true;
}
4. Service “Context.startForegroundService() did not then call Service.startForeground()” anr原因
结合之前2和3对startForegroundService和startForeground的分析,可以很清楚的判断出Service anr原因:
Service没有在AMS SERVICE_FOREGROUND_TIMEOUT_MSG发出5s内将其移除,简单地对应于应用描述就是调用startForegroundService后5s内没有及时在Service内调用startForeground。(5s在这的描述是不精确的,但差不了多少,startForeground建议在Service onCreate一开始就调用,也许能争取点时间)
5. Service “Context.startForegroundService() did not then call Service.startForeground()” crash原因
之前都梳理的anr,其实Android O这边还埋了个crash的坑。如果5s之内没有及时调用startForeground,然后Service destroy了,比如stopService,那Android O很人性化地不让Service anr了,让Service crash。
private final void bringDownServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r) {
//Slog.i(TAG, "Bring down service:");
//r.dump(" ");
// Report to all of the connections that the service is no longer
// available.
for (int conni=r.connections.size()-1; conni>=0; conni--) {
ArrayList c = r.connections.valueAt(conni);
for (int i=0; i=0; i--) {
IntentBindRecord ibr = r.bindings.valueAt(i);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Bringing down binding " + ibr
+ ": hasBound=" + ibr.hasBound);
if (ibr.hasBound) {
try {
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, false, "bring down unbind");
mAm.updateOomAdjLocked(r.app, true);
ibr.hasBound = false;
ibr.requested = false;
r.app.thread.scheduleUnbindService(r,
ibr.intent.getIntent());
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when unbinding service "
+ r.shortName, e);
serviceProcessGoneLocked(r);
}
}
}
}
// Check to see if the service had been started as foreground, but being
// brought down before actually showing a notification. That is not allowed.
if (r.fgRequired) {
Slog.w(TAG_SERVICE, "Bringing down service while still waiting for start foreground: "
+ r);
r.fgRequired = false;
r.fgWaiting = false;
mAm.mHandler.removeMessages(
ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_FOREGROUND_TIMEOUT_MSG, r);
if (r.app != null) {
Message msg = mAm.mHandler.obtainMessage(
ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_FOREGROUND_CRASH_MSG);
msg.obj = r.app;
mAm.mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
}
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) {
RuntimeException here = new RuntimeException();
here.fillInStackTrace();
Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Bringing down " + r + " " + r.intent, here);
}
r.destroyTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (LOG_SERVICE_START_STOP) {
EventLogTags.writeAmDestroyService(
r.userId, System.identityHashCode(r), (r.app != null) ? r.app.pid : -1);
}
final ServiceMap smap = getServiceMapLocked(r.userId);
ServiceRecord found = smap.mServicesByName.remove(r.name);
// Note when this method is called by bringUpServiceLocked(), the service is not found
// in mServicesByName and found will be null.
if (found != null && found != r) {
// This is not actually the service we think is running... this should not happen,
// but if it does, fail hard.
smap.mServicesByName.put(r.name, found);
throw new IllegalStateException("Bringing down " + r + " but actually running "
+ found);
}
smap.mServicesByIntent.remove(r.intent);
r.totalRestartCount = 0;
unscheduleServiceRestartLocked(r, 0, true);
// Also make sure it is not on the pending list.
for (int i=mPendingServices.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
if (mPendingServices.get(i) == r) {
mPendingServices.remove(i);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Removed pending: " + r);
}
}
cancelForegroundNotificationLocked(r);
if (r.isForeground) {
decActiveForegroundAppLocked(smap, r);
}
r.isForeground = false;
r.foregroundId = 0;
r.foregroundNoti = null;
// Clear start entries.
r.clearDeliveredStartsLocked();
r.pendingStarts.clear();
if (r.app != null) {
synchronized (r.stats.getBatteryStats()) {
r.stats.stopLaunchedLocked();
}
r.app.services.remove(r);
if (r.whitelistManager) {
updateWhitelistManagerLocked(r.app);
}
if (r.app.thread != null) {
updateServiceForegroundLocked(r.app, false);
try {
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, false, "destroy");
mDestroyingServices.add(r);
r.destroying = true;
mAm.updateOomAdjLocked(r.app, true);
r.app.thread.scheduleStopService(r);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when destroying service "
+ r.shortName, e);
serviceProcessGoneLocked(r);
}
} else {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(
TAG_SERVICE, "Removed service that has no process: " + r);
}
} else {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(
TAG_SERVICE, "Removed service that is not running: " + r);
}
if (r.bindings.size() > 0) {
r.bindings.clear();
}
if (r.restarter instanceof ServiceRestarter) {
((ServiceRestarter)r.restarter).setService(null);
}
int memFactor = mAm.mProcessStats.getMemFactorLocked();
long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (r.tracker != null) {
r.tracker.setStarted(false, memFactor, now);
r.tracker.setBound(false, memFactor, now);
if (r.executeNesting == 0) {
r.tracker.clearCurrentOwner(r, false);
r.tracker = null;
}
}
smap.ensureNotStartingBackgroundLocked(r);
} 上面代码中让Service用crash代替anr的代码如下:
// Check to see if the service had been started as foreground, but being
// brought down before actually showing a notification. That is not allowed.
if (r.fgRequired) {
Slog.w(TAG_SERVICE, "Bringing down service while still waiting for start foreground: "
+ r);
r.fgRequired = false;
r.fgWaiting = false;
mAm.mHandler.removeMessages(
ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_FOREGROUND_TIMEOUT_MSG, r);
if (r.app != null) {
Message msg = mAm.mHandler.obtainMessage(
ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_FOREGROUND_CRASH_MSG);
msg.obj = r.app;
mAm.mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
}
5. 总结
其实startForegroundService的流程和startService总体来讲是差不多的,区别就在于5s 的anr时间限制内Service要调用startForeground。
如果没有及时调用,则会anr。又或者5s之内Service destroy了,那就来一个差不多的crash。
anr和crash中都会带有如下信息:“Context.startForegroundService() did not then call Service.startForeground()”