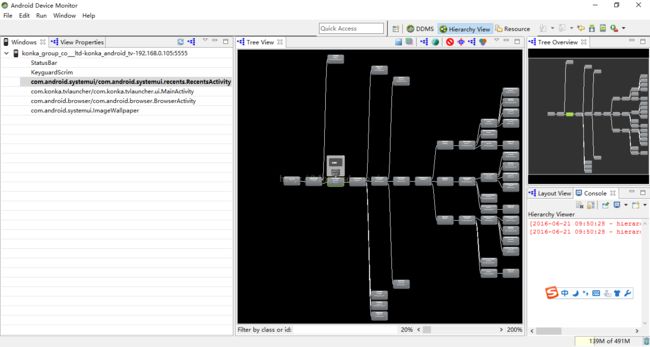
Adnroid5.1 最近应用分析(systemui-recents)
最近由于工作需要,需要重新定制Recents部分的UI。recents就是长按home键后弹出的最近应用列表。为了能更好的理解这部分代码,可以使用Monitor工具看一下这个应用的view结构图。可以在android studio的tools下的Android下,打开Android device Monitor工具。然后连接上设备,USB或者网线都可以,网线的话要使用adb connect命令连接上设备。连接上后长按Home键打开最近应用,在Monitor中选择hierarchy view,然后可以在左边选择要查看的应用,选择我们的systemui.recents.RecentsActivity,view结构图就出来了。如下图所示:
下面是对对于源码的分析,源码在framework/base/packages/Systemui,recents的入口是RecentsActivity,所以从RecentsActivity的onCreate开始分析。
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// For the non-primary user, ensure that the SystemServicesProxy and configuration is
// initialized
RecentsTaskLoader.initialize(this);
SystemServicesProxy ssp = RecentsTaskLoader.getInstance().getSystemServicesProxy();RecentsActivity的OnCreate一开始就调用RecentsTaskLoader.initialize(this);这部分整个后台应用显示的入口了。这里就出现了两个很重要的核心类:RecentsTaskLoader和SystemServicesProxy。RecentsTaskLoader是全局的最近任务的装载器类,它内部会创建SystemServicesProxy,并且在需要的时候返回给类的实例。RecentsActivity里面有这样几个重要的的函数:
getAndUpdateActivityIcon
getAndUpdateThumbnail等
这几个函数从名字上看可以知道是得到最近应用的Icon,thumbnail等的,那是怎么获得的呢?
以这个函数为例:
/** Returns the bitmap using as many cached values as we can. */
public Bitmap getAndUpdateThumbnail(Task.TaskKey taskKey, SystemServicesProxy ssp,
boolean loadIfNotCached) {
// Return the cached thumbnail if it exists
Bitmap thumbnail = mThumbnailCache.getAndInvalidateIfModified(taskKey);
if (thumbnail != null) {
return thumbnail;
}
RecentsConfiguration config = RecentsConfiguration.getInstance();
if (config.svelteLevel < RecentsConfiguration.SVELTE_DISABLE_LOADING && loadIfNotCached) {
// Load the thumbnail from the system
thumbnail = ssp.getTaskThumbnail(taskKey.id);
if (thumbnail != null) {
mThumbnailCache.put(taskKey, thumbnail);
return thumbnail;
}
}这个函数可以看出要获得缩略图,首先查找缓冲区里面有没有,有的话直接返回,没有的话通过ssp获取。ssp就是前面说的SystemServicesProxy,这个类内部又是通过ActivityManager获得的。ActivityManager又会调用ActivityManagerNative中的相关方法。大家顺着这个链看一下就会明白。
通过RecentsTaskLoader和SystemServicesProxy可以获得最近应用的缩略图,图标,名字,描述信息等,具体的方法之前已经说了,就是RecentTaskLoader内部调用SystemServicesProxy,SystemServicesProxy调用ActivityManager,ActivityManager又调用ActivityManagerNative最终获得这些信息。
第三个很重要的类是:RecentsTaskLoadPlan
这个类用来构造task Stack.
最近应用列表的结构是这样的,首先系统会有一个stacks:任务栈,任务栈里面有很多任务:task。RecentsTaskLoadPlan类就是用之前的两个很重要的类RecentTaskLoader、SystemServicesProxy类构造task stacks和task。每个task里面就装载了所有task的信息,包括缩略图,icon等。因此,只要获得了taskstacks和task,那就可以自己来显示最近应用了。那么系统中是怎么显示的呢?
然后再onStart里面会调用
// Update the recent tasks
updateRecentsTasks();
这个方法很重要,它是显示最近应用的入口。我用注释的方式对其进行解释。
/** Updates the set of recent tasks */
void updateRecentsTasks() {
// If AlternateRecentsComponent has preloaded a load plan, then use that to prevent
// reconstructing the task stack
RecentsTaskLoader loader = RecentsTaskLoader.getInstance();
RecentsTaskLoadPlan plan = Recents.consumeInstanceLoadPlan();
//以上就是第三个重要的类,它会构造taskstack和task.
if (plan == null) {
plan = loader.createLoadPlan(this);
}
// Start loading tasks according to the load plan
if (!plan.hasTasks()) {
loader.preloadTasks(plan, mConfig.launchedFromHome);//开始构造taskstacks和task
}
RecentsTaskLoadPlan.Options loadOpts = new RecentsTaskLoadPlan.Options();
loadOpts.runningTaskId = mConfig.launchedToTaskId;
loadOpts.numVisibleTasks = mConfig.launchedNumVisibleTasks;
loadOpts.numVisibleTaskThumbnails = mConfig.launchedNumVisibleThumbnails;
loader.loadTasks(this, plan, loadOpts);
ArrayList stacks = plan.getAllTaskStacks();
//从plan中获得taskstacks了吧。有了taskstacks就可以用来显示了。
mConfig.launchedWithNoRecentTasks = !plan.hasTasks();
if (!mConfig.launchedWithNoRecentTasks) {
mRecentsView.setTaskStacks(stacks);
//把taskstack传递给mRecentsView用来显示。
}
...//只摘选了以上部分
} 所以显示的入口就传递到了mRecentsView.setTaskStacks(stacks);
该函数如下:
/** Set/get the bsp root node */
public void setTaskStacks(ArrayList stacks) {
int numStacks = stacks.size();
// Make a list of the stack view children only
ArrayList stackViews = new ArrayList();
int childCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child != mSearchBar) {
stackViews.add((TaskStackView) child);
}
}
// Remove all/extra stack views
int numTaskStacksToKeep = 0; // Keep no tasks if we are recreating the layout
if (mConfig.launchedReuseTaskStackViews) {
numTaskStacksToKeep = Math.min(childCount, numStacks);
}
for (int i = stackViews.size() - 1; i >= numTaskStacksToKeep; i--) {
removeView(stackViews.get(i));
stackViews.remove(i);
}
// Update the stack views that we are keeping
for (int i = 0; i < numTaskStacksToKeep; i++) {
TaskStackView tsv = stackViews.get(i);
// If onRecentsHidden is not triggered, we need to the stack view again here
tsv.reset();
tsv.setStack(stacks.get(i));
}
// Add remaining/recreate stack views
mStacks = stacks;
for (int i = stackViews.size(); i < numStacks; i++) {
TaskStack stack = stacks.get(i);
TaskStackView stackView = new TaskStackView(getContext(), stack);
//这里,会给每一个新的stacks创建一个TaskStackView来显示一个taskstacks.
stackView.setCallbacks(this);
addView(stackView);
}
// Enable debug mode drawing on all the stacks if necessary
if (mConfig.debugModeEnabled) {
for (int i = childCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
View v = getChildAt(i);
if (v != mSearchBar) {
TaskStackView stackView = (TaskStackView) v;
stackView.setDebugOverlay(mDebugOverlay);
}
}
}
// Trigger a new layout
requestLayout();
这里,RcentsView的child是TaskStackView,并在构造函数中传递stacks给TaskStackView。TaskStackView的child是TaskView,TaskView当然就对应一个task了。TaskView又由一个Head和缩略图组成。Head又有图标和名字组成。这样就完整显示出来了。
这里最后一行非常重要,requestLayout();是的,new TaskStackView后就没有做其他事情了,可以整个最近应用列表还是显示出来了,关键就在这里。requestLayout()会导致onMeasure树和OnLayout树被遍历,而在TaskStackView中,onMeasute和onLayout就是用来构造子View并显示的。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
// Compute our stack/task rects
Rect taskStackBounds = new Rect(mTaskStackBounds);
taskStackBounds.bottom -= mConfig.systemInsets.bottom;
computeRects(width, height, taskStackBounds, mConfig.launchedWithAltTab,
mConfig.launchedFromHome);
// If this is the first layout, then scroll to the front of the stack and synchronize the
// stack views immediately to load all the views
if (mAwaitingFirstLayout) {
mStackScroller.setStackScrollToInitialState();
requestSynchronizeStackViewsWithModel(); synchronizeStackViewsWithModel();//这个里面会是创建TaskView的关键
}TaskStackView中,进入on Measure后首先判断是不是第一次进入,如果是第一次的话会调用synchronizeStackViewsWithModel();该函数并没有直接new TaskView,而是首先会去查找mTmpTaskViewMap,如果没有,tv = mViewPool.pickUpViewFromPool(task, task);这里面又会调用回调函数v = mViewCreator.createView(mContext);,而这个函数就在TaskStackView中:
@Override
public TaskView createView(Context context) {
return (TaskView) mInflater.inflate(R.layout.recents_task_view, this, false);
}加载布局文件,从而穿件TaskView.穿件好后会用task来初始化它:
调用过程是这样的:
synchronizeStackViewsWithModel();/
->v = mViewPool.pickUpViewFromPool(task, task);
-> v = mViewCreator.createView(mContext);
-> V pickUpViewFromPool(T preferredData, T prepareData) {
-> prepareViewToLeavePool
->RecentsTaskLoader.getInstance().loadTaskData(task);
-> t.notifyTaskDataloaded(null, mDefaultApplicationIcon);
-> t.notifyTaskDataLoaded(thumbnail == mDefaultThumbnail ? null : thumbnail, applicationIcon); (回调TaskView中的notifyTaskDataLoaded,完成资源加载);
最后:大致流程是这样的,如果哪里分析的不对,欢迎指出来!